创作背景:在加强for循环中使用了remove操作
原因:
在官方文档中ConcurrentModificationException的介绍如下:
public class ConcurrentModificationException extends RuntimeException
某个线程在 Collection 上进行遍历时,通常不允许其他线程修改该 Collection,这会导致遍历的结果是不确定的。当方法检测到集合发生并发修改时,不允许这种修改,抛出此异常。
在执行增删操作以后,集合的expectedModCount和modCount的值不一致,这两个变量的作用都是记录修改次数的,二者不相等,就会抛错。
expectedModCount:表示对ArrayList修改次数的期望值,它的初始值为modCount。
modCount是AbstractList类中的一个成员变量。
先说解决方法:
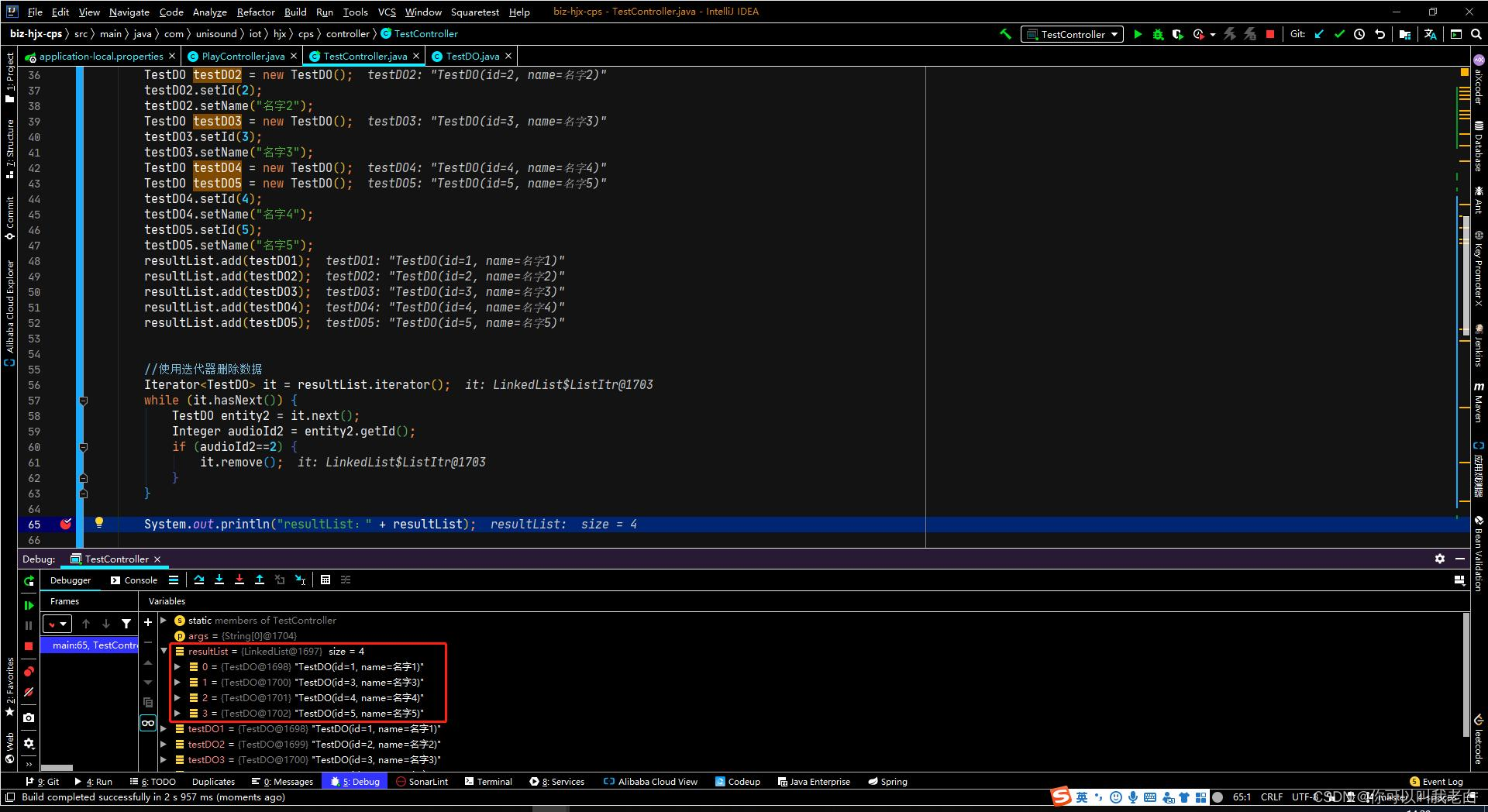
使用增强for循环遍历,增删操作使用迭代器实现。原因我们后面说,没空看的直接看到测试代码就可以了,先把工作解决了。
实战代码实现:
//先保证两个集合有值,LinkedList可以,这里省略赋值步骤
LinkedList<PlayAudioEntity> audioList = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<PlayAudioEntity> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
//入栈,redis有数据则需要比较是否有相同专辑下同一作品,有则放入队头
for (PlayAudioEntity entity : audioList) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resultList)) {
String audioId = entity.getAudioId();
//使用迭代器删除数据
Iterator<PlayAudioEntity> it = resultList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
PlayAudioEntity entity2 = it.next();
String audioId2 = entity2.getAudioId();
if (audioId2.equals(audioId)) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
resultList.push(entity);
}
看不懂的看这里,测试代码和结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//赋值
LinkedList<TestDO> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
TestDO testDO1 = new TestDO();
testDO1.setId(1);
testDO1.setName("名字1");
TestDO testDO2 = new TestDO();
testDO2.setId(2);
testDO2.setName("名字2");
TestDO testDO3 = new TestDO();
testDO3.setId(3);
testDO3.setName("名字3");
TestDO testDO4 = new TestDO();
TestDO testDO5 = new TestDO();
testDO4.setId(4);
testDO4.setName("名字4");
testDO5.setId(5);
testDO5.setName("名字5");
resultList.add(testDO1);
resultList.add(testDO2);
resultList.add(testDO3);
resultList.add(testDO4);
resultList.add(testDO5);
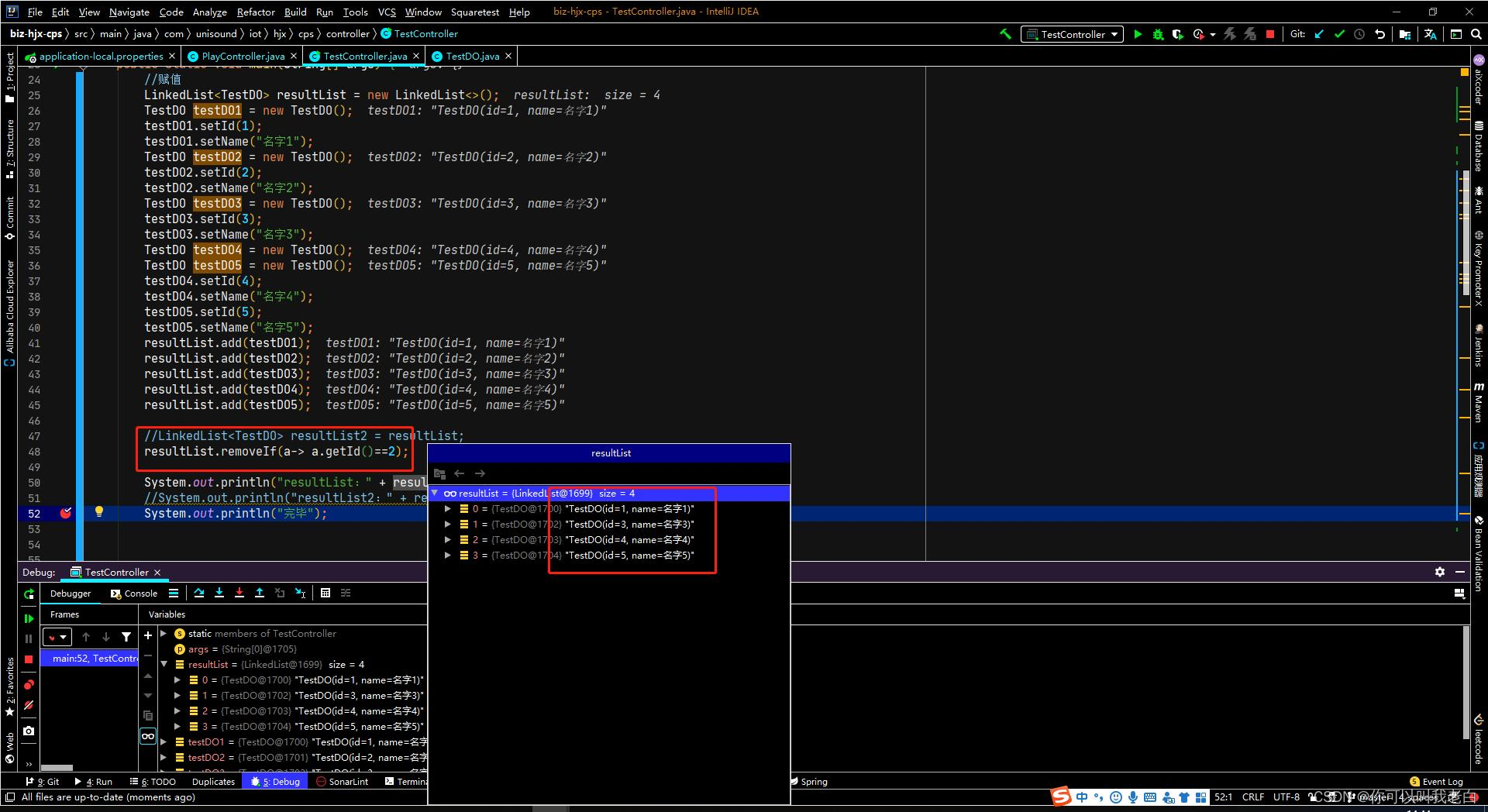
//LinkedList<TestDO> resultList2 = resultList;
//resultList.removeIf(a-> a.getId()==2);
System.out.println("resultList:" + resultList);
//System.out.println("resultList2:" + resultList2);
System.out.println("完毕");
//使用迭代器删除数据
/*Iterator<TestDO> it = resultList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
TestDO entity2 = it.next();
Integer audioId2 = entity2.getId();
if (audioId2 == 2) {
it.remove();
}
}
System.out.println("resultList:" + resultList);*/
//使用普通for循环删除数据
/*for (int i = 0; i < resultList2.size(); i++) {
TestDO testDO = resultList2.get(i);
Integer id = testDO.getId();
if (id == 3) {
resultList2.remove(testDO);
}
}*/
// System.out.println("resultList:" + resultList2);
}
1.迭代器
2.stream
3.还有一种网上方法叫使用索引(普通for循环)遍历。用了用,结果是只能是ArrayList才可以使用。普通for循环删除元素存在一个问题,那就是remove操作会改变List中元素的下标,可能存在漏删的情况。所以建议使用迭代器删除。

有时间的话会在研究下问什么不允许加强for循环删除的,懂得大佬也可以在下面评论指正。
创作不易,如果这篇文章对你有用,请点赞。有其他建议请在下方留言评论,谢谢♪(・ω・)ノ!