文章目录
- 前情回顾
- map/multimap
- 概念
- 差别
- 构造函数
- 赋值操作
- 大小操作函数
- 交换函数
- 插入函数
- 删除函数
- 查找函数
- 统计函数
- 排序规则
- 下一座石碑
🎉welcome🎉
✒️博主介绍:一名大一的智能制造专业学生,在学习C/C++的路上会越走越远,后面不定期更新有关C/C++语法,数据结构,算法,Linux,ue5使用,制作游戏的心得,和大家一起共同成长。
✈️C++专栏:C++爬塔日记
😘博客制作不易,👍点赞+⭐收藏+➕关注
前情回顾
在上一块石碑中,我学到了set/multiset容器,同时下一块石碑也显露出来…
- 🚄上章地址:第九层(8):STL之set/multiset
map/multimap
概念
- 在map/multimap中所有元素都是pair数组,在这个pair数组中,第一个元素是key(键值),起到引索的作用,可以根据key快速定位到对应的value(实值),所有元素是会根据key值来进行排序的,底层与set一样,也是二叉树
差别
- map和multimap的差别在于key值的重复插入,在map中同样的key只可以有一个,但是multimap可以有多个
构造函数
- map和set的构造函数是基本一样的,但是它的模板参数列表必须要两个参数,第一个代表键值,第二个代表实值
map<T1 ,T2>;//map的默认构造函数
map(vonst map &m);//将m的值拷贝给本身
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void print(map<int ,int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second<< " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
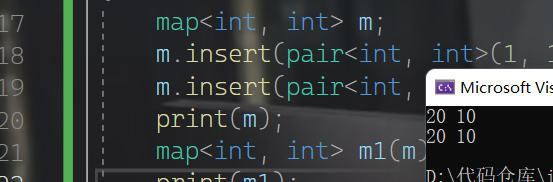
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(0, 20));
print(m);
map<int, int> m1(m);
print(m1);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
赋值操作
- 和set一样,只有操作符重载
map& operator=(const map& m);//将m的值拷贝到本身
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void print(map<int ,int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second<< " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
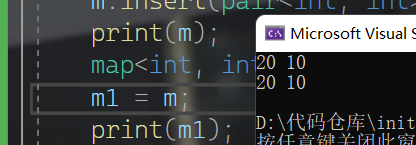
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(0, 20));
print(m);
map<int, int> m1;
m1 = m;
print(m1);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
大小操作函数
- map对于大小是不能重新定义的,只能知道有多少个元素,或者是否为空,与set一样
size()://返回容器中元素个数
empty();//判断容器是否为空
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
map<int, int> m;
if (m.empty())
{
cout << "m为空" << endl;
}
cout << m.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
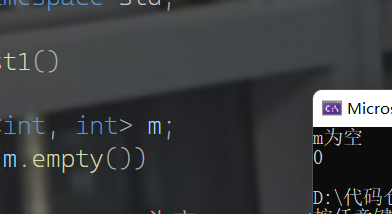
交换函数
- 与set是一样的,都利用swap交换
swap(m);//与m交换数据
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void print(map<int,int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
map<int,int> m;
m.insert(pair<int,int>(0,10));
map<int,int> m1;
m1.insert(pair<int,int>(0,20));
cout << "交换前" << endl;
print(m);
print(m1);
m.swap(m1);
cout << "交换后" << endl;
print(m);
print(m1);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
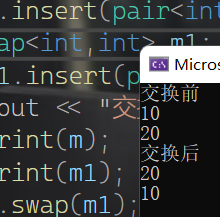
插入函数
- map的插入有三种不同的写法
insert(pair<int,T>(key,T elem));//插入键值为key的elem
insert(make_pair(key,T elem));//插入键值为key的elem
insert(map<int ,T>::value_type(key,T elem));//插入键值为key的elem
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void print(map<int,int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
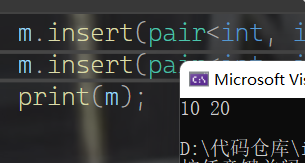
map<int, int> m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(0, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 20));
print(m);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
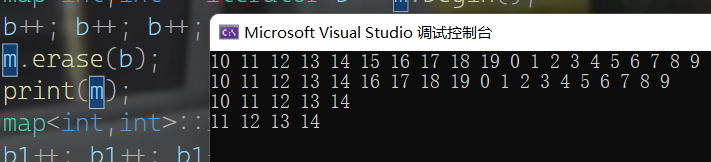
删除函数
- 同样与set是一样的,具有四个删除函数
clear();//删除容器中所有元素
erase(pos);//删除迭代器pos指向的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
erase(beg,end);//删除迭代器beg到end之间的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
erase(T elme);//删除容器中所有的实值为elem的元素
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void print(map<int,int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
map<int,int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
m.insert(pair<int,int>(i,i+10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(i+10, i));
}
print(m);
map<int,int>::iterator b = m.begin();
b++; b++; b++; b++; b++;
m.erase(b);
print(m);
map<int,int>::iterator b1 = m.begin();
b1++; b1++; b1++; b1++; b1++;
m.erase(b1, m.end());
print(m);
m.erase(0);
print(m);
m.clear();
print(m);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
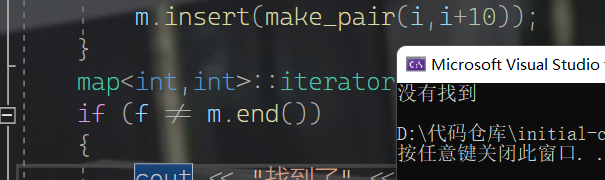
查找函数
- 同set
find(key);//查找key是否存在,存在返回该键值所指元素的迭代器,不存在返回end()
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
map<int,int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
m.insert(make_pair(i,i+10));
}
map<int,int>::iterator f = m.find(10);
if (f != m.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
统计函数
- 可以统计这个容器有多少个这个键值,对于map来说,只有0和1,因为map是不可以拥有重复键值的
count(key);//统计键值key的个数
使用:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
void test1()
{
map<int,int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
m.insert(pair<int,int>(i,i+10));
}
cout << m.count(1) << endl;
cout << m.count(9) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
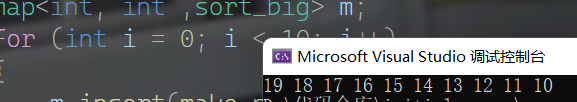
排序规则
- 与set一样,利用仿函数去改变排序规则
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
class sort_big
{
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test1()
{
map<int, int ,sort_big> m;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
m.insert(make_pair(i,i+10));
}
; for (map<int,int, sort_big>::iterator b = m.begin(); b != m.end(); b++)
{
cout << (*b).second << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
下一座石碑
- 这座石碑倒下了,露出了下一座石碑…
😘预知后事如何,关注新专栏,和我一起征服C++这座巨塔
🚀专栏:C++爬塔日记
🙉都看到这里了,留下你们的👍点赞+⭐收藏+📋评论吧🙉