深度学习(20)—— ConvNext 使用
本篇主要使用convnext做分类任务,其中使用convnext-tiny,其主要有5块
- stage0
- stage1
- stage2
- stage3
- head
文章目录
- 深度学习(20)—— ConvNext 使用
- Part 1 Model
- Part 2 Training
- Part 3 Predict
Part 1 Model
model.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
original code from facebook research:
https://github.com/facebookresearch/ConvNeXt
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn import init
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
r""" LayerNorm that supports two data formats: channels_last (default) or channels_first.
The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs. channels_last corresponds to inputs with
shape (batch_size, height, width, channels) while channels_first corresponds to inputs
with shape (batch_size, channels, height, width).
"""
def __init__(self, normalized_shape, eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_last"):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(normalized_shape), requires_grad=True)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(normalized_shape), requires_grad=True)
self.eps = eps
self.data_format = data_format
if self.data_format not in ["channels_last", "channels_first"]:
raise ValueError(f"not support data format '{self.data_format}'")
self.normalized_shape = (normalized_shape,)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.data_format == "channels_last":
return F.layer_norm(x, self.normalized_shape, self.weight, self.bias, self.eps)
elif self.data_format == "channels_first":
# [batch_size, channels, height, width]
mean = x.mean(1, keepdim=True)
var = (x - mean).pow(2).mean(1, keepdim=True)
x = (x - mean) / torch.sqrt(var + self.eps)
x = self.weight[:, None, None] * x + self.bias[:, None, None]
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
r""" ConvNeXt Block. There are two equivalent implementations:
(1) DwConv -> LayerNorm (channels_first) -> 1x1 Conv -> GELU -> 1x1 Conv; all in (N, C, H, W)
(2) DwConv -> Permute to (N, H, W, C); LayerNorm (channels_last) -> Linear -> GELU -> Linear; Permute back
We use (2) as we find it slightly faster in PyTorch
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
drop_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, drop_rate=0., layer_scale_init_value=1e-6):
super().__init__()
self.dwconv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=7, padding=3, groups=dim) # depthwise conv
self.norm = LayerNorm(dim, eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_last")
self.pwconv1 = nn.Linear(dim, 4 * dim) # pointwise/1x1 convs, implemented with linear layers
self.act = nn.GELU()
self.pwconv2 = nn.Linear(4 * dim, dim)
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim,)),
requires_grad=True) if layer_scale_init_value > 0 else None
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_rate) if drop_rate > 0. else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
shortcut = x
x = self.dwconv(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # [N, C, H, W] -> [N, H, W, C]
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.pwconv1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.pwconv2(x)
if self.gamma is not None:
x = self.gamma * x
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # [N, H, W, C] -> [N, C, H, W]
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
return x
class MiniConvNext(nn.Module):
r""" ConvNeXt
A PyTorch impl of : `A ConvNet for the 2020s` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.03545.pdf
Args:
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
depths (tuple(int)): Number of blocks at each stage. Default: [3, 3, 9, 3]
dims (int): Feature dimension at each stage. Default: [96, 192, 384, 768]
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
head_init_scale (float): Init scaling value for classifier weights and biases. Default: 1.
"""
def __init__(self, in_chans: int = 3, num_classes: int = 1000, depths: list = None,
dims: list = None, drop_path_rate: float = 0., layer_scale_init_value: float = 1e-6,
head_init_scale: float = 1.):
super().__init__()
self.downsample_layers = nn.ModuleList() # stem and 3 intermediate downsampling conv layers
stem = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_chans, dims[0], kernel_size=4, stride=4),
LayerNorm(dims[0], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"))
self.downsample_layers.append(stem)
# ¶ÔÓ¦stage2-stage4Ç°µÄ3¸ödownsample
for i in range(3):
downsample_layer = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(dims[i], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"),
nn.Conv2d(dims[i], dims[i + 1], kernel_size=2, stride=2))
self.downsample_layers.append(downsample_layer)
self.stages = nn.ModuleList() # 4 feature resolution stages, each consisting of multiple blocks
dp_rates = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
cur = 0
# ¹¹½¨Ã¿¸östageÖжѵþµÄblock
for i in range(4):
stage = nn.Sequential(
*[Block(dim=dims[i], drop_rate=dp_rates[cur + j], layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value)
for j in range(depths[i])]
)
self.stages.append(stage)
cur += depths[i]
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=0.2)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
d_0 = self.downsample_layers[0](x)
x_0 = self.stages[0](d_0)
d_1 = self.downsample_layers[1](x_0)
x_1 = self.stages[1](d_1)
d_2 = self.downsample_layers[2](x_1)
x_2 = self.stages[2](d_2)
d_3 = self.downsample_layers[3](x_2)
x_3 = self.stages[3](d_3)
return x_3 #
class ConvNeXt(nn.Module):
r""" ConvNeXt
A PyTorch impl of : `A ConvNet for the 2020s` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.03545.pdf
Args:
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
depths (tuple(int)): Number of blocks at each stage. Default: [3, 3, 9, 3]
dims (int): Feature dimension at each stage. Default: [96, 192, 384, 768]
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.
layer_scale_init_value (float): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: 1e-6.
head_init_scale (float): Init scaling value for classifier weights and biases. Default: 1.
"""
def __init__(self, in_chans: int = 3, num_classes: int = 1000, depths: list = None,
dims: list = None, drop_path_rate: float = 0., layer_scale_init_value: float = 1e-6,
head_init_scale: float = 1.):
super().__init__()
self.downsample_layers = nn.ModuleList() # stem and 3 intermediate downsampling conv layers
stem = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_chans, dims[0], kernel_size=4, stride=4),
LayerNorm(dims[0], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"))
self.downsample_layers.append(stem)
# ¶ÔÓ¦stage2-stage4Ç°µÄ3¸ödownsample
for i in range(3):
downsample_layer = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(dims[i], eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_first"),
nn.Conv2d(dims[i], dims[i + 1], kernel_size=2, stride=2))
self.downsample_layers.append(downsample_layer)
self.stages = nn.ModuleList() # 4 feature resolution stages, each consisting of multiple blocks
dp_rates = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
cur = 0
# ¹¹½¨Ã¿¸östageÖжѵþµÄblock
for i in range(4):
stage = nn.Sequential(
*[Block(dim=dims[i], drop_rate=dp_rates[cur + j], layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value)
for j in range(depths[i])]
)
self.stages.append(stage)
cur += depths[i]
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dims[-1], eps=1e-6) # final norm layer
self.head = nn.Linear(dims[-1], num_classes)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
self.head.weight.data.mul_(head_init_scale)
self.head.bias.data.mul_(head_init_scale)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Linear)):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=0.2)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward_features(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
for i in range(4):
x = self.downsample_layers[i](x)
x = self.stages[i](x)
return self.norm(x.mean([-2, -1])), x # global average pooling, (N, C, H, W) -> (N, C)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x, x_original = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
def convnext_tiny(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_tiny_1k_224_ema.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 9, 3],
dims=[96, 192, 384, 768],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_small(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_small_1k_224_ema.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[96, 192, 384, 768],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_base(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_base_1k_224_ema.pth
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_base_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[128, 256, 512, 1024],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_large(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_large_1k_224_ema.pth
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_large_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[192, 384, 768, 1536],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def convnext_xlarge(num_classes: int):
# https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/convnext/convnext_xlarge_22k_224.pth
model = ConvNeXt(depths=[3, 3, 27, 3],
dims=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
'''
Part 2 Training
- convnext有很多种规格,一般做分类使用tiny
- 可以自己写一个dataloader,但是分类任务有一个相对方便的函数datasets.ImageFolder,前提是需要一个这样结构的文件夹-
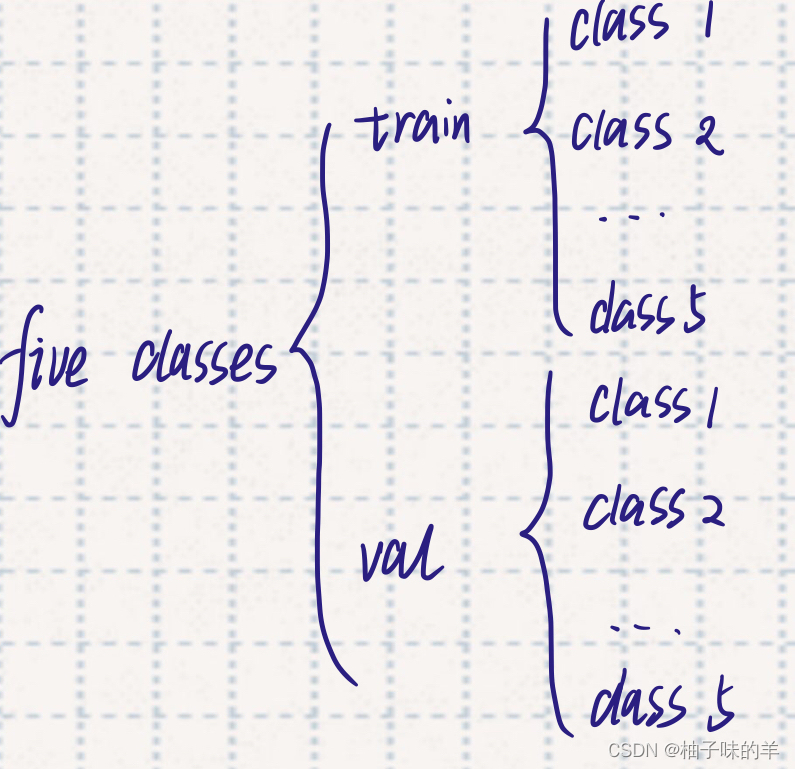
- convnext-tiny主要有五块组成(一次是stage0,stage1,stage2,stage3,head),使用freeze_layers,第一次学习冻结除了head的全部层,在训练过程中逐层开始解冻
train.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Sep 2 15:25:18 2022
@author: Lenovo
"""
import os
import json
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from pandas.core.frame import DataFrame
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from model import convnext_tiny as create_model # 导入tiny
from utils import get_params_groups, train_one_epoch, evaluate, setup_seed, create_lr_scheduler
global log
log = []
import time
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"using {device} device.")
start_time = time.time()
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M", time.localtime(start_time))
image_path = '/data/home/yangjy/data/five_class/' # 数据地址,具体格式如上
# pretrained_weight = '/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/weights/convnext_tiny_1k_224_ema.pth' # 使用convnext在imagenet上的权重作为初始权重
pretrained_weight = '/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/weights/2022-12-12-00-29.pth' # 自已之前已将训练过的权重作为初始权重
weight_path = f"/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/weights/{start_time}.pth" #训练权重保存位置
csv_path = f'/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/results/train/{start_time}.csv'# 用于保存loss和acc的csv地址
num_classes = 5 # 类别数目,主要用于创建模型时候最后一层全连接层
batch_size = 64
freeze_layers = False #将模型冻结一部分还是全部训练
learning_rate = 1e-4
weight_decay = 1e-3
#学习率衰减
step_size = 20
gamma = 0.95
#早停策略
early_stop_step = 30
epochs = 200
best_acc = 0.5
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5),
transforms.ColorJitter(0.1, 0.1, 0.1),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
# 实例化训练数据集
# 训练加载数据
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path) # 确保图片路径无误
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
# 具体分类写入json
# {"0": "grade0","1": "grade1","2": "grade2","3": "grade3","4": "grade4"}
grade_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in grade_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=5)
with open('./class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
# 转为dataloader型
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw)
# 加载验证数据集
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "val"),
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num, val_num))
model = create_model(num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
#其实这里可以使用另外一个变量进行判断,但是我懒就都使用pretrained_weight了,如果pretrained_weight的地址是ImageNet的地址(第一次训练)使用这个作为初始权重
if pretrained_weight == '/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/weights/convnext_tiny_1k_224_ema.pth':
assert os.path.exists(pretrained_weight), "weights file: '{}' not exist.".format(pretrained_weight)
weights_dict = torch.load(pretrained_weight, map_location=device)["model"]
# 删除有关分类类别的权重
for k in list(weights_dict.keys()):
if "head" in k:
del weights_dict[k]
print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False))
print("Loaded convnext pretrained in ImageNet!")
elif os.path.exists(pretrained_weight):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_weight, map_location=device))
print("Loaded weight pretrained in our data!")
else:
print("SORRY! No pretrained weight!!")
if freeze_layers == True:
for name, para in model.named_parameters():
# 初次训练除head外,其他权重全部冻结,后面逐层(stage3-stage0)解冻
if ("head" not in name) and ("stages.3" not in name) and ("stages.2" not in name) and ("stages.1" not in name) and ("stages.0" not in name):
para.requires_grad_(False)
else:
print("training {}".format(name))
# pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
pg = get_params_groups(model, weight_decay=weight_decay)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(pg, lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)
lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=step_size, gamma=gamma) # 每十次迭代,学习率减半
# lr_scheduler = create_lr_scheduler(optimizer, len(train_loader), epochs,warmup=True, warmup_epochs=10)
# 设置早停
total_batch = 0
last_decrease = 0
min_loss = 1000
flag = False
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
train_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
data_loader=train_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch, )
# validate
val_loss, val_acc = evaluate(model=model,
data_loader=validate_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
lr_scheduler.step()
if val_acc > best_acc: # acc improve save weight
best_acc = val_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), weight_path)
if val_loss < min_loss: # loss decrease save epoch
min_loss = val_loss
last_decrease = total_batch
print((min_loss, last_decrease))
total_batch += 1
if total_batch - last_decrease > early_stop_step:
print("No optimization for a long time, auto-stopping...")
flag = True
break
log.append([epoch, train_loss, val_loss, train_acc, val_acc])
print('Finished Training')
data = DataFrame(data=log, columns=['epoch', 'train_loss', 'val_loss', 'train_acc', 'val_acc'])
data.to_csv(csv_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
注:convnext在训练过程中需要的学习率大,最好不要小于1e-5,我一般初始设为1e-3,完全解冻后设为1e-4。且weight-decay不像resnet设置的较小,convnext的weight-decay一般在5e-2到1e-4,我一般设1e-3
Part 3 Predict
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from model import convnext_tiny as create_model
from pandas.core.frame import DataFrame
from utils import setup_seed
import torch
import os
log = []
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.456, 0.485, 0.406], [0.224, 0.229, 0.225])])
num_classes = 5
grade = 'grade4'
img_dir = f'/home/yangjy/data/five_class/val/{grade}' # 图片地址
pretrained_weight_path = '/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/weights/2022-12-12-00-29.pth' # 权重
save_predict_path = f'/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/results/predict/{grade}.csv'# 保存结果地址
# read class_indict
json_path = '/home/yangjy/projects/Jane_TF_classification/convnext/code/class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
model = create_model(num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_weight_path,map_location=device))
color_list = os.listdir(img_dir)
for picture in color_list:
img_path = os.path.join(img_dir, picture)
try:
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = data_transform(img)
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
res = [picture, class_indict[str(predict_cla)], grade]
log.append(res)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
continue
data = DataFrame(data=log, columns=['pic_name', 'predict_result', 'label'])
data.to_csv(save_predict_path)
print('Finished Predicting')