集合
- 14.11 Map集合
- 14.11.1 Map集合特点
- 14.11.2 Map集合体系结构
- 14.12 HashMap
- 14.12.1 HashMap基本使用
- 14.12.2 HashMap实际应用
- 14.12.3 HashMap练习
- 14.12.4 HashMap底层实现原理
- 14.12.5 put的过程原码
- 14.12.6 resize过程原码
- 14.12.7 get的过程原码
- 14.13 HashTable
- 14.14 泛型高级使用
- 14.14.1 泛型类
- 14.14.2 泛型接口
- 14.14.3 泛型方法
- 14.14.4 泛型上下边界
- 14.15 常见的集合面试面试题
``
14.11 Map集合
14.11.1 Map集合特点
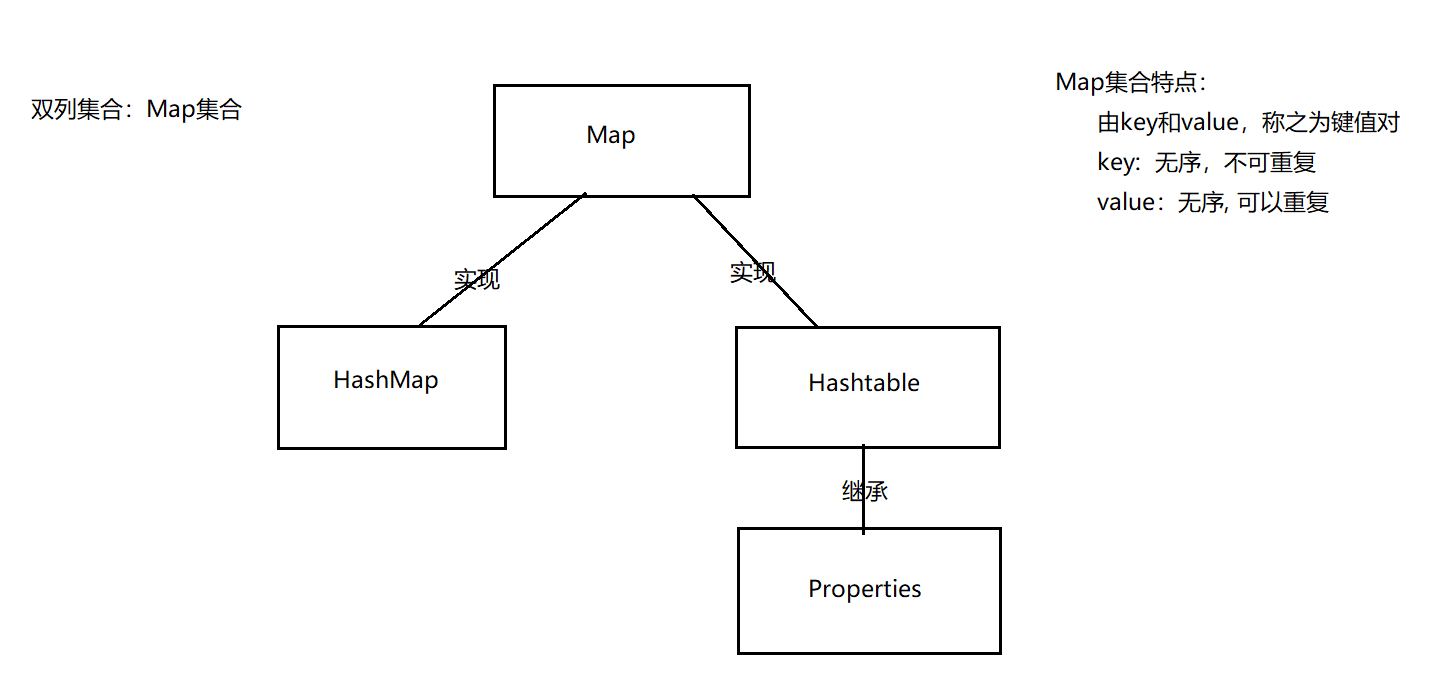
- Map集合是双列集合,由key和value组成。称之为键值对
- 键的特点:无序,无下标,不重复。
- 值的特点:无序,无下标,可重复
14.11.2 Map集合体系结构
| Map集合体系结构 |
|---|
 |
14.12 HashMap
14.12.1 HashMap基本使用
常用方法
- put(K key, V value)
- get(Object key)
- Set keySet()
- Collection values()
- Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
- boolean containsKey(Object key)
- boolean containsValue(Object value)
- V remove(Object key)
- int size()
package com.qf.demo01;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建HashMap
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(12);
//向map集合中添加元素
map.put("usa", "漂亮国");
map.put("jp", "日本");
map.put("en", "英国");
map.put("ca", "加拿大");
map.put("cn", "中华人民共和国");
map.put("cn", "中国");
map.put("china", "中国");
System.out.println(map);
//从集合中获取元素的值。 根据key获取对应value
System.out.println(map.get("cn"));
System.out.println(map.get("usa"));
//清空map集合中的元素
//map.clear();
//System.out.println(map);
//判断是否包含指定的key
System.out.println(map.containsKey("xjp"));
//判断是否包含指定的value
System.out.println(map.containsValue("中国"));
//判断集合中的元素长度是否为0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//根据key移除map中的元素
map.remove("jp");
System.out.println(map);
//返回map集合中元素的个数
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println("=================================");
//返回map集合中所有的key
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key);
}
System.out.println("=================================");
//返回map集合中所有的value
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("=================================");
//返回map集合中所有的key和value (Entry)
Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("=================================");
}
}
14.12.2 HashMap实际应用
- 可以使用Map<String , Obeject> 表示一个实体类
- 可以使用List<Map<String,Object>> 表示一个实体类集合
public class HashMapDemo02 {
/**
* 表示一件商品:商品编号、名称、价格、产地、上架时间....
*
* 实体类表示:
* 一件商品:Product对象
* public class Product{
* private int id;
* private String name;
* private double price;
* .....
* }
* Product product = new Product(1,"手机",3000...);
*
* 多件商品:List<Product>
*
* Map表示:
* 一件商品:Map对象
* Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
* map.put("id",1);
* map.put("name","电脑");
* map.put("price",3000.5);
*
* 多件商品:List<Map<String,Object>>
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Map表示一件商品
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("id", 1);
map.put("name", "电脑");
map.put("price",3000.5);
map.put("createDate", new Date());
Map<String, Object> map1 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map1.put("id", 2);
map1.put("name", "电脑2");
map1.put("price",3002.5);
map1.put("createDate", new Date());
//使用List<Map>表示多件商品
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
list.add(map);
list.add(map1);
for (Map<String, Object> map2 : list) {
System.out.println(map2);
}
//使用集合实现存储省市信息
}
}
14.12.3 HashMap练习
案例:使用集合保存省市数据
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
List<String> city1 = new ArrayList<String>();
city1.add("武汉");
city1.add("监利");
city1.add("黄冈");
city1.add("荆州");
map.put("湖北省", city1);
List<String> city2 = new ArrayList<String>();
city2.add("长沙");
city2.add("岳阳");
city2.add("常德");
city2.add("湘潭");
map.put("湖南省", city2);
System.out.println(map.get("湖北省"));
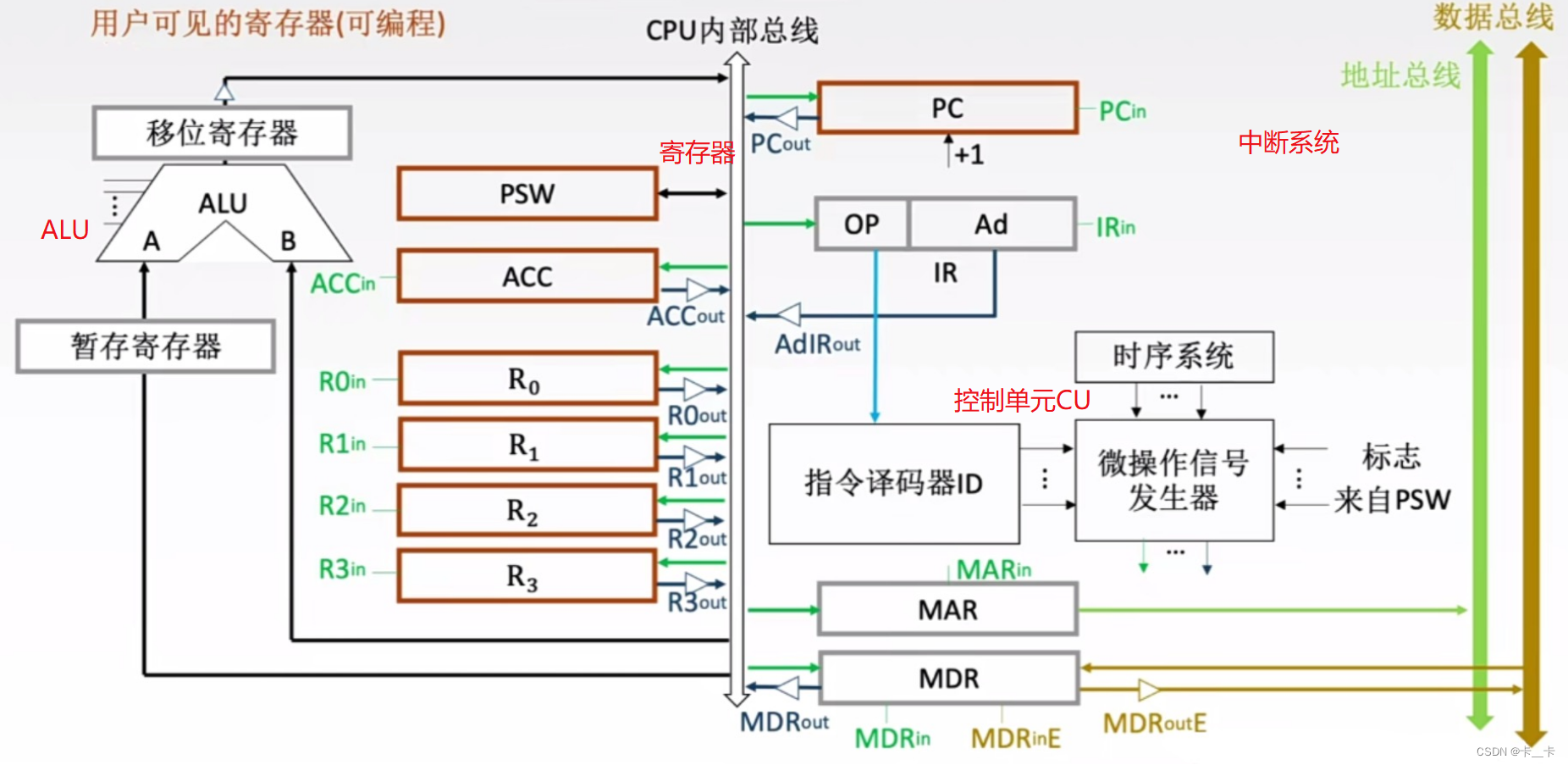
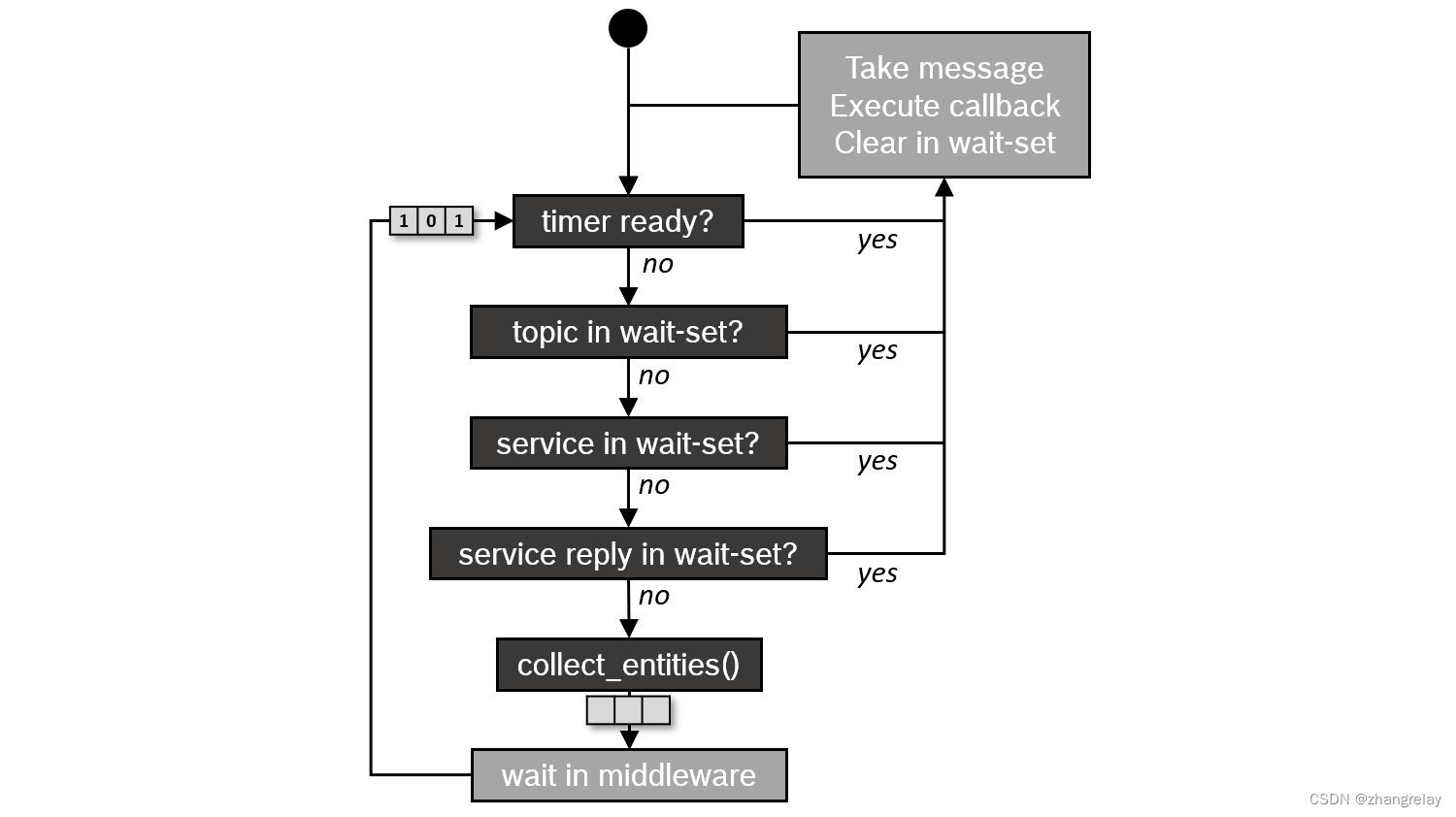
14.12.4 HashMap底层实现原理
| HashMap底层实现原理 |
|---|
 |
14.12.5 put的过程原码
| put流程 |
|---|
 |
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//tab表示存放Node节点的数据 p表示当前节点 n表示长度 i表示节点在数组中的下标
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//判断数组如果为空或者数组长度为0,那么就对数组进行扩容,数组默认初始大小为16
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//将数组的长度-1与hash值进行与运算(计算的结果一定是0~数组长度-1)得到元素应该存放的下标
//如果当前下标位置为空,那么直接将Node节点存放在当前位置
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//如果当前位置不为空(分为三种情况)
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//情况1:要添加的元素与当前位置上的元素相同(hash(hashCode)、key(equals)一致),则直接替换
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//情况2:如果要添加的元素是红黑树节点,那么将其添加到红黑树上
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//情况3:如果要添加的元素是链表,则需要遍历
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//将当前元素的下一个节点赋给e
//如果e为空,则创建新的元素节点放在当前位置的下一个元素上,并退出循环
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//如果链表的元素个数大于8个(且当数组中的元素个数大于64),则将其转换成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//要添加的元素与当前位置上的元素相同(hash(hashCode)、key(equals)一致),则直接退出循环
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//如果返回的e不为null
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
//将e的值赋给oldValue
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
//返回以前的值(当添加的元素已经存在返回的是以前的值)
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
//如果数组的元素个数大于阈值则进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
14.12.6 resize过程原码
| 扩容流程 |
|---|
 |
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//oldTab 表示原来数组(如果是第二次扩容:长度为16的那个)
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//oldCap 表示原数组的容量(长度)
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//oldThr 表示数组原来的阈值 12
int oldThr = threshold;
//newCap 新数组的容量 newThr 新数组的阈值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//新数组的容量扩大一半 newCap 32
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
//新阈值扩大老阈值的一半 newThr 24
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//threshold 24
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
//创建一个长度为32的数组
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
//table指向新数组
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
//将原数组中的元素拷贝到新数组中
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
//如果当前位置元素不为空
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
//情况1:当前位置上的下一个元素为空,则直接将这个元素拷贝到新数组中
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//情况2:当前位置上的元素红黑树类型,则需要进行切割
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
//情况3:当前位置上的元素链表类型,则需要进行分散拷贝
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
14.12.7 get的过程原码
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//当前first与要找到的hash和key都相等直接返回当前这个first元素
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//如果当前first不为空(有两种情况)
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//当前位置是一个红黑树
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
//根据hash、key从红黑树上找到对应的元素
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//当前位置是一个链表
do {
//循环进行比较直到找到向的hash和key的元素,并返回
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//如果数组的为空、数组的长度为0、当前下标位置上的值为null,这三种情况都返回null
return null;
}
14.13 HashTable
Hashtable常用方法与HashMap一致
HashMap与Hashtable区别:
- 1、Hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap是线程不安全的
- 2、Hashtable中不允许存储null作为key和value,而HashMap可以
在实际开发中一般都是用HashMap。考虑线程安全使用ConCurrentHashMap
14.14 泛型高级使用
14.14.1 泛型类
泛型类 类名
public class Box<T> { //T:表示任意的java类型 E、K、V
private T data;
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
14.14.2 泛型接口
泛型接口 接口名
public interface MyInterface<T> {
public void show(T t);
}
14.14.3 泛型方法
泛型方法 public T 方法名(T t,…){}
//泛型可以作为参数,(必须得先定义 <T> )
public <T> void m1(T t) {
}
14.14.4 泛型上下边界
泛型上下边界
- 语法:
- 上边界 ? extends 类型
- 下边界 ? super 类型
public class Demo01 {
//? 表示不确定类型 此时的?表示Object
public static void test01(List<?> list) {
}
/**
* 定义泛型上边界
*
* <? extends 类型>
*/
public static void test02(List<? extends Number> list) {
}
/**
* 定义泛型下边界
*
* <? super 类型>
*/
public static void test03(List<? super Number> list) {
}
public static <T> void test04(List<? extends Comparable<T>> list) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Number> list3 = new ArrayList<Number>();
List<Object> list4 = new ArrayList<Object>();
test01(list1);
test01(list2);
test01(list3);
test01(list4);
//test02(list1); //错误,方法定义泛型的上边界,泛型只能是Number及其Number子类
test02(list2);
test02(list3);
//test02(list4); //错误,方法定义泛型的上边界,泛型只能是Number及其Number子类
//test03(list1); //错误,方法定义泛型的下边界,泛型只能是Number及其Number父类
//test03(list2);
test03(list3);
test03(list4);
test04(list1);
test04(list2);
//test04(list3); //错误,方法定义泛型的上边界,泛型必须实现Comparable接口
//test04(list4); //错误,方法定义泛型的上边界,泛型必须实现Comparable接口
}
}
14.15 常见的集合面试面试题
- 1、简述:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的区别
- 2、简述:HashSet、TreeSet的去重原理
- 3、ArrayList、LinkedList底层实现
- 4、HashMap、HashTable的区别
- 5、HashMap底层实现原理
- 6、HashMap扩容机制
- 7、HashMap的数组容量为什么是2的次方数
- 8、HashMap的负载因子为什么是0.75
- 9、HashMap添加元素的过程
- 10、谈谈了解的数据结构