VeLO: Training Versatile Learned Optimizers by Scaling Up
通过扩展模型的规模来训练一个通用的优化器。
设计上,优化器的原理基于元学习的思路,即从相关任务上学习经验,来帮助学习目标任务。
相比迁移学习,元学习更强调获取元知识,它是一类任务上的通用知识,可以被泛化到更多任务上去。
基于这一思想,VeLO也会吸收梯度并自动输出参数更新,无需任何超参数调优,并自适应需要优化的各种任务。
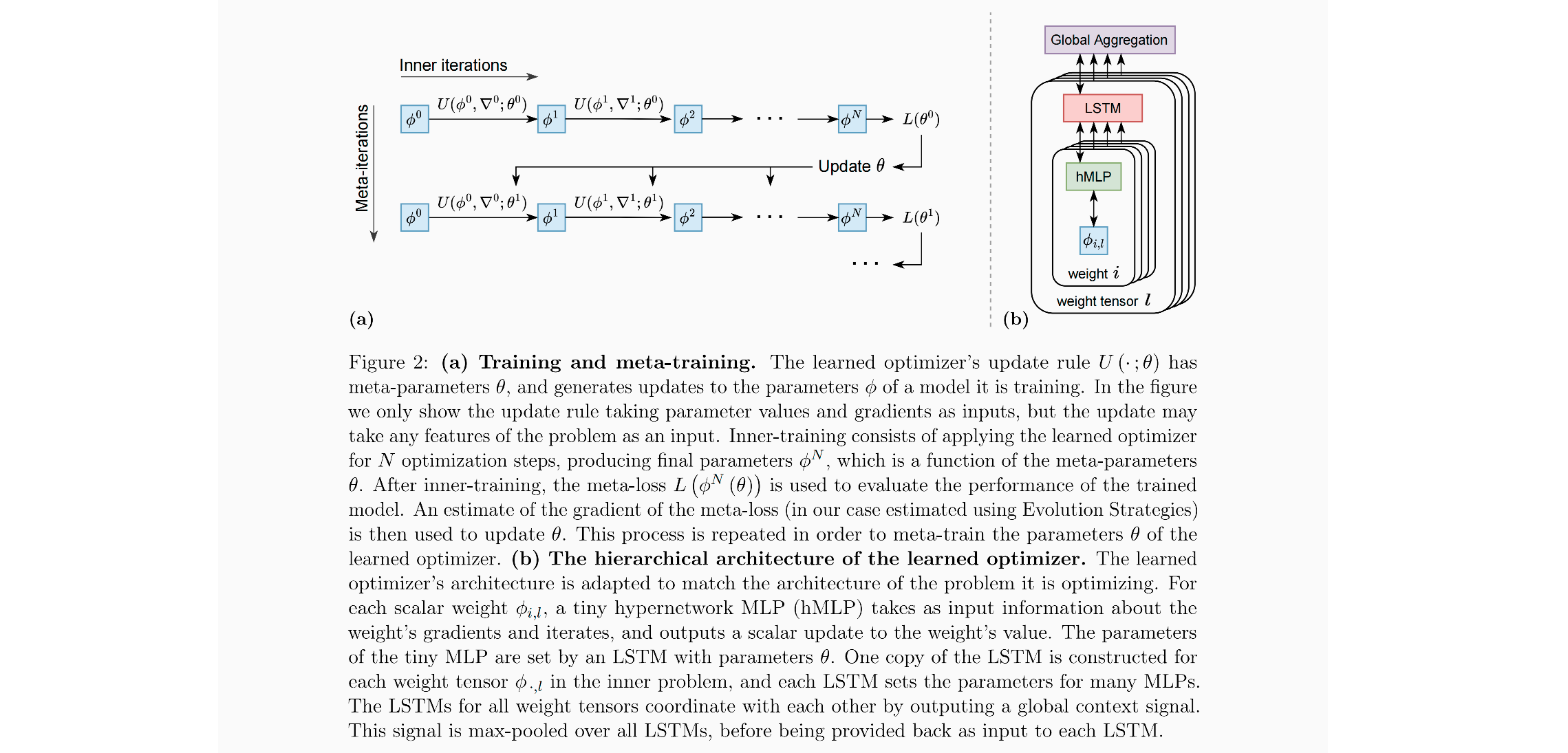
架构上,AI优化器整体由LSTM(长短期记忆网络)和超网络MLP(多层感知机)构成。
其中每个LSTM负责设置多个MLP的参数,各个LSTM之间则通过全局上下文信息进行相互协作。
训练上,AI优化器采用元训练的方式,以参数值和梯度作为输入,输出需要更新的参数。
Introduction
在meta-training中存在的问题?
在meta-learning中,数据集(也就是大量的Tasks)不容易收集(不像image、text这样的任务):In meta-learning, a large training dataset corresponds to a large set of tasks, which are representative of the tasks a practitioner might want to optimize. Unlike image and text data that can be gathered from the internet, there is no standardized or automated way to collect these tasks
什么是一个Learned update rules呢?
回忆一下SGD,其中优化器的更新是一个fixed-form,即下一个参数=上一个参数-梯度*学习率(也有可能不是一个固定的学习率,但必然是一个超参数)。而在Learned update rules中,我们可以把这个更新函数进行参数化,变成一个可学习的neural networks with meat-parameters, 它使用梯度信息作为输入, U ( g , . . . ; θ ) U(g, ...; θ) U(g,...;θ)。
进一步地,除了梯度信息作为输入,还可以讲loss、当前的参数值等信息作为参数输入进来。
什么是Meta-training?
Meta-training is the process of fifinding the (meta-)parameters θ of the update rule U(·; θ) such that the resulting optimizer performs well on some specifified meta-objective.


![[硬核] Bootstrap Blazor Table 综合演示例子](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/83cc3b1324c50758031c1c2cf53d6547.gif)
![[Android Studio] 如何查看Android Studio的版本信息](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/24b696d76d374a9992017e1625389592.gif)