6DRepNet360全范围头部姿态估计
- 标题
- 摘要
- 关键词
- 主要贡献
- 方法概述
- 实验
- 结论
- 模型转换和onnxruntime推理
- 模型和代码下载
- 可视化结果
- 代码
这篇论文的核心内容是关于一种用于全范围旋转头部姿态估计的新方法。以下是关键点的总结:
标题
- Towards Robust and Unconstrained Full Range of Rotation Head Pose Estimation
摘要
- 提出了一种新的方法,用于在没有约束的情况下估计全范围旋转的头部姿态。
- 引入了旋转矩阵形式来解决模糊的旋转标签问题,并提出了一种连续的6D旋转矩阵表示方法,以实现高效且鲁棒的直接回归。
- 通过新累积的训练数据集和基于测地线的损失函数,设计了一个能够预测更广泛头部姿态的高级模型。
- 在公共数据集上的广泛评估表明,该方法在效率和鲁棒性方面显著优于其他最先进的方法。
关键词
- 头部姿态估计
- 全范围旋转
- 旋转矩阵
- 6D表示
- 测地线损失
主要贡献
- 提出了一种简化且高效的6参数旋转矩阵表示方法,用于准确回归头部姿态,避免了歧义问题。
- 提出了一种基于测地距离的方法,用于网络惩罚,以封装训练损失在特殊正交群SO(3)流形几何内。
- 利用CMU Panoptic数据集扩展了传统的300W-LP头部姿态数据集,包含了全头部姿态旋转数据。
- 创建了一个新的头部姿态预测模型,其预测范围超过了当前方法,并且在常见测试数据集上实现了更低的误差。
- 在多个实验设置中展示了该方法在准确性和鲁棒性方面的优势。
- 进行了消融研究,以评估模型的每个组成部分对结果的影响。
方法概述
- 使用了旋转矩阵作为旋转表示,以克服欧拉角和四元数表示中的歧义和不连续性问题。
- 提出了一种基于测地距离的损失函数,以稳定学习过程。
- 利用CMU Panoptic数据集和300W-LP数据集,创建了一个新的数据集,用于训练模型。
实验
- 在多个公共数据集上进行了广泛的评估,包括AFLW2000、BIWI和CMU Panoptic数据集。
- 与当前最先进的方法进行了比较,证明了该方法在准确性和鲁棒性方面的优势。
结论
-
该研究解决了全范围头部姿态估计的挑战,并提出了一种新的6D旋转矩阵表示方法,该方法在准确性和鲁棒性方面都取得了显著的改进。
-
源码:https://github.com/thohemp/6DRepNet360
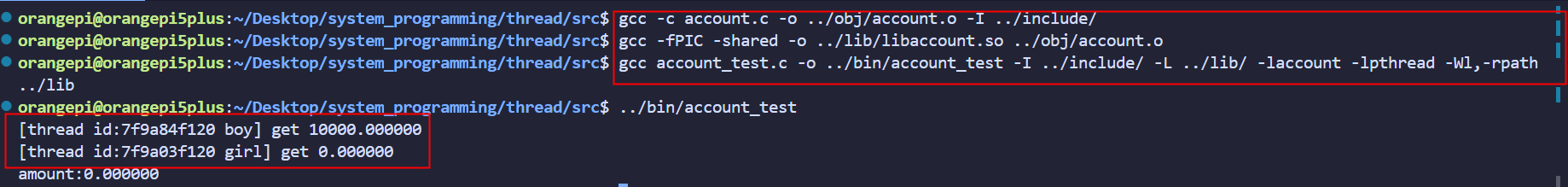
模型转换和onnxruntime推理
将官网的模型Fine-tuned on 300W-LP + Panoptic,Fine-tuned on 300W-LP转为onnx后,使用onnxruntime运行,全部实现代码如下;

-
安装依赖,只需要安装一下几个包即可运行
pip install numpy onnxruntime-gpu tqdm opencv-python -
可以在添加人头检测或者人脸检测模型首先提取人头框,并外扩一定区域后送入到人头姿态估计模型中推理;
模型和代码下载
- 6DRepNet360全范围旋转头部姿态估计onnx模型+onnxruntime推理代码+测试视频
资源中的内容如下:

可视化结果

人头姿态估计
代码
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import copy
import os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import onnxruntime as ort
from math import cos, sin
#from torch.utils.serialization import load_lua
import scipy.io as sio
from tqdm import tqdm
sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
def plot_pose_cube(img, yaw, pitch, roll, tdx=None, tdy=None, size=150.):
# Input is a cv2 image
# pose_params: (pitch, yaw, roll, tdx, tdy)
# Where (tdx, tdy) is the translation of the face.
# For pose we have [pitch yaw roll tdx tdy tdz scale_factor]
p = pitch * np.pi / 180
y = -(yaw * np.pi / 180)
r = roll * np.pi / 180
if tdx != None and tdy != None:
face_x = tdx - 0.50 * size
face_y = tdy - 0.50 * size
else:
height, width = img.shape[:2]
face_x = width / 2 - 0.5 * size
face_y = height / 2 - 0.5 * size
x1 = size * (cos(y) * cos(r)) + face_x
y1 = size * (cos(p) * sin(r) + cos(r) * sin(p) * sin(y)) + face_y
x2 = size * (-cos(y) * sin(r)) + face_x
y2 = size * (cos(p) * cos(r) - sin(p) * sin(y) * sin(r)) + face_y
x3 = size * (sin(y)) + face_x
y3 = size * (-cos(y) * sin(p)) + face_y
# Draw base in red
cv2.line(img, (int(face_x), int(face_y)), (int(x1),int(y1)),(0,0,255),3, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(face_x), int(face_y)), (int(x2),int(y2)),(0,0,255),3, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x2), int(y2)), (int(x2+x1-face_x),int(y2+y1-face_y)),(0,0,255),3, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x1+x2-face_x),int(y1+y2-face_y)),(0,0,255),3, cv2.LINE_AA)
# Draw pillars in blue
cv2.line(img, (int(face_x), int(face_y)), (int(x3),int(y3)),(255,0,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x1+x3-face_x),int(y1+y3-face_y)),(255,0,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x2), int(y2)), (int(x2+x3-face_x),int(y2+y3-face_y)),(255,0,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x2+x1-face_x),int(y2+y1-face_y)), (int(x3+x1+x2-2*face_x),int(y3+y2+y1-2*face_y)),(255,0,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
# Draw top in green
cv2.line(img, (int(x3+x1-face_x),int(y3+y1-face_y)), (int(x3+x1+x2-2*face_x),int(y3+y2+y1-2*face_y)),(0,255,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x2+x3-face_x),int(y2+y3-face_y)), (int(x3+x1+x2-2*face_x),int(y3+y2+y1-2*face_y)),(0,255,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x3), int(y3)), (int(x3+x1-face_x),int(y3+y1-face_y)),(0,255,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(x3), int(y3)), (int(x3+x2-face_x),int(y3+y2-face_y)),(0,255,0),2, cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
def draw_axis(img, yaw, pitch, roll, tdx=None, tdy=None, size = 100):
pitch = pitch * np.pi / 180
yaw = -(yaw * np.pi / 180)
roll = roll * np.pi / 180
if tdx != None and tdy != None:
tdx = tdx
tdy = tdy
else:
height, width = img.shape[:2]
tdx = width / 2
tdy = height / 2
# X-Axis pointing to right. drawn in red
x1 = size * (cos(yaw) * cos(roll)) + tdx
y1 = size * (cos(pitch) * sin(roll) + cos(roll) * sin(pitch) * sin(yaw)) + tdy
# Y-Axis | drawn in green
# v
x2 = size * (-cos(yaw) * sin(roll)) + tdx
y2 = size * (cos(pitch) * cos(roll) - sin(pitch) * sin(yaw) * sin(roll)) + tdy
# Z-Axis (out of the screen) drawn in blue
x3 = size * (sin(yaw)) + tdx
y3 = size * (-cos(yaw) * sin(pitch)) + tdy
cv2.line(img, (int(tdx), int(tdy)), (int(x1),int(y1)),(0,0,255),4, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(tdx), int(tdy)), (int(x2),int(y2)),(0,255,0),4, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.line(img, (int(tdx), int(tdy)), (int(x3),int(y3)),(255,0,0),4, cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
def get_pose_params_from_mat(mat_path):
# This functions gets the pose parameters from the .mat
# Annotations that come with the Pose_300W_LP dataset.
mat = sio.loadmat(mat_path)
# [pitch yaw roll tdx tdy tdz scale_factor]
pre_pose_params = mat['Pose_Para'][0]
# Get [pitch, yaw, roll, tdx, tdy]
pose_params = pre_pose_params[:5]
return pose_params
def get_ypr_from_mat(mat_path):
# Get yaw, pitch, roll from .mat annotation.
# They are in radians
mat = sio.loadmat(mat_path)
# [pitch yaw roll tdx tdy tdz scale_factor]
pre_pose_params = mat['Pose_Para'][0]
# Get [pitch, yaw, roll]
pose_params = pre_pose_params[:3]
return pose_params
def get_pt2d_from_mat(mat_path):
# Get 2D landmarks
mat = sio.loadmat(mat_path)
pt2d = mat['pt2d']
return pt2d
# batch*n
def normalize_vector(v):
batch = v.shape[0]
v_mag = torch.sqrt(v.pow(2).sum(1))# batch
gpu = v_mag.get_device()
if gpu < 0:
eps = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.FloatTensor([1e-8])).to(torch.device('cpu'))
else:
eps = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.FloatTensor([1e-8])).to(torch.device('cuda:%d' % gpu))
v_mag = torch.max(v_mag, eps)
v_mag = v_mag.view(batch,1).expand(batch,v.shape[1])
v = v/v_mag
return v
# u, v batch*n
def cross_product(u, v):
batch = u.shape[0]
#print (u.shape)
#print (v.shape)
i = u[:,1]*v[:,2] - u[:,2]*v[:,1]
j = u[:,2]*v[:,0] - u[:,0]*v[:,2]
k = u[:,0]*v[:,1] - u[:,1]*v[:,0]
out = torch.cat((i.view(batch,1), j.view(batch,1), k.view(batch,1)),1) #batch*3
return out
#poses batch*6
#poses
def compute_rotation_matrix_from_ortho6d(poses):
x_raw = poses[:,0:3] #batch*3
y_raw = poses[:,3:6] #batch*3
x = normalize_vector(x_raw) #batch*3
z = cross_product(x,y_raw) #batch*3
z = normalize_vector(z) #batch*3
y = cross_product(z,x) #batch*3
x = x.view(-1,3,1)
y = y.view(-1,3,1)
z = z.view(-1,3,1)
matrix = torch.cat((x,y,z), 2) #batch*3*3
return matrix
#input batch*4*4 or batch*3*3
#output torch batch*3 x, y, z in radiant
#the rotation is in the sequence of x,y,z
def compute_euler_angles_from_rotation_matrices(rotation_matrices):
batch = rotation_matrices.shape[0]
R = rotation_matrices
sy = torch.sqrt(R[:,0,0]*R[:,0,0]+R[:,1,0]*R[:,1,0])
singular = sy<1e-6
singular = singular.float()
x = torch.atan2(R[:,2,1], R[:,2,2])
y = torch.atan2(-R[:,2,0], sy)
z = torch.atan2(R[:,1,0],R[:,0,0])
xs = torch.atan2(-R[:,1,2], R[:,1,1])
ys = torch.atan2(-R[:,2,0], sy)
zs = R[:,1,0]*0
gpu = rotation_matrices.get_device()
if gpu < 0:
out_euler = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(batch,3)).to(torch.device('cpu'))
else:
out_euler = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(batch,3)).to(torch.device('cuda:%d' % gpu))
out_euler[:,0] = x*(1-singular)+xs*singular
out_euler[:,1] = y*(1-singular)+ys*singular
out_euler[:,2] = z*(1-singular)+zs*singular
return out_euler
def get_R(x,y,z):
''' Get rotation matrix from three rotation angles (radians). right-handed.
Args:
angles: [3,]. x, y, z angles
Returns:
R: [3, 3]. rotation matrix.
'''
# x
Rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(x), -np.sin(x)],
[0, np.sin(x), np.cos(x)]])
# y
Ry = np.array([[np.cos(y), 0, np.sin(y)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(y), 0, np.cos(y)]])
# z
Rz = np.array([[np.cos(z), -np.sin(z), 0],
[np.sin(z), np.cos(z), 0],
[0, 0, 1]])
R = Rz.dot(Ry.dot(Rx))
return R
if __name__ == '__main__':
onnx_path = "./snapshots/6DRepNet360_Full-Rotation_300W_LP+Panoptic_1.onnx"
vid_file = "./test_vid/11-FemaleGlasses.avi.avi"
vid_result_path = './test_vid_result'
vid_save_file = os.path.join(vid_result_path, os.path.basename(vid_file))
if not os.path.exists(vid_result_path):
os.makedirs(vid_result_path)
device=torch.device(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device('cpu')
ort_session = ort.InferenceSession(onnx_path, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'])
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(vid_file)
nums = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT)
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
ret, frame = cap.read()
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
out = cv2.VideoWriter(vid_save_file, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID'), fps, (width, height))
for i in tqdm(range(int(nums))):
ret, img = cap.read()
if not ret or img is None:
break
# 125, 45 410, 350
image = copy.deepcopy(img)
img = img[45:250, 125:410] # 根据人头位置更改
img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img = np.array(img)
img = torch.tensor(img.transpose(2, 0, 1).astype('float32')).unsqueeze(0)
# mean = [0., 0., 0.]
# std = [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
img = img / 255
mean = torch.tensor(mean).reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
std = torch.tensor(std).reshape(1, 3, 1, 1)
img = (img - mean) / std
inputs = {ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name: img.numpy()}
outs = ort_session.run(None, inputs)
R_pred = compute_rotation_matrix_from_ortho6d(torch.Tensor(outs[0]).to(device))
euler = compute_euler_angles_from_rotation_matrices(R_pred) * 180 / np.pi
p_pred_deg = euler[:, 0].cpu()
y_pred_deg = euler[:, 1].cpu()
r_pred_deg = euler[:, 2].cpu()
draw_axis(image, y_pred_deg[0], p_pred_deg[0], r_pred_deg[0], tdx=60, tdy=100, size=50)
plot_pose_cube(image, y_pred_deg[0], p_pred_deg[0], r_pred_deg[0] ,size=50)
txt = "pitch: %.4f, yaw: %.4f, roll: %.4f" % (float(p_pred_deg[0]), float(y_pred_deg[0]), float(r_pred_deg[0]))
image = cv2.putText(image, txt, (int(50), int(40)), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=0.5,
color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
out.write(image)
out.release()