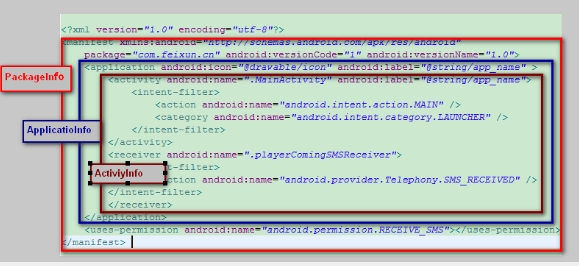
Android系统为我们提供了很多服务管理类,PackageManager管理类,它的主要职责是管理应用程序包。 通过PackageManager获取的应用程序信息来自AndroidManifest.xml。
AndroidManifest.xml是Android应用程序中最重要的文件之一,它是Android程序的全局配置文件,是每个 android程序中必须的文件。它位于我们开发的应用程序的根目录下,描述了package中的全局数据,包括package中暴露的组件 (activities, services, 等等),以及他们各自的实现类,各种能被处理的数据和启动位置等重要信息。 因此,该文件提供了Android系统所需要的关于该应用程序的必要信息,即在该应用程序的任何代码运行之前系统所必须拥有的信息。
AndroidManifest.xml文件节点说明:
PackageManager相关类
1.1 PackageItemInfo类
说明: AndroidManifest.xml文件中所有节点的基类,提供了这些节点的基本信息:label、icon、 meta-data。它并不 直接使用,而是由子类继承然后调用相应方法。
常用字段:
public int icon 获得该资源图片在R文件中的值 (对应于android:icon属性)
public int labelRes 获得该label在R文件中的值(对应于android:label属性)
public String name 获得该节点的name值 (对应于android:name属性)
public String packagename 获得该应用程序的包名 (对应于android:packagename属性)
常用方法:
Drawable loadIcon(PackageManager pm) 获得当前应用程序的图像
CharSequence loadLabel(PackageManager pm) 获得当前应用程序的label
PackageItemInfo的子类:ActivityInfo、ServiceInfo、ApplicationInfo
ActivityInfo 类
获得应用程序中<activity/>或者 <receiver />节点的信息 。我们可以通过它来获取我们设置的任何属性,包括 theme 、launchMode、launchmode等
常用方法继承至PackageItemInfo类中的loadIcon()和loadLabel()
ServiceInfo 类
同ActivityInfo类似,同样继承自 PackageItemInfo,只不过它表示的是<service>节点信息。
ApplicationInfo 类
获取一个特定引用程序中<application>节点的信息。
flags字段:
FLAG_SYSTEM 系统应用程序
FLAG_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 表示该应用安装在sdcard中
常用方法继承继承至PackageItemInfo类中的loadIcon()和loadLabel()
1.2 ResolveInfo类
说明:根据节点来获取其上一层目录的信息,通常是<activity>、<receiver>、<service>节点信息。
常用字段:
public ActivityInfo activityInfo 获取 ActivityInfo对象,即<activity>或<receiver >节点信息
public ServiceInfo serviceInfo 获取 ServiceInfo对象,即<activity>节点信息
常用方法:
Drawable loadIcon(PackageManager pm) 获得当前应用程序的图像
CharSequence loadLabel(PackageManager pm) 获得当前应用程序的label
1.3 PackageInfo类
说明:手动获取AndroidManifest.xml文件的信息 。
常用字段:
public String packageName 包名
public ActivityInfo[] activities 所有<activity>节点信息
public ApplicationInfo applicationInfo <application>节点信息,只有一个
public ActivityInfo[] receivers 所有<receiver>节点信息,多个
public ServiceInfo[] services 所有<service>节点信息 ,多个
1.4 PackageManger 类
说明: 获得已安装的应用程序信息 。可以通过getPackageManager()方法获得。
常用方法:
// 功能:获得一个PackageManger对象
public abstract PackageManager getPackageManager()
// 功能:返回给定包名的图标,否则返回null
public abstrac tDrawable getApplicationIcon(String packageName)
// 功能:返回该ApplicationInfo对象
// packageName 包名
// flags 该ApplicationInfo是此flags标记,通常可以直接赋予常数**0**即可
public abstract ApplicationInfo **getApplicationInfo**(String packageName, int flags)
// 功能:返回给定条件的所有PackageInfo
// flag为一般为GET_UNINSTALLED_PACKAGES,那么此时会返回所有ApplicationInfo。我们可以对ApplicationInfo 的flags过滤,得到我们需要的
public abstract List <ApplicationInfo> getInstalledApplications(int flags)
// 功能:返回给定条件的所有PackageInfo
public abstract List <PackageInfo> getInstalledPackages(int flags)
// 功能:返回给定条件的ResolveInfo对象(本质上是Activity)
// intent 查寻条件,Activity所配置的action和category
// flags: MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY :Category必须带有CATEGORY_DEFAULT的Activity,才匹配
// GET_INTENT_FILTERS :匹配Intent条件即可
// GET_RESOLVED_FILTER :匹配Intent条件即可
public abstractResolveInfo resolveActivity(Intent intent, int flags)
// 功能:返回给定条件的所有ResolveInfo对象(本质上是Activity),集合对象
public abstract List <ResolveInfo> queryIntentActivities(Intent intent, int flags)
// 功能:返回给定条件的ResolveInfo对象(本质上是Service)
public abstract ResolveInfo resolveService(Intent intent, int flags)
// 功能 :返回给定条件的所有ResolveInfo对象(本质上是Service),集合对象
public abstract List<ResolveInfo> queryIntentServices(Intent intent, int flags)
Android软件包可见性
Google文档说明:https://developer.android.com/training/package-visibility
如果应用以 Android 11(API 级别 30)或更高版本为目标平台,并查询与设备上已安装的其他应用相关的信息,则系统在默认情况下会过滤此信息。此过滤行为意味着您的应用无法检测设备上安装的所有应用,这有助于最大限度地减少您的应用可以访问但在执行其用例时不需要的潜在敏感信息。
有限的应用可见性会影响提供其他应用相关信息的方法的返回结果,例如 queryIntentActivities()、getPackageInfo() 和 getInstalledApplications()。有限的可见性还会影响与其他应用的显式交互,例如启动另一个应用的服务。
部分软件包是自动可见的。您的应用始终可以在查询其他已安装的应用时检测这些软件包。如需查看其他软件包,请使用 元素声明您的应用需要提高软件包可见性,在 元素中,按软件包名称、按 intent 签名或按提供程序授权指定其他应用。
<manifest package="com.example.game">
<queries>
<!-- Specific apps you interact with, eg: -->
<package android:name="com.example.store" />
<package android:name="com.example.service" />
<!--
Specific intents you query for,
eg: for a custom share UI
-->
<intent>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" />
<data android:mimeType="image/jpeg" />
</intent>
</queries>
<!-- Specific provider you interact with, eg: -->
<queries>
<provider android:authorities="com.example.settings.files" />
</queries>
...
</manifest>
在极少数情况下,如果遇到 <queries> 元素无法提供适当的软件包可见性,您还可以使用 QUERY_ALL_PACKAGES 权限。
判断某个具体包名是否存在的方法
public static boolean isApplicationAvailable(Context context) {
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
try {
packageManager.getPackageInfo(PACKAGE_NAME, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
return true;
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
return false;
}
}
adb pm 常用命令
adb shell pm install apkPath 安装应用
adb shell pm uninstall packageName 卸载应用
adb shell pm clear packageName 清除应用缓存
adb shell pm path packageName 查看应用路径
adb shell pm dump packageName 打印应用信息
adb shell pm list package 列出所有应用
adb shell pm list package -3 列出第三方应用
adb shell pm list instrumentation 列出所有测试包
pm list features 列出所有硬件相关信息
pm list libraries 列出当前设备支持的libs
pm list users 列出系统上所有的users
pm list permissions 列出所有已知的权限
pm enable ‘pkgname’ 使package或component可用。(如:pm enable “package/class”)
pm disable ‘pkgname’ 使package或component不可用
pm grant <PACKAGE_PERMISSION> 授权给应用
pm revoke <PACKAGE_PERMISSION> 撤销权限
$ adb shell pm -h
Package manager (package) commands:
help
Print this help text.
path [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE
Print the path to the .apk of the given PACKAGE.
dump PACKAGE
Print various system state associated with the given PACKAGE.
has-feature FEATURE_NAME [version]
Prints true and returns exit status 0 when system has a FEATURE_NAME,
otherwise prints false and returns exit status 1
list features
Prints all features of the system.
list instrumentation [-f] [TARGET-PACKAGE]
Prints all test packages; optionally only those targeting TARGET-PACKAGE
Options:
-f: dump the name of the .apk file containing the test package
list libraries
Prints all system libraries.
list packages [-f] [-d] [-e] [-s] [-3] [-i] [-l] [-u] [-U]
[--show-versioncode] [--apex-only] [--uid UID] [--user USER_ID] [FILTER]
Prints all packages; optionally only those whose name contains
the text in FILTER. Options are:
-f: see their associated file
-a: all known packages (but excluding APEXes)
-d: filter to only show disabled packages
-e: filter to only show enabled packages
-s: filter to only show system packages
-3: filter to only show third party packages
-i: see the installer for the packages
-l: ignored (used for compatibility with older releases)
-U: also show the package UID
-u: also include uninstalled packages
--show-versioncode: also show the version code
--apex-only: only show APEX packages
--uid UID: filter to only show packages with the given UID
--user USER_ID: only list packages belonging to the given user
list permission-groups
Prints all known permission groups.
list permissions [-g] [-f] [-d] [-u] [GROUP]
Prints all known permissions; optionally only those in GROUP. Options are:
-g: organize by group
-f: print all information
-s: short summary
-d: only list dangerous permissions
-u: list only the permissions users will see
list staged-sessions [--only-ready] [--only-sessionid] [--only-parent]
Prints all staged sessions.
--only-ready: show only staged sessions that are ready
--only-sessionid: show only sessionId of each session
--only-parent: hide all children sessions
list users
Prints all users.
resolve-activity [--brief] [--components] [--query-flags FLAGS]
[--user USER_ID] INTENT
Prints the activity that resolves to the given INTENT.
query-activities [--brief] [--components] [--query-flags FLAGS]
[--user USER_ID] INTENT
Prints all activities that can handle the given INTENT.
query-services [--brief] [--components] [--query-flags FLAGS]
[--user USER_ID] INTENT
Prints all services that can handle the given INTENT.
query-receivers [--brief] [--components] [--query-flags FLAGS]
[--user USER_ID] INTENT
Prints all broadcast receivers that can handle the given INTENT.
install [-rtfdgw] [-i PACKAGE] [--user USER_ID|all|current]
[-p INHERIT_PACKAGE] [--install-location 0/1/2]
[--install-reason 0/1/2/3/4] [--originating-uri URI]
[--referrer URI] [--abi ABI_NAME] [--force-sdk]
[--preload] [--instant] [--full] [--dont-kill]
[--enable-rollback]
[--force-uuid internal|UUID] [--pkg PACKAGE] [-S BYTES]
[--apex] [--wait TIMEOUT]
[PATH [SPLIT...]|-]
Install an application. Must provide the apk data to install, either as
file path(s) or '-' to read from stdin. Options are:
-R: disallow replacement of existing application
-t: allow test packages
-i: specify package name of installer owning the app
-f: install application on internal flash
-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only)
-p: partial application install (new split on top of existing pkg)
-g: grant all runtime permissions
-S: size in bytes of package, required for stdin
--user: install under the given user.
--dont-kill: installing a new feature split, don't kill running app
--restrict-permissions: don't whitelist restricted permissions at install
--originating-uri: set URI where app was downloaded from
--referrer: set URI that instigated the install of the app
--pkg: specify expected package name of app being installed
--abi: override the default ABI of the platform
--instant: cause the app to be installed as an ephemeral install app
--full: cause the app to be installed as a non-ephemeral full app
--install-location: force the install location:
0=auto, 1=internal only, 2=prefer external
--install-reason: indicates why the app is being installed:
0=unknown, 1=admin policy, 2=device restore,
3=device setup, 4=user request
--force-uuid: force install on to disk volume with given UUID
--apex: install an .apex file, not an .apk
--wait: when performing staged install, wait TIMEOUT milliseconds
for pre-reboot verification to complete. If TIMEOUT is not
specified it will wait for 60000 milliseconds.
install-existing [--user USER_ID|all|current]
[--instant] [--full] [--wait] [--restrict-permissions] PACKAGE
Installs an existing application for a new user. Options are:
--user: install for the given user.
--instant: install as an instant app
--full: install as a full app
--wait: wait until the package is installed
--restrict-permissions: don't whitelist restricted permissions
install-create [-lrtsfdg] [-i PACKAGE] [--user USER_ID|all|current]
[-p INHERIT_PACKAGE] [--install-location 0/1/2]
[--install-reason 0/1/2/3/4] [--originating-uri URI]
[--referrer URI] [--abi ABI_NAME] [--force-sdk]
[--preload] [--instant] [--full] [--dont-kill]
[--force-uuid internal|UUID] [--pkg PACKAGE] [--apex] [-S BYTES]
[--multi-package] [--staged]
Like "install", but starts an install session. Use "install-write"
to push data into the session, and "install-commit" to finish.
install-write [-S BYTES] SESSION_ID SPLIT_NAME [PATH|-]
Write an apk into the given install session. If the path is '-', data
will be read from stdin. Options are:
-S: size in bytes of package, required for stdin
install-remove SESSION_ID SPLIT...
Mark SPLIT(s) as removed in the given install session.
install-add-session MULTI_PACKAGE_SESSION_ID CHILD_SESSION_IDs
Add one or more session IDs to a multi-package session.
install-commit SESSION_ID
Commit the given active install session, installing the app.
install-abandon SESSION_ID
Delete the given active install session.
set-install-location LOCATION
Changes the default install location. NOTE this is only intended for debugging;
using this can cause applications to break and other undersireable behavior.
LOCATION is one of:
0 [auto]: Let system decide the best location
1 [internal]: Install on internal device storage
2 [external]: Install on external media
get-install-location
Returns the current install location: 0, 1 or 2 as per set-install-location.
move-package PACKAGE [internal|UUID]
move-primary-storage [internal|UUID]
uninstall [-k] [--user USER_ID] [--versionCode VERSION_CODE]
PACKAGE [SPLIT...]
Remove the given package name from the system. May remove an entire app
if no SPLIT names specified, otherwise will remove only the splits of the
given app. Options are:
-k: keep the data and cache directories around after package removal.
--user: remove the app from the given user.
--versionCode: only uninstall if the app has the given version code.
clear [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE
Deletes all data associated with a package.
enable [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
disable [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
disable-user [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
disable-until-used [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
default-state [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
These commands change the enabled state of a given package or
component (written as "package/class").
hide [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
unhide [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
suspend [--user USER_ID] TARGET-PACKAGE
Suspends the specified package (as user).
unsuspend [--user USER_ID] TARGET-PACKAGE
Unsuspends the specified package (as user).
grant [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE PERMISSION
revoke [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE PERMISSION
These commands either grant or revoke permissions to apps. The permissions
must be declared as used in the app's manifest, be runtime permissions
(protection level dangerous), and the app targeting SDK greater than Lollipop MR1.
reset-permissions
Revert all runtime permissions to their default state.
set-permission-enforced PERMISSION [true|false]
get-privapp-permissions TARGET-PACKAGE
Prints all privileged permissions for a package.
get-privapp-deny-permissions TARGET-PACKAGE
Prints all privileged permissions that are denied for a package.
get-oem-permissions TARGET-PACKAGE
Prints all OEM permissions for a package.
set-app-link [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE {always|ask|never|undefined}
get-app-link [--user USER_ID] PACKAGE
trim-caches DESIRED_FREE_SPACE [internal|UUID]
Trim cache files to reach the given free space.
list users
Lists the current users.
create-user [--profileOf USER_ID] [--managed] [--restricted] [--ephemeral]
[--guest] [--pre-create-only] [--user-type USER_TYPE] USER_NAME
Create a new user with the given USER_NAME, printing the new user identifier
of the user.
USER_TYPE is the name of a user type, e.g. android.os.usertype.profile.MANAGED.
If not specified, the default user type is android.os.usertype.full.SECONDARY.
--managed is shorthand for '--user-type android.os.usertype.profile.MANAGED'.
--restricted is shorthand for '--user-type android.os.usertype.full.RESTRICTED'.
--guest is shorthand for '--user-type android.os.usertype.full.GUEST'.
remove-user USER_ID
Remove the user with the given USER_IDENTIFIER, deleting all data
associated with that user
set-user-restriction [--user USER_ID] RESTRICTION VALUE
get-max-users
get-max-running-users
compile [-m MODE | -r REASON] [-f] [-c] [--split SPLIT_NAME]
[--reset] [--check-prof (true | false)] (-a | TARGET-PACKAGE)
Trigger compilation of TARGET-PACKAGE or all packages if "-a". Options are:
-a: compile all packages
-c: clear profile data before compiling
-f: force compilation even if not needed
-m: select compilation mode
MODE is one of the dex2oat compiler filters:
assume-verified
extract
verify
quicken
space-profile
space
speed-profile
speed
everything
-r: select compilation reason
REASON is one of:
first-boot
boot
install
bg-dexopt
ab-ota
inactive
shared
--reset: restore package to its post-install state
--check-prof (true | false): look at profiles when doing dexopt?
--secondary-dex: compile app secondary dex files
--split SPLIT: compile only the given split name
--compile-layouts: compile layout resources for faster inflation
force-dex-opt PACKAGE
Force immediate execution of dex opt for the given PACKAGE.
bg-dexopt-job
Execute the background optimizations immediately.
Note that the command only runs the background optimizer logic. It may
overlap with the actual job but the job scheduler will not be able to
cancel it. It will also run even if the device is not in the idle
maintenance mode.
reconcile-secondary-dex-files TARGET-PACKAGE
Reconciles the package secondary dex files with the generated oat files.
dump-profiles TARGET-PACKAGE
Dumps method/class profile files to
/data/misc/profman/TARGET-PACKAGE.txt
snapshot-profile TARGET-PACKAGE [--code-path path]
Take a snapshot of the package profiles to
/data/misc/profman/TARGET-PACKAGE[-code-path].prof
If TARGET-PACKAGE=android it will take a snapshot of the boot image
set-home-activity [--user USER_ID] TARGET-COMPONENT
Set the default home activity (aka launcher).
TARGET-COMPONENT can be a package name (com.package.my) or a full
component (com.package.my/component.name). However, only the package name
matters: the actual component used will be determined automatically from
the package.
set-installer PACKAGE INSTALLER
Set installer package name
get-instantapp-resolver
Return the name of the component that is the current instant app installer.
set-harmful-app-warning [--user <USER_ID>] <PACKAGE> [<WARNING>]
Mark the app as harmful with the given warning message.
get-harmful-app-warning [--user <USER_ID>] <PACKAGE>
Return the harmful app warning message for the given app, if present
uninstall-system-updates [<PACKAGE>]
Removes updates to the given system application and falls back to its
/system version. Does nothing if the given package is not a system app.
If no package is specified, removes updates to all system applications.
get-moduleinfo [--all | --installed] [module-name]
Displays module info. If module-name is specified only that info is shown
By default, without any argument only installed modules are shown.
--all: show all module info
--installed: show only installed modules
log-visibility [--enable|--disable] <PACKAGE>
Turns on debug logging when visibility is blocked for the given package.
--enable: turn on debug logging (default)
--disable: turn off debug logging
<INTENT> specifications include these flags and arguments:
[-a <ACTION>] [-d <DATA_URI>] [-t <MIME_TYPE>] [-i <IDENTIFIER>]
[-c <CATEGORY> [-c <CATEGORY>] ...]
[-n <COMPONENT_NAME>]
[-e|--es <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_STRING_VALUE> ...]
[--esn <EXTRA_KEY> ...]
[--ez <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_BOOLEAN_VALUE> ...]
[--ei <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_INT_VALUE> ...]
[--el <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_LONG_VALUE> ...]
[--ef <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_FLOAT_VALUE> ...]
[--eu <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_URI_VALUE> ...]
[--ecn <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_COMPONENT_NAME_VALUE>]
[--eia <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_INT_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_INT_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as Integer[])
[--eial <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_INT_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_INT_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as List<Integer>)
[--ela <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_LONG_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_LONG_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as Long[])
[--elal <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_LONG_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_LONG_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as List<Long>)
[--efa <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_FLOAT_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_FLOAT_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as Float[])
[--efal <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_FLOAT_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_FLOAT_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as List<Float>)
[--esa <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_STRING_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_STRING_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as String[]; to embed a comma into a string,
escape it using "\,")
[--esal <EXTRA_KEY> <EXTRA_STRING_VALUE>[,<EXTRA_STRING_VALUE...]]
(mutiple extras passed as List<String>; to embed a comma into a string,
escape it using "\,")
[-f <FLAG>]
[--grant-read-uri-permission] [--grant-write-uri-permission]
[--grant-persistable-uri-permission] [--grant-prefix-uri-permission]
[--debug-log-resolution] [--exclude-stopped-packages]
[--include-stopped-packages]
[--activity-brought-to-front] [--activity-clear-top]
[--activity-clear-when-task-reset] [--activity-exclude-from-recents]
[--activity-launched-from-history] [--activity-multiple-task]
[--activity-no-animation] [--activity-no-history]
[--activity-no-user-action] [--activity-previous-is-top]
[--activity-reorder-to-front] [--activity-reset-task-if-needed]
[--activity-single-top] [--activity-clear-task]
[--activity-task-on-home] [--activity-match-external]
[--receiver-registered-only] [--receiver-replace-pending]
[--receiver-foreground] [--receiver-no-abort]
[--receiver-include-background]
[--selector]
[<URI> | <PACKAGE> | <COMPONENT>]



![[网络工程师]-传输层协议-UDP协议](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3a0d530be29e41e4b9b824d6f98cc098.png)