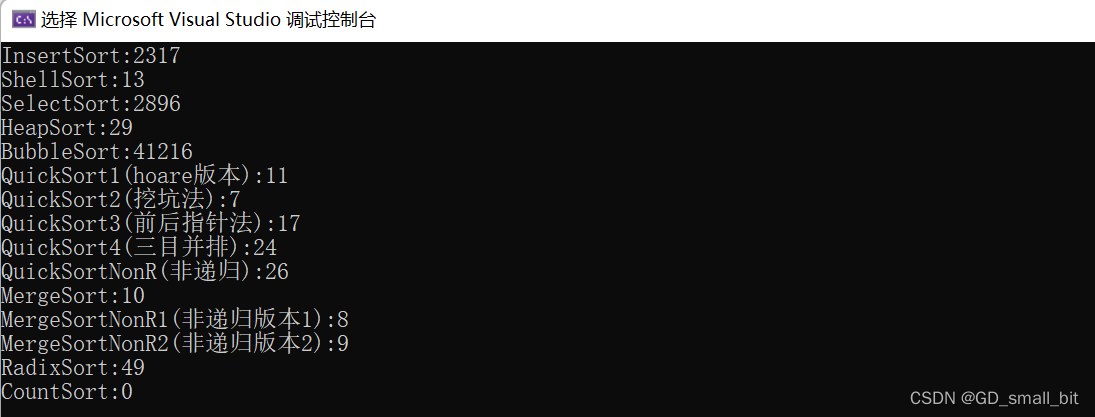
各种点云采样算法
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41485242/article/details/107150963
Inverse Density
1.2 Inverse Density Importance Sampling (IDIS):
这个也比较好理解,简而言之就是根据每个点的密度来对其重新进行排序,尽可能地保留密度比较低的地方的点。
应该是参考点的密度来对点进行表示
密度小 点的数量保留多
密度大 点的数量保留小
Monte Carlo Gradient Estimation(一)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/110588068
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/223042372
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinxiangnan-charles/p/4999549.html
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av23323837/?vd_source=e7d12c9f66ab8294c87125a95510dac9
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39373480/article/details/90511915
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangchangshuo/p/13959789.html
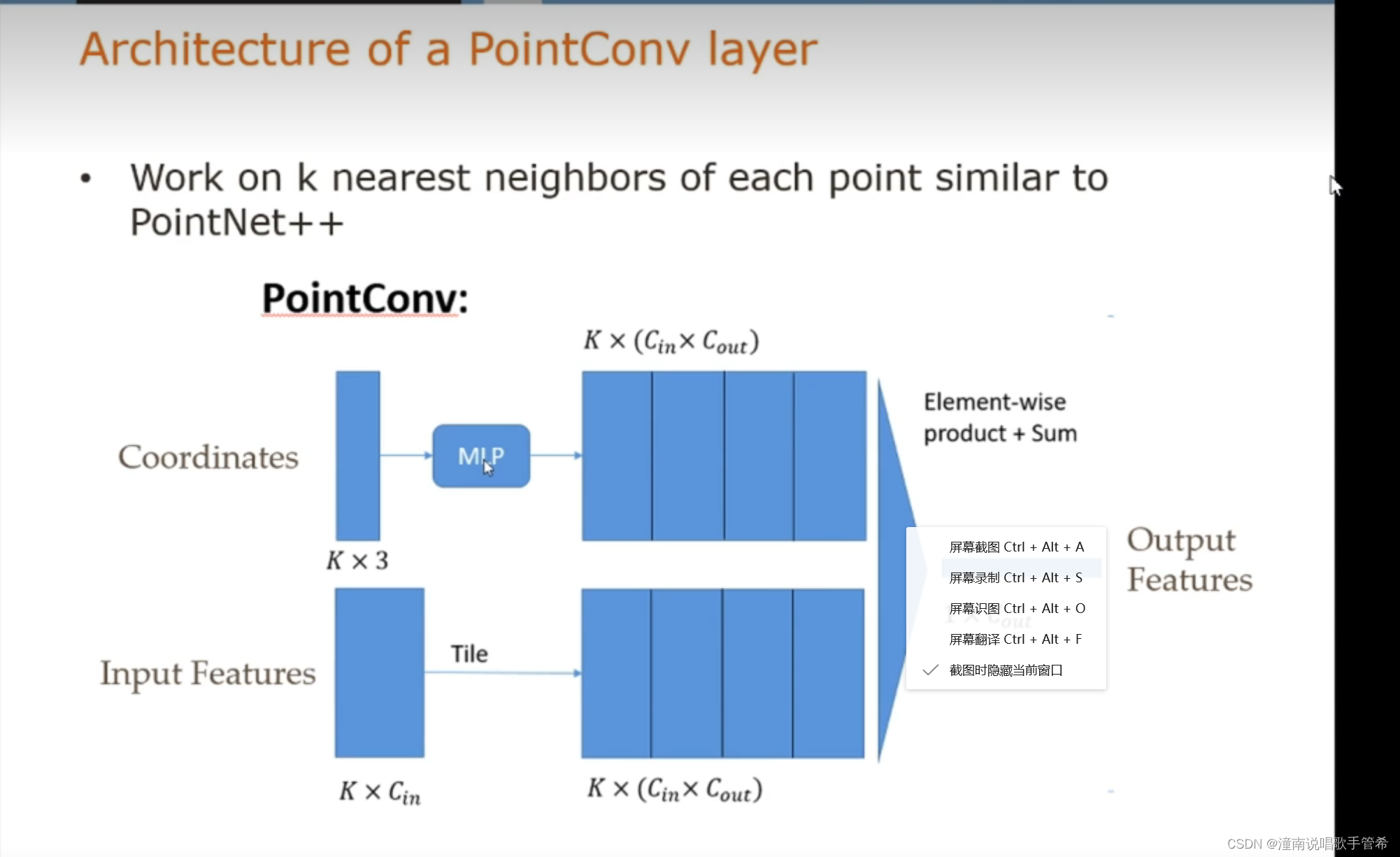
置换不变性
The weights of the MLP in PointConv are shared across
all the points in order to maintain the permutation invari-
ance.
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1BE411K7P9/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=e7d12c9f66ab8294c87125a95510dac9
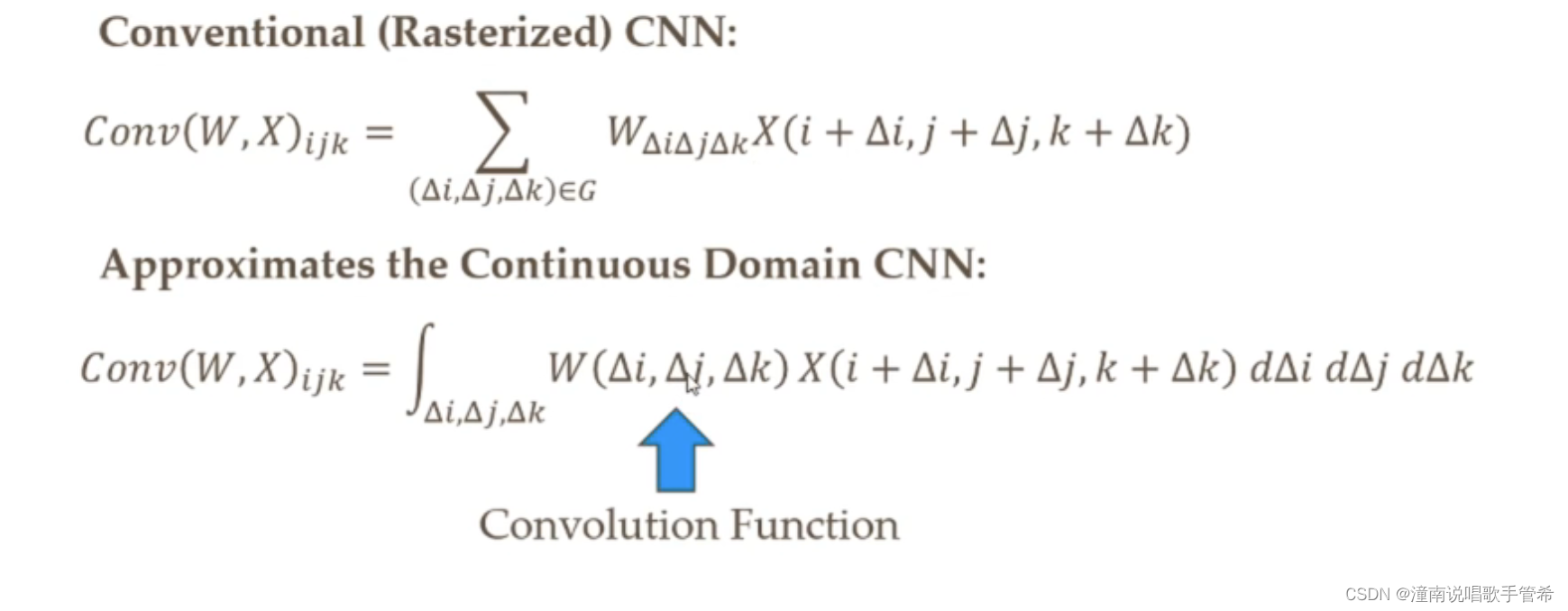

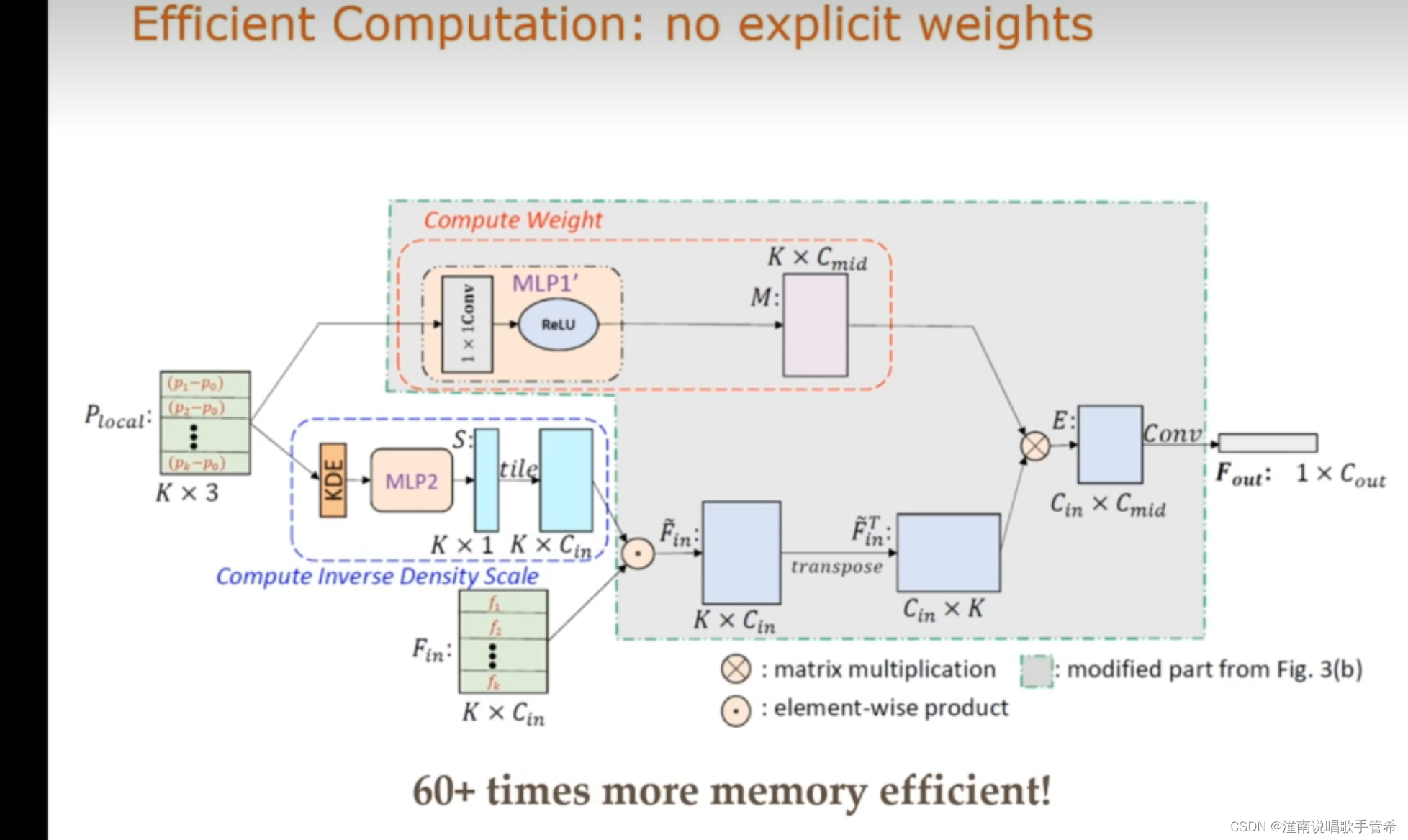
用网络近似该卷积函数(用全连接层)
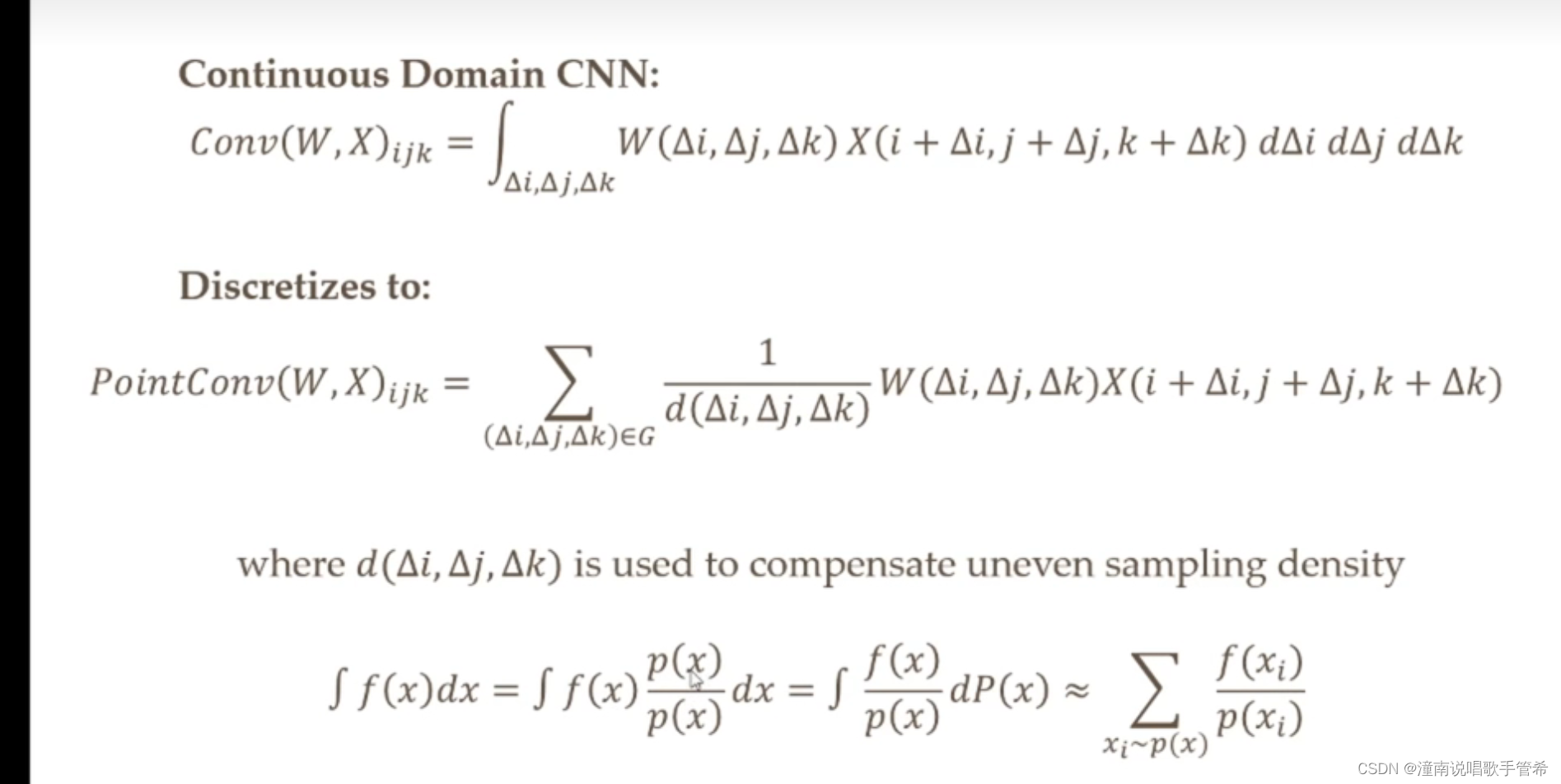
连续域卷积
点云由于采样时非均匀的 需要把采样误差去除
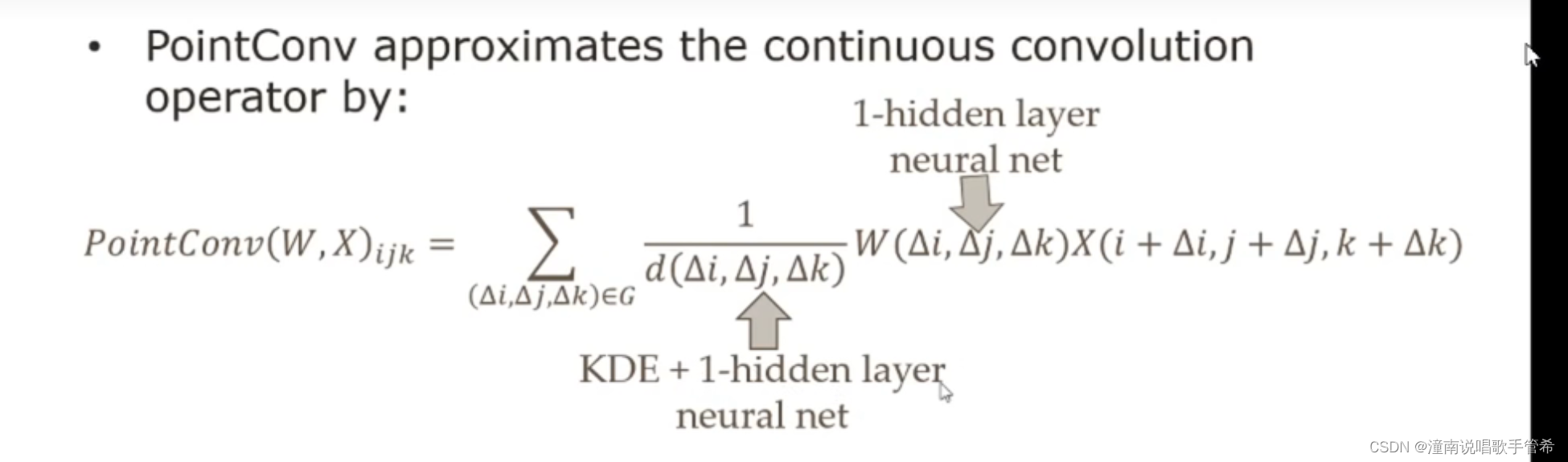
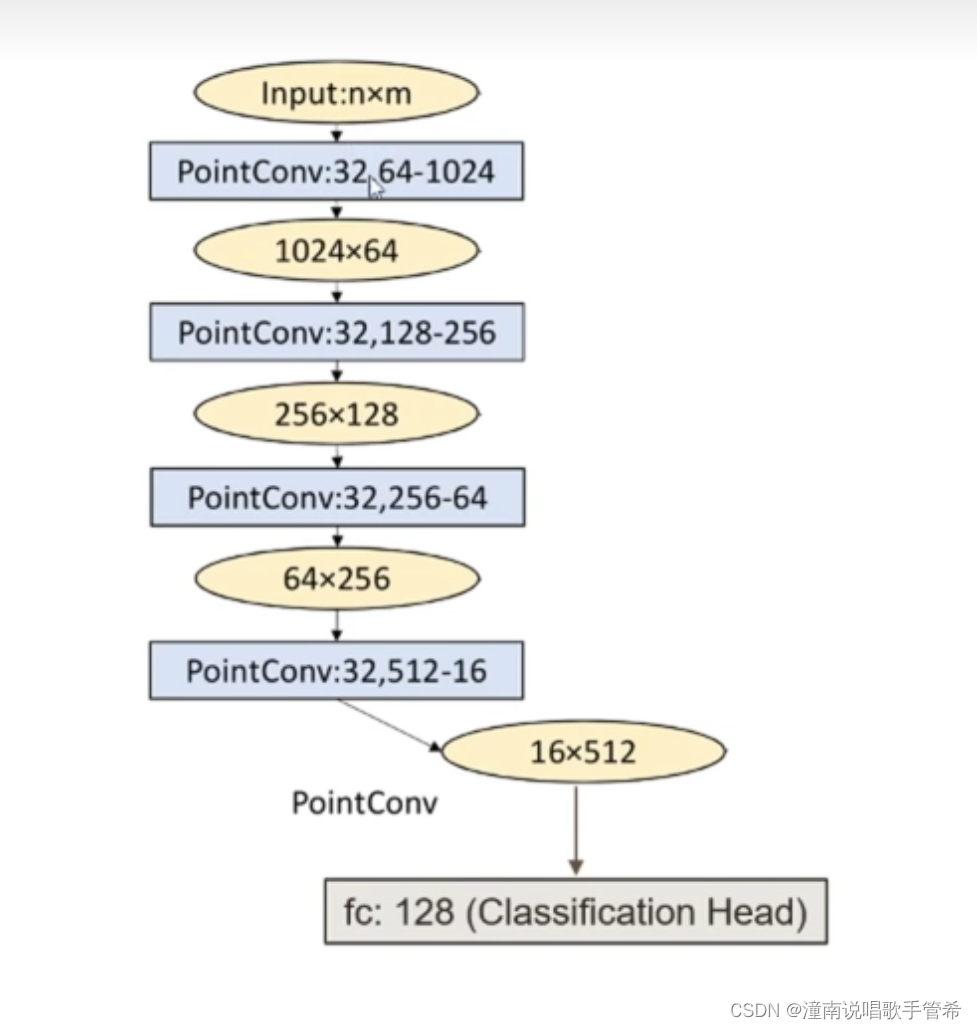
实验过程中发现加个隐藏层效果好