1、Vue3相关语法内容
- 赋值语句(ref、reactive系列)
- 组件传值(父子,子父)
- watch,watchEffect监听
- slot具名插槽
1、赋值语法(ref,reactive)
1.1、ref 、isRef、 shallowRef、triggerRef、customRef 支持所有的类型(原因没有泛型约束)
##### 1、ref
// 简单数据类型 可以直接通过 赋值
type M {
name:string;
}
const name = ref<M>('')
// 复杂数据类型 可以直接通过 赋值
import type {Ref} from 'vue';
type M {
name:string;
}
const name:Ref<M> = ref('屈小康')
// 取值
name.value // 屈小康
name // Object
// 为什么?
ref返回值是一个ES6的class的类,里面有一个 .value的属性,所以取值和赋值 都必须通过 .value 固定语法
### 2、isRef
isRef(name) // 判断定义的内容是否为一个ref定义的内容 返回 true/false.
### 3、shallowRef //浅层响应式
const a = ref({name:'a'})
const b = shallowRef('b')
// 改变值
const handleClick = () =>{
a.value.name = 'aa' // 页面展示 aa
b.value.name = 'bb' // 页面展示 b 页面没有发生改变,但是值已经发生改变 (也就是说没有双向数据绑定)
b.value = {
name:'bb' // 页面展示 bb 修改成功 这就是浅层 只绑定到 value属性
}
}
### 4、triggerRef 强制跟新 shallowRef
### 5、customRef 自定义一个ref
function MyRef(value){
return customRef((track,trigger)=>{
return {
get(){
track();
},
set(newVal){
value = newVal;
trigger();
},
}
})
}
const name = customRef('1');
name.value // 1 输出内容
## 6、获取 元素 相当于 v2的 this.$refs
<div ref="dom"></div>
// 获取 元素
const dom= ref(); // dom 必须和 ref="dom" 中的 dom 保持一致
// 获取
dom.value 相当于 this.$refs.dom
1.2、 reactive、readonly、shallowReactive (支持引用数据类型,泛型约束)
reactive (target:T) // 源码实例 继承与 object。
const stu = reactive({
name:'屈小康'
})
### 1.1 获取值
stu.name // 屈小康
### 1.2 修改值
stu.name = '张三'
### 1.3 修改值(错误做法)
let obj = {name:'张三'}
stu = obj;
引用数据类型无法进行重新赋值
### 2.1 readonly 只读属性
const name = raeadonly({}) // 不可进行操作后续属性(相对情况下,如果你的readonly依赖于reactive,这个时候修改reactive的时候就会变更)
### 3.1 shallowReactive 浅层的 只到第一个属性。
const stu= reactive({
age:14,
person:{
sex:'男'
}
})
// 只影响到 stu.age
2、to系列(toRef、toRefs、toRaw)
2.1 toRef
用法:毫无卵用的用法(不能说这种用法是错的,只能说没有任何意义)
const stu = {name:"张三"};
const stus = toRef(stu,'name')
stus.name = '李四'; 值发生了改变,但是页面不会变还是 张三
如何发生改变
const stu = reactive({name:"张三"}) // 这样进行 修改就好了
总结:非响应式使用的时候 没有任何作用。只能修改响应式的。
2.2 toRefs
const stu = {name:"1",age:"2"};
const {name,age} = toRefs(stu);
总结:非响应式使用的时候 没有任何作用。只能修改响应式的。
2.3 toRaw
脱离响应式对象
const stu = {name:“1”,age:“2”};
toRaw(stu) // {name:“1”,age:“2”}
2、组件传值
2.1.1、父—>子 基本数据传参 [不是TS版](defineProps )
### Father 组件
<template>
我是Father
<Son :title="title"></Son>
</template>
<script setup>
import Son from './b.vue';
import { ref } from 'vue';
const title = ref('把这个值传给孩子组件');
</script>
#### Son 组件
<template>
<div>
我是孩子
{{ title }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
## 简单 用法 不带默认值
defineProps ({
title: String,
});
## 带默认值
const props = defineProps({
title: {
type: String,
default: '我是默认值'
}
})
</script>
2.1.2、父—>子 事件数据传参 [不是TS版](defineExpose)(父调用子组件的方法)
###### Fatner
<template>
我是Father
<Son ref="son"></Son>
<button @click="handleClick">点我</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import Son from './b.vue';
import { ref } from 'vue';
const son = ref(null);
const handleClick = () => {
son.value.handleClick();
}
</script>
###### Son
<template>
<div>
我是孩子
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('我被点击了!!')
}
defineExpose({ handleClick })
</script>
2.1.3 子—> 父 事件传参【不是TS版本】($emit)
###### Fatner
<template>
我是Father
<Son @childEmit="childEmit"></Son>
</template>
<script setup>
import Son from './b.vue';
import { ref } from 'vue';
const childEmit = (value) => {
console.log(value)
}
</script>
########### Son
<template>
<div>
我是孩子
<button @click="handleSend">点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
const emit = defineEmits(['childEmit']);
const handleSend = () => {
emit('childEmit', '数据')
}
</script>
2.2.1 基本数据类型传参(TS版本)(withDefaults)
<template>
我是Father
<Son :title="title"></Son>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import Son from './b.vue';
import { ref } from 'vue';
const title = ref<string>()
</script>
<template>
<div>
我是孩子
{{ props.title }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { defineProps } from 'vue';
const props = withDefaults(
defineProps<{
title: string,
}>(),
{
title: '默认值'
}
)
</script>
3、监听函数(watch,watchEffect)
3.1 watch
<template>
<input v-model="inputValue" />
<input v-model="inputValues" />
<input v-model="obj.stu.name" />
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { reactive, ref, watch } from 'vue';
const inputValue = ref<string>('')
const inputValues = ref<string>('')
const obj = reactive({
stu: {
name: ''
}
})
watch([inputValue, inputValues], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
},
{
deep: true // 深度监听(新值和旧值是一样的如果是深层次的对象)
}
)
// 监听 对象的 某个属性
// reactive 会自动开启 deep:tru e
watch((()=> obj.stu.name), (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
})
### 同时还有以下属性
1、deep: true //开启深度监听
2、immediate:true //立即执行
3、flush:“pre” // pre 跟新之前调用,sync 同步执行 , post 组件更新之后执行
</script>
<style scoped lang="less"></style>
### 主要源码解释(算了太多了没法解释了)
https://github.com/vuejs/core.git
位置
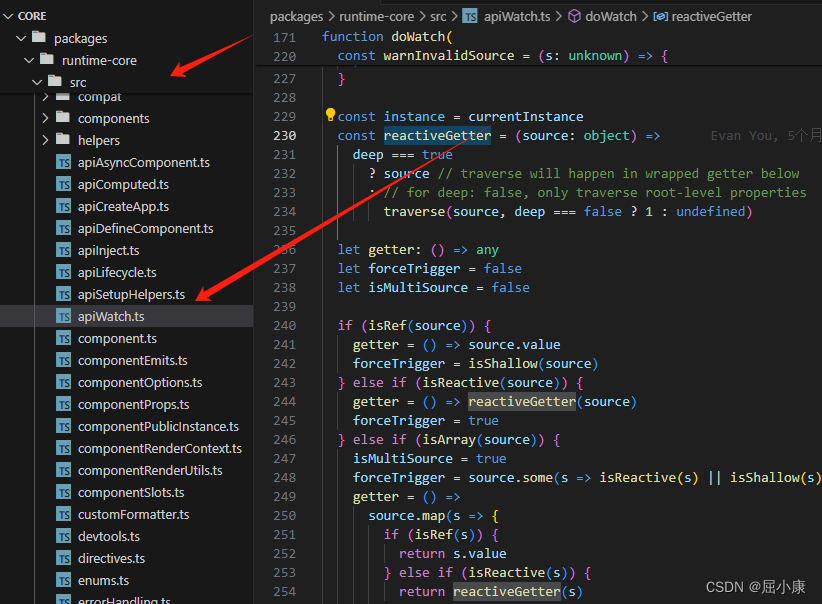
3.2 watchEffect
// 立即执行
const stop = watchEffect((oninvalidate) => {
console.log(inputValue); // 被改变后后执行
oninvalidate(() => {
console.log('我第一个执行!!!')
})
})
// 停止监听 stop()
cosnt click = () => stop(); //监听函数就会停止
1、flush:“pre” // pre 跟新之前调用,sync 同步执行 , post 组件更新之后执行
4、插槽(slot)
插槽就是子组件中的提供给父组件使用的一个占位符,用(< slot > </ slot>) 表示,父组件可以在这个占位符中填充任何模板代码,填充的内容会替换子组件的< slot>< /slot>标签。
4.1、具名插槽
// ### 子组件
<div>
<slot name="header"></slot>
<slot></slot>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
// ### 父组件使用
<template v-slot:header>
<div>header</div>
</template>
<template v-slot>
<div>默认插槽</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div>footer</div>
</template>
4.2、作用于插槽
<slot name="header" :data=""></slot>
const data = reactive({
message:"我是一条消息"
})
// #header ==== v-slot:header
<template #header="{data}">
{{data.message}} // 我是一条消息
</template>
4.3、动态变量插槽
<template #[slot]>
啦啦啦啦
</template>
const slot = ref('header')