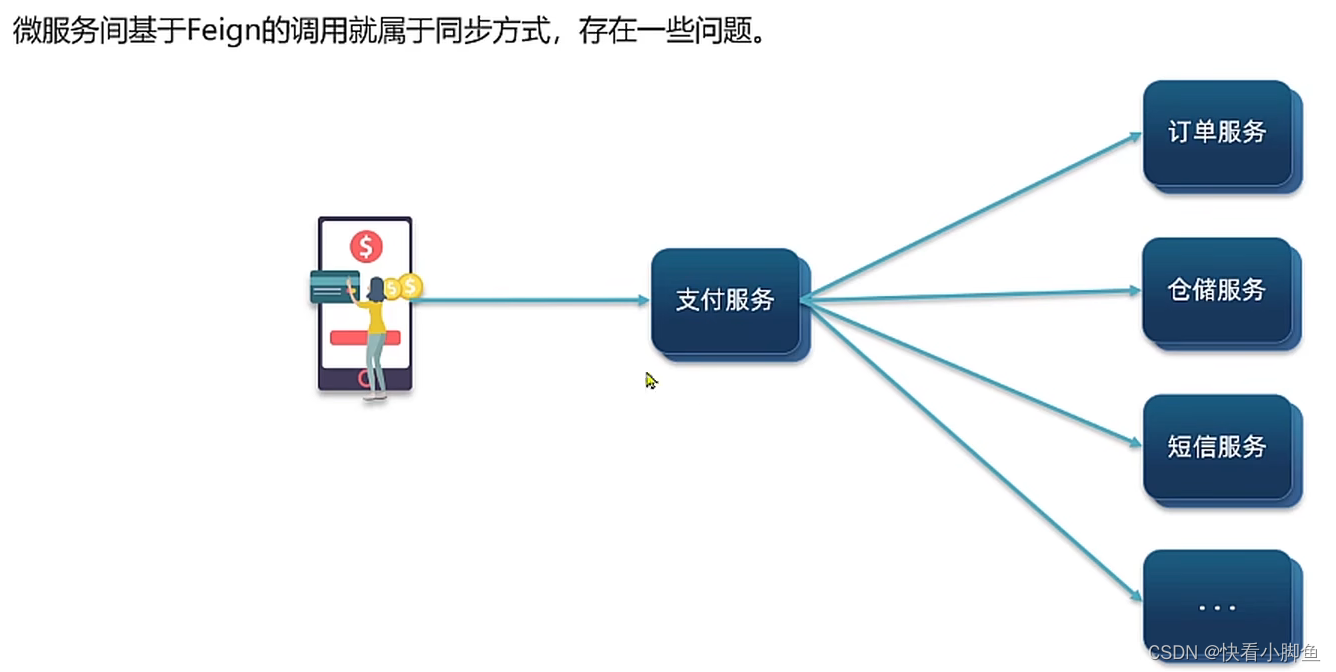
同步和异步
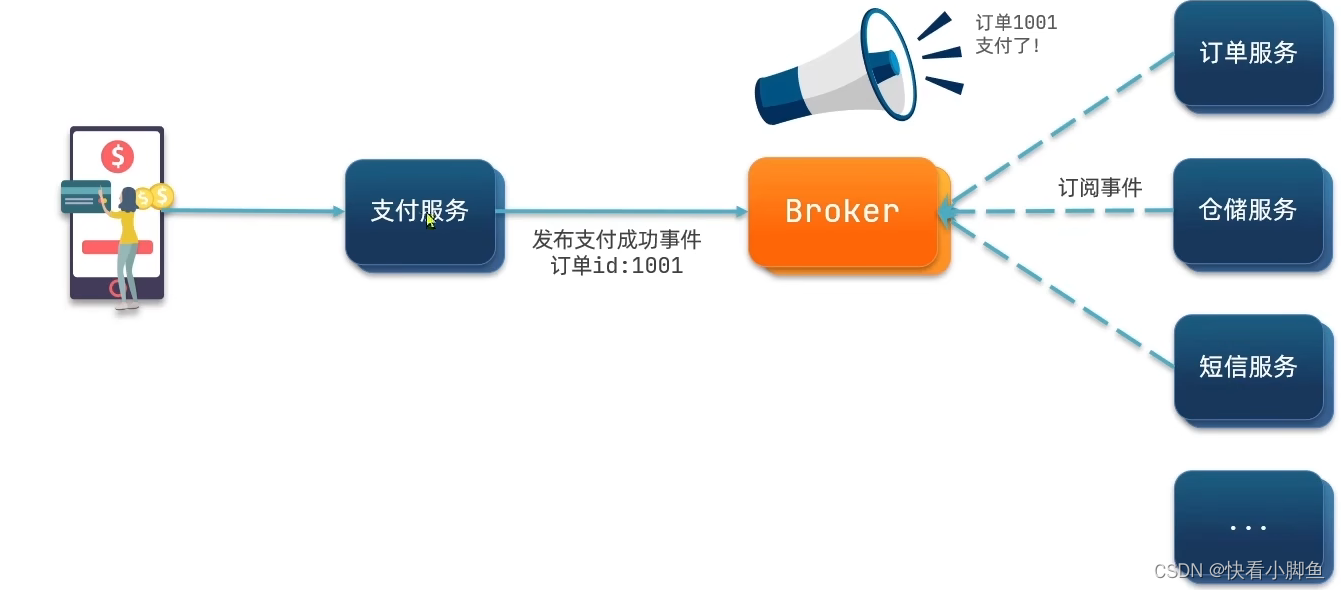
异步调用
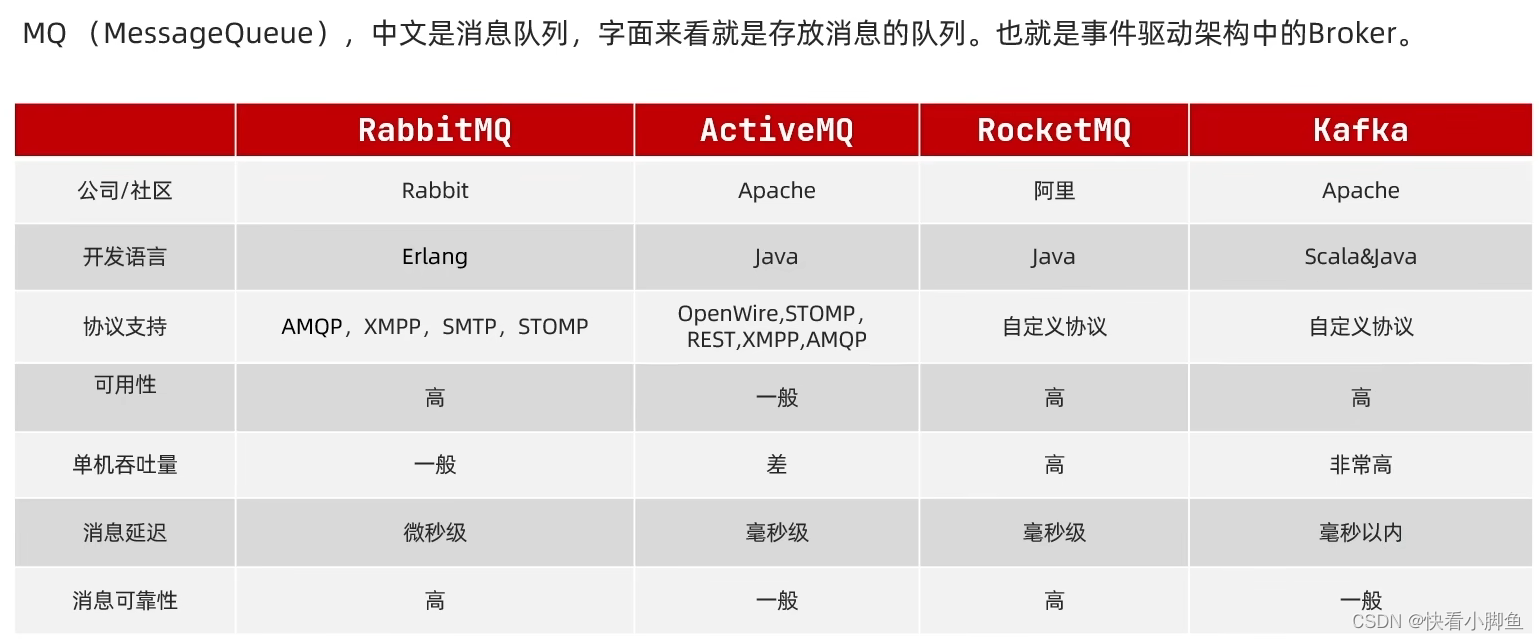
MQ
MQ优势:①服务解耦 ②异步调用 ③流量削峰
结构
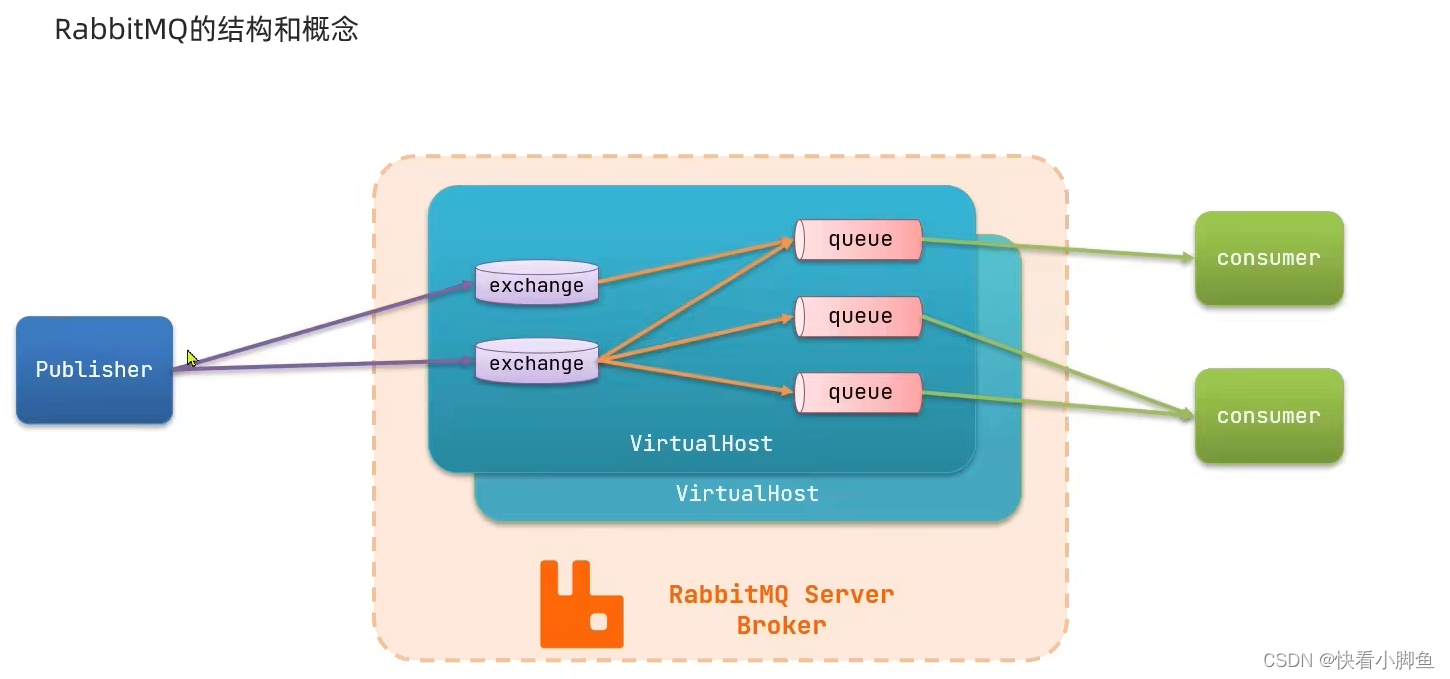

消息模型
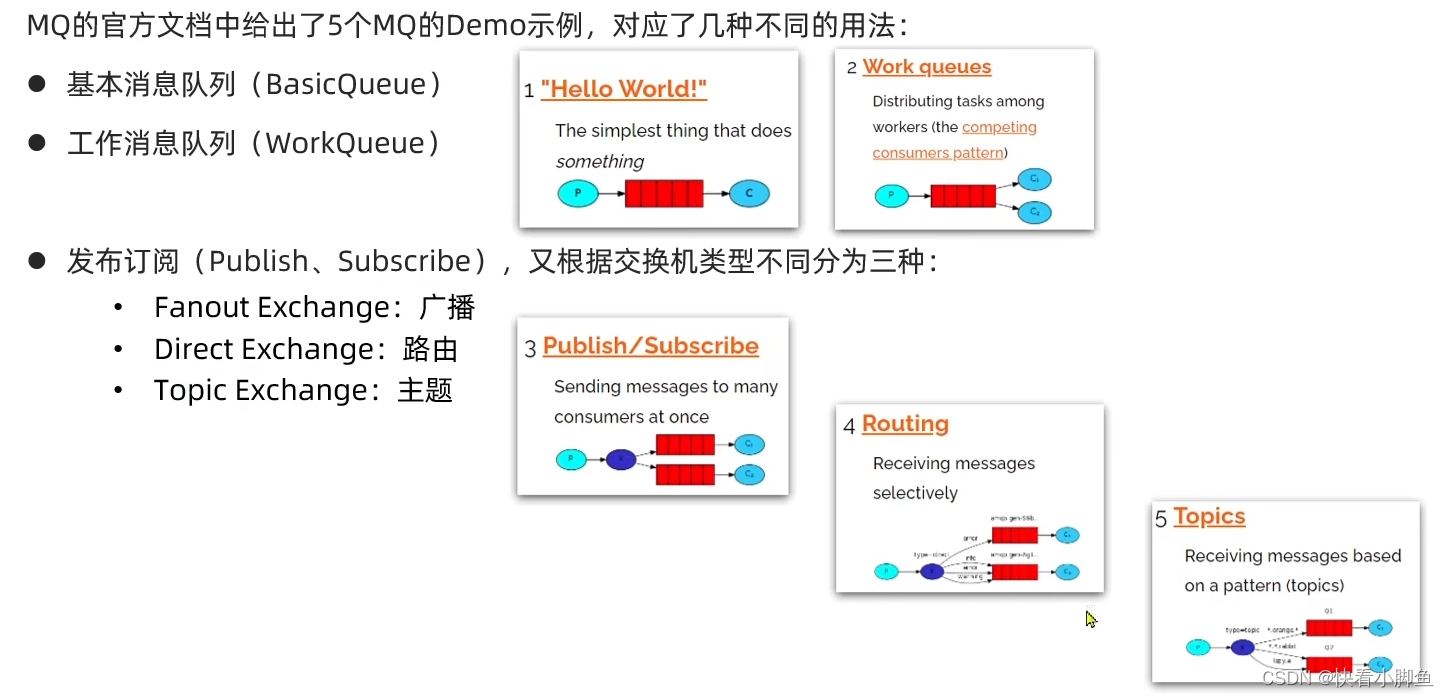
RabbitMQ入门案例,实现消息发送和消息接收

生产者:
public class PublisherTest {
@Test
public void testSendMessage() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
// 1.1.设置连接参数,分别是:主机名、端口号、vhost、用户名、密码
factory.setHost("192.168.136.132");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("itcast");
factory.setPassword("123321");
// 1.2.建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
// 2.创建通道Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3.创建队列
String queueName = "simple.queue";
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
// 4.发送消息
String message = "hello, rabbitmq!";
channel.basicPublish("", queueName, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("发送消息成功:【" + message + "】");
// 5.关闭通道和连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}消费者:
public class ConsumerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
// 1.1.设置连接参数,分别是:主机名、端口号、vhost、用户名、密码
factory.setHost("192.168.136.132");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("itcast");
factory.setPassword("123321");
// 1.2.建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
// 2.创建通道Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3.创建队列
String queueName = "simple.queue";
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
// 4.订阅消息
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 5.处理消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println("接收到消息:【" + message + "】");
}
});
System.out.println("等待接收消息。。。。");
}
}SpringAMQP

引入依赖
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>普通队列
第一步:publisher服务配置文件,发消息
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.136.132
port: 5672
username: itcast
password: 123321
virtual-host: /@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAMQPTest {
//获取RabbitTemplateAPI
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void test(){
String queueName = "simple.queue";
String message = "hello SpringAMQP";
//使用API传入队列名和消息即可直接发送
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
}
}
第二步:Consumer服务配置信息监听消息
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.136.132
port: 5672
username: itcast
password: 123321
virtual-host: /import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//定义一个监听类去监听消息
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void ListenSimpleQueue(String msg){
System.out.println("msg = " + msg);
}
}Work Queue队列
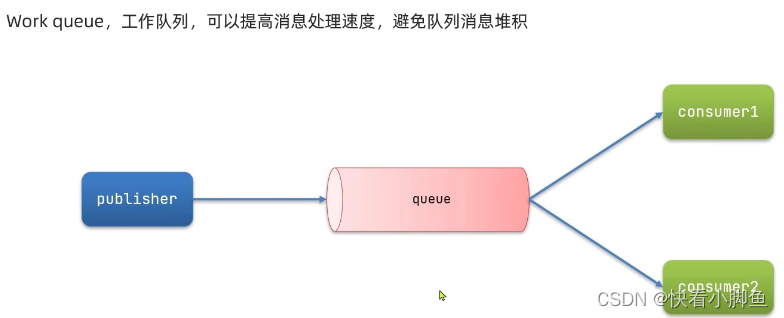
多个消费者绑定到同一个队列,可以通过prefetch来控制消费者消息预取的数量
第一步: 生产者发送消息
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAMQPTest {
//获取RabbitTemplateAPI
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void test01() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName = "simple.queue";
String message = "hello SpringAMQP--";
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
//使用API传入队列名和消息即可直接发送
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message+i);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
}第二步:消费者设置多个监听消息
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void ListenWorkQueue(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者一接收到消息---- = " + msg + LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void ListenWorkQueue01(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者二接收到消息---- = " + msg + LocalDateTime.now());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
第三步:消费者可通过prehtch设置消息预取数量
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.136.132
port: 5672
username: itcast
password: 123321
virtual-host: /
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1发布-订阅模型

Fanout广播交换机 --->多个队列收到交换机的消息
第一步:Consumer声明交换机,队列并进行绑定。
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
//声明交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("itcast.fanout");
}
//声明队列1
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue1");
}
//绑定队列1到交换机上
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBanding1(Queue fanoutQueue1,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder
.bind(fanoutQueue1)
.to(fanoutExchange);
}
//声明队列2
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue2");
}
//绑定队列2到交换机上
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBanding2(Queue fanoutQueue2,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder
.bind(fanoutQueue2)
.to(fanoutExchange);
}
}第二步:Consumer进行监听消息
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void ListenSimpleQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到fanout.queue1的消息 = " + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void ListenSimpleQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到fanout.queue2的消息 = " + msg);
}
}第三步:Publisher向交换机发送消息
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAMQPTest {
//获取RabbitTemplateAPI
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void testExchange() {
//声明交换机名称
String exchangeName = "itcast.fanout";
//消息
String message = "Hello Everyone";
//发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"",message);
}
}
Direct路由交换机 --->将消息发给指定key的队列

第一步:在Listener中声明队列,交换机以及key
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
//声明队列1,交换机以及队列1的bindingKey
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "derict.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct",type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red","blue"}
))
public void ListenDirectQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue1的消息 = " + msg);
}
//声明队列2,交换机以及队列2的bindingKey
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "derict.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct",type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red","yellow"}
))
public void ListenDirectQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue2的消息 = " + msg);
}
}第二步:向指定key的队列发送消息
@Test
public void testDirect() {
//声明交换机名称
String exchangeName = "itcast.direct";
//消息
String message = "Hello Blue!!";
//发送消息,指定交换机,队列以及要发送的key
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"red",message);
}Topic主题交换机 ---->key必须是多个单词列表,统一主题,支持通配符
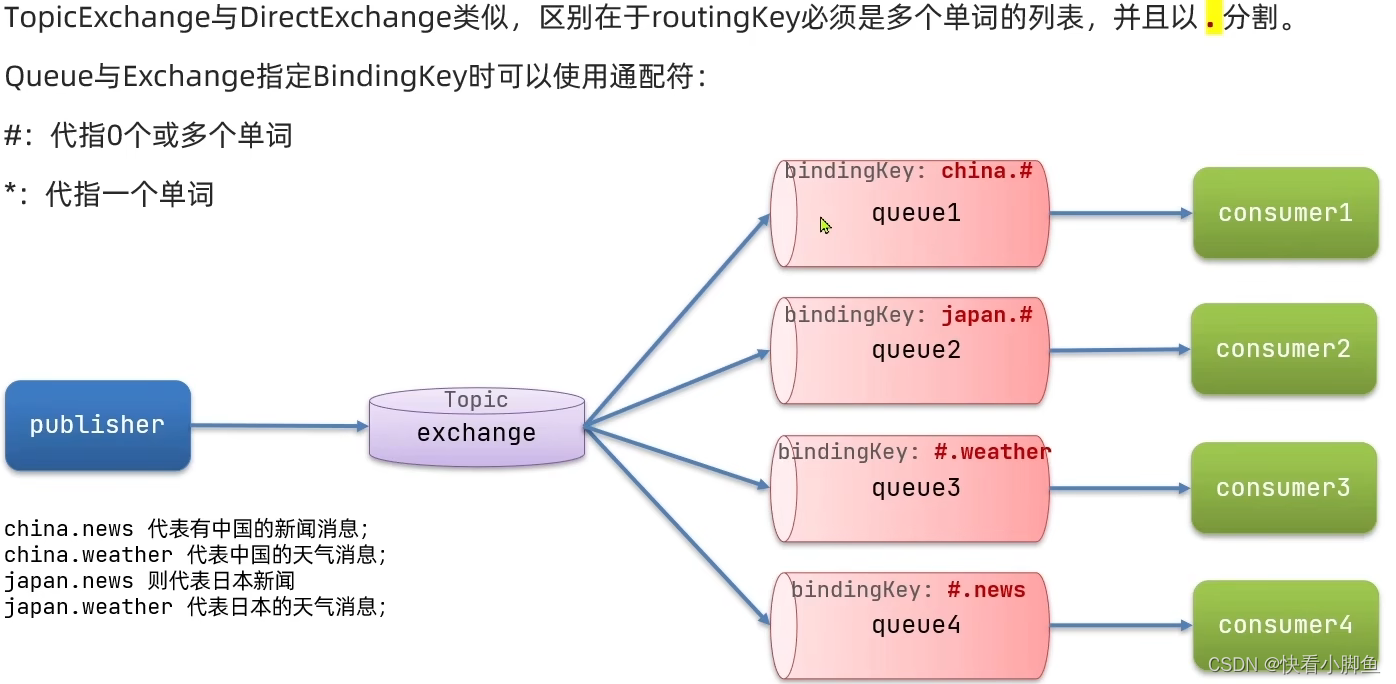
第一步:在Listener中声明队列,交换机以及通配符key
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
//声明队列2的交换机,队列以及通配符key
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic",type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "china.#"
))
public void ListenTopicQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue1的消息 = " + msg);
}
//声明队列2的交换机,队列以及通配符key
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic",type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "#.news"
))
public void ListenTopicQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue2的消息 = " + msg);
}
}第二步:向主题通配符发送消息
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAMQPTest {
//获取RabbitTemplateAPI
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void testTopic() {
//声明交换机名称
String exchangeName = "itcast.topic";
//消息
String message = "Hello China!!";
//发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"china.news",message);
}
}消息转换器
RabbitMQ发的消息体都是Object类型,所有还可以发送对象数据。而且默认的消息转换器是MessageConverter实现的,当使用的是Map数据类型时,就会序列化成很多字节,所以推荐使用JSON的序列化和反序列化,直接修改默认的MessageConverter的类型
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
对于RabbitMQ高级部分:死信队列,延迟队列,发布确认,幂等性,优先,惰性队列等有时间再学