一、概述
execute和submit都是线程池中执行任务的方法。
execute是Executor接口中的方法
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
submit是ExecuteService接口中的方法。
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
}
通过源码可以看出execute方法无返回值,参数为Runnable对象。
submit方法有三个重载方法,都有Future类型的返回值,参数可以是Runnable对象,Callable对象,Runnable对象和一个其他类型的对象。
那么在执行过程中有异常抛出会怎么样呢,先说答案,execute方法会直接抛出异常,submit方法不会抛出异常,只有在通过Future的get方法获取结果的时候才会抛出异常,下面进行测试:
public class ExecutorTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ExecutorTest1 test1 = new ExecutorTest1();
executorService.execute(() -> test1.say("execute方法"));
executorService.submit(() -> test1.say("submit方法"));
executorService.shutdown();
}
private void say(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
throw new RuntimeException("抛出了异常:"+ msg);
}
}
执行结果如下:
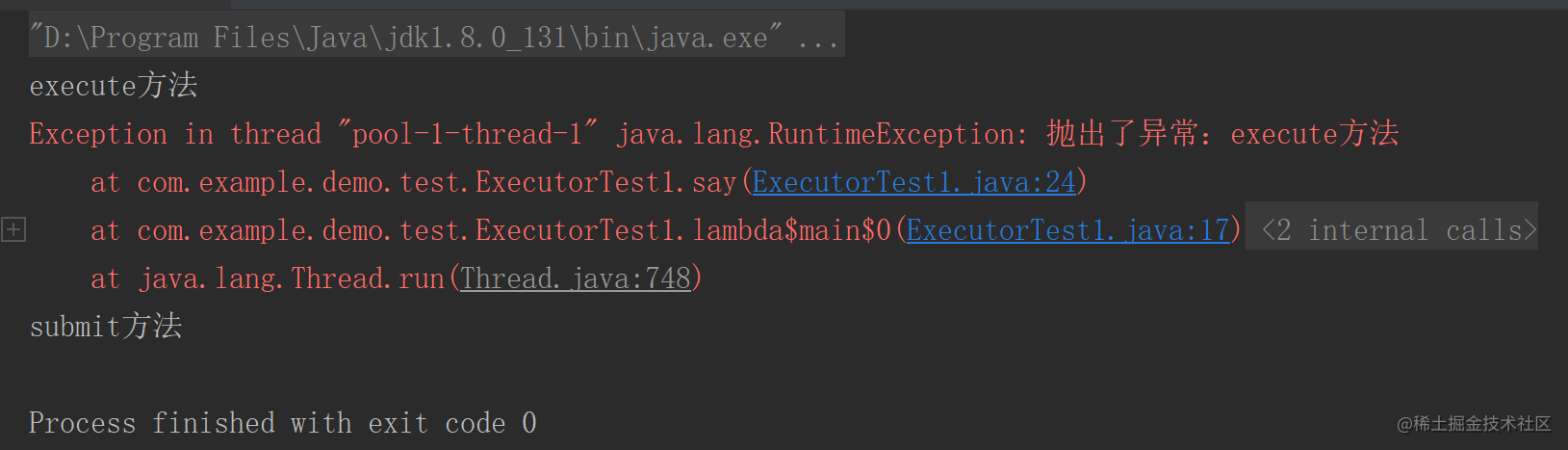
可见execute方法直接抛出了异常,submit方法只打印了参数没有抛出异常,下面测试使用Future的get方法获取结果:
public class ExecutorTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ExecutorTest1 test1 = new ExecutorTest1();
executorService.execute(() -> test1.say("execute方法"));
Future<?> submitFuture = executorService.submit(() -> test1.say("submit方法"));
try {
Object o = submitFuture.get();
System.out.println("这是submit的返回值:"+o);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
private void say(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
throw new RuntimeException("抛出了异常:"+ msg);
}
}
结果如下:
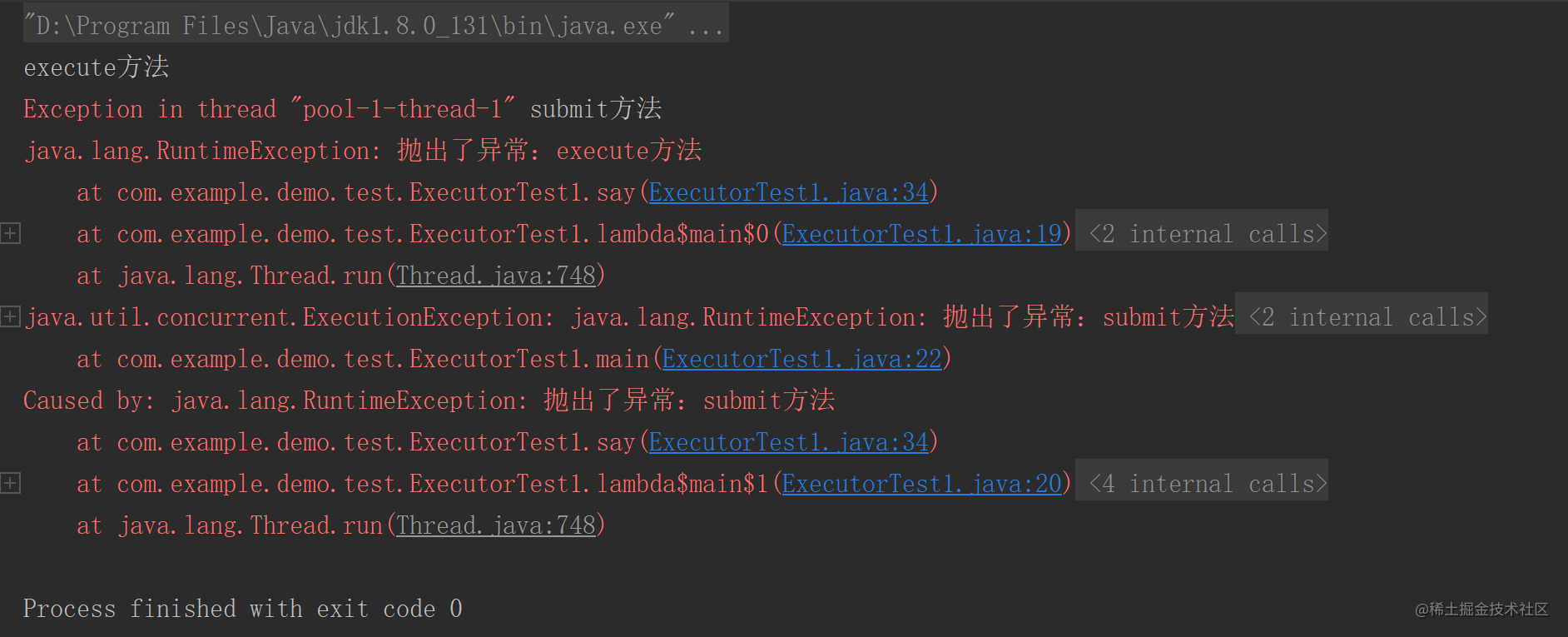
可见使用submit方法时只有在使用Future的get方法时才会抛出异常,并且get方法也会抛出ExecutionException异常。
那么还有一个问题,如果线程中执行方法抛出的异常已经被捕获了,那么submit会怎么处理呢,其实在方法中如果异常已经被捕获了,那么就是方法的正常运行,有异常打印的话在执行的时候就会打印,不会等到调用Future的get方法时候才会打印。测试如下:
public class ExecutorTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ExecutorTest1 test1 = new ExecutorTest1();
executorService.execute(() -> test1.say("execute方法"));
Future<?> submitFuture = executorService.submit(() -> test1.say("submit方法"));
try {
Object o = submitFuture.get();
System.out.println("这是submit的返回值:"+o);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
private void say(String msg){
System.out.println(msg);
try{
throw new RuntimeException("抛出了异常:"+ msg);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果如下:
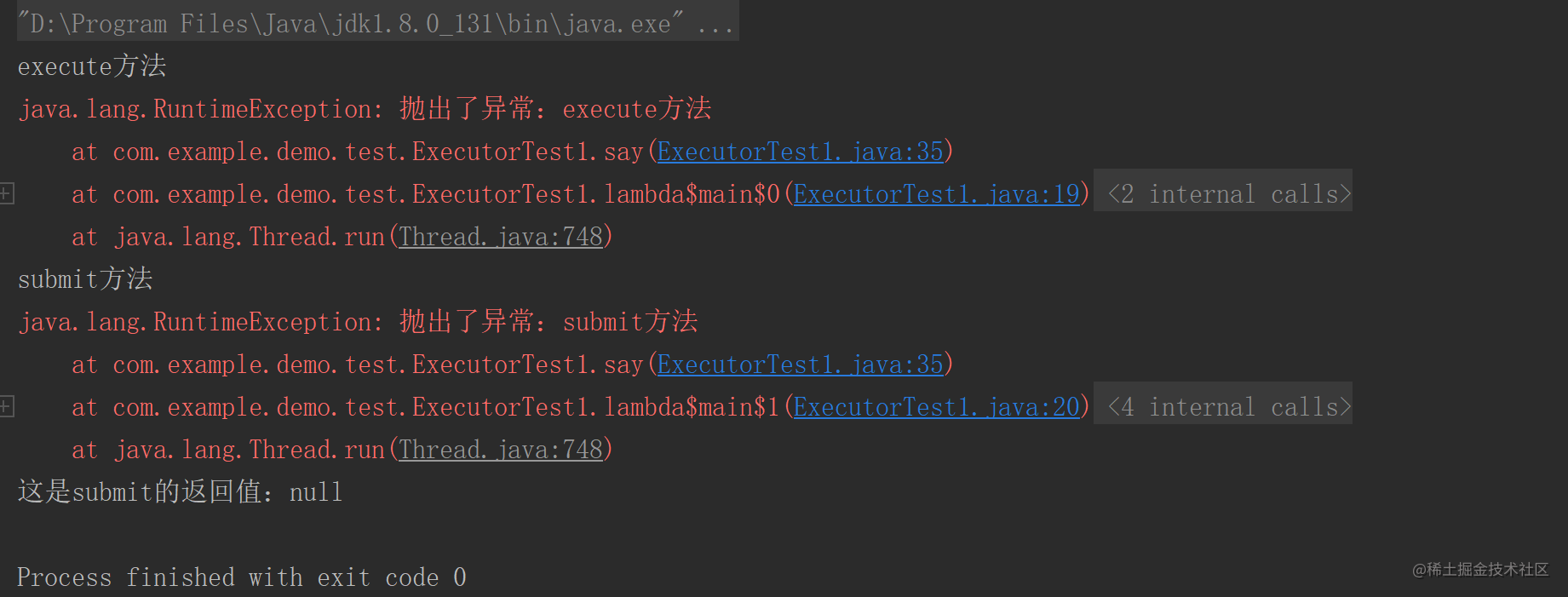
可见execute和submit都正常执行了方法,Future的get方法也获取到了结果,因为say方法没有返回值,所以打印的结果是null。
二、结论
execute和submit的区别如下:
- execute是Executor接口的方法,submit是ExecuteService接口的方法。
- execute的入参是Runnable,submit的入参可以是Runnable、Callable、Runnable和一个返回值。
- execute没有返回值,submit有返回值。
- 方法中抛出异常,execute会直接抛出异常,submit会在获取结果的时候抛出异常,如果不获取结果,submit不抛出异常。
关于Future可以查看:
Java多线程:Future和FutureTask
之前文章:
HashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.8)
Java线程池详解