LeetCode 654.最大二叉树
题目链接🔗
LeetCode 654.最大二叉树
思路
最大二叉树的构建过程如下:

构造树一般采用的是前序遍历,因为先构造中间节点,然后递归构造左子树和右子树。
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, 0, nums.length);
}
private TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1(int[] nums, int leftIndex, int rightIndex){
if(rightIndex - leftIndex < 1){
return null;
}
if(rightIndex - leftIndex == 1){
return new TreeNode(nums[leftIndex]);
}
int maxIndex = leftIndex;
int maxValue = nums[maxIndex];
for(int i = leftIndex + 1; i < rightIndex; i++){
if(nums[i] > maxValue){
maxValue = nums[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxValue);
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, leftIndex, maxIndex);
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, maxIndex + 1, rightIndex);
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 617.合并二叉树
题目链接🔗
LeetCode 617.合并二叉树
思路
其实和遍历一个树逻辑是一样的,只不过传入两个树的节点,同时操作。
我们下面以前序遍历为例。
动画如下:

使用递归法
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
}
}
使用迭代法
class Solution {
// 使用栈迭代
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root2);
stack.push(root1);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node1 = stack.pop();
TreeNode node2 = stack.pop();
node1.val += node2.val;
if(node1.left != null && node2.left != null){
stack.push(node2.left);
stack.push(node1.left);
}else{
if(node1.left == null){
node1.left = node2.left;
}
}
if(node1.right != null && node2.right != null){
stack.push(node2.right);
stack.push(node1.right);
}else{
if(node1.right == null){
node1.right = node2.right;
}
}
}
return root1;
}
}
class Solution {
// 使用队列迭代
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null) return root2;
if (root2 ==null) return root1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root1);
queue.offer(root2);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node1 = queue.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue.poll();
// 此时两个节点一定不为空,val相加
node1.val = node1.val + node2.val;
// 如果两棵树左节点都不为空,加入队列
if (node1.left != null && node2.left != null) {
queue.offer(node1.left);
queue.offer(node2.left);
}
// 如果两棵树右节点都不为空,加入队列
if (node1.right != null && node2.right != null) {
queue.offer(node1.right);
queue.offer(node2.right);
}
// 若node1的左节点为空,直接赋值
if (node1.left == null && node2.left != null) {
node1.left = node2.left;
}
// 若node1的右节点为空,直接赋值
if (node1.right == null && node2.right != null) {
node1.right = node2.right;
}
}
return root1;
}
}
LeetCode 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
题目链接🔗
LeetCode 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
思路
二叉搜索树是一个有序树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
这就决定了,二叉搜索树,递归遍历和迭代遍历和普通二叉树都不一样。
递归法
class Solution {
// 递归,普通二叉树
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val == val) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left, val);
if (left != null) {
return left;
}
return searchBST(root.right, val);
}
}
class Solution {
// 递归,利用二叉搜索树特点,优化
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val == val) {
return root;
}
if (val < root.val) {
return searchBST(root.left, val);
} else {
return searchBST(root.right, val);
}
}
}
迭代法
一提到二叉树遍历的迭代法,可能立刻想起使用栈来模拟深度遍历,使用队列来模拟广度遍历。
对于二叉搜索树可就不一样了,因为二叉搜索树的特殊性,也就是节点的有序性,可以不使用辅助栈或者队列就可以写出迭代法。
对于一般二叉树,递归过程中还有回溯的过程,例如走一个左方向的分支走到头了,那么要调头,在走右分支。
而对于二叉搜索树,不需要回溯的过程,因为节点的有序性就帮我们确定了搜索的方向。
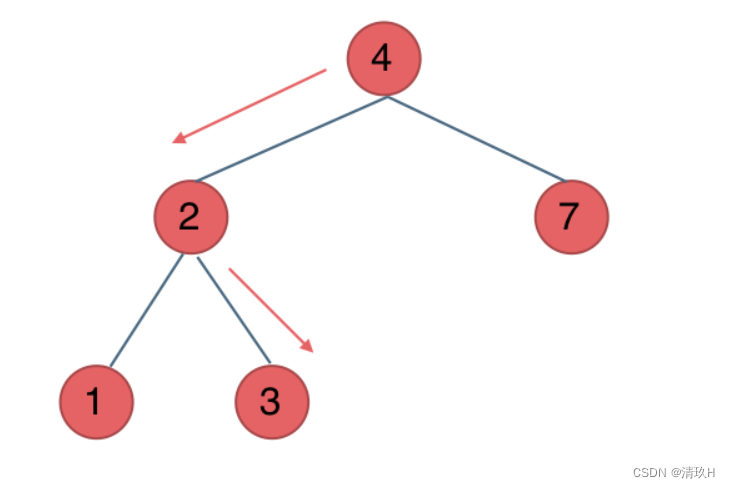
例如要搜索元素为3的节点,我们不需要搜索其他节点,也不需要做回溯,查找的路径已经规划好了。
中间节点如果大于3就向左走,如果小于3就向右走,如图:
class Solution {
// 迭代,普通二叉树
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val == val) {
return root;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode pop = stack.pop();
if (pop.val == val) {
return pop;
}
if (pop.right != null) {
stack.push(pop.right);
}
if (pop.left != null) {
stack.push(pop.left);
}
}
return null;
}
}
class Solution {
// 迭代,利用二叉搜索树特点,优化,可以不需要栈
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while (root != null){
if (val < root.val) root = root.left;
else if (val > root.val) root = root.right;
else return root;
}
return null;
}
}
LeetCode 98.验证二叉搜索树
题目链接🔗
LeetCode 98.验证二叉搜索树
思路
要知道中序遍历下,输出的二叉搜索树节点的数值是有序序列。
有了这个特性,验证二叉搜索树,就相当于变成了判断一个序列是不是递增的了。
递归法
class Solution {
TreeNode max;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
// 左
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if (!left) {
return false;
}
// 中
if (max != null && root.val <= max.val) {
return false;
}
max = root;
// 右
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return right;
}
}
迭代法
class Solution {
// 迭代
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;// 左
}
// 中,处理
TreeNode pop = stack.pop();
if (pre != null && pop.val <= pre.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pop;
root = pop.right;// 右
}
return true;
}
}