1.问题
Given the array nums, for each nums[i] find out how many numbers in the array are smaller than it. That is, for each nums[i] you have to count the number of valid j’s such that j != i and nums[j] < nums[i].
Return the answer in an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [8,1,2,2,3]
Output: [4,0,1,1,3]
Explanation:
For nums[0]=8 there exist four smaller numbers than it (1, 2, 2 and 3).
For nums[1]=1 does not exist any smaller number than it.
For nums[2]=2 there exist one smaller number than it (1).
For nums[3]=2 there exist one smaller number than it (1).
For nums[4]=3 there exist three smaller numbers than it (1, 2 and 2).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [6,5,4,8]
Output: [2,1,0,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [7,7,7,7]
Output: [0,0,0,0]
Constraints:
- 2 <= nums.length <= 500
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 100
2. 解题思路
方法1:
1.新建数组长度和nums相等
2.定义sum,有多少数字小于当前数字
3.for遍历数组,两数据比较,如果nums[i] > nums[j],sum加1,
4.sum的值存入result中
5.添加后sum为0,其他数据再次使用
5.返回result
方法2:
利用桶的思想,数据存放在桶中,然后查询数据,数据的索引值
方法3:
1.复制数组,从小到大排序
2.新建map,将值为key,将键设为value
3.遍历数组,元数据的值和map的值比较,获得map中的value(也就索引值)
4.将索引值存入新建的result数组中
5.返回result
3. 代码
代码1:
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length];//1.新建数组长度和nums相等
int sum = 0;//2.定义sum,有多少数字小于当前数字
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {//3.for遍历数组,两数据比较,如果nums[i] > nums[j],sum加1,
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) sum++;
}
result[i] = sum;//4.sum的值存入result中
sum=0;//5.添加后sum为0,其他数据再次使用
}
return result;//6.返回result
}
}
代码和上面代码的解题思路基本相同
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
for (int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
for (int j=0;j<nums.length;j++){
if (nums[i]>nums[j]){
result[i]++;//i本身为0,自增后的数据直接为当前当前和其他数据相比后的个数
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
代码2:
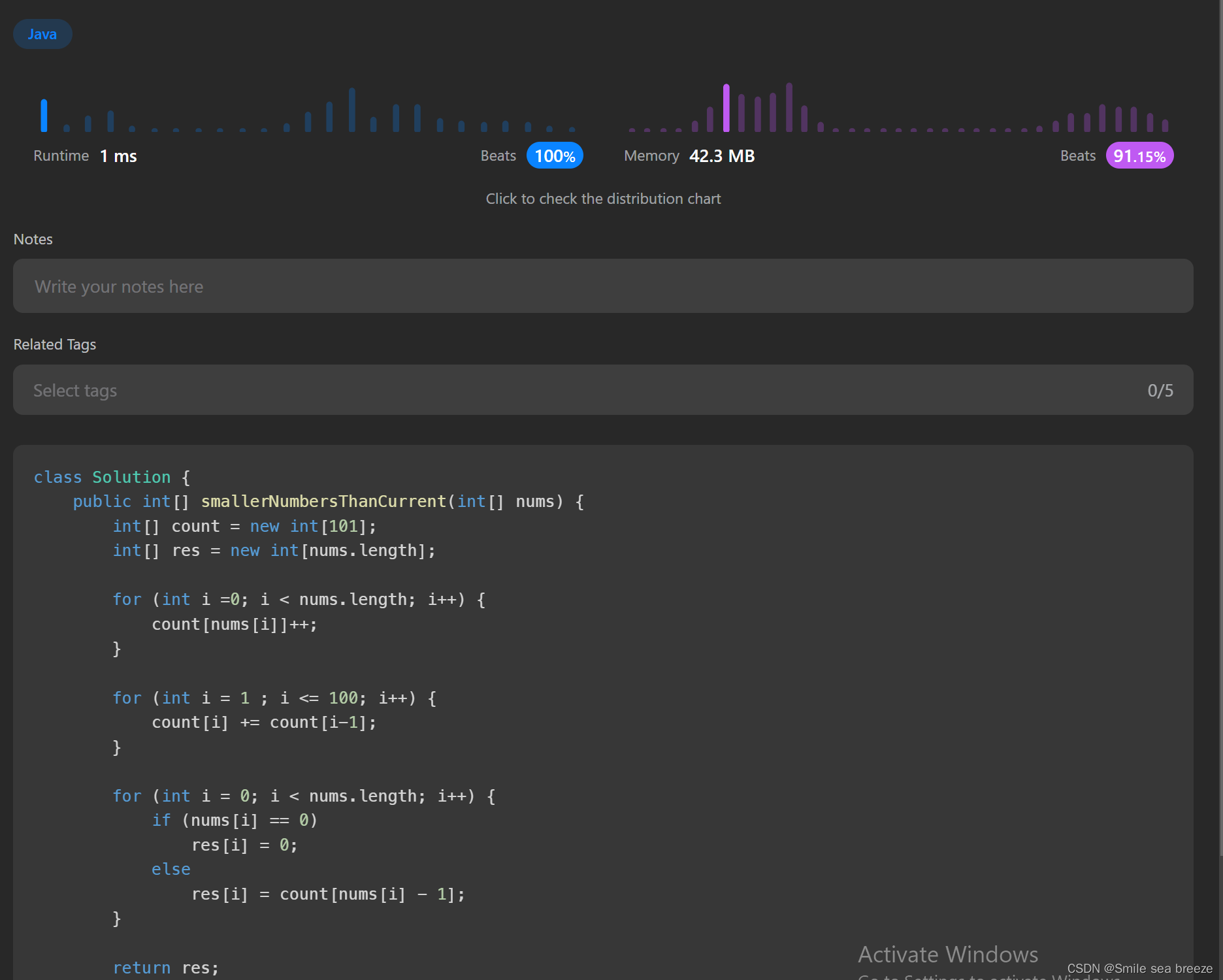
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] count = new int[101];//1.新建数组count,目的是存值,值为0-100,长度为101
int[] result = new int[nums.length];//2.新建数组result,存储比较后的个数
for (int i =0; i < nums.length; i++) {//3.for循环遍历,将nums的值存入到count中
count[nums[i]]++;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
for (int i = 1 ; i <= 100; i++) {//4.for循环遍历,i小于等于100,count的前一个值相加等于本身
count[i] += count[i-1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {//5.for循环遍历,如果nums的值为0,存入到result中为0,否则result的个数为count[nums的值减去1]
if (nums[i] == 0)
result[i] = 0;
else
result[i] = count[nums[i] - 1];
}
return result;//6.返回result
}
}
解题思路和以上基本相同,不同的是用foreach遍历
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] freq = new int[101];
int[] count = new int[nums.length];
for(int a : nums)
freq[a]++;
for(int i = 1 ; i < freq.length ; i++){
freq[i] += freq[i-1];
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++){
if(nums[i]==0)continue;
count[i]=freq[nums[i]-1];
}
return count;
}
}
代码3
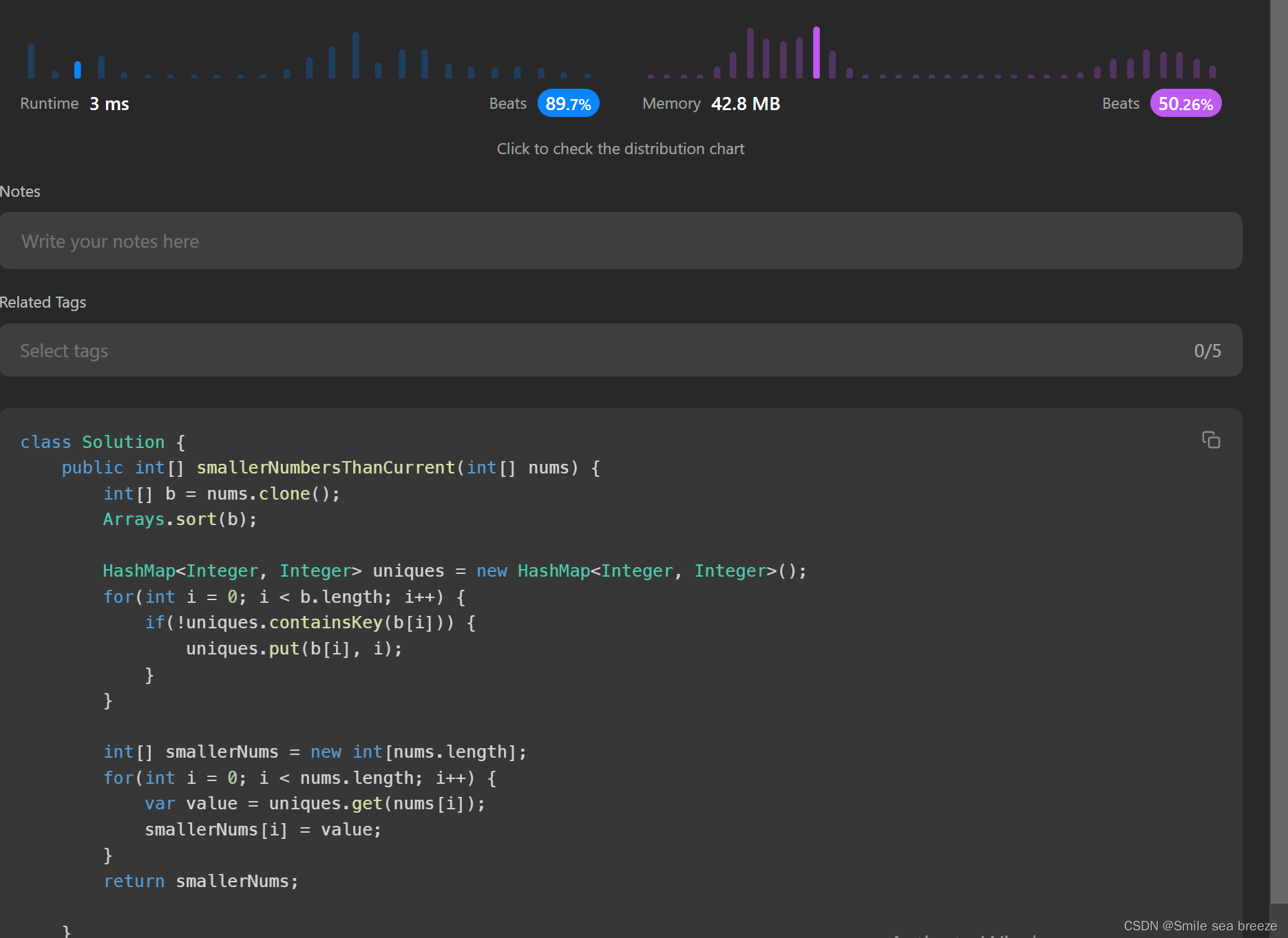
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] cloneNums = nums.clone();//1.clone数据并从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(cloneNums);//[1, 2, 2, 3, 8]
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();//2.新建map,如果没有相同的值,存入key为值,value为索引
for(int i = 0; i < cloneNums.length; i++) {
if(!map.containsKey(cloneNums[i])) {
map.put(cloneNums[i], i);//{1=0, 2=1, 3=3, 8=4}
}
}
int[] result = new int[nums.length];//3.新建数组result
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {//4. 遍历数组,取出map中的索引值,并赋值给result
int value = map.get(nums[i]);
result[i] = value;//[4, 0, 1, 1, 3]
}
return result;//5.返回result
}
}
解题思路和以上基本相同
class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(nums, n);//1.创建输入数组的副本。
Arrays.sort(copy);//2.从小到大排序
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//3.新建map,排序后的数组,值从大到小排入,将数值为key,i的值为value
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
map.put(copy[i], i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//4.新建map,排序后的数组,值从大到小排入,将数值为key,i的值为value
nums[i] = map.get(nums[i]);//5.从map中取出nums的值,key的个数就是nums的值
}
return nums;//6.返回nums
}
}