目录
memcpy
模拟实现memcpy
memmove
模拟实现memmove
memcmp
memcpy
它的函数原型为:
void * memcpy ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );函数memcpy从source的位置开始向后复制num个字节的数据到destination的内存位置。
这个函数在遇到 '\0' 的时候并不会停下来。
如果source和destination有任何的重叠,复制的结果都是未定义的。
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct
{
char name[40];
int age;
} person, person_copy;
int main()
{
char myname[] = "Pierre de Fermat";
//用memcpy拷贝字符串
memcpy(person.name, myname, strlen(myname) + 1);
person.age = 46;
//用memcpy拷贝结构体
memcpy(&person_copy, &person, sizeof(person));
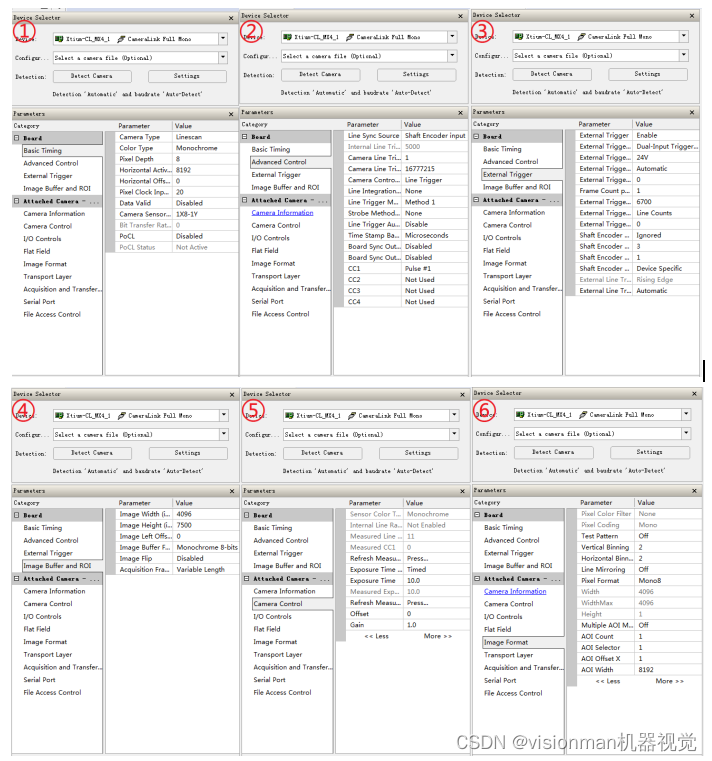
printf("person_copy: %s, %d \n", person_copy.name, person_copy.age);
return 0;
}输出结果为:
模拟实现memcpy
void* memcpy(void* dst, const void* src, size_t count)
{
void* ret = dst;
assert(dst);
assert(src);
//拷贝从低地址到高地址
while (count--) {
*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;
dst = (char*)dst + 1;
src = (char*)src + 1;
}
return(ret);
}memmove
memmove的函数原型是:
void * memmove ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );和memcpy的差别就是memmove函数处理的源内存块和目标内存块是可以重叠的。
如果源空间和目标空间出现重叠,就得使用memmove函数处理。
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char str[] = "memmove can be very useful......";
memmove(str + 20, str + 15, 11);
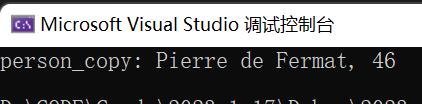
puts(str);
return 0;
}输出结果为:
模拟实现memmove
void* memmove(void* dst, const void* src, size_t count)
{
void* ret = dst;
if (dst <= src || (char*)dst >= ((char*)src + count)) {
/*
* Non-Overlapping Buffers* copy from lower addresses to higher addresses
*/
while (count--) {
*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;
dst = (char*)dst + 1;
src = (char*)src + 1;
}
}
else {
/*
* Overlapping Buffers
* copy from higher addresses to lower addresses
*/
dst = (char*)dst + count - 1;
src = (char*)src + count - 1;
while (count--) {
*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;
dst = (char*)dst - 1;
src = (char*)src - 1;
}
}
return(ret);
}memcmp
它的函数原型为:
int memcmp( const void *buf1, const void *buf2, size_t count );作用是比较从ptr1和ptr2指针开始的num个字节。
查找它的文档:
Return Value
The return value indicates the relationship between the buffers.
Return Value Relationship of First count Bytes of buf1 and buf2 < 0 buf1 less than buf2 0 buf1 identical to buf2 > 0 buf1 greater than buf2
由此可知buf1小于buf2时返回值小于0,buf1等于buf2时返回值为0,buf1大于buf2时返回值大于0。
例子:
void* memmove(void* dst, const void* src, size_t count)
{
void* ret = dst;
if (dst <= src || (char*)dst >= ((char*)src + count)) {
while (count--) {
*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;
dst = (char*)dst + 1;
src = (char*)src + 1;
}
}
else {
dst = (char*)dst + count - 1;
src = (char*)src + count - 1;
while (count--) {
*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;
dst = (char*)dst - 1;
src = (char*)src - 1;
}
}
return(ret);
}![104、【树与二叉树】leetcode ——98. 验证二叉搜索树:递归法[先序+中序+后序]+迭代法(C++版本)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/6a4c11d957321a265045e8185e99b215.png)