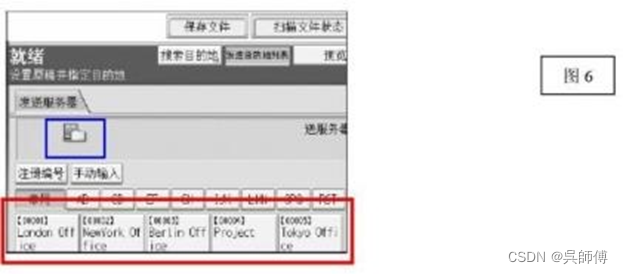
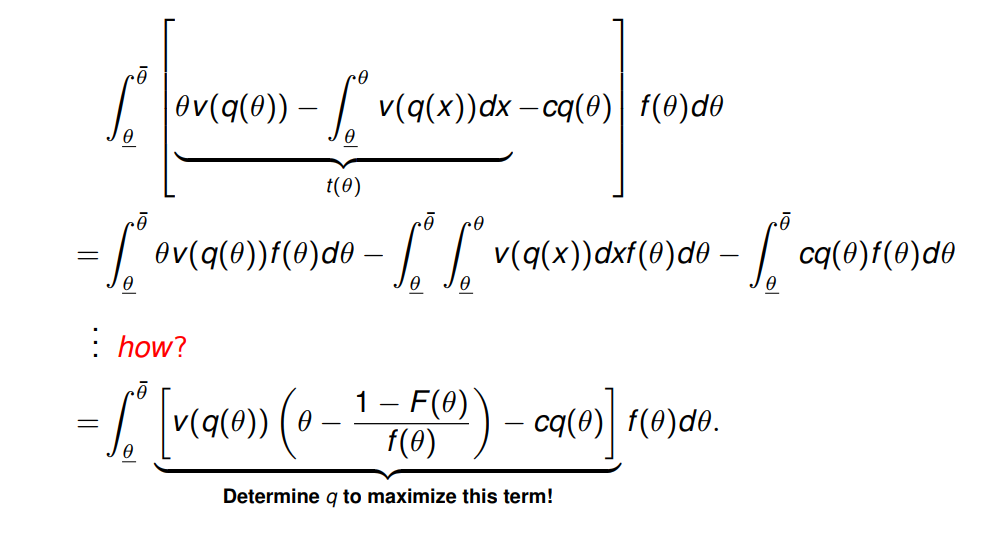
1. 测试函数
get_name.py
def combination(first, last):
'''将姓名组合在一起'''
name = first + ' ' + last
return name.title()hello_world.py
from get_name import combination
print("Enter 'q' to quit!")
while True:
first = input('Please input your first name: ')
if first == 'q':
break
last = input('Please input your last name: ')
if last == 'q':
break
name = combination(first, last)
print(name)
# Enter 'q' to quit!
# Please input your first name: tom
# Please input your last name: riddle
# Tom Riddle
# Please input your first name: q1.1. 单元测试和测试用例
单元测试:用于核实函数的某个方面没有问题。
测试用例:是一组单元测试,这些单元测试一起核实函数在各种情形下的行为都符号要求。
全覆盖式侧式用例:包含一整套单元测试,涵盖了各种可能的函数使用方式。
1.1.1 可通过的测试
注意:
导入模块unittest以及要测试的函数
创建一个继承unittest.TestCase的类,编写一系列方法对函数行为的不同方面进行测试
方法名使用test_或test,会在我们运行.py时自动运行这个方法
断言方法,即调用unittest的方法assertEqual(测试的结果,期望的结果)
在最后加上 if __name__=='__main__' : unittest.main()
get_name.py
def combination(first, last):
'''将姓名组合在一起'''
name = first + ' ' + last
return name.title()hello_world.py
from get_name import combination
print("Enter 'q' to quit!")
while True:
first = input('Please input your first name: ')
if first == 'q':
break
last = input('Please input your last name: ')
if last == 'q':
break
name = combination(first, last)
print(name)
# Enter 'q' to quit!
# Please input your first name: tom
# Please input your last name: riddle
# Tom Riddle
# Please input your first name: qtest_name.py
import unittest
from get_name import combination
class TestName(unittest.TestCase):
def test_name(self):
result_name = combination('harry', 'potter')
self.assertEqual(result_name, 'Harry Potter')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# Ran 1 test in 0.008s
# OK1.1.2 不能通过的测试
get_name.py
def combination(first, middle, last):
'''将姓名组合在一起'''
name = first + ' ' + middle + ' ' + last
return name.title()再次运行test_name.py,运行结果如下:
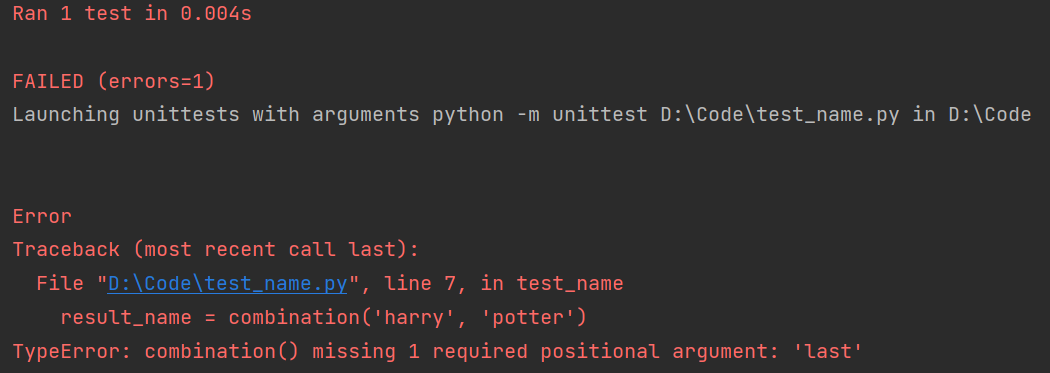
1.1.3 测试未通过时进行处理
修改get_name.py
def combination(first, last, middle=''):
'''将姓名组合在一起'''
if middle:
name = first + ' ' + middle + ' ' + last
else:
name = first + ' ' + last
return name.title()test_name.py运行结果:
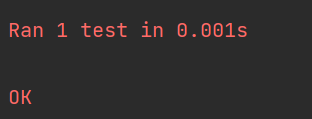
1.1.4 添加新测试
注意:测试类中的函数名要带有描述性,这样才能明白测试未通过时的输出
test_name.py
import unittest
from get_name import combination
class TestName(unittest.TestCase):
def test_name(self):
result_name = combination('harry', 'potter')
self.assertEqual(result_name, 'Harry Potter')
def test_middle_name(self):
result_name = combination('li', 'xiao', 'ming')
self.assertEqual(result_name, 'Li Ming Xiao')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# Ran 2 tests in 0.002s
# OK2. 测试类
2.1. 各种断言方法
unittest.TestCase类中提供了很多断言的方法:
方法 | 用途 |
assertEqual(a,b) | 核实 a==b |
assertNotEqual(a,b) | 核实 a!=b |
assertTrue(x) | 核实x为True |
assertFalse(x) | 核实x为False |
assertIn(item,list) | 核实item在list中 |
assertNotIn(item,list) | 核实item不在list中 |
2.2. 一个要测试的类
investigate.py
class Investigation():
'''调查问卷'''
def __init__(self, question):
self.question = question
self.responses = []
def show_question(self):
print(self.question)
def store_new_response(self, new_response):
self.responses.append(new_response)
def show_results(self):
for response in self.responses:
print(response)language_investigate.py
from investigate import Investigation
question = '你喜欢哪种编程语言?'
my_investigate = Investigation(question)
my_investigate.show_question()
print("Enter 'q' to quit!")
while True:
response = input('Language: ')
if response == 'q':
break
my_investigate.store_new_response(response)
my_investigate.show_results()
# 你喜欢哪种编程语言?
# Enter 'q' to quit!
# Language: Python
# Language: C
# Language: q
# Python
# C2.3. 测试Investigation类
investigate_test.py
import unittest
from investigate import Investigation
class TestInvestigate(unittest.TestCase):
def test_store_single_response(self):
question = '你喜欢哪种编程语言?'
my_investigate = Investigation(question)
my_investigate.store_new_response('Python')
self.assertIn('Python', my_investigate.responses)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# Ran 1 test in 0.002s
# OKinvestigate_test.py(针对多个回答做测试)
import unittest
from investigate import Investigation
class TestInvestigate(unittest.TestCase):
def test_store_single_response(self):
question = '你喜欢那种编程语言?'
my_investigate = Investigation(question)
my_investigate.store_new_response('Python')
self.assertIn('Python', my_investigate.responses)
def test_store_three_responses(self):
question = '你喜欢哪些编程语言?'
my_investigate = Investigation(question)
responses = ['C', 'Java', 'Python']
for response in responses:
my_investigate.store_new_response(response)
for response in responses:
self.assertIn(response, my_investigate.responses)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# Ran 2 tests in 0.002s
# OK2.4. setUp方法
注意:
unittest.TestCase类包含setUp方法,这样我们只需创建一次对象,并在各个测试方法中使用它。
Python会先运行setUp方法,再运行以test_打头的方法,因此我们编写的每个测试方法就都可以使用在setUp中创建的对象了。
import unittest
from investigate import Investigation
class TestInvestigate(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
question = '你喜欢什么编程语言?'
self.investigate = Investigation(question)
self.responses = ['C', 'Python', 'Java']
def test_store_single_response(self):
self.investigate.store_new_response(self.responses[1])
self.assertIn(self.responses[1], self.investigate.responses)
def test_store_three_responses(self):
for response in self.responses:
self.investigate.store_new_response(response)
for response in self.responses:
self.assertIn(response, self.investigate.responses)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
# Ran 2 tests in 0.002s
# OK