问题描述
A服务提供了个RPC接口给B服务使用,入参里有个参数是List类型,B服务在传参时使用Guava里的 ImmutableList,结果发生报错。
其中,B服务即consumer端的异常为:「com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.RemotingException: Fail to decode request due to: RpcInvocation [methodName=…」 。consumer端异常截图:

A服务即provider端的异常为:「com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianFieldException: com.pdd.service.smart.contract.request.agreement.QueryCarrierAgreementEffectiveWarehouseInfoRequest.agreementTypeList: java.util.List cannot be assigned from null」。provider端异常截图:

然而,当将 ImmutableList 改成 ArrayList 时报错消失,接口恢复正常。
环境说明
已知我司使用的RPC框架是dubbo,其中的序列化协议是dubbo默认的hessian2,对应版本是:hessian-lite:3.2.1-fixed-2。

< 上图出自:https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs3-v2/java-sdk/reference-manual/protocol/dubbo/ >
问题复现
从第一部分【问题描述】中的异常堆栈信息可知,问题主要出在hessian2序列化的过程中,更准确一点是consumer反序列化时解析出错,导致异常。因此问题定位为dubbo的Serialize 数据序列化层,仅从hessian2序列化和反序列化来复现和分析问题。
< dubbo代码架构 https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs3-v2/java-sdk/concepts-and-architecture/code-architecture/ >
public class HessianLiteUtils {
/**
* 序列化
*/
public static byte[] serialize(Object object) {
Hessian2Output h2o = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
h2o = new Hessian2Output(outputStream);
h2o.writeObject(object);
h2o.flush();
return outputStream.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("HessianUtils.serialize exception " + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("HessianUtils.serialize 异常", e);
} finally {
if (h2o != null) {
try {
h2o.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 反序列化.
*/
public static Object deserialize(byte[] bytes) {
Hessian2Input h2i = null;
try {
ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
h2i = new Hessian2Input(inputStream);
return h2i.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("HessianUtils.deserialize exception " + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("HessianUtils.deserialize 异常", e);
} finally {
if (h2i != null) {
try {
h2i.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static String hex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
result.append(String.format("%02x", b));
// upper case
// result.append(String.format("%02X", aByte));
}
return result.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("胖嘟嘟");
person.setMale(true);
person.setAge(10);
person.setList(Lists.newArrayList(1, 2));
// Person 可正常序列化和反序列化
byte[] bytes = serialize(person);
System.out.println("serialized hex bytes: " + hex(bytes));
Object object = deserialize(bytes);
System.out.println("deserialized object: " + object.toString());
// Request 序列化成功,反序列化失败
Request request = new Request();
request.setList(ImmutableList.of(1, 2));
byte[] bytesRequest = serialize(request);
System.out.println("serialized hex bytes: " + hex(bytesRequest));
Object objectReq = deserialize(bytesRequest);
System.out.println("deserialized object: " + objectReq.toString());
}
}
// 其中Person和Request的定义为
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7242674494415301661L;
private String name;
private boolean isMale;
private int age;
private List<Integer> list;
// 此处省略getter、setter和toString
}
public class Request implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 408723925489378046L;
private List<Integer> list;
public List<Integer> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<Integer> list) {
this.list = list;
}
}
在上述代码中Person可正常序列化,输出结果为:
serialized hex bytes: 4306506572736f6e94046c697374036167650669734d616c65046e616d65607a91929a5403e88396e5989fe5989f
deserialized object: Person{name='胖嘟嘟', isMale=true, age=10, list=[1, 2]}
Request中List参数传ImmutableList会导致反序列化异常,表现和rpc接口异常一样,问题复现。
serialized hex bytes: 43075265717565737491046c69737460433036636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d9108656c656d656e74736172075b6f626a6563749192
HessianUtils.deserialize exception Request.list: com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList cannot be assigned from null
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: HessianUtils.deserialize 异常
at HessianLiteUtils.deserialize(HessianLiteUtils.java:59)
at HessianLiteUtils.main(HessianLiteUtils.java:99)
Caused by: com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianFieldException: Request.list: com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList cannot be assigned from null
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.JavaDeserializer.logDeserializeError(JavaDeserializer.java:171)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.JavaDeserializer$ObjectFieldDeserializer.deserialize(JavaDeserializer.java:414)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.JavaDeserializer.readObject(JavaDeserializer.java:275)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.JavaDeserializer.readObject(JavaDeserializer.java:199)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.SerializerFactory.readObject(SerializerFactory.java:529)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObjectInstance(Hessian2Input.java:2803)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2743)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2272)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2717)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2272)
at HessianLiteUtils.deserialize(HessianLiteUtils.java:56)
... 1 more
Caused by: java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.CollectionDeserializer@7bb11784
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.AbstractDeserializer.readObject(AbstractDeserializer.java:121)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObjectInstance(Hessian2Input.java:2801)
Caused by: com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.HessianFieldException: Request.list: com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList cannot be assigned from null
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2140)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2069)
Caused by: java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.CollectionDeserializer@7bb11784
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2113)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input.readObject(Hessian2Input.java:2069)
at com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io.JavaDeserializer$ObjectFieldDeserializer.deserialize(JavaDeserializer.java:410)
... 10 more
为什么ArrayList可以正常序列化和反序列化,而ImmutableList只能序列化却不可以反序列化呢?我们先看下Hessian2协议的内容。
Hessian 2 协议
-
Hessian 的对象序列化支持八种基本类型:
- 原始 二进制数据(binary)
- 布尔型数据(boolean)
- 64位 毫秒 日期类型数据(date)
- 64位 双精度 浮点类型数据(double)
- 32位 整数类型数据(int)
- 64位 长整数类型数据(long)
- null(null)
- UTF-8 编码的 字符串类型数据(string)
-
支持三种递归类型(recursive type):
- 支持链表(list)和数组(array)的 (list)
- 支持映射(map)和字典(dictionary)的( map)
- 支持对象的(object)。
-
支持一种特殊的结构:
- 支持共享和循环引用的(ref)。
-
Hessian 2.0 有三种内部引用映射:
- 一种 object/list 引用映射
- 一种类定义引用映射
- 一种类型(类名)引用映射
字节码映射
Hessian是一个字节码协议,反序列化过程本质上是对8位字节进行switch语句转换的过程。
x00 - x1f # utf-8 string length 0-32
x20 - x2f # binary data length 0-16
x30 - x33 # utf-8 string length 0-1023
x34 - x37 # binary data length 0-1023
x38 - x3f # three-octet compact long (-x40000 to x3ffff)
x40 # reserved (expansion/escape)
x41 # 8-bit binary data non-final chunk ('A')
x42 # 8-bit binary data final chunk ('B')
x43 # object type definition ('C')
x44 # 64-bit IEEE encoded double ('D')
x45 # reserved
x46 # boolean false ('F')
x47 # reserved
x48 # untyped map ('H')
x49 # 32-bit signed integer ('I')
x4a # 64-bit UTC millisecond date
x4b # 32-bit UTC minute date
x4c # 64-bit signed long integer ('L')
x4d # map with type ('M')
x4e # null ('N')
x4f # object instance ('O')
x50 # reserved
x51 # reference to map/list/object - integer ('Q')
x52 # utf-8 string non-final chunk ('R')
x53 # utf-8 string final chunk ('S')
x54 # boolean true ('T')
x55 # variable-length list/vector ('U')
x56 # fixed-length list/vector ('V')
x57 # variable-length untyped list/vector ('W')
x58 # fixed-length untyped list/vector ('X')
x59 # long encoded as 32-bit int ('Y')
x5a # list/map terminator ('Z')
x5b # double 0.0
x5c # double 1.0
x5d # double represented as byte (-128.0 to 127.0)
x5e # double represented as short (-32768.0 to 327676.0)
x5f # double represented as float
x60 - x6f # object with direct type
x70 - x77 # fixed list with direct length
x78 - x7f # fixed untyped list with direct length
x80 - xbf # one-octet compact int (-x10 to x3f, x90 is 0)
xc0 - xcf # two-octet compact int (-x800 to x7ff)
xd0 - xd7 # three-octet compact int (-x40000 to x3ffff)
xd8 - xef # one-octet compact long (-x8 to xf, xe0 is 0)
xf0 - xff # two-octet compact long (-x800 to x7ff, xf8 is 0)
先对Hessian序列化协议的基本结构和字节码映射有个印象,具体每种类型对应的语法在遇到的时候我们再回来查阅协议文档: Hessian 2.0 Serialization Protocol.
示例
本节,我们通过对前文 Person 序列化后的字节码进行反序列化来熟悉下Hessian2协议。
serialized hex bytes: 4306506572736f6e94046c697374036167650669734d616c65046e616d65607a91929a5403e88396e5989fe5989f
deserialized object: Person{name='胖嘟嘟', isMale=true, age=10, list=[1, 2]}
- 该16进制字节数组首位是43,查阅字节码映射可知 x43 表示
object type definition ('C'),即对象类型定义,查阅协议文档找到对应的Object语法为class-def ::= 'C' string int string*,表示 C后面拼接的是个String然后再拼接int和string,对照Class def的解释The object definition includes a mandatory type string, the number of fields, and the field names.可知,C后面先拼接类型,再拼接字段数和字段名; - 第2位06表示长度为6的utf-8 string;
x00 - x1f # utf-8 string length 0-32 - 接下来我们找到长度为6的string部分,即‘ 506572736f6e ’,16进制转utf-8得到‘ Person ’;
- 接下来是94,对应字节码映射
x80 - xbf # one-octet compact int (-x10 to x3f, x90 is 0),x94-x90表示int 4,表示接下来的是Person的4个字段; - 04 表示长为4的string,即Person第一个字段的名字长度;
- 6c697374 16进制转utf-8得到 list,第一个字段为list;
- 03 第2个字段 长为3的string;
- 616765 age;
- 06 第3个字段长度为6
- 69734d616c65 isMale
- 04 第4个字段长度为4
- 6e616d65 name
- 60 第1个字段是object with direct type
- 7a 字节码映射
x78 - x7f # fixed untyped list with direct length表示长度为2的list - 91 92
x80 - xbf # one-octet compact int (-x10 to x3f, x90 is 0)表示list的值分别为1和2 - 9a 第2个字段的值是 10
- 54 第3个字段是boolean true (‘T’)
- 03 第4个字段是长度为3的string
- e88396e5989fe5989f 第4个字段为‘胖嘟嘟’

问题分析
回到最初的问题,我们构建如下三个测试Case:
// # Case 1
Request request = new Request();
request.setList(ImmutableList.of(1, 2));
byte[] bytes = serialize(request);
// 43075265717565737491046c69737460433036636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d9108656c656d656e74736172075b6f626a6563749192
// # Case 2
byte[] bytes = serialize(ImmutableList.of(1, 2));
// 433036636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d9108656c656d656e74736072075b6f626a6563749192
// # Case 3
byte[] bytes = serialize(Lists.newArrayList(1, 2));
// 7a9192
实际测试发现,Case 1序列化结果无法反序列化,Case 2和Case 3序列化结果可以正常反序列化。
(这里刚开始复现时用的Case 2,怎么都无法复现线上报错,以为是hessian协议版本/dubbo实现问题,在这耗费了大半天时间。这里也是比较奇怪的,直接将ImmutableList作为参数可以反序列化,将其作为其他对象的参数后就不能正常序列化了)
接下来,先尝试根据Hessian2协议对前两种Case的序列化结果进行初步分析,然后再去深入分析二者在序列化和反序列化代码逻辑实现上的差异。
// # Case 1
43-07-52657175657374-91-04-6c697374-60-43-30-36-636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d-91-08656c656d656e7473-61-72-07-5b6f626a656374-91-92
43 # object type definition ('C')
07 # 字符长度7
52657175657374 # Request
91 # 1个字段
04 # 4
6c697374 # list
60 # x60 - x6f 表示 object with direct type 接下来是对象中的值
43 # object type definition ('C')
30 # x30 - x33 utf-8 string length 0-1023 类型为string,语法:[x30-x33] b0 <utf8-data>
36 # 54个
636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d # com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm
91 # x80 - xbf # one-octet compact int (-x10 to x3f, x90 is 0) 1个int
08656c656d656e7473 # elements
61 # x60 - x6f # object with direct type ----
72 # x70 - x77 # fixed list with direct length 长度为2的list
07 # x00 - x1f # utf-8 string length 0-32 list的type为 长度为7的string
5b6f626a656374 # [object
91 # 数值 1
92 # 数值 2
// # Case 2
43-30-36-636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d-91-08-656c656d656e7473-60-72-07-5b6f626a656374-91-92
43 # object type definition ('C')
30 # x30 - x33 utf-8 string length 0-1023 类型为string // readString
36 # 十进制 54
636f6d2e676f6f676c652e636f6d6d6f6e2e636f6c6c6563742e496d6d757461626c654c6973742453657269616c697a6564466f726d # com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm
91 # 1个字段
08 # 第1个字段为8位string
656c656d656e7473 # elements
60 # object with direct type
72 # x70 - x77 # fixed list with direct length 长度为2的object list
07 # x00 - x1f # utf-8 string length 0-32 list的type为 长度为7的string
5b6f626a656374 # [object
91 # 数值 1
92 # 数值 2
// # Case 3
7a-91-92
7a # x78 - x7f # fixed untyped list with direct length 长度为7a-78=2的list
91 # 数值 1
92 # 数值 2
初步看下来,Case1 和Case2 都有个名为 com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm 的对象定义,里面有个字段叫elements,它的值是个object数组([object)。不同点是Case1中有两个对象定义,相比Case2多了Request。
目前看起来一切正常,需要进一步深入源码。
源码分析
序列化
序列化代码入口在Hessian2Output,对着协议理解代码。


三个reference map分别存储value、class、type的映射,value reference的可以实现图/递归/循环等特殊数据结构,class和type用于减少重复数据,节省空间。
_buffer字节数组用于缓存序列化后的结果,缓存不足时将缓存结果输出到OutputStream,提高性能。
/**
* Writes any object to the output stream.
*/
public void writeObject(Object object) throws IOException
{
if (object == null) {
writeNull();
return;
}
Serializer serializer;
serializer = findSerializerFactory().getSerializer(object.getClass());
serializer.writeObject(object, this);
}
public void writeNull() throws IOException
{
int offset = _offset;
byte []buffer = _buffer;
if (SIZE <= offset + 16) {
flush();
offset = _offset;
}
buffer[offset++] = 'N';
_offset = offset;
}
Hessian2Output.writeObject:对象为null,直接写null后结束;非null对象,先根据class获取对应的序列化实现,然后不同类型按各自协议进行序列化。
其中,Serializer是个接口定义,不同类型的序列化协议实现在对应的实现类中。在我们的例子中,writeObject的具体实现在JavaSerializer中。对于其他实现可自行研究。
对于按class获取序列化实现的逻辑可参阅SerializerFactory,之所以提这点是因为我们上面人工解码出来的[object就在这里定义的,表示Object数组类的typeName。
wireteNull的逻辑比较简单,写字符N即可。只不过多了字节数组缓存空间的判断,一个字符2个字节16位,先判断缓存空间不够就先将缓存写到输出流。
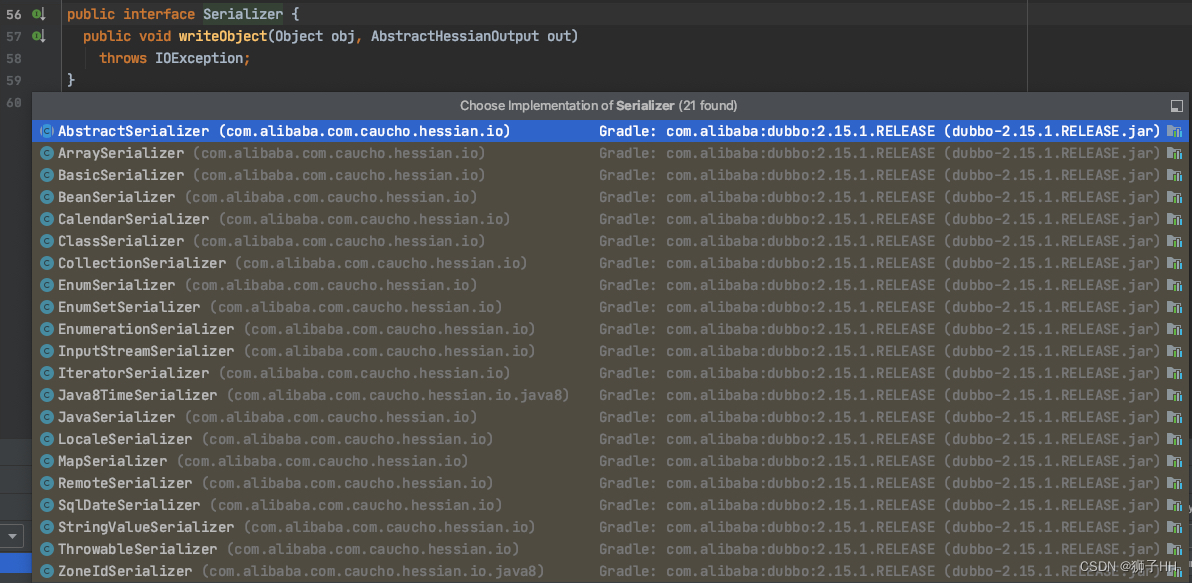
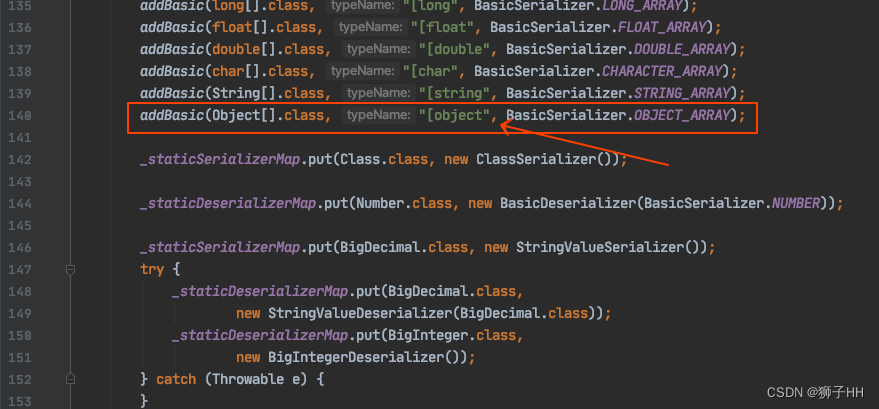
对于Case 2 调试下,要序列化的对象是size为2的 com.google.common.collect.RegularImmutableList ,其上注释:用writeReplace来序列化,而非默认序列化。

在ImmutableList中重写了writeReplace,具体实现如下。看到这段代码再比对之前我们人工解码出来的内容,是不是恍然大悟。
com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm 、 elements 和 [object Object数组 的由来找到了,前途一片光明:)
@Override
Object writeReplace() {
return new SerializedForm(toArray());
}
/*
* Serializes ImmutableLists as their logical contents. This ensures that
* implementation types do not leak into the serialized representation.
*/
static class SerializedForm implements Serializable {
final Object[] elements;
SerializedForm(Object[] elements) {
this.elements = elements;
}
Object readResolve() {
return copyOf(elements);
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 0;
}
后面的逻辑就简单了:
更新reference(删掉老的,用新的替换。主要为了优化性能,跟本文关系不大,忽略);
循环序列化(对Case 2,共进行了2次JavaSerializer.writeObject:先序列化RegularImmutableList、再ImmutableList.SerializedForm,和一次BasicSerializer:OBJECT_ARRAY,详见下面第2张截图)。
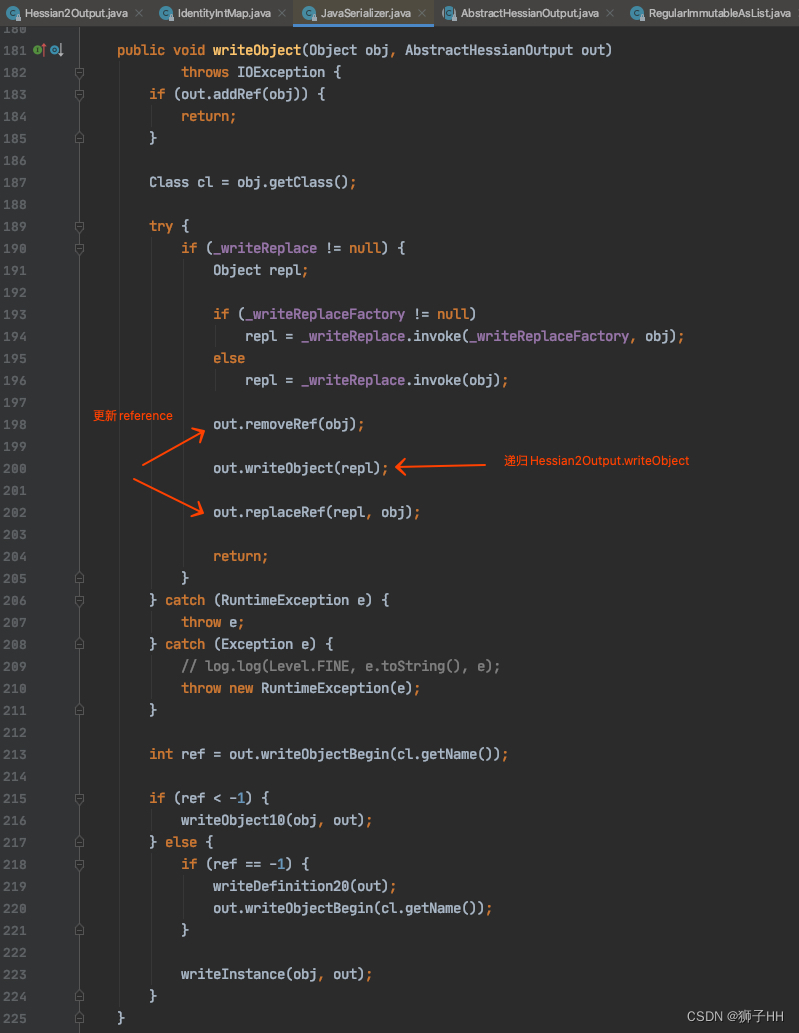
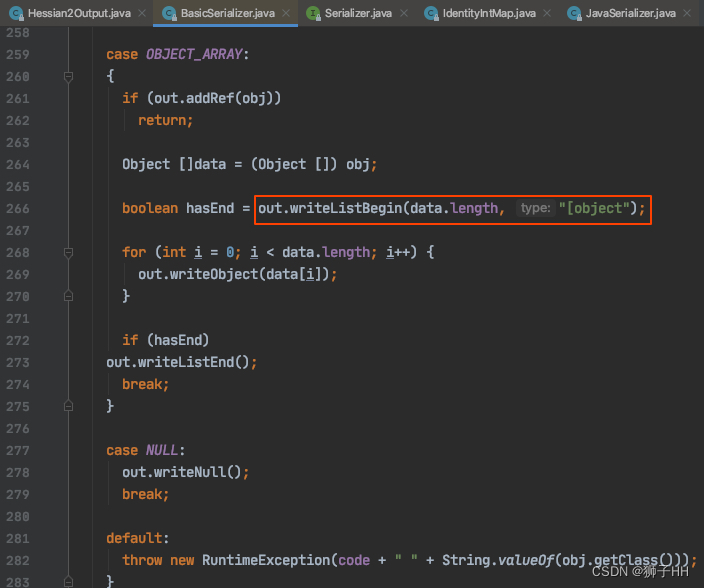
到这序列化过程就结束了,上述第一张图后面还有部分逻辑在此不再讨论,自行学习吧。
反序列化
反序列化代码在Hessian2Input.readObject中,主要结构为:1)取offset位置对应的字节码作为tag;2)按tag类型反序列化。
【注意下面代码有删减,标识为注释:/// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** …】
public Object readObject(List<Class<?>> expectedTypes) throws IOException {
int tag = _offset < _length ? (_buffer[_offset++] & 0xff) : read();
switch (tag) {
case 'N':
return null;
case 'T':
return Boolean.valueOf(true);
case 'F':
return Boolean.valueOf(false);
// direct integer
case 0x80: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0xbf:
return Integer.valueOf(tag - BC_INT_ZERO);
/* byte int */
case 0xc0: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0xcf:
return Integer.valueOf(((tag - BC_INT_BYTE_ZERO) << 8) + read());
/* short int */
case 0xd0: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0xd7:
return Integer.valueOf(((tag - BC_INT_SHORT_ZERO) << 16)
+ 256 * read() + read());
case 'I':
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt());
// direct long
case 0xd8: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0xef:
return Long.valueOf(tag - BC_LONG_ZERO);
/* byte long */
case 0xf0: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0xff:
return Long.valueOf(((tag - BC_LONG_BYTE_ZERO) << 8) + read());
/* short long */
case 0x38: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0x3f:
return Long.valueOf(((tag - BC_LONG_SHORT_ZERO) << 16) + 256 * read() + read());
case BC_LONG_INT:
return Long.valueOf(parseInt());
case 'L':
return Long.valueOf(parseLong());
case BC_DOUBLE_ZERO:
return Double.valueOf(0);
case BC_DOUBLE_ONE:
return Double.valueOf(1);
case BC_DOUBLE_BYTE:
return Double.valueOf((byte) read());
case BC_DOUBLE_SHORT:
return Double.valueOf((short) (256 * read() + read()));
case BC_DOUBLE_MILL: {
int mills = parseInt();
return Double.valueOf(0.001 * mills);
}
case 'D':
return Double.valueOf(parseDouble());
case BC_DATE:
return new Date(parseLong());
case BC_DATE_MINUTE:
return new Date(parseInt() * 60000L);
case BC_STRING_CHUNK:
case 'S': {
_isLastChunk = tag == 'S';
_chunkLength = (read() << 8) + read();
int data;
_sbuf.setLength(0);
while ((data = parseChar()) >= 0)
_sbuf.append((char) data);
return _sbuf.toString();
}
case 0x00: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0x1f: {
_isLastChunk = true;
_chunkLength = tag - 0x00;
int data;
_sbuf.setLength(0);
while ((data = parseChar()) >= 0)
_sbuf.append((char) data);
return _sbuf.toString();
}
case 0x30:
case 0x31:
case 0x32:
case 0x33: {
_isLastChunk = true;
_chunkLength = (tag - 0x30) * 256 + read();
_sbuf.setLength(0);
int ch;
while ((ch = parseChar()) >= 0)
_sbuf.append((char) ch);
return _sbuf.toString();
}
case BC_BINARY_CHUNK:
case 'B': {
_isLastChunk = tag == 'B';
_chunkLength = (read() << 8) + read();
int data;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((data = parseByte()) >= 0)
bos.write(data);
return bos.toByteArray();
}
case 0x20: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0x2f: {
_isLastChunk = true;
int len = tag - 0x20;
_chunkLength = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
data[i] = (byte) read();
return data;
}
case 0x34:
case 0x35:
case 0x36:
case 0x37: {
_isLastChunk = true;
int len = (tag - 0x34) * 256 + read();
_chunkLength = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
buffer[i] = (byte) read();
}
return buffer;
}
case BC_LIST_VARIABLE: {
// variable length list
String type = readType();
return findSerializerFactory().readList(this, -1, type);
}
case BC_LIST_VARIABLE_UNTYPED: {
return findSerializerFactory().readList(this, -1, null);
}
case BC_LIST_FIXED: {
// fixed length lists
String type = readType();
int length = readInt();
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getListDeserializer(type, null);
boolean valueType = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 1;
return reader.readLengthList(this, length, valueType ? expectedTypes.get(0) : null);
}
case BC_LIST_FIXED_UNTYPED: {
// fixed length lists
int length = readInt();
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getListDeserializer(null, null);
boolean valueType = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 1;
return reader.readLengthList(this, length, valueType ? expectedTypes.get(0) : null);
}
// compact fixed list
case 0x70:
case 0x71:
case 0x72:
case 0x73:
case 0x74:
case 0x75:
case 0x76:
case 0x77: {
// fixed length lists
String type = readType();
int length = tag - 0x70;
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getListDeserializer(type, null);
boolean valueType = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 1;
return reader.readLengthList(this, length, valueType ? expectedTypes.get(0) : null);
}
// compact fixed untyped list
case 0x78:
case 0x79:
case 0x7a:
case 0x7b:
case 0x7c:
case 0x7d:
case 0x7e:
case 0x7f: {
// fixed length lists
int length = tag - 0x78;
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getListDeserializer(null, null);
boolean valueType = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 1;
return reader.readLengthList(this, length, valueType ? expectedTypes.get(0) : null);
}
case 'H': {
boolean keyValuePair = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 2;
// fix deserialize of short type
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getDeserializer(Map.class);
return reader.readMap(this
, keyValuePair ? expectedTypes.get(0) : null
, keyValuePair ? expectedTypes.get(1) : null);
}
case 'M': {
String type = readType();
return findSerializerFactory().readMap(this, type);
}
case 'C': {
readObjectDefinition(null);
return readObject();
}
case 0x60: /// !注意:出于篇幅考虑,此处省略了一大波 case ** ...
case 0x6f: {
int ref = tag - 0x60;
if (_classDefs == null)
throw error("No classes defined at reference '{0}'" + tag);
ObjectDefinition def = (ObjectDefinition) _classDefs.get(ref);
return readObjectInstance(null, def);
}
case 'O': {
int ref = readInt();
ObjectDefinition def = (ObjectDefinition) _classDefs.get(ref);
return readObjectInstance(null, def);
}
case BC_REF: {
int ref = readInt();
return _refs.get(ref);
}
default:
if (tag < 0)
throw new EOFException("readObject: unexpected end of file");
else
throw error("readObject: unknown code " + codeName(tag));
}
}
private void readObjectDefinition(Class cl)
throws IOException {
String type = readString(); // com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm
int len = readInt(); // length=1
String[] fieldNames = new String[len]; // String[1]
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
fieldNames[i] = readString(); // elements
ObjectDefinition def = new ObjectDefinition(type, fieldNames);
if (_classDefs == null)
_classDefs = new ArrayList();
_classDefs.add(def); // 确定对象定义,类型和字段列表
}
private Object readObjectInstance(Class cl, ObjectDefinition def)
throws IOException {
String type = def.getType();
String[] fieldNames = def.getFieldNames();
if (cl != null) {
Deserializer reader;
reader = findSerializerFactory().getObjectDeserializer(type, cl);
return reader.readObject(this, fieldNames);
} else {
return findSerializerFactory().readObject(this, type, fieldNames);
}
}
对于我们的Case 1或Case 2,第一个字符是16进制的43(debug的时候是十进制67,可以调idea View as 进行转化),按hessian2协议【x43 # object type definition (‘C’)】表示C,走到上述代码的266行分支。
接下来readObjectDefinition,读取type为 com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm ,length为1,有一个字段,字段名为elements。
然后继续readObject,tag为0x60,此时走到上述代码的272行分支,ref为0,从对象定义中拿到对应类型,readObjectInstance读取具体实例,class为null,走到334行,通过SerializerFactory.readObject读为对象。
先按type获取反序列化器Deserializer,JavaDeserializer readObject 读出Object为ImmutableList$SerializedForm(构造函数new个实例),对每个字段获取FieldDeserializer,elements字段的值为Object[];BasicDeserializer readLengthList中的OBJECT_ARRAY。
// # SerializerFactory
public Object readObject(AbstractHessianInput in,
String type,
String[] fieldNames)
throws HessianProtocolException, IOException {
Deserializer deserializer = getDeserializer(type);
if (deserializer != null)
return deserializer.readObject(in, fieldNames);
else if (_hashMapDeserializer != null)
return _hashMapDeserializer.readObject(in, fieldNames);
else {
_hashMapDeserializer = new MapDeserializer(HashMap.class);
return _hashMapDeserializer.readObject(in, fieldNames);
}
}
public Deserializer getDeserializer(String type)
throws HessianProtocolException {
if (type == null || type.equals("") || UNKNOWN_CLASSES.containsKey(type)) {
return null;
}
Deserializer deserializer;
if (_cachedTypeDeserializerMap != null) {
deserializer = (Deserializer) _cachedTypeDeserializerMap.get(type);
if (deserializer != null)
return deserializer;
}
deserializer = (Deserializer) _staticTypeMap.get(type);
if (deserializer != null)
return deserializer;
if (type.startsWith("[")) {
Deserializer subDeserializer = getDeserializer(type.substring(1));
if (subDeserializer != null)
deserializer = new ArrayDeserializer(subDeserializer.getType());
else
deserializer = new ArrayDeserializer(Object.class);
} else {
try {
Class cl = Class.forName(type, false, _loader); // 按class获取deserializer
deserializer = getDeserializer(cl); // cl=com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList$SerializedForm -> JavaDeserializer
} catch (Exception e) {
UNKNOWN_CLASSES.computeIfAbsent(type, s -> {
log.error("[EX-DUBBO-0020] Hessian/Burlap: '" + type + "' 是未知的类在"
+ _loader + ":\n" + e.getMessage(), e);
return 1;
});
}
}
if (deserializer != null) {
if (_cachedTypeDeserializerMap == null)
_cachedTypeDeserializerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(8);
_cachedTypeDeserializerMap.put(type, deserializer);
}
return deserializer;
}
对象反序列化步骤:读对象定义readObjectDefinition、获取对象实例readObjectInstance、各字段反序列化FieldDeserializer。
报错分析
对于Case 1 将ImmutableList作为Request参数进行序列化时,反序列化失败问题进行分析。
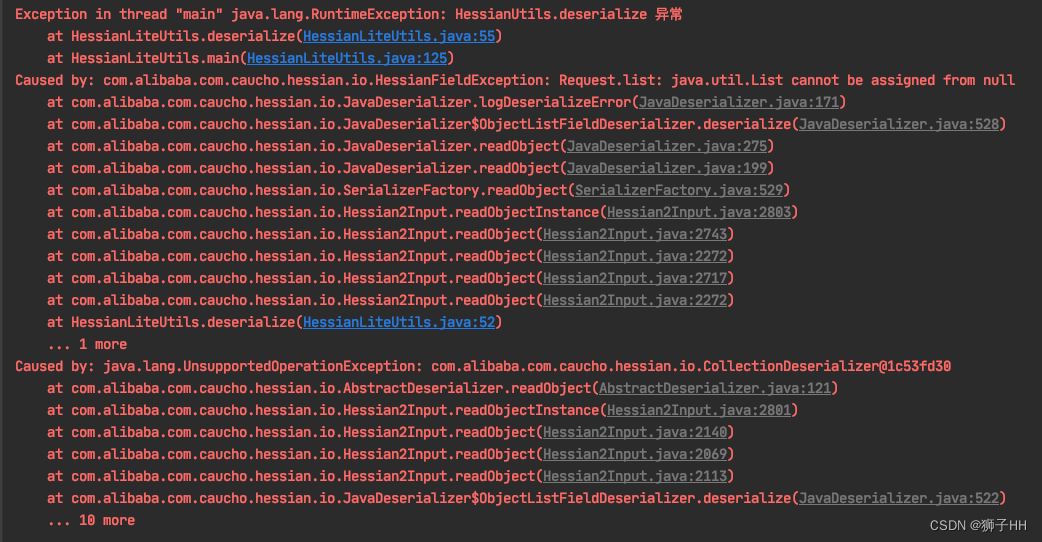
interface java.util.List 获取反序列化器 getObjectDeserializer 得到 CollectionDeserializer,但他未实现 readObject,导致走到AbstractDeserializer中的readObject,从而抛异常 UnsupportedOperationException,Request.list的字段解析失败,异常被 ObjectListFieldDeserializer.deserialize 捕获,打日志:HessianFieldException: Request.list: java.util.List cannot be assigned from null。

总结
- Java中的不可变集合(guava的 ImmutableList、ImmutableSet等,Java9引入的ImmutableCollections相关类型)不能作为POJO参数进行序列化,但是可以直接作为对象进行序列化;
- float 反序列化后精度丢失,double 没问题;
- keySet()返回的Set未实现Serializable,Hessian反序列化结果为ArrayList;
- 二维long数组、LocalDate可以正常序列化反序列化(针对参考资料3中提到的坑试验了下,发现我司使用版本没有该问题,可正常使用二维long数组和Java8引入的LocalDate)。
# 1 ImmutableList、ImmutableSet 作为参数序列化异常,作为对象可以序列化
// request.setList(ImmutableList.of(1, 2));
// byte[] bytes1 = serialize(request);
// object = deserialize(bytes1); // [x] HessianFieldException
// byte[] bytes2 = serialize(ImmutableList.of(1, 2));
// object = deserialize(bytes2); // [OK]
// request.setSet(ImmutableSet.of(1, 1, 2));
// byte[] bytes3 = serialize(request);
// object = deserialize(bytes3); // [x] HessianFieldException
// byte[] bytes4 = serialize(ImmutableSet.of(1, 1, 2));
// object = deserialize(bytes4); // [OK]
# 2 float 精度丢失,double 没问题
// float f = 3.1415926f; // [x] 精度丢失变成3.1415925
// double d = 3.1415926d; // [OK]
# 3 keySet()返回的Set未实现Serializable,Hessian反序列化结果为ArrayList
// Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("A", 1);
// map.put("B", 2);
// byte[] bytes = serialize(map.keySet());
// object = deserialize(bytes); // [x] 反序列化为ArrayList
# 4.1 LocalDate 可正常使用
// LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
// byte[] bytes = serialize(now);
// object = deserialize(bytes); // [OK]
# 4.2 二维long数组可以正常序列化/反序列化
// long[][] array = new long[][]{new long[]{1L, 2L, 3L}, new long[]{4L, 5L, 6L}};
// byte[] bytes = serialize(array);
// object = deserialize(bytes); // OK
// request.setArray(array);
// byte[] bytes = serialize(request);
// object = deserialize(bytes); // OK
扩展:Java序列化框架对比
既然hessian2有上述这些问题,那为什么dubbo还将其作为默认的序列化协议?接下来我们扩展对比下hessian2和常用的Java序列化框架,对hessian2的优劣有个更全面的认识。(参考:几种Java常用序列化框架的选型与对比 )
Java序列化是把Java对象转化为字节序列,以便在网络中传输或存到文件里。反序列化是把字节序列恢复为Java对象。
影响序列化协议选型的因素主要有两个:1)序列化后字节序列的大小,如果太大将影响网络传输性能;2)序列化和反序列化过程的性能。
-
大小和性能
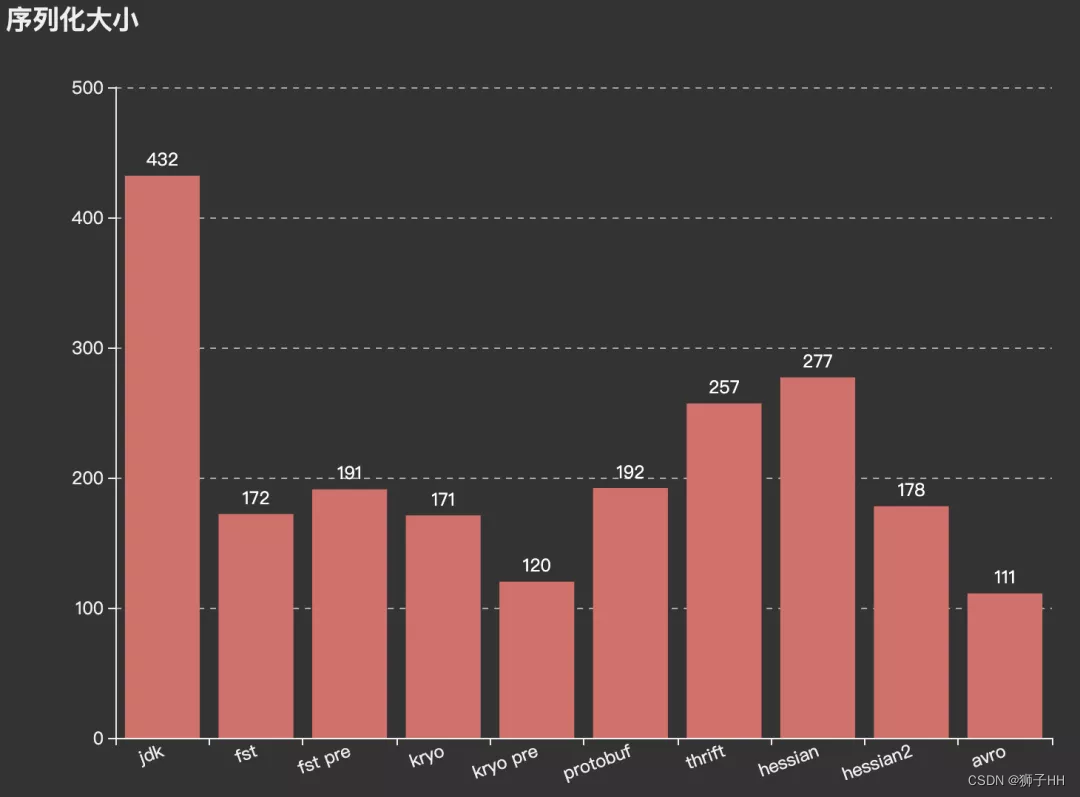

jdk和hessian1的序列化大小和性能相对最差;其他几种(kryo, hessian2, protobuf, fst等)差别不大。 -
扩展性

- kryo不支持字段扩展比较坑,提供出去的rpc接口不能修改字段,如果入参或出参要新增字段则需要提供新接口;
- FST通过@Version注解能够支持新增字段与旧的数据流兼容,但使用起来比较繁琐。
-
数据类型支持
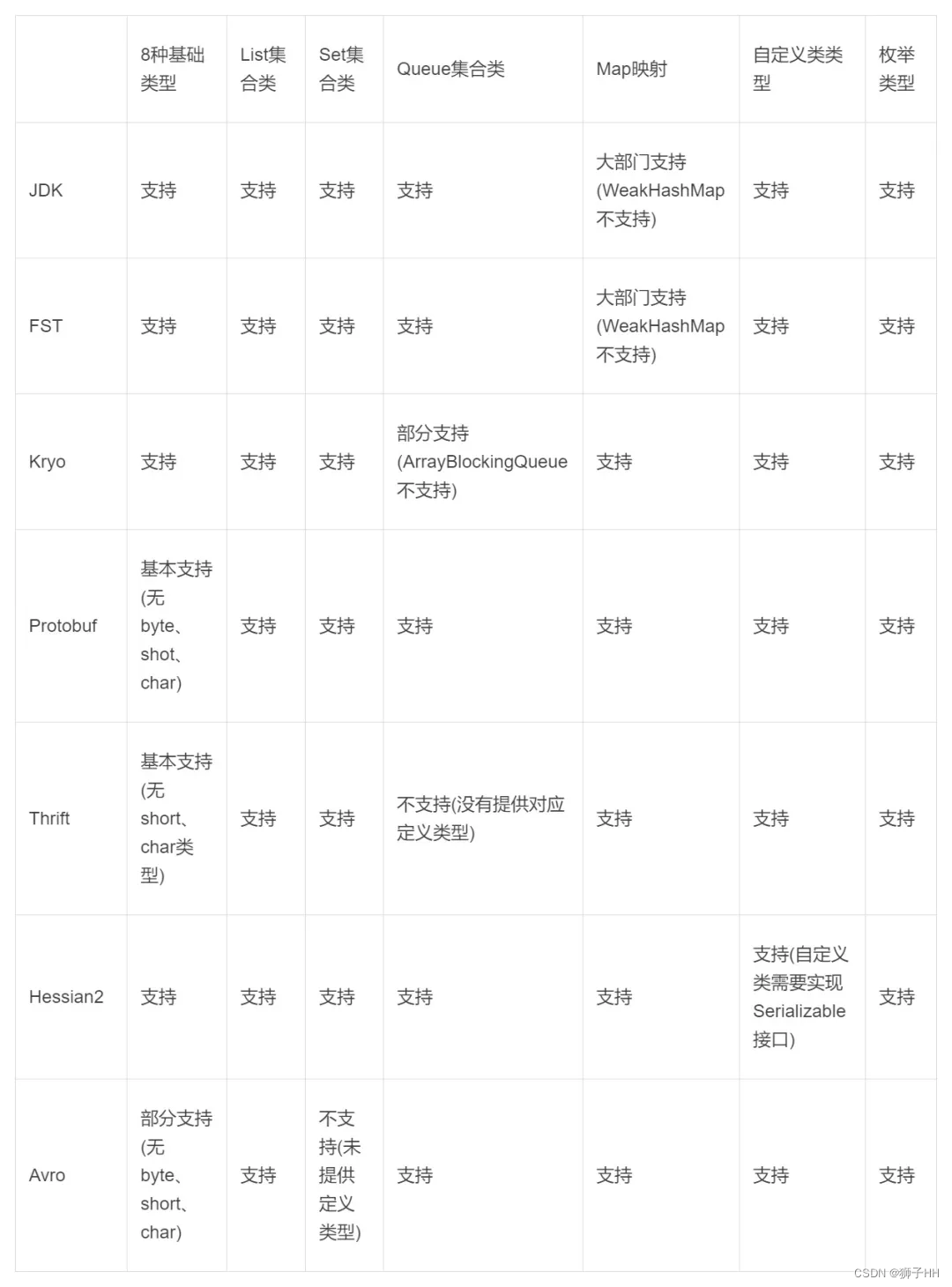
Hessian2 自定义类需要实现Serializable接口,这也就是rpc接口的request和response都要实现Serializable接口的原因。
注:集合类型测试包括如下实现类:- List测试内容:ArrayList、LinkedList、Stack、CopyOnWriteArrayList、Vector。
- Set测试内容:HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet、CopyOnWriteArraySet。
- Map测试内容:HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、WeakHashMap、ConcurrentHashMap、Hashtable。
- Queue测试内容:PriorityQueue、ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、ConcurrentLinkedQueue、SynchronousQueue、ArrayDeque、LinkedBlockingDeque和ConcurrentLinkedDeque。
-
语法结构支持

-
小结
- hessian2在Java序列化框架对比中的综合表现还是不错的,小巧、好用、性能还算不错。
参考
- 几种Java常用序列化框架的选型与对比
- Hessian 2.0 Serialization Protocol
- 论Hessian的各种坑爹骚操作





![[电商实时数仓] 用户行为数据和业务数据采集以及ODS层](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8d5a0268932544fc995056ee36f0d513.png)