目录
题型一、克隆含有rand指针的链表
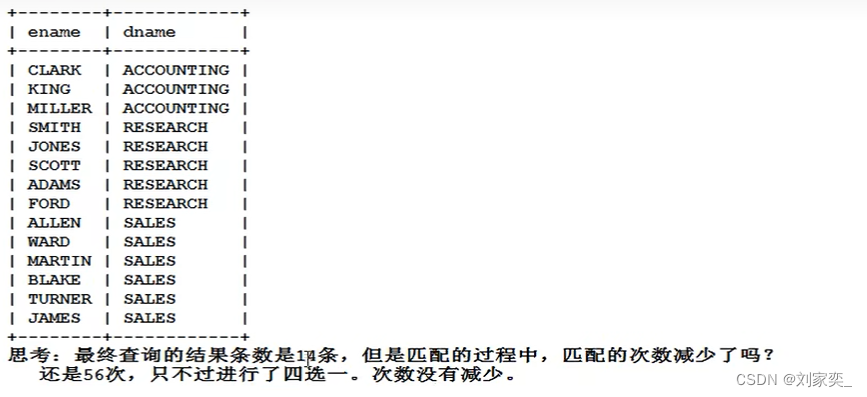
笔试:哈希表
面试:不用容器,模拟哈希表的功能
题型二、给一个单链表头节点Head,判断是否构成回文
题型三、将单链表按某值划分为左边小,中间相等,右边大
6个变量,不用容器,还能保证稳定性
题型四、找到两条链表的第一个相交节点
1、先找到两个链表的入环节点
2、接下来分情况讨论
题型五、不给头节点,要求删一个给定的节点 ?
1、小聪明法:借尸还魂
对于笔试:不用太在乎空间复杂度,一切为了时间复杂度。
对于面试:时间复杂度依然放在第一位,但一定要找到空间最省的办法。
题型一、克隆含有rand指针的链表

笔试:哈希表
代码:
Node* Hashfunc(Node* head)
{
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> Node_map;
Node* cur = head;
while (cur!= nullptr)
{
Node* new_cur = new Node(cur->value);
Node_map.insert(make_pair(cur, new_cur));
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node_map.find(cur)->second->next = cur->next;
Node_map.find(cur)->second->rand = cur->rand;
cur = cur->next;
}
return Node_map.find(head)->second;
}面试:不用容器,模拟哈希表的功能
Node* copyRandomList2(Node* head) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
Node* cur = head;
Node* next = nullptr;
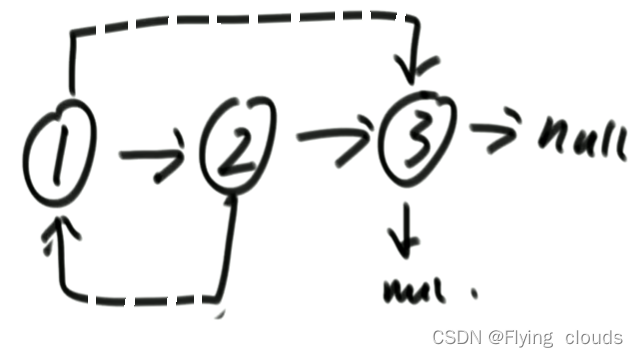
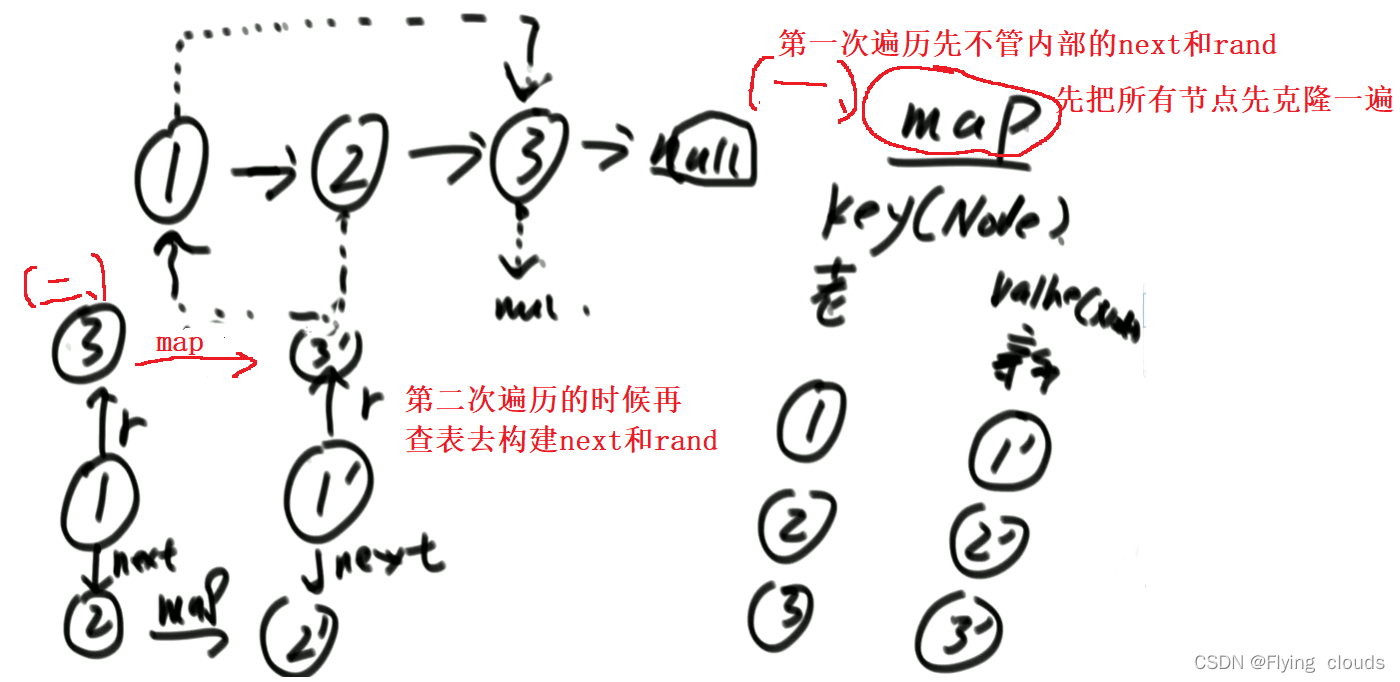
// 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> nullptr
// 1 -> 1' -> 2 -> 2' -> 3 -> 3'
while (cur != nullptr) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = new Node(cur->value);
cur->next->next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
Node* copy = nullptr;
// 1 1' 2 2' 3 3'
// 依次设置 1' 2' 3' random指针
while (cur != nullptr) {
next = cur->next->next;
copy = cur->next;
copy->rand = cur->rand != nullptr ? cur->rand->next : nullptr;
cur = next;
}
Node* res = head->next;
cur = head;
// 老 新 混在一起,next方向上,random正确
// next方向上,把新老链表分离
while (cur != nullptr) {
next = cur->next->next;
copy = cur->next;
cur->next = next;
copy->next = next != nullptr ? next->next : nullptr;
cur = next;
}
return res;
}题型二、给一个单链表头节点Head,判断是否构成回文
笔试:
依次遍历,放于栈中,然后再弹出去对比
面试:
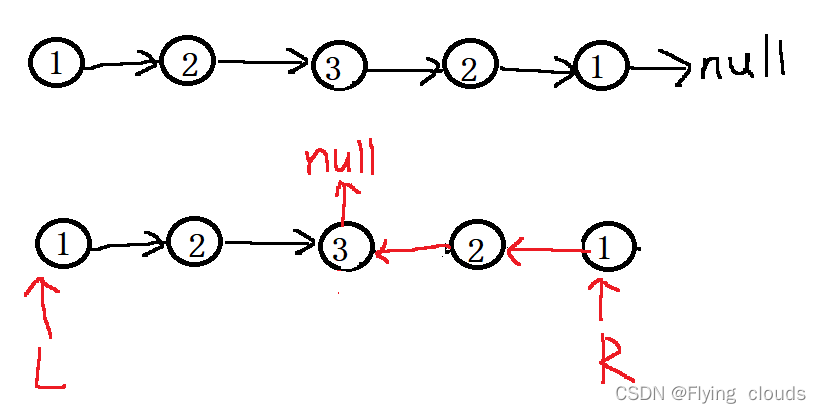
1.先通过快慢指针找到中间的节点,中间节点的next指向null
2.然后再把后半部分给逆序一下,并保存最后一个节点,
3.逆序以后再从L和R依次遍历比较,有不相同的就返回
4.不管满足不满足回文,最后一定要记得把链表的结构给恢复原状
代码实现:
class FindLink_Mid;
class Node
{
friend class FindLink_Mid;
public:
Node(int v)
{
value = v;
}
private:
int value;
Node* next;
};
class FindLink_Mid
{
public:
//奇数返回中点偶数返回上中点
Node* midOrUpMidNode(Node* head)
{
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || head->next->next == nullptr) {
return head;
}
// 链表有3个点或以上
Node* slow = head->next;
Node* fast = head->next->next;
while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
//奇数返回中点,偶数返回下中点
Node* midOrDownMidNode(Node* head)
{
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
{
return head;
}
Node* slow = head->next;
Node* fast = head->next;
while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
//奇数返回中点前一个,偶数返回上中点前一个
Node* midOrUpMidPreNode(Node* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || head->next->next == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head->next->next;
while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
}
//奇数返回中点前一个,偶数返回下中点前一个
Node* midOrDownMidPreNode(Node* head)
{
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
{
return head;
}
if (head->next->next == nullptr)
{
return head;
}
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head->next;
while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
};题型三、将单链表按某值划分为左边小,中间相等,右边大
笔试:
把链表放在数组中,然后再去partition
面试:
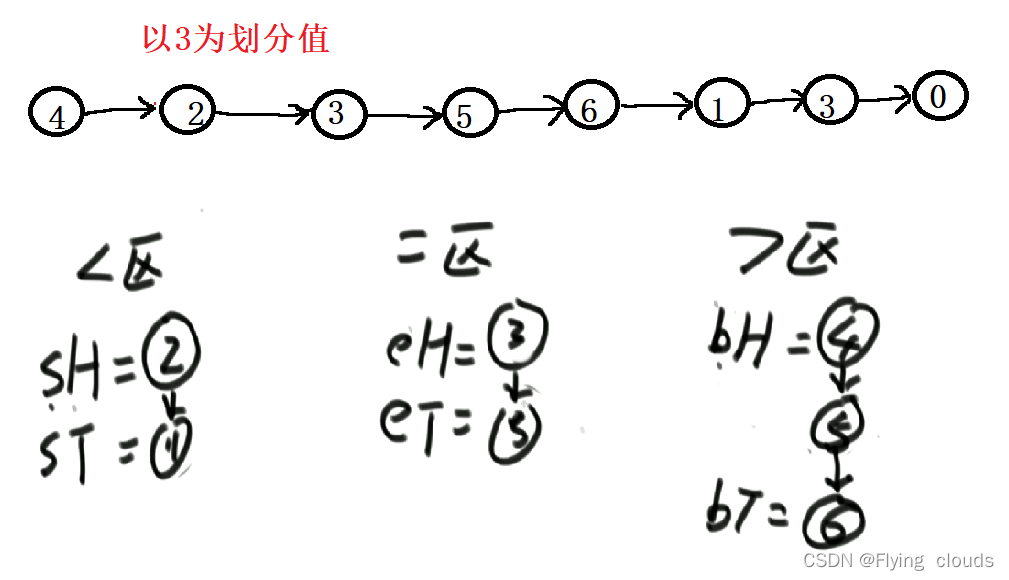
6个变量,不用容器,还能保证稳定性
流程示意图:
我们要先构造三个区域,然后再把三个区域给串起来
代码实现:
class SmallerEqualBigger
{
public:
Node* listPartition2(Node* head, int pivot)
{
Node* sH = nullptr; // small head
Node* sT = nullptr; // small tail
Node* eH = nullptr; // equal head
Node* eT = nullptr; // equal tail
Node* mH = nullptr; // big head
Node* mT = nullptr; // big tail
Node* next = nullptr; // save next node
// every node distributed to three lists
while (head != nullptr)
{
next = head->next;
head->next = nullptr;
if (head->value < pivot)
{
if (sH == nullptr)
{
sH = head;
sT = head;
}
else
{
sT->next = head;
sT = head;
}
}
else if (head->value == pivot)
{
if (eH == nullptr)
{
eH = head;
eT = head;
}
else {
eT->next = head;
eT = head;
}
}
else {
if (mH == nullptr)
{
mH = head;
mT = head;
}
else {
mT->next = head;
mT = head;
}
}
head = next;
}
// 小于区域的尾巴,连等于区域的头,等于区域的尾巴连大于区域的头
if (sT != nullptr)
{ // 如果有小于区域
sT->next = eH;
eT = eT == nullptr ? sT : eT; // 下一步,谁去连大于区域的头,谁就变成eT
}
// 下一步,一定是需要用eT 去接 大于区域的头
// 有等于区域,eT -> 等于区域的尾结点
// 无等于区域,eT -> 小于区域的尾结点
// eT 尽量不为空的尾巴节点
if (eT != nullptr)
{ // 如果小于区域和等于区域,不是都没有
eT->next = mH;
}
//return sH != nullptr ? sH : (eH != nullptr ? eH : mH);
return sH;
}
public:
void printList(Node* node)
{
cout<<"Linked List: ";
while (node != nullptr)
{
cout<<node->value <<" ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}题型四、找到两条链表的第一个相交节点
这个题和约瑟夫环问题并称链表的两大噩梦

1、先找到两个链表的入环节点
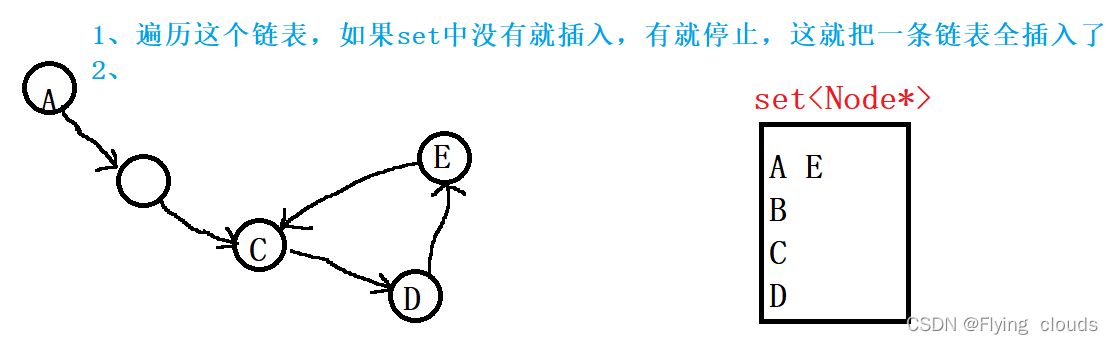
1.利用set直接就能找到入环节点
2.利用快慢指针

写一个函数实现这个功能
// 找到链表第一个入环节点,如果无环,返回nullptr
Node* GetLoopNode(Node* head)
{
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr || head->next->next == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
// 快慢指针
Node* slow = head->next;
Node* fast = head->next->next;
while (slow != fast)
{
if (fast->next == nullptr || fast->next->next == nullptr)
return nullptr;//说明这个链表就没有环
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
//这时候是找到了第一个相遇的位置
fast = head;
while (slow != fast)//第二次是两个指针都一次走一步
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
2、接下来分情况讨论
我们已经有了能找到第一个入环节点的函数,head1 对应 loop1,head是loop2
2.1、loop1==nullptr && loop2==nullptr
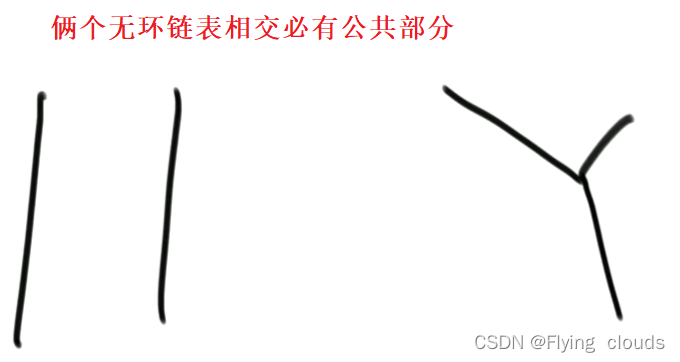
1.可以使用hash表去查第一个相交的部分
把一个链表全放入set中,然后第二个链表遍历去查在不在set中
2.也可以不用容器
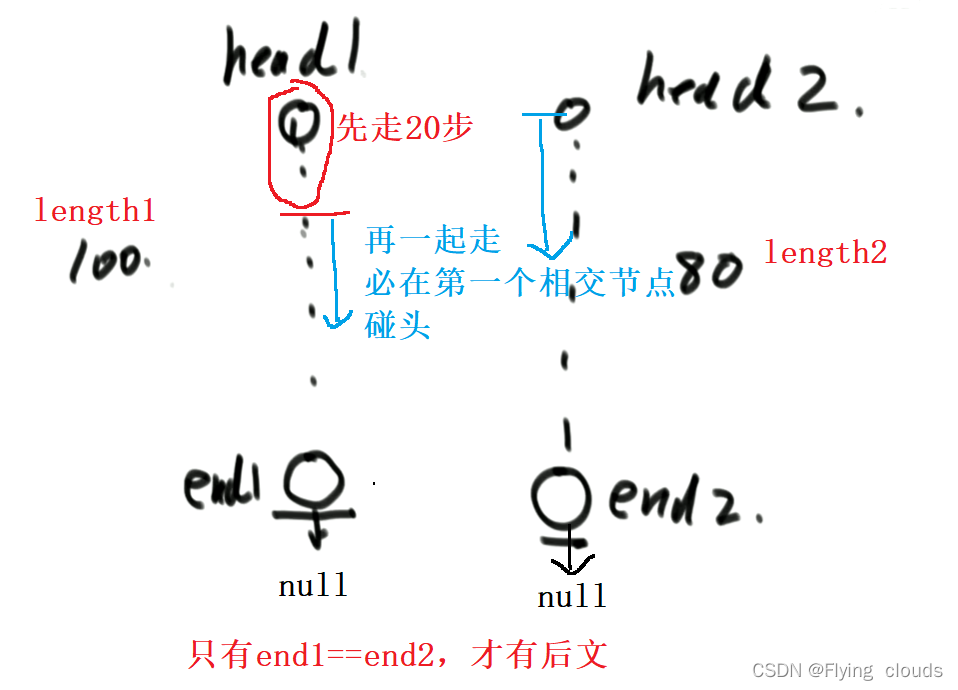
代码:
// 如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不相交,返回nullptr
Node* NoLoop(Node* head1, Node* head2) {
if (head1 == nullptr || head2 == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
Node* cur1 = head1;
Node* cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1->next != nullptr)
{
n++;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
while (cur2->next != nullptr)
{
n--;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
if (cur1 != cur2) {//说明没有相交的部分
return nullptr;
}
if (n < 0)
{
cur1 = head2;
cur2 = head1;
}
// n : 链表1长度减去链表2长度的值
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; // 谁长,谁的头变成cur1
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; // 谁短,谁的头变成cur2
n = abs(n);
while (n)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
n--;
}
while (cur1 != cur2)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return cur1;
}2.2、两条链表都有环(因为不可能一个有环一个没有环)
两个又换链表相交,一定是共用环的
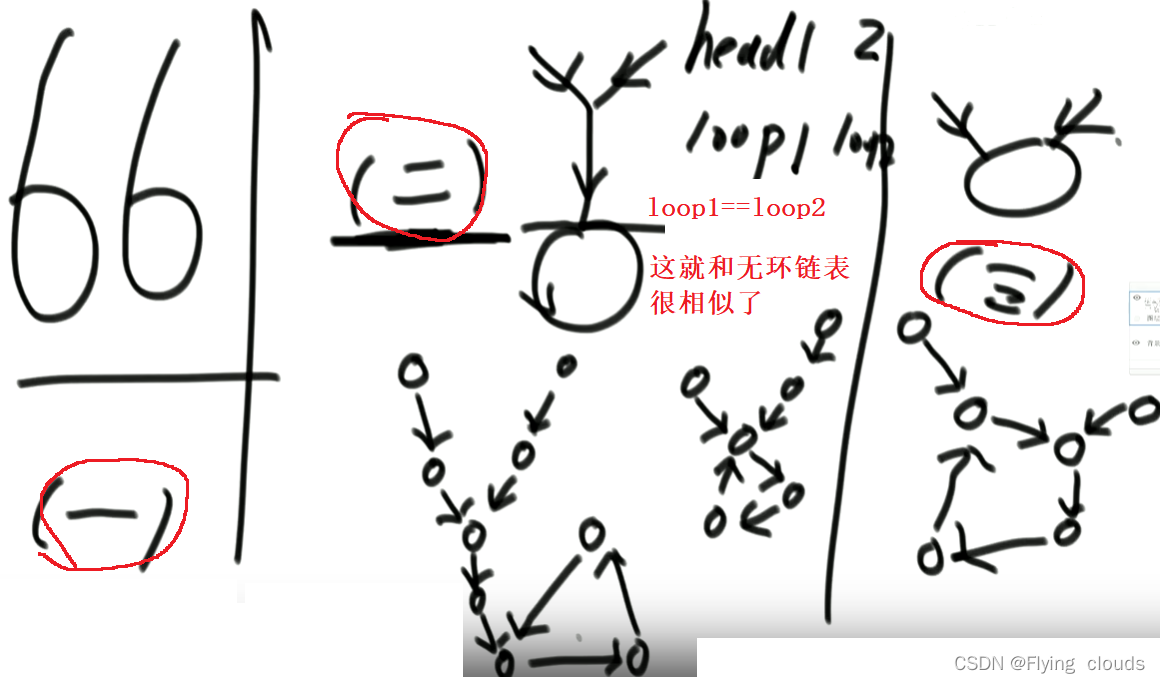
情况(二)很好做,就和上面的无环链表的做法差不多了,
直接可以无视这个环,把两条链表的end看成是loop1就行了,然后做法就和上面的一样
(一)和 (二) 也可以区分开来
一个指针指向loop1->next,然后遍历一圈,看有没有loop2的存在,有就是(三)返回loop1和loop2都行,
没有就是(二)直接返回nullptr
// 两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回nullptr
Node* BothLoop(Node* head1, Node* loop1, Node* head2, Node* loop2) {
Node* cur1 = nullptr;
Node* cur2 = nullptr;
if (loop1 == loop2)
{
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1->next != loop1)
{
n++;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
while (cur2->next != loop2)
{
n--;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;//让cur1表示长的,cur2表示短的
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = abs(n);
while (n) {
cur1 = cur1->next;
n--;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return cur1;
}
else
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
while (cur1 != loop1)
{
if (cur1 == loop2)
return loop1;
}
return nullptr;
}
}题型五、不给头节点,要求删一个给定的节点 ?

1、小聪明法:借尸还魂
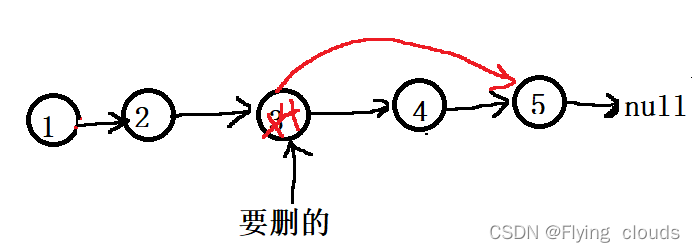
但这个方法有很多问题
1、假如拷贝函数难以调用,就挂了
2、永远删不了最后一个节点
所以这是不行的,要删一个节点必须要给头节点