目录
1.STL诞生
2.STL概念
3.STL六大主件
4.STL容器 算法 迭代器
5.容器算法迭代器初识,vector
5.1vector存放内置数据类型,
5.2vector存放自定义数据类型,解引用.访问,指针->访问,存放自定义数据类型指针。迭代器it看成指针,vector<>,<>里面是什么*it就是什么
5.3vector容器嵌套容器
1.STL诞生

2.STL概念

3.STL六大主件

4.STL容器 算法 迭代器

算法通过迭代器才能访问容器中的元素


5.容器算法迭代器初识,vector

5.1vector存放内置数据类型,
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
//vector容器存放内置数据类型
void myPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建一个vector容器 数组
vector<int>v;//需要头文件#include<vector>
//<>里面是vector存放的数据类型
//像容器中插入数据
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
//通过迭代器访问数组中的数据
vector<int>::iterator itBegin = v.begin();
//begin()起始迭代器,指向容器中第一个元素
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = v.end();
//end()结束迭代器,指向容器中最后一个元素的下一个位置
//第一种遍历
cout << "第一种遍历" << endl;
while (itBegin != itEnd)
{
//迭代器当指针去用,解引用取出数据
cout << *itBegin << " ";
itBegin++;
}
cout << endl;
//第二种遍历方式
cout << "第二种遍历" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//第三种遍历方式 利用STL提供的遍历算法
cout << "第三种遍历" << endl;
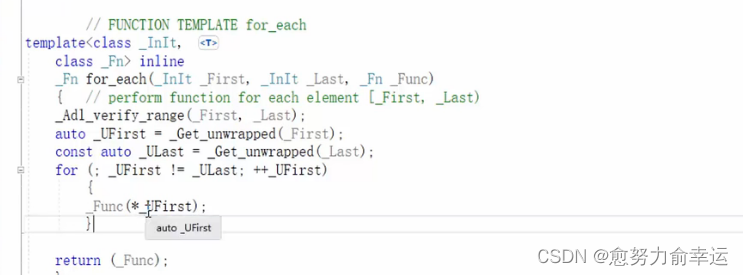
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);//需要算法头文件#include<algorithm>
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}

5.2vector存放自定义数据类型,解引用.访问,指针->访问,存放自定义数据类型指针。迭代器it看成指针,vector<>,<>里面是什么*it就是什么
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
//vector存放自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name,int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
vector<Person>v;//v中放的是Person数据类型
Person p1("a", 10);
Person p2("b", 20);
Person p3("c", 30);
Person p4("d", 40);
Person p5("e", 50);
//向容器中添加数据
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
//遍历容器中的数据
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//我们讲把迭代器当指针来看
//vector类似数组,*it就是Person
//*it就是vector<Person>尖括号里的东西
cout <<"姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------------" << endl;
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//it是指向Person的指针
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
//存放自定义数据类型指针
void test02()
{
cout << "****************test02*************" << endl;
vector<Person*>v;
Person p1("a", 10);
Person p2("b", 20);
Person p3("c", 30);
Person p4("d", 40);
Person p5("e", 50);
//向容器中添加数据
v.push_back(&p1);
v.push_back(&p2);
v.push_back(&p3);
v.push_back(&p4);
v.push_back(&p5);
//遍历容器中的数据
for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//我们讲把迭代器当指针来看
//vector类似数组,*it就是Person*
//*it就是vector<Person*>尖括号里的东西
//指针访问数据就是->
cout << "姓名:" << (*it)->m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it)->m_Age << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------------------" << endl;
for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//it是指向Person*的指针
cout << "姓名:" << (*(*it)).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*(*it)).m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
5.3vector容器嵌套容器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法头文件
//容器嵌套容器
void test01()
{
vector<vector<int>>v;
//创建小容器
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
vector<int>v3;
vector<int>v4;
//向小容器中添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
v4.push_back(i + 4);
}
//将小容器放到大容器中
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
v.push_back(v4);
//通过大容器把所有的数据遍历一遍
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//*it是vector<int>,是一个容器
for (vector<int>::iterator vit = (*it).begin(); vit != (*it).end(); vit++)
{
cout << *vit << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}