高级IO
- 一.五种IO模型
- 二.多路转接(select)
- 三.非阻塞IO(funcl)
- 四.POLL
IO=等待+拷贝。单位时间内,IO过程中,等的比例越小,IO就越高效。几乎所有提高IO效率的方式本质都是基于此。
一.五种IO模型
举个例子:一群人在河边钓鱼。

同步IO:要参与IO。例如上面例子同步都参与了钓鱼这一IO。
异步IO:不参与IO,只发起IO。
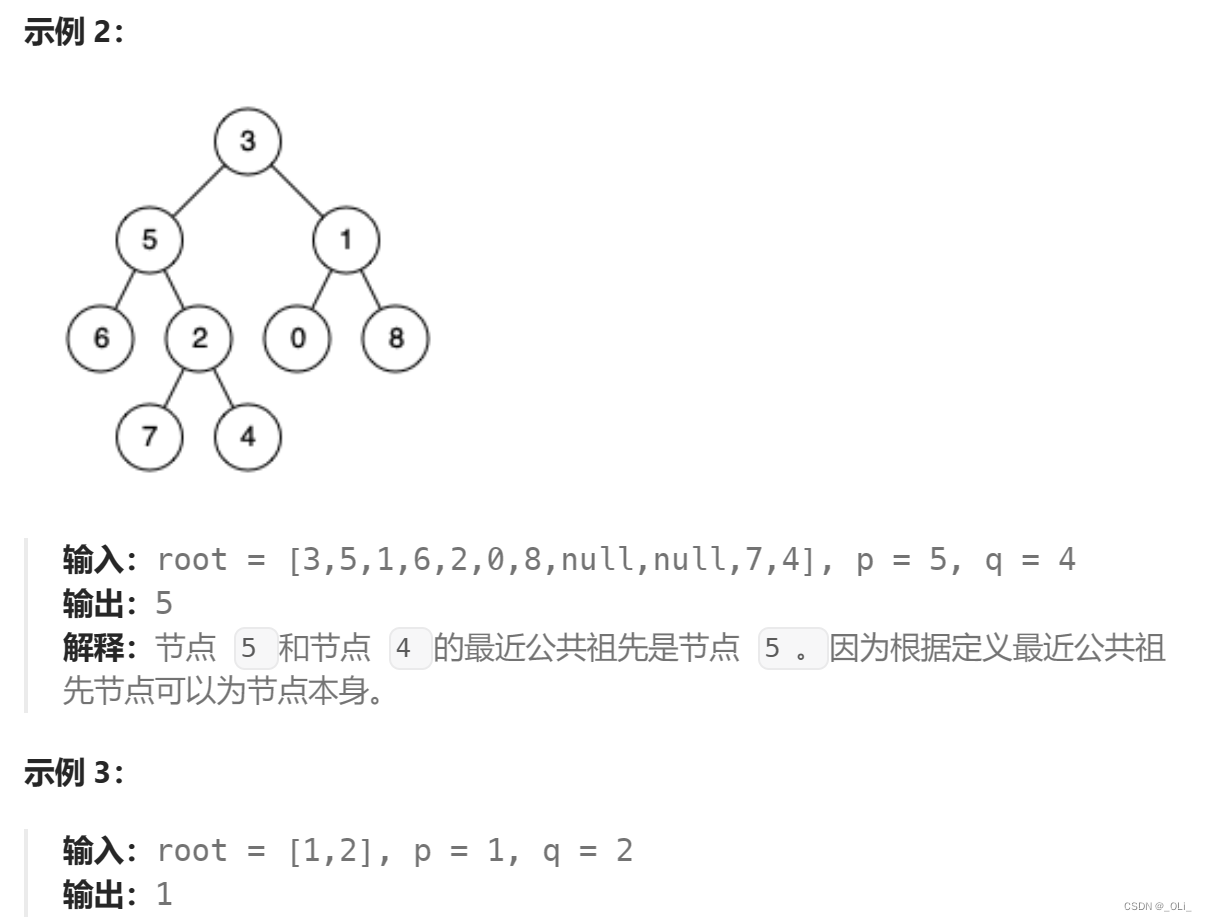
1.阻塞IO
阻塞IO: 在内核将数据准备好之前, 系统调用会一直等待. 所有的套接字, 默认都是阻塞方式。
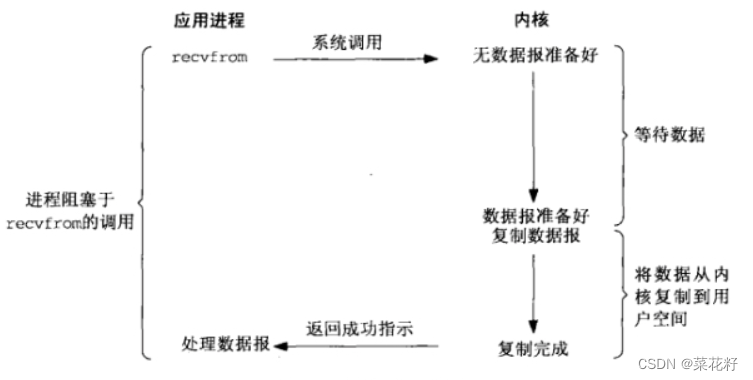
2.非阻塞IO
非阻塞IO: 如果内核还未将数据准备好, 系统调用仍然会直接返回, 并且返回EWOULDBLOCK错误码。
非阻塞IO往往需要程序员循环的方式反复尝试读写文件描述符, 这个过程称为轮询. 这对CPU来说是较大的浪费, 一般只有特定场景下才使用。
3.信号驱动IO
信号驱动IO: 内核将数据准备好的时候, 使用SIGIO信号通知应用程序进行IO操作。

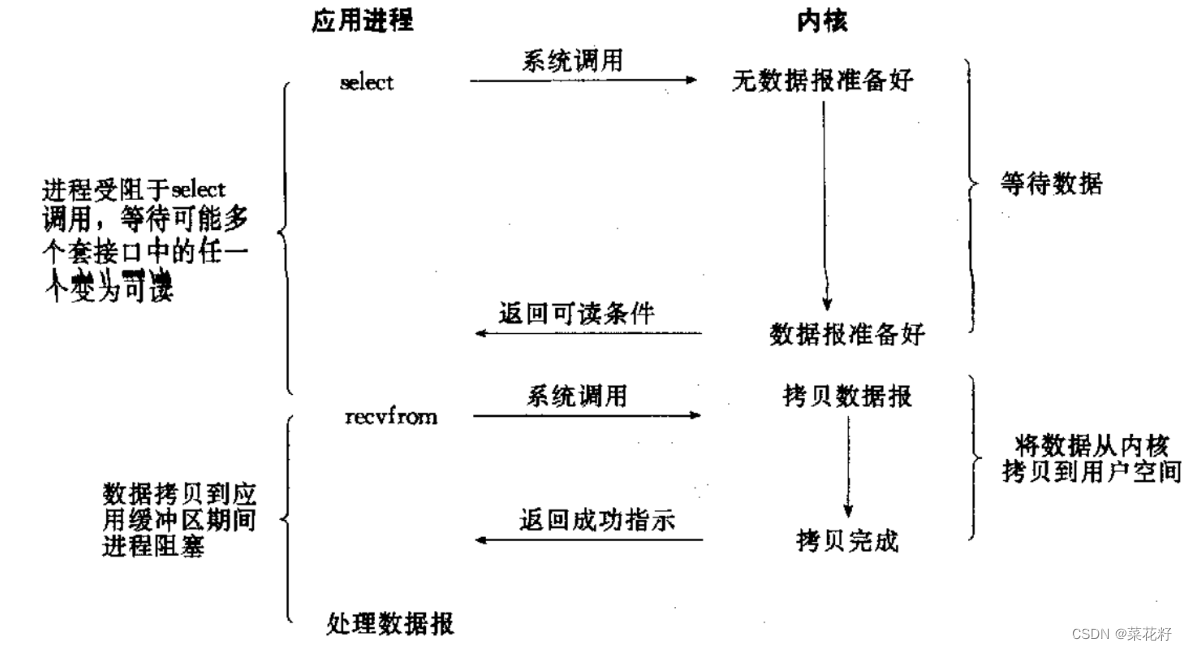
4.IO多路转接
IO多路转接: 虽然从流程图上看起来和阻塞IO类似. 实际上最核心在于IO多路转接能够同时等待多个文件描述符的就绪状态。
5.异步IO
异步IO: 由内核在数据拷贝完成时, 通知应用程序(而信号驱动是告诉应用程序何时可以开始拷贝数据)。
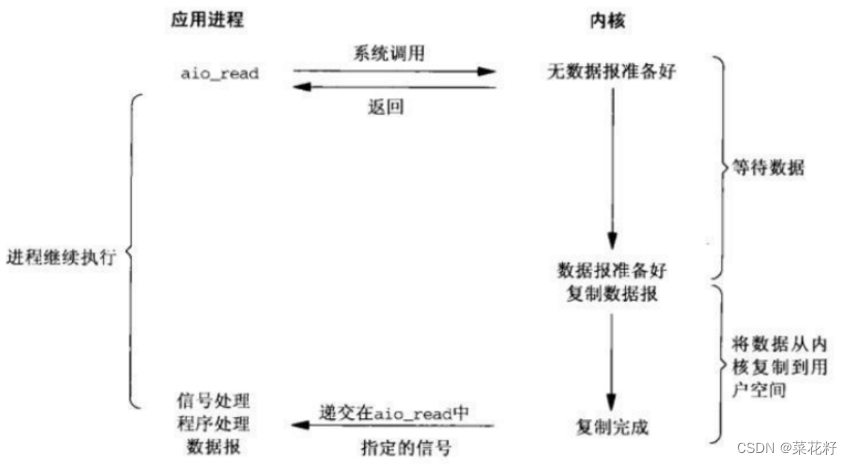
小结:
任何IO过程中, 都包含两个步骤. 第一是等待, 第二是拷贝. 而且在实际的应用场景中, 等待消耗的时间往往都远远高于拷贝的时间. 让IO更高效, 最核心的办法就是让等待的时间尽量少。
二.多路转接(select)
系统提供select函数来实现多路复用输入/输出模型.
select系统调用是用来让我们的程序监视多个文件描述符的状态变化的;
程序会停在select这里等待,直到被监视的文件描述符有一个或多个发生了状态改变;
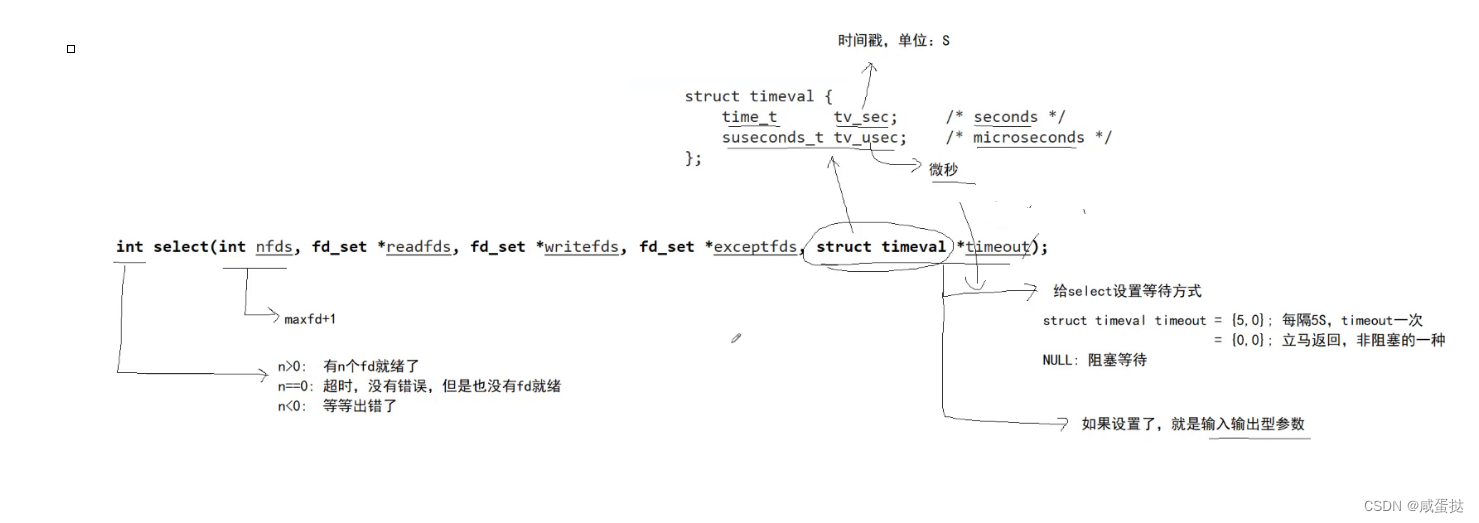
select的函数原型如下: #include <sys/select.h>

nfds
参数nfds是需要监视的最大的文件描述符值+1;
fd_set
rdset(读合集),wrset(写合集),exset(错误合集)分别对应于需要检测的可读文件描述符的集合,可写文件描述符的集 合及异常文件描述符的集合;(输入输出型)
其实这个结构就是一个整数数组, 更严格的说, 是一个 “位图”. 使用位图中对应的位来表示要监视的文件描述符。

比特位的位置表示文件描述符编号,例如输入0000 1111,代表让操作系统关注0,1,2,3号文件;如果2号文件准备就绪,就会输出0000 0100。
提供了一组操作fd_set的接口, 来比较方便的操作位图。

一般我们关心fd的三种状态,读,写和异常。如果我们只需要关注读,就把文件描述符设置到readfds即可。
timeout
参数timeout为结构timeval,用来设置select()的等待时间。NULL:则表示select()没有timeout,select将一直被阻塞,直到某个文件描述符上发生了事件;0:仅检测描述符集合的状态,然后立即返回,并不等待外部事件的发生。特定的时间值:如果在指定的时间段里没有事件发生,select将超时返回。(输入输出型)
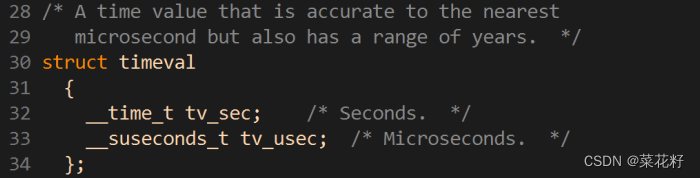
timeval结构用于描述一段时间长度,如果在这个时间内,需要监视的描述符没有事件发生则函数返回,返回值为0。
返回值
返回值:n>0代表有n个fd就绪了;n==0代表超时,没有错误也没有就绪;n<0代表等待出错。
使用例子
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "Socket.hpp"
using namespace std;
static const uint16_t defaultport = 8888;
static const int fd_num_max = (sizeof(fd_set) * 8);
int defaultfd = -1;
class SelectServer
{
public:
SelectServer(uint16_t port = defaultport) : _port(port)
{
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++)
{
fd_array[i] = defaultfd;
// std::cout << "fd_array[" << i << "]" << " : " << fd_array[i] << std::endl;
}
}
bool Init()
{
_listensock.Socket();
_listensock.Bind(_port);
_listensock.Listen();
return true;
}
void Accepter()
{
// 我们的连接事件就绪了
std::string clientip;
uint16_t clientport = 0;
int sock = _listensock.Accept(&clientip, &clientport); // 会不会阻塞在这里?不会
if (sock < 0) return;
lg(Info, "accept success, %s: %d, sock fd: %d", clientip.c_str(), clientport, sock);
// sock -> fd_array[]
int pos = 1;
for (; pos < fd_num_max; pos++) // 第二个循环
{
if (fd_array[pos] != defaultfd)
continue;
else
break;
}
if (pos == fd_num_max)
{
lg(Warning, "server is full, close %d now!", sock);
close(sock);
}
else
{
fd_array[pos] = sock;
PrintFd();
// TODO
}
}
void Recver(int fd, int pos)
{
// demo
char buffer[1024];
ssize_t n = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1); // bug?
if (n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
cout << "get a messge: " << buffer << endl;
}
else if (n == 0)
{
lg(Info, "client quit, me too, close fd is : %d", fd);
close(fd);
fd_array[pos] = defaultfd; // 这里本质是从select中移除
}
else
{
lg(Warning, "recv error: fd is : %d", fd);
close(fd);
fd_array[pos] = defaultfd; // 这里本质是从select中移除
}
}
void Dispatcher(fd_set &rfds)
{
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++) // 这是第三个循环
{
int fd = fd_array[i];
if (fd == defaultfd)
continue;
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &rfds))
{
if (fd == _listensock.Fd())
{
Accepter(); // 连接管理器
}
else // non listenfd
{
Recver(fd, i);
}
}
}
}
void Start()
{
int listensock = _listensock.Fd();
fd_array[0] = listensock;
for (;;)
{
fd_set rfds;
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
int maxfd = fd_array[0];
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++) // 第一次循环
{
if (fd_array[i] == defaultfd)
continue;
FD_SET(fd_array[i], &rfds);
if (maxfd < fd_array[i])
{
maxfd = fd_array[i];
lg(Info, "max fd update, max fd is: %d", maxfd);
}
}
// accept?不能直接accept!检测并获取listensock上面的事件,新连接到来,等价于读事件就绪
// struct timeval timeout = {1, 0}; // 输入输出,可能要进行周期的重复设置
struct timeval timeout = {0, 0}; // 输入输出,可能要进行周期的重复设置
// 如果事件就绪,上层不处理,select会一直通知你!
// select告诉你就绪了,接下来的一次读取,我们读取fd的时候,不会被阻塞
// rfds: 输入输出型参数。 1111 1111 -> 0000 0000
int n = select(maxfd + 1, &rfds, nullptr, nullptr, /*&timeout*/ nullptr);
switch (n)
{
case 0:
cout << "time out, timeout: " << timeout.tv_sec << "." << timeout.tv_usec << endl;
break;
case -1:
cerr << "select error" << endl;
break;
default:
// 有事件就绪了,TODO
cout << "get a new link!!!!!" << endl;
Dispatcher(rfds); // 就绪的事件和fd你怎么知道只有一个呢???
break;
}
}
}
void PrintFd()
{
cout << "online fd list: ";
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++)
{
if (fd_array[i] == defaultfd)
continue;
cout << fd_array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
~SelectServer()
{
_listensock.Close();
}
private:
Sock _listensock;
uint16_t _port;
int fd_array[fd_num_max]; // 数组, 用户维护的!
// int wfd_array[fd_num_max];
};

三.非阻塞IO(funcl)
一个文件描述符, 默认都是阻塞IO。

传入的cmd的值不同, 后面追加的参数也不相同。



使用F_GETFL将当前的文件描述符的属性取出来(这是一个位图).
然后再使用F_SETFL将文件描述符设置回去. 设置回去的同时, 加上一个O_NONBLOCK参数
设置文件描述符非阻塞的方式非常多,例如:open时采用非阻塞方式。但functl方式是最常用的。
四.POLL
它的特点是将输入事件和输出事件进行了分离(不像select用同一个位图标识输入和输出)。
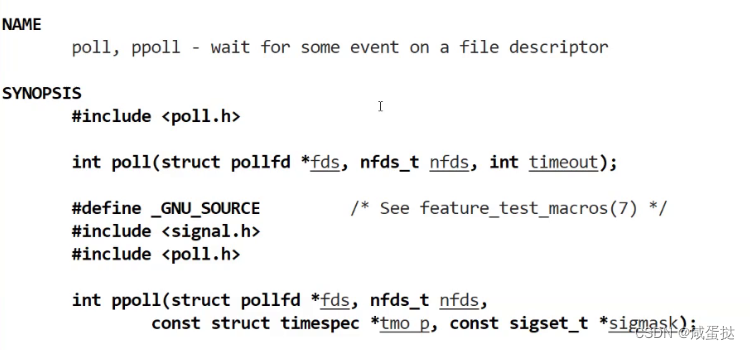
poll的作用与select一样,它的设计只是为了解决select的缺点。fds是一个poll函数监听的结构列表. 每一个元素中, 包含了三部分内容:
fds 文件描述符, 监听的事件集合, 返回的事件集合.
nfds表示fds数组的长度.
timeout表示poll函数的超时时间, 单位是毫秒(ms)设为-1代表阻塞。
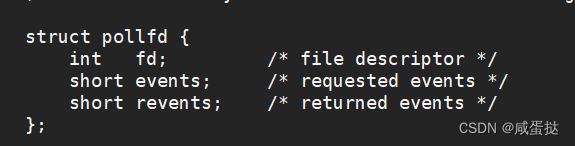
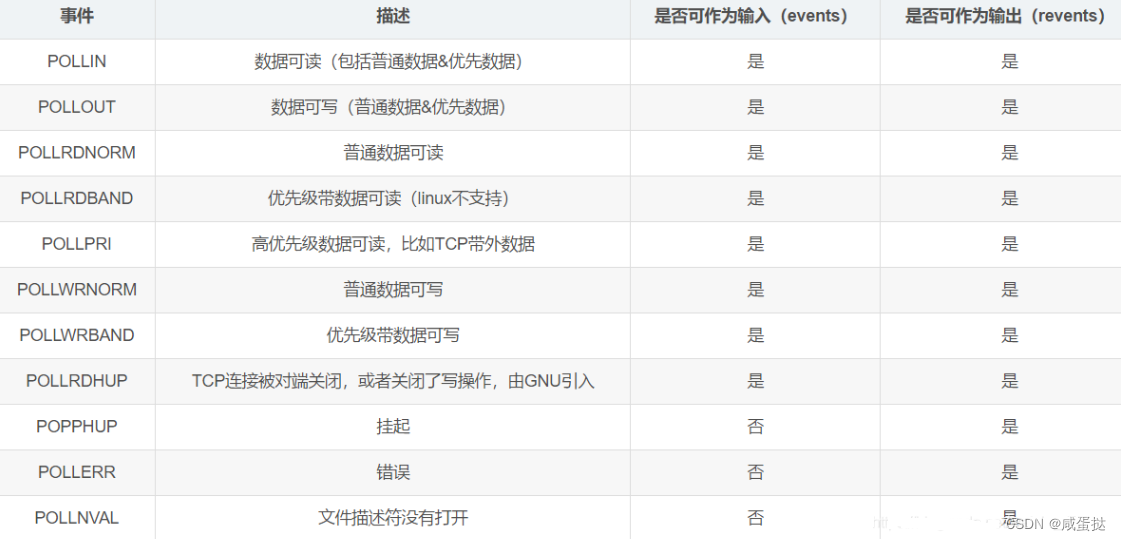
同select不同的是,它通过宏的方式告诉系统,该文件是什么类型。例如:event_fds[1].events = POLLIN,代表该输入事件关心读。
使用例子
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "Socket.hpp"
using namespace std;
static const uint16_t defaultport = 8888;
static const int fd_num_max = 64;
int defaultfd = -1;
int non_event = 0;
class PollServer
{
public:
PollServer(uint16_t port = defaultport) : _port(port)
{
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++)
{
_event_fds[i].fd = defaultfd;
_event_fds[i].events = non_event;
_event_fds[i].revents = non_event;
// std::cout << "fd_array[" << i << "]" << " : " << fd_array[i] << std::endl;
}
}
bool Init()
{
_listensock.Socket();
_listensock.Bind(_port);
_listensock.Listen();
return true;
}
void Accepter()
{
// 我们的连接事件就绪了
std::string clientip;
uint16_t clientport = 0;
int sock = _listensock.Accept(&clientip, &clientport); // 会不会阻塞在这里?不会
if (sock < 0) return;
lg(Info, "accept success, %s: %d, sock fd: %d", clientip.c_str(), clientport, sock);
// sock -> fd_array[]
int pos = 1;
for (; pos < fd_num_max; pos++) // 第二个循环
{
if (_event_fds[pos].fd != defaultfd)
continue;
else
break;
}
if (pos == fd_num_max)
{
lg(Warning, "server is full, close %d now!", sock);
close(sock);
// 扩容
}
else
{
// fd_array[pos] = sock;
_event_fds[pos].fd = sock;
_event_fds[pos].events = POLLIN;
_event_fds[pos].revents = non_event;
PrintFd();
// TODO
}
}
void Recver(int fd, int pos)
{
// demo
char buffer[1024];
ssize_t n = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1); // bug?
if (n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
cout << "get a messge: " << buffer << endl;
}
else if (n == 0)
{
lg(Info, "client quit, me too, close fd is : %d", fd);
close(fd);
_event_fds[pos].fd = defaultfd; // 这里本质是从select中移除
}
else
{
lg(Warning, "recv error: fd is : %d", fd);
close(fd);
_event_fds[pos].fd = defaultfd; // 这里本质是从select中移除
}
}
void Dispatcher()
{
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++) // 这是第三个循环
{
int fd = _event_fds[i].fd;
if (fd == defaultfd)
continue;
if (_event_fds[i].revents & POLLIN)
{
if (fd == _listensock.Fd())
{
Accepter(); // 连接管理器
}
else // non listenfd
{
Recver(fd, i);
}
}
}
}
void Start()
{
_event_fds[0].fd = _listensock.Fd();
_event_fds[0].events = POLLIN;
int timeout = 3000; // 3s
for (;;)
{
int n = poll(_event_fds, fd_num_max, timeout);
switch (n)
{
case 0:
cout << "time out... " << endl;
break;
case -1:
cerr << "poll error" << endl;
break;
default:
// 有事件就绪了,TODO
cout << "get a new link!!!!!" << endl;
Dispatcher(); // 就绪的事件和fd你怎么知道只有一个呢???
break;
}
}
}
void PrintFd()
{
cout << "online fd list: ";
for (int i = 0; i < fd_num_max; i++)
{
if (_event_fds[i].fd == defaultfd)
continue;
cout << _event_fds[i].fd << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
~PollServer()
{
_listensock.Close();
}
private:
Sock _listensock;
uint16_t _port;
struct pollfd _event_fds[fd_num_max]; // 数组, 用户维护的!
// struct pollfd *_event_fds;
// int fd_array[fd_num_max];
// int wfd_array[fd_num_max];
};
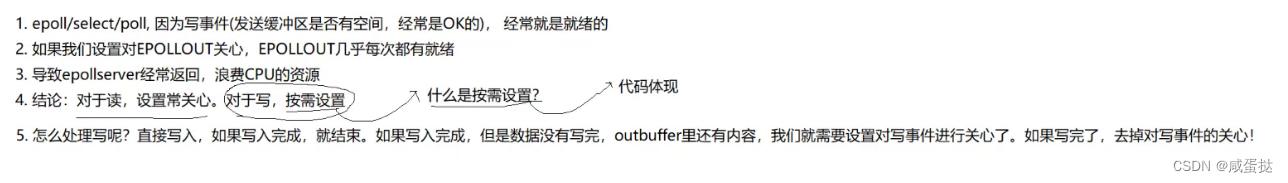
但实际上,它依然存在遍历问题,所以为此我们又引入了epoll,请看下一篇博客。