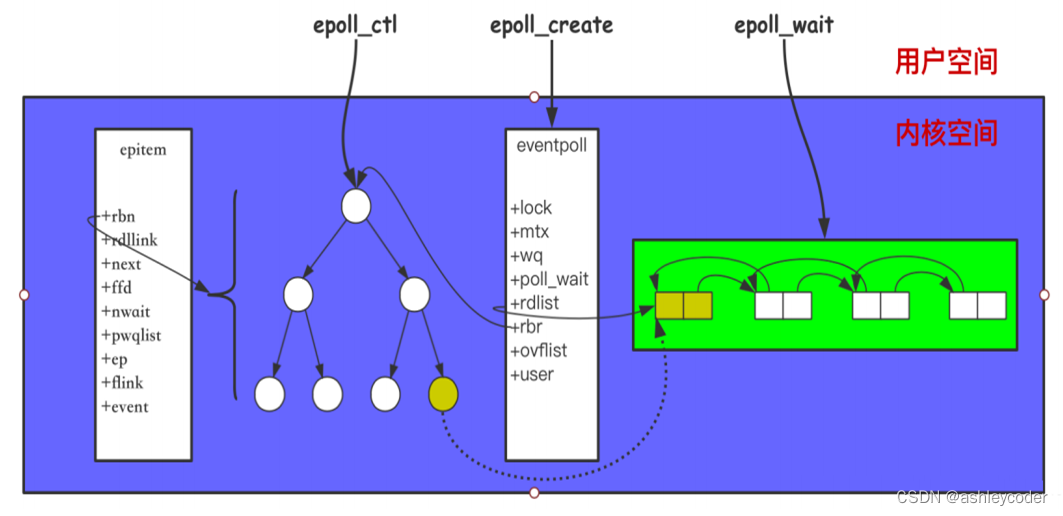
(图是网上的,懒得自己画了)
1 epoll_ctl是向红黑树rbr插入、删除、修改fd。epoll_wait在双向链表rdllist中查询IO可读、可写、错误事件。
为什么使用红黑树?从插入、删除考虑。
2 epoll_ctl插入新fd时,新建epitem,会设置回调函数ep_poll_callback,把pwq->wait(等待队列)跟socket的等待队列关联起来。网卡有事件到来,直接插入到rdllist中,所以epoll不需要像select一样遍历事件。
3 epoll模型也需要把数据从内核态拷贝到用户态。
4 LT水平模型,默认的,数据没有读完,epoll_wait还能读到数据。ET边缘模式,只能在非阻塞模式下,使用者需要自己处理完所有可读数据。
zlm怎么做?
try {} catch (std::exception &ex) {}
5 几个结构体的关系
//eventpoll,epitem相互包括,
struct eventpoll {
/** This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations. */
struct mutex mtx;
wait_queue_head_t wq; //重要变量—等待队列
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
struct list_head rdllist; //List of ready file descriptors
struct rb_root rbr; // RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs
rwlock_t lock; //Lock which protects rdllist and ovflist //自旋锁:得不到锁不会引起进程休眠
struct epitem *ovflist;
struct file *file;
}
struct epitem {
struct rb_node rbn;
struct list_head rdllink; //跟eventpoll同变量
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct eppoll_entry *pwqlist; //重要,其中结构体wait有回调函数
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct epoll_event event;
}
struct eppoll_entry {
struct epitem *base; //有epitem
wait_queue_entry_t wait;
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
}
typedef struct wait_queue_entry wait_queue_entry_t;
struct wait_queue_entry {
unsigned int flags;
void *private;
wait_queue_func_t func; //ep_poll_callback
struct list_head entry;
};
6 epoll惊群(指在accept下):多个线程或多进程等待同一事件,比如accept,系统会唤醒所有线程,但只有一个线程得到该事件,导致效率低。设置epoll_event的events EPOLLEXCLUSIVE属性,可以解决该问题。
7 epmutex、ep->mtx、ep->lock、 三把锁的区别?
epmutex:用得少。This mutex is used to serialize ep_free() and eventpoll_release_file().
ep->mtx:保护结构体eventpoll的数据。
rwlock_t lock; //Lock which protects rdllist and ovflist.
8 epoll_wait事件主要是可读事件,可写只回调一次。通过写日志知道的。
9 sock有poll函数,需要实现,如tcp_poll、udp_poll。







![[LeetCode周赛复盘] 第 330 场周赛20230129](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ea2a50c625fc4dcc9234d38f37ac074c.png)