清楚姐姐学信息论
数学,只需要求x的y次方和y的x次方那个大选哪个,除了2和3时是3多,其他情况都是数越小能代表的数越多
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int maxx = max(x, y), minn = min(x, y);
if (maxx == 3 && minn == 2) {
cout << 3 << '\n';
} else {
cout << minn << '\n';
}
return 0;
}清楚姐姐学构造
通过同余方程式可以看出,a是关于中点对称的,b的绝对值是关于中点对称的
因为
c[i]=a[i]+b[i]
所以
c[i]+c[n-1-i]=2*a[i]
c[n-1-i]-c[i]=2*b[i]
有了上述计算公式,发现c[i]+c[n-1-i]和c[n-1-i]-c[i]必须都是偶数才行,因为模数m一定是质数,也可知的是质数除了2都是奇素数,因此,除了2一定存在若干个m可以把c[i]+c[n-1-i]和c[n-1-i]-c[i]变成偶数来得到a[i],b[i],但如果是2,则不可能,所以当m=2时如果存在奇数,则输出No
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> x, y;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
if (n == 1) {
cout << "Yes\n";
cout << a[0] << '\n';
cout << "0\n";
return 0;
}
if (m == 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
if ((a[i] + a[n - 1 - i]) % 2 == 1) {
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
int p = (a[i] + a[n - 1 - i]) / 2;
x.push_back(p % m);
if (((a[n - 1 - i] - a[i] + m) % m) % 2 == 1) {
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
p = ((a[n - 1 - i] - a[i] + m) % m) / 2;
y.push_back(p % m);
}
if (n & 1) {
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
y.push_back(0);
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
cout << x[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << x[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
cout << m - y[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << y[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
} else {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
cout << x[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << x[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
cout << m - y[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << y[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
}
return 0;
}
if (n & 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
int p = (a[i] + a[n - 1 - i]);
while (p & 1) {
p += m;
}
x.push_back(p / 2 % m);
p = (a[n - 1 - i] - a[i] + m) % m;
while (p & 1) {
p += m;
}
y.push_back(p / 2 % m);
}
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
y.push_back(0);
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
cout << x[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << x[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n / 2; i++) {
cout << m - y[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << y[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
int p = (a[i] + a[n - 1 - i]);
while (p & 1) {
p += m;
}
x.push_back(p / 2 % m);
p = (a[n - 1 - i] - a[i] + m) % m;
while (p & 1) {
p += m;
}
y.push_back(p / 2 % m);
}
x.push_back(a[n / 2]);
y.push_back(0);
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
cout << x[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << x[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
cout << m - y[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << y[i] << " \n"[i == 0];
}
}
return 0;
}清楚姐姐学01背包(Easy Version)
01背包,因为数据范围比较小,可以n的3次方暴力通过,即在01背包的基础上多了一维枚举去掉的是哪一个蝴蝶结,即dp[i][j]表示的是去掉第i个蝴蝶结后的n-1个蝴蝶结中,体积为j的最大好看程度总和
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<pair<int, int>> a(n + 1);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;
sum = max(sum, a[i].second);
}
vector<int> dp1(m + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = m; j >= a[i].first; j--) {
dp1[j] = max(dp1[j], dp1[j - a[i].first] + a[i].second);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int> (m + 2));
int maxx = *max_element(dp1.begin(), dp1.end());
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == k) {
continue;
}
for (int j = m; j >= a[i].first; j--) {
dp[k][j] = max(dp[k][j], dp[k][j - a[i].first] + a[i].second);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int max1 = *max_element(dp[i].begin(), dp[i].end());
if (max1 != maxx) {
cout << "0\n";
} else {
int ans = 1e18;
for (int j = 0; j <= m - a[i].first; j++) {
ans = min(ans, maxx - dp[i][j] + 1 - a[i].second);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}清楚姐姐打怪升级
根据题意可以发现,当a>=h[i]的时候,可以一秒秒杀怪,当h[i]>a的时候,能杀死怪的前提是a-v[i]*t>0,否则每次攻击后怪都能把血量恢复起来
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
LL n, t, a;
cin >> n >> t >> a;
vector<pair<LL, LL>> x(n);
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> x[i].first >> x[i].second;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
if (x[i].first <= a) {
ans = 1;
} else {
ans = 1;
x[i].first -= a;
if (x[i].second * t >= a) {
ans = -1;
break;
} else {
LL p = a - x[i].second * t, z = (x[i].first + p - 1) / p;
ans += z * t;
}
}
} else {
if (x[i].first <= a) {
ans += t;
} else {
x[i].first -= a;
ans += t;
if (x[i].second * t >= a) {
ans = -1;
break;
} else {
LL p = a - x[i].second * t, z = (x[i].first + p - 1) / p;
ans += z * t;
}
}
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}清楚姐姐学树状数组
根据题意,二叉树中序遍历的结果是1~n,所以只需要考虑前序和后序遍历的结果。
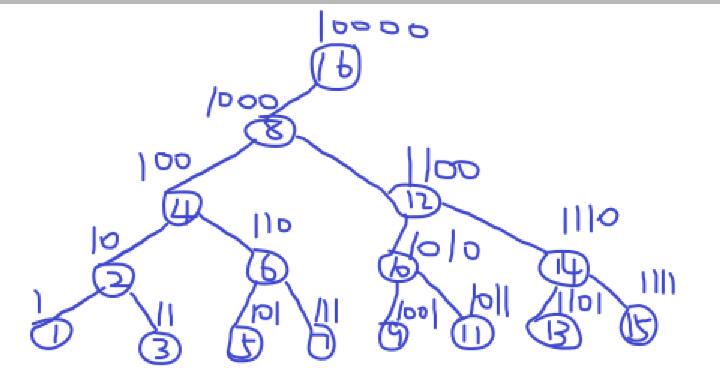
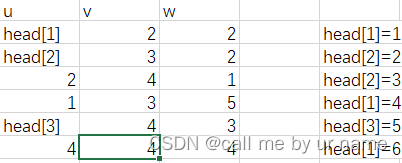
根据这张图我们可以看出,我们能够计算出一个数到根的路径,即对于一个从低位往高位走的二进制,如果当前位为1的,如果他的高一位的二进制位仍然是1,那么去往根的下一个结点就是把这一位变成0,如果他的高一位的二进制位为0,去往根的下一个结点就是在加一个lowbit,从而我们得到了从某一结点到根的路径,这样我们就可以从根再往要求的结点走,可知,如果当前结点的值大于x,说明x在左子树,否则在右子树上,对于前序遍历,往左子树走,步数只需要+1,而往右子树走的话需要把左子树的儿子节点个数及其父节点都加上,也就是lowbit(当前节点编号)。再考虑后序遍历,如果当前节点编号小于x,说明x在右子树,因为是后序遍历,所以需要加上左子树的儿子节点个数,如果走到了x,并且x为奇数,可知x为叶子节点,不存在子树,不需要操作,如果x为偶数,说明x不是叶子节点,存在子树,所以需要加上x的儿子节点个数,即(lowbit(x)-1)*2
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
#define int long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
map<int, int> mp;
int res = 1;
mp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 61; i++) {
res <<= 1;
mp[res] = i;
}
int k, q;
cin >> k >> q;
while (q--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x;
if (x == (1LL << k)) {
cout << 1 << " " << (1LL << k) << " " << (1LL << k) << '\n';
continue;
}
y = x;
int ans = 1, ans1 = 1;
vector<int> z;
z.push_back(x);
for (int i = mp[lowbit(x)] + 1; i <= 61; i++) {
if (x >= (1LL << k)) {
break;
}
if (x >> i & 1 && x >> (i - 1) & 1) {
x -= lowbit(x);
z.push_back(x);
} else if ((x >> i) % 2 == 0 && (x >> (i - 1)) & 1) {
x += lowbit(x);
z.push_back(x);
} else {
break;
}
}
int len = z.size();
for (int i = len - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (y > z[i]) {
ans += lowbit(z[i]);
} else {
ans++;
}
}
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (y > z[i]) {
ans1 += lowbit(z[i]) - 1;
} else if (y == z[i] && y % 2 == 0) {
ans1 += (lowbit(z[i]) - 1) * 2;
}
}
cout << ans << " " << y << " " << ans1 << "\n";
}
return 0;
}清楚姐姐的三角形I
因为
Va=Lb+Lc
Vb=La+Lc
Vc=La+Lb
所以联立可得
2*La=Vb+Vc-Va
2*Lb=Va+Vc-Vb
2*Lc=Va+Vb-Vc
因此,如果有奇数则不可能成立,并且如果边有小于等于0的也不成立,两条较小的边的和必须大于最大的边,注意输出顺序
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
LL x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
vector<LL> a(3);
LL sum = x + y + z;
if (sum % 2 == 1) {
cout << "No\n";
continue;
}
sum /= 2;
LL xx = sum - x, yy = sum - y, zz = sum - z;
a[0] = sum - x;
a[1] = sum - y;
a[2] = sum - z;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
if (a[0] <= 0) {
cout << "No\n";
} else if (a[0] + a[1] <= a[2]) {
cout << "No\n";
} else {
cout << "Yes\n";
cout << xx << " " << yy << " " << zz << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}清楚姐姐的三角形II
很多种构造方式,只要不满足三角形即可
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL = long long;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(45);
a[1] = 1, a[2] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= 44; i++) {
a[i] = a[i - 1] + a[i - 2];
}
int x = n / 44, y = n % 44;
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 44; j++) {
cout << a[j] << " ";
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= y; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}