一. 论文总结
1.1 核心贡献
- 提出了一种改进的图卷积操作,称为语义图卷积(SemGConv),它源自cnn。其关键思想是学习图中暗示的边的信道权值,然后将它们与核矩阵结合起来。这大大提高了图卷积的能力。
- 其次,我们引入了SemGCN,其中SemGConv层与非局部[65]层交叉。该体系结构捕获节点之间的本地和全局关系。
- 第三,我们提出了一个端到端学习框架,以表明SemGCN还可以合并外部信息,如图像内容,以进一步提高3D人体姿态回归的性能。
1.2 语义图卷积(SemGConv)
1.2.1 ResGCN
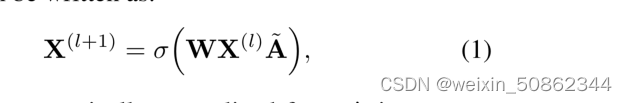
∈
和
∈
分别是节点i在第l个卷积之前和之后的表示。
- 可学习参数矩阵W∈
- 其中
是在常规GCNs中对A进行对称归一化。A∈
是G的邻接矩阵,对于节点j∈N (i)有
= 1,
= 1
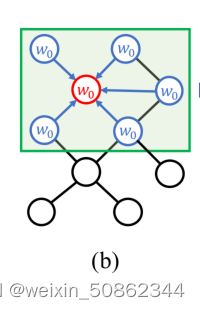
两个明显的缺点:
- 首先,为了使图卷积在具有任意拓扑结构的节点上工作,所有边共享学习的核矩阵W。结果,相邻节点的关系或图中的内部结构,不能很好地利用。
- 其次,之前的工作只收集每个节点的第一个序列上的(应该是最近邻的意思)邻居的特征。因为接受野被固定为1,这也是存在不足的。
1.2.2 SemGConv
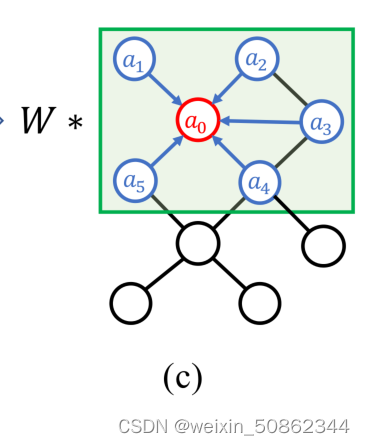
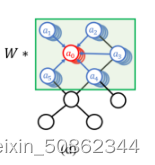
在传统的图卷积中添加了一个可学习的权重矩阵M∈(按我的理解就是上图中的
)。然后转化为:
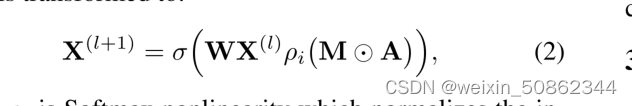
- 其中
是Softmax非线性,它在节点
的所有选择上归一化输入矩阵;
- ⊙是一个元素级运算,如果
= 1则返回mij,或者在
后饱和到零的大指数为负数;
- A作为一个掩码,它迫使图中的节点i,我们只计算其相邻节点j∈N (i)的权值。
学习每一个通道的加权权重,将公式进一步扩展:
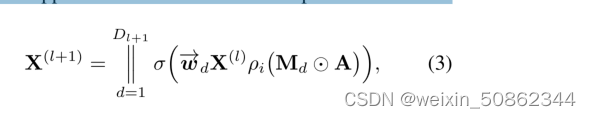
- 其中 || 表示对所有层的输入进行拼接,
是变换矩阵w的第d行。
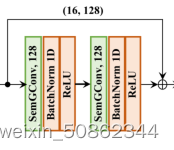
1.3 网络架构
整体结构
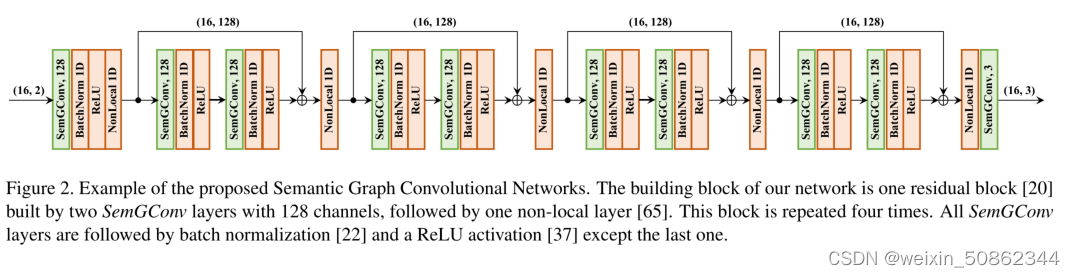
SemGCN网络架构是通过SemGConv和 Non-Local层交错以捕获节点的局部和全局语义关系
Non-Local来自2018年cvpr论文Non-local Neural Networks
(翻译和解析后面会更新)
1.3.1 基本结构
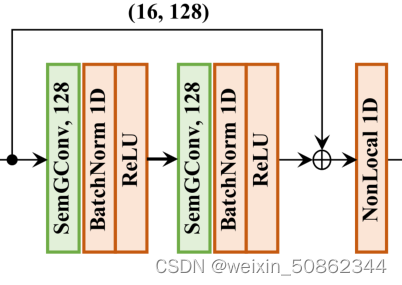
在这项工作中,所有块中的SemGCN具有相同的结构,由两个具有128通道的SemGConv层构建的一个残差块[20]组成,然后再跟随一个非本地层。
二.代码实现
2.1 生成 邻接矩阵
adj = adj_mx_from_skeleton(dataset.skeleton())#建立对称邻接矩阵以human36M为例:
dataset.skeleton()返回的就是
h36m_skeleton = Skeleton(parents=[-1,
0, 1, 2, 3, 4,
0, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0, 11, 12, 13, 14, 12,
16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 19, 22, 12, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 27, 30],
joints_left=[6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23],
joints_right=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31])具体来看一下adj_mx_from_skeleton这个生成邻接矩阵的函数:
from __future__ import absolute_import
import torch
import numpy as np
import scipy.sparse as sp
def normalize(mx):
"""Row-normalize sparse matrix"""
rowsum = np.array(mx.sum(1))
r_inv = np.power(rowsum, -1).flatten()
r_inv[np.isinf(r_inv)] = 0.
r_mat_inv = sp.diags(r_inv)
mx = r_mat_inv.dot(mx)
return mx
def sparse_mx_to_torch_sparse_tensor(sparse_mx):
"""将scipy稀疏矩阵转换为torch稀疏张量。Convert a scipy sparse matrix to a torch sparse tensor."""
sparse_mx = sparse_mx.tocoo().astype(np.float32)
indices = torch.from_numpy(np.vstack((sparse_mx.row, sparse_mx.col)).astype(np.int64))
values = torch.from_numpy(sparse_mx.data)
shape = torch.Size(sparse_mx.shape)
return torch.sparse.FloatTensor(indices, values, shape)
def adj_mx_from_edges(num_pts, edges, sparse=True):
edges = np.array(edges, dtype=np.int32)
data, i, j = np.ones(edges.shape[0]), edges[:, 0], edges[:, 1]
adj_mx = sp.coo_matrix((data, (i, j)), shape=(num_pts, num_pts), dtype=np.float32)
#sp.coo_matrix() 的作用是生成矩阵
#sp.coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape=(4, 4))用指定数据生成矩阵
# 建立对称邻接矩阵 build symmetric adjacency matrix
adj_mx = adj_mx + adj_mx.T.multiply(adj_mx.T > adj_mx) - adj_mx.multiply(adj_mx.T > adj_mx)
adj_mx = normalize(adj_mx + sp.eye(adj_mx.shape[0]))
if sparse:
adj_mx = sparse_mx_to_torch_sparse_tensor(adj_mx)
else:
adj_mx = torch.tensor(adj_mx.todense(), dtype=torch.float)
return adj_mx
def adj_mx_from_skeleton(skeleton):
num_joints = skeleton.num_joints()
edges = list(filter(lambda x: x[1] >= 0, zip(list(range(0, num_joints)), skeleton.parents())))
#盆骨父节点为-1
return adj_mx_from_edges(num_joints, edges, sparse=False)
2.2 SemGCN
2.2.1 SemGraphConv
class SemGraphConv(nn.Module):
"""
Semantic graph convolution layer
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, adj, bias=True):
super(SemGraphConv, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(2, in_features, out_features), dtype=torch.float))
#作为nn.Module中的可训练参数使用,与torch.Tensor的区别就是nn.Parameter会自动被认为是module的可训练参数
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.W.data, gain=1.414)
self.adj = adj#邻接矩阵
self.m = (self.adj > 0)
self.e = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, len(self.m.nonzero()), dtype=torch.float))
nn.init.constant_(self.e.data, 1)
if bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(out_features, dtype=torch.float))
stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.W.size(2))
self.bias.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
else:
self.register_parameter('bias', None)
def forward(self, input):
h0 = torch.matmul(input, self.W[0])
h1 = torch.matmul(input, self.W[1])
adj = -9e15 * torch.ones_like(self.adj).to(input.device)
adj[self.m] = self.e
adj = F.softmax(adj, dim=1)
M = torch.eye(adj.size(0), dtype=torch.float).to(input.device)
output = torch.matmul(adj * M, h0) + torch.matmul(adj * (1 - M), h1)
if self.bias is not None:
return output + self.bias.view(1, 1, -1)
else:
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' + str(self.out_features) + ')'
2.2.2 GraphNonLocal
from __future__ import absolute_import, division
import torch
from torch import nn
class _NonLocalBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, dimension=3, sub_sample=1, bn_layer=True):
super(_NonLocalBlock, self).__init__()
assert dimension in [1, 2, 3]
self.dimension = dimension
self.sub_sample = sub_sample
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.inter_channels = inter_channels
if self.inter_channels is None:
self.inter_channels = in_channels // 2
assert self.inter_channels > 0
if dimension == 3:
conv_nd = nn.Conv3d
max_pool = nn.MaxPool3d
bn = nn.BatchNorm3d
elif dimension == 2:
conv_nd = nn.Conv2d
max_pool = nn.MaxPool2d
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d
elif dimension == 1:
conv_nd = nn.Conv1d
max_pool = nn.MaxPool1d
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d
else:
raise Exception('Error feature dimension.')
self.g = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.theta = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.phi = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.concat_project = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inter_channels * 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.ReLU()
)
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.concat_project[0].weight)
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.g.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.g.bias, 0)
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.theta.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.theta.bias, 0)
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.phi.weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.phi.bias, 0)
if bn_layer:
self.W = nn.Sequential(
conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
bn(self.in_channels)
)
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.W[0].weight)
nn.init.constant_(self.W[0].bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].bias, 0)
else:
self.W = conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W.weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W.bias, 0)
if sub_sample > 1:
self.g = nn.Sequential(self.g, max_pool(kernel_size=sub_sample))
self.phi = nn.Sequential(self.phi, max_pool(kernel_size=sub_sample))
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0) # x: (b, c, t, h, w)
g_x = self.g(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1)
g_x = g_x.permute(0, 2, 1)
# (b, c, N, 1)
theta_x = self.theta(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1, 1)
# (b, c, 1, N)
phi_x = self.phi(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, 1, -1)
h = theta_x.size(2)
w = phi_x.size(3)
theta_x = theta_x.expand(-1, -1, -1, w)
phi_x = phi_x.expand(-1, -1, h, -1)
concat_feature = torch.cat([theta_x, phi_x], dim=1)
f = self.concat_project(concat_feature)
b, _, h, w = f.size()
f = f.view(b, h, w)
N = f.size(-1)
f_div_C = f / N
y = torch.matmul(f_div_C, g_x)
y = y.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
y = y.view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, *x.size()[2:])
W_y = self.W(y)
z = W_y + x
return z
class GraphNonLocal(_NonLocalBlock):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=1, bn_layer=True):
super(GraphNonLocal, self).__init__(in_channels, inter_channels=inter_channels, dimension=1,
sub_sample=sub_sample, bn_layer=bn_layer)
2.2.3 ResGraphConv
表示的是如下这个部分: