table(布局方面不建议使用,而是使用CSS来完成):
标签解释:
~table标签顾名思义,是表格的意思
~table其中可以使用boder属性来显示表格的线,最好使用CSS来配合HTML的使用
~table内的内容可以使用colspan来定义内容所占的单元格在行中的格子数
【类似于excel中合并行单元格】
~table内的内容可以使用rowspan来定义内容所占的单元格在列中的格子数
【类似于excel中合并列单元格】
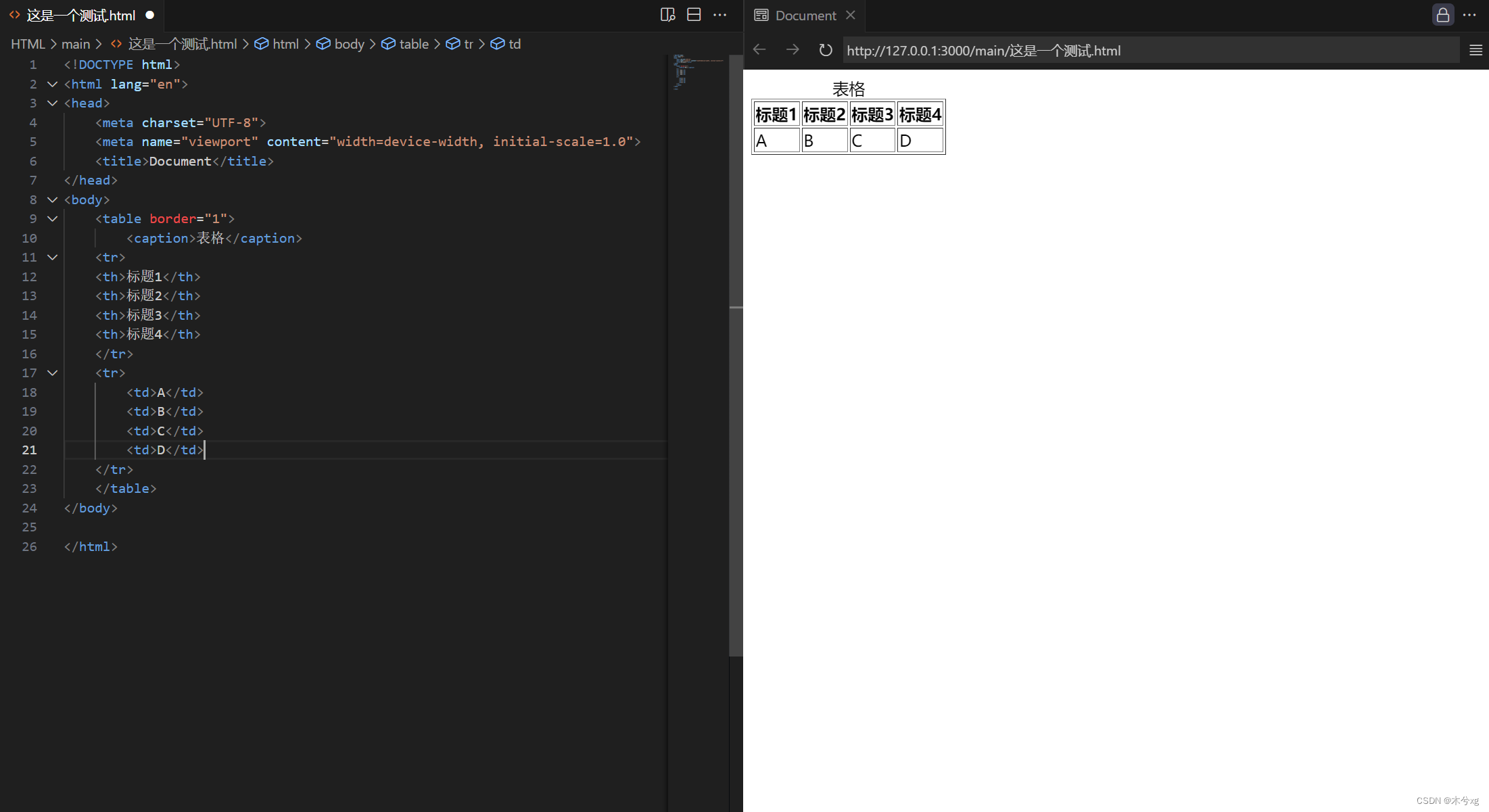
<表现形式1>
~caption表示表格的标题,可以通过其他的方式去实现
~其中使用 tr 表示第一行中的内容
~在 tr 中使用 th 表示列的内容
~在其他行中使用 td 来表示这一行所对应列中的数据
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <caption>表格</caption> <tr> <th>标题1</th> <th>标题2</th> <th>标题3</th> <th>标题4</th> </tr> <tr> <td>A</td> <td>B</td> <td>C</td> <td>D</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
<表现形式2>
【方便CSS来控制的结构,对应内容即为上当的内容】
~thead 表头的意思
~tbody 表的主体部分
~tfoot 表的底部内容
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <table> <thead> <tr> <th>标题1</th> <th>标题2</th> <th>标题3</th> <th>标题4</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td>A</td> <td>B</td> <td>C</td> <td>D</td> </tr> </tbody> <tfoot> <tr> <td>1</td> <td>2</td> <td>3</td> <td>4</td> </tr> </tfoot> </table> </body> </html>
input:
说明:
~输入框,像我们登陆界面的一样
~基本结构为:<input type="" name="" value="">
~其中内部可以设置id,方便使用javascript进行管理
~name是为了给后台服务器进行管理使用
~value是指给定初始值
~type用于指定输入框中输入的内容(如password,text,radio等)
【当使用radio时,若要单选,则name值要相同】
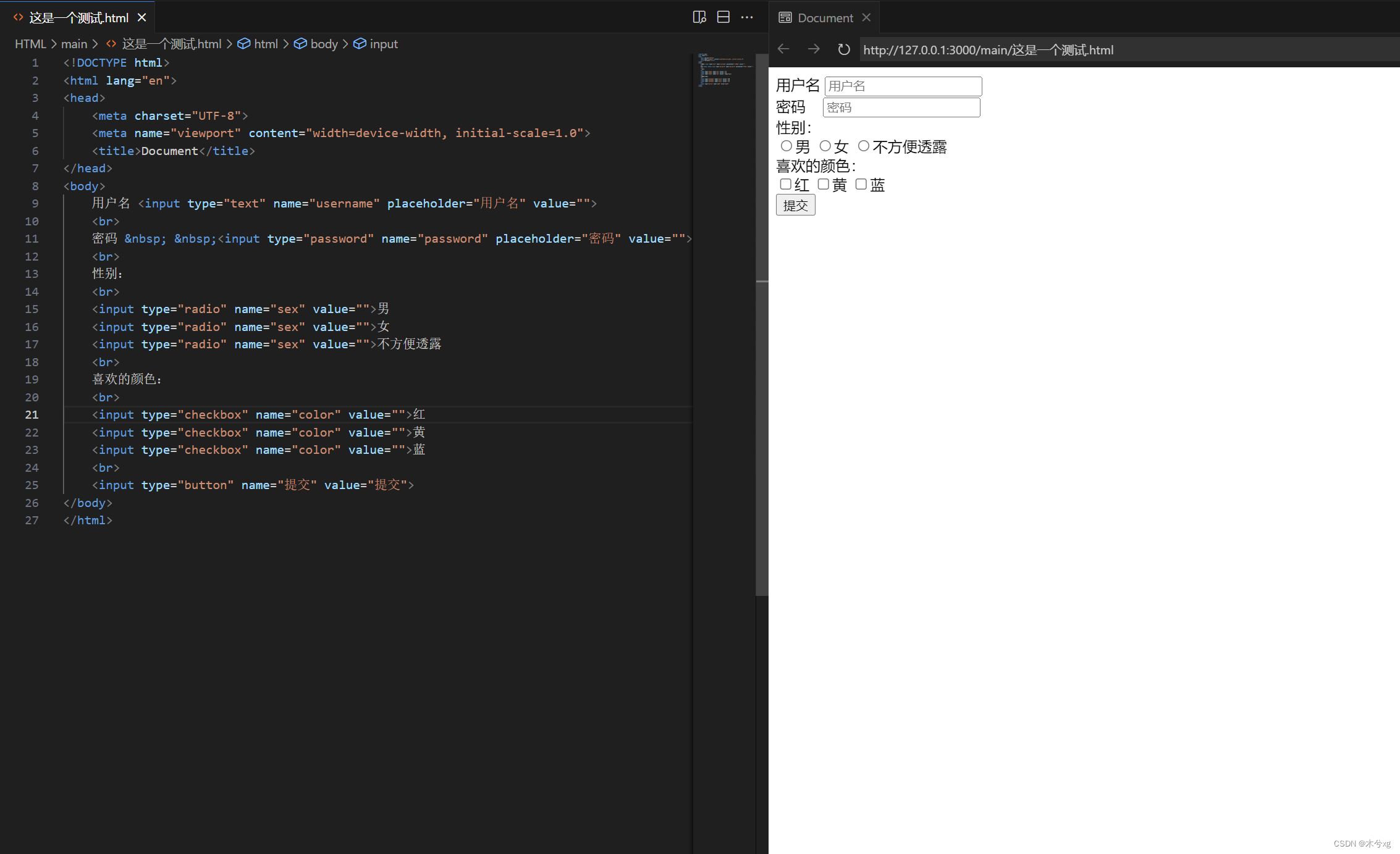
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> 用户名 <input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名" value=""> <br> 密码 <input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码" value=""> <br> 性别: <br> <input type="radio" name="sex" value="">男 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="">女 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="">不方便透露 <br> 喜欢的颜色: <br> <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="">红 <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="">黄 <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="">蓝 <br> <input type="button" name="提交" value="提交"> </body> </html>
lable:
标签解释:
~标签的含义,用于给元素说明。
~其结构为:<label for="说明元素的id">说明的内容</label>
举例(iput和lable举例):
<1>不指定说明对象时
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <label for="">用户名</label> <input type="text"> </body> </html>
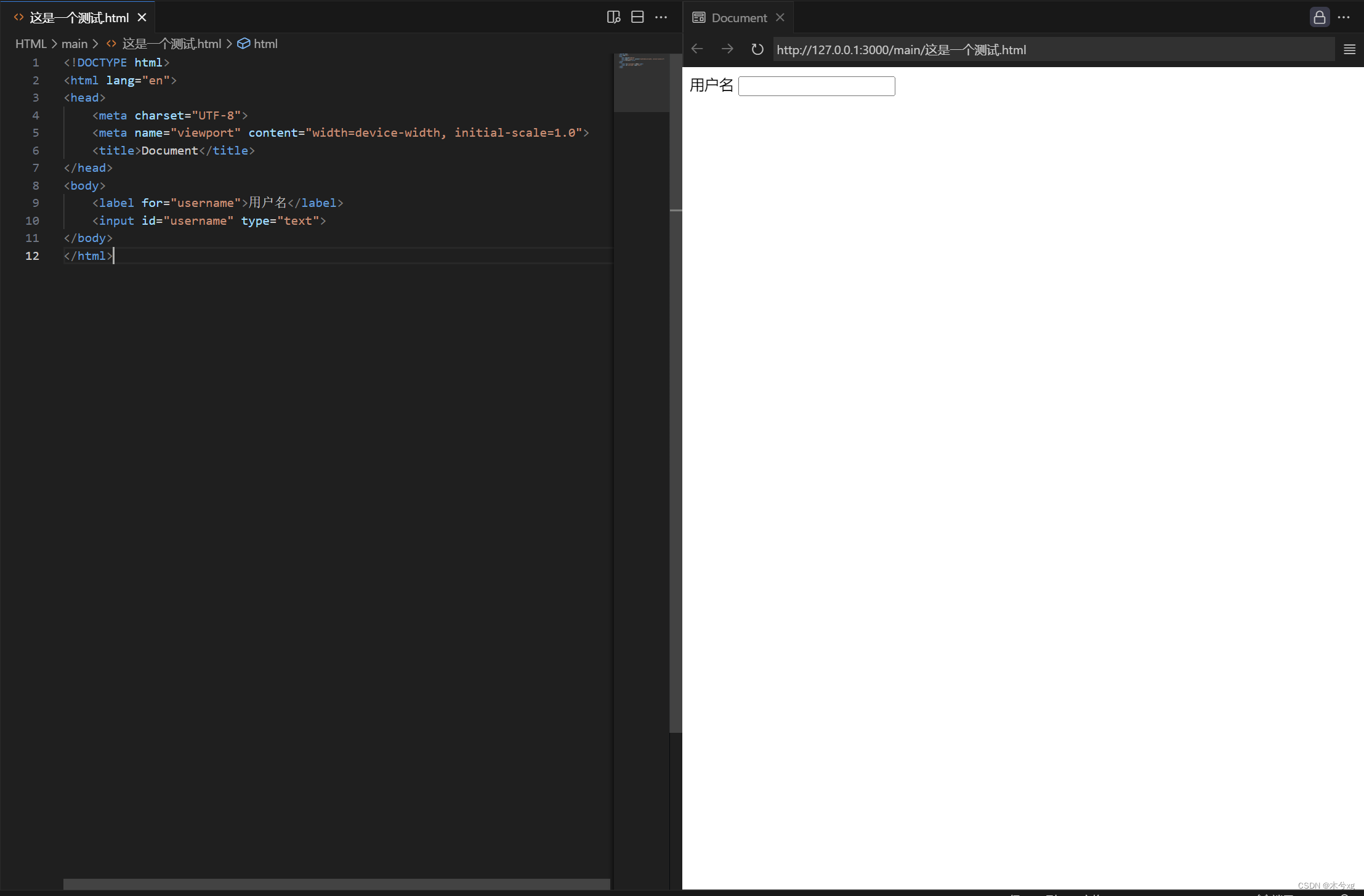
<2>指定说明对象时 将对象看作整体
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <label for="username">用户名</label> <input id="username" type="text"> </body> </html>
button:
解释:
~按钮的标签,一般在form当中使用,也可以作为input的style的属性值(通过form传入到服务器当中交由后台做判断等)
~其默认值为submit
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <form action="传入对象" method="post"> <select name="city"> <option value="1">上海</option> <option value="2">北京</option> <option selected value="3">江苏</option> <option value="4">广州</option> </select> <button type="submit">提交</button> </form> </body> </html>
slect:
解释:
~下拉框
~结构为
<select name="" >
内容
</select>
~内容为:
<option value="数值">选项名称</option>
内容可以选择selected来表示默认选项
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <select name="city"> <option value="1">上海</option> <option value="2">北京</option> <option selected value="3">江苏</option> <option value="4">广州</option> </select> </body> </html>
div:
例子:
当我们使用F12去查看网页时可以发现div字样的标签:
标签解释:
div 是一个没有语义的元素,相当于一个盒子,可以放任何东西,其中所有元素所占据宽度是整个浏览器的宽度,高度则为div的宽度。
举例说明(以 div 和 p 标签为例对比):
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div> <p>这是一个div标签展示</p> </div> <p>这是一个p标签展示</p> </body> </html>div占空间的大小为如图颜色区域:
p标签的占空间大小为如图所示区域:
p标签上下所占空间增加了一定的空格,而div却只有自身内容高度的大小。
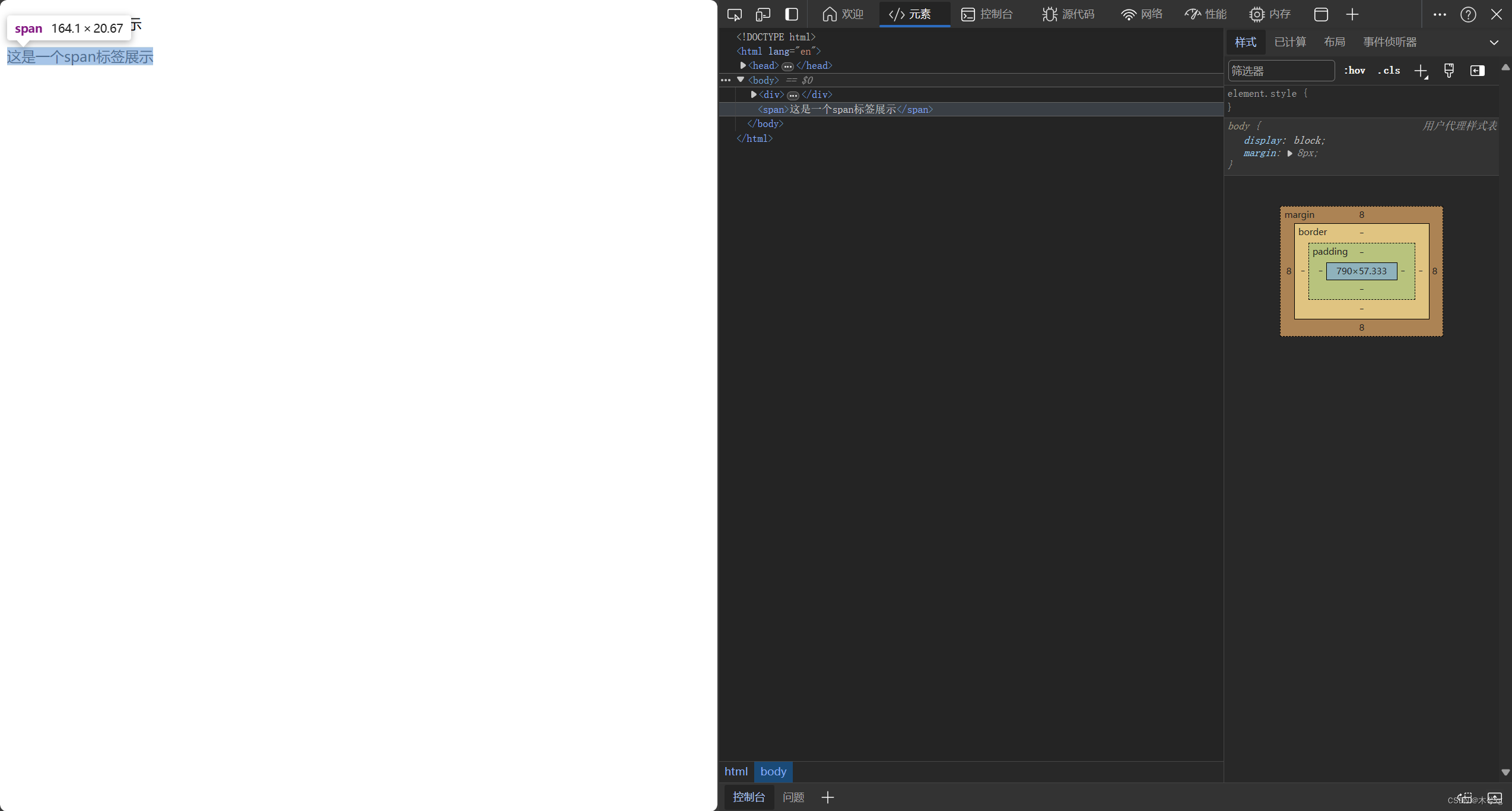
span:
标签解释:
span标签没有语义,所占空间只有内容的大小。
举例说明(以div标签和span标签为例对比):
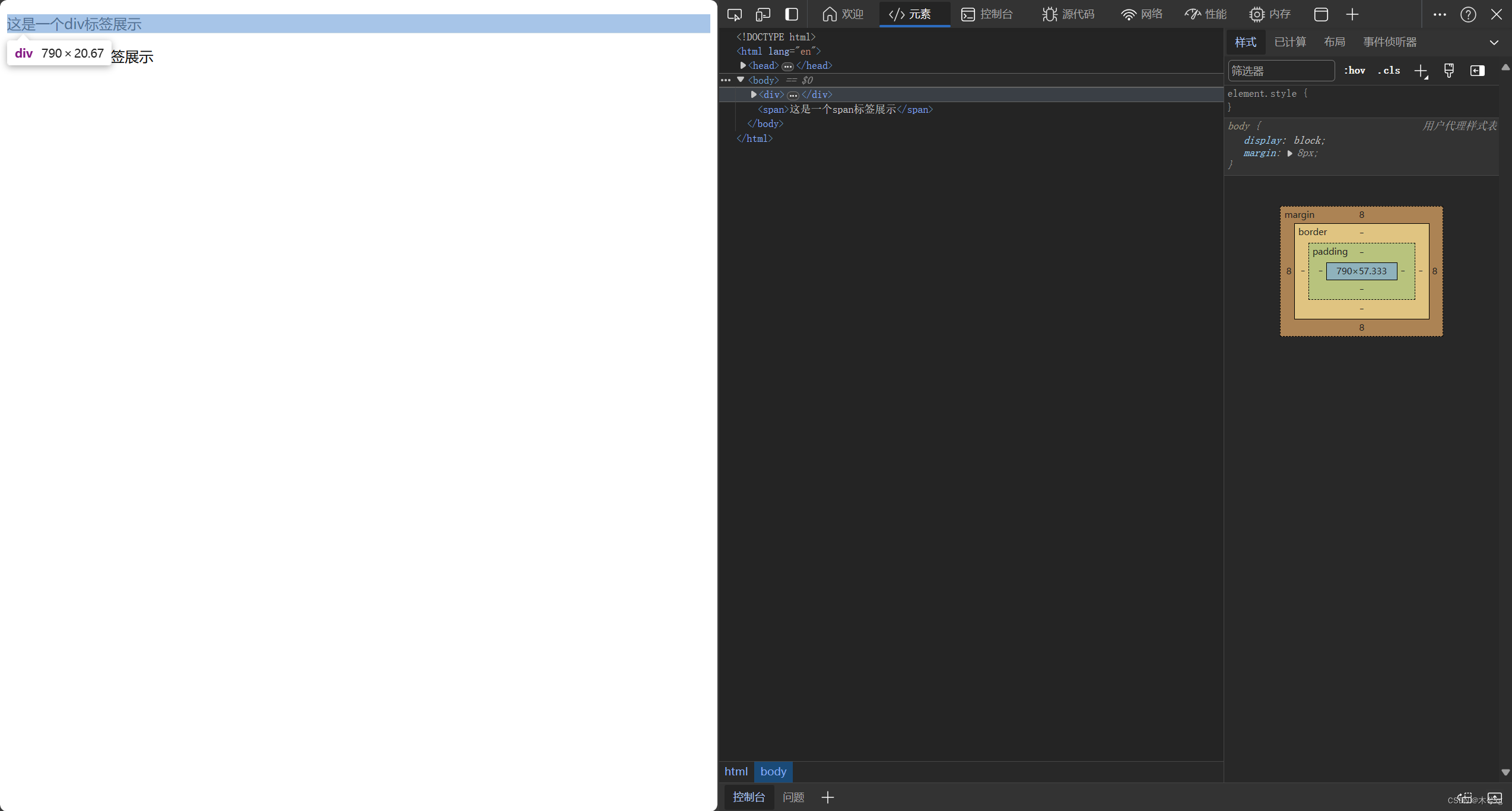
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div> <p>这是一个div标签展示</p> </div> <span>这是一个span标签展示</span> </body> </html>div所占空间大小如图所示:
span标签所占大小如图所示:
其中div所占空间大小充满了整个网页的宽度,而span只占据了自身的宽度。