3.1 Bean的配置
Spring可以看作一个大型工厂,生产和管理Spring容器中的bean。如何使用这个工厂生产和管理bean,需要开发者将bean配置在Spring的配置文件中。Spring框架支持XML和Properties两种格式的配置文件,在实际开发中,常用XML格式的配置文件。

3.2 Bean的实例化
在面向对象编程中,想使用某个对象时,需要事先实例化该对象。同样,在Spring框架中,想使用Spring容器中的bean,也需要实例化bean。Spring框架实例化bean有三种方式:构造方法实例化、静态工厂实例化和实例工厂实例化。
在Spring框架中,Spring容器可以调用bean对应类中无参数构造方法来实例化bean,这种方式称为构造方法实例化。
构造方法实例化bean:
<!-- 构造方法实例化Bean -->
<bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass"/>
使用静态工厂实例化bean时,要求开发者在工厂类中创建一个静态方法来创建bean的实例。配置bean时,class属性指定静态工厂类,同时还需要使用factory-method属性指定工厂类中的静态方法。
静态工厂实例化bean:
<!-- 静态工厂方法实例化Bean,createInstance为静态工厂类BeanStaticFactory中的静态方法-->
<bean id="staticFactoryInstance" class="instance.BeanStaticFactory" factory-method="createInstance"/>
使用实例工厂实例化bean时,要求开发者在工厂类中创建一个实例方法来创建bean的实例。配置bean时,需要使用factory-bean属性指定配置的实例工厂,同时还需要factory-method属性指定实例工厂中的实例方法。
实例工厂实例化bean:
<!-- 配置实例工厂 -->
<bean id="myFactory" class="instance.BeanInstanceFactory"/>
<!-- 使用factory-bean属性指定配置工厂,使用factory-method属性指定使用工厂中哪个方法实例化Bean-->
<bean id="instanceFactoryInstance" factory-bean="myFactory" factory-method="createBeanClassInstance"/>
3.3 Bean的作用域

当将bean的scope设置为singleton时,Spring IoC容器仅生成和管理一个bean实例。使用id或name获取bean实例时,IoC容器将返回共享的bean实例。
由于singleton是scope的默认方式,因此有两种方式将bean的scope设置为singleton。
bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass"/>
或
<bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass" scope="singleton"/>
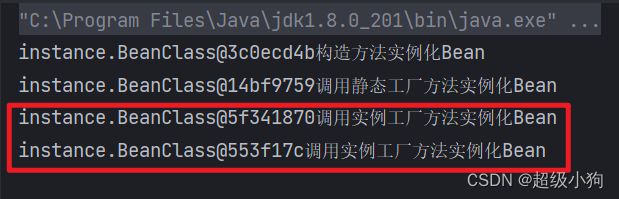
下面这个例子用来测试singleton作用域。
//测试实例工厂方法实例化Bean
BeanClass b3 = (BeanClass)appCon.getBean("instanceFactoryInstance");
System.out.println(b3 + b3.message);
BeanClass b4 = (BeanClass)appCon.getBean("instanceFactoryInstance");
System.out.println(b4 + b4.message);
当bean的scope设置为prototype时,Spring IoC容器将为每次请求创建一个新的实例。如果将实例工厂实例化bean中id为instanceFactoryInstance的bean定义修改如下:
<bean id="instanceFactoryInstance" factory-bean="myFactory" factory-method="createBeanClassInstance" scope="prototype"/>
3.4 Bean的生命周期
Spring容器可以管理singleton作用域bean的生命周期,在此作用域下,Spring能够精确地知道bean何时被创建,何时初始化完成,以及何时被销毁。而对于prototype作用域的 bean,Spring只负责创建,当容器创建了bean的实例后,bean实例就交给了客户端的代码管理,Spring容器将不再跟踪其生命周期,并且不会管理那些被配置成prototype作用域的bean。Spring中bean的生命周期的执行是一个很复杂的过程,可借鉴Servlet的生命周期:实例化、初始化init、接收请求service、销毁destroy,理解bean的生命周期。
在Spring 中,通过实现特定的接口或通过<bean>元素的属性设置,可以对bean的生命周期过程产生影响。开发者可以随意地配置<bean>元素的属性,但不建议过多地使用bean实现接口,因为这样将使代码和Spring聚合比较紧密。
下面这个例子演示bean的生命周期:
创建包life,在life包下创建类BeanLife。在类BeanLife中有两个方法,一个演示初始化过程,一个演示销毁过程:
package life;
public class BeanLife {
BeanLife() {
System.out.println("执行构造方法,创建对象。");
}
public void initMyself() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + "执行自定义的初始化方法");
}
public void destroyMyself() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + "执行自定义的销毁方法");
}
}
创建Spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml,在配置文件中定义一个id为beanLife的bean,使用init-method属性指定初始化方法,使用 destroy-method属性指定销毁方法:
<!-- 配置bean,使用init-method属性指定初始化方法,使用 destroy-method属性指定销毁方法-->
<bean id="beanLife" class="life.BeanLife" init-method="initMyself" destroy-method="destroyMyself"/>创建一个名为test的包,并在该包中创建测试类TestLife:
package test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import life.BeanLife;
public class TestLife {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
// 为了方便演示销毁方法的执行,这里使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println("获得对象前");
BeanLife blife = (BeanLife) ctx.getBean("beanLife");
System.out.println("获得对象后" + blife);
ctx.close();// 关闭容器,销毁Bean对象
}
}
运行结果:
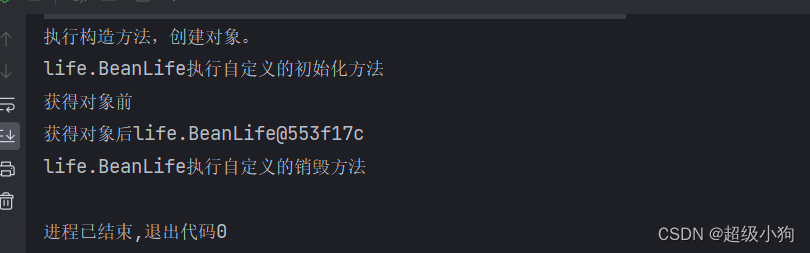
从运行结果中可以看出,加载配置文件时,创建bean对象,执行了bean的构造方法和初始化方法initMyself();获得对象后,关闭容器时,执行了bean的销毁方法destroyMyself()。
3.5 Bean的装配方式
3.5.1 基于XML配置的装配
bean的装配可以理解为将bean依赖注入到Spring容器中,bean的装配方式即bean依赖注入的方式。Spring容器支持基于XML配置的装配、基于注解的装配以及自动装配等多种装配方式。其中,最受青睐的装配方式是基于注解的装配(在本书后续章节中,采用基于注解的装配方式装配bean)。
使用构造方法注入方式装配bean时,bean的实现类需要提供带参数的构造方法,并在配置文件中使用<bean>元素的子元素<constructor-arg>来定义构造方法的参数;使用属性Setter方法注入方式装配bean时,bean的实现类需要提供一个默认无参数的构造方法,并为需要注入的属性提供对应的Setter方法,另外还需要使用<bean>元素的子元素<property>为每个属性注入值。
基于XML配置的装配方式:
1.创建包assemble,并在该包中创建类ComplexUser。在类ComplexUser中分别使用构造方法注入和Setter注入。
package assemble;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class ComplexUser {
private String uname;
private List<String> hobbyList;
private Map<String,String> residenceMap;
private Set<String> aliasSet;
private String[] array;
/*
* 使用构造方法注入,需要提供带参数的构造方法
*/
public ComplexUser(String uname, List<String> hobbyList, Map<String, String> residenceMap, Set<String> aliasSet,
String[] array) {
super();
this.uname = uname;
this.hobbyList = hobbyList;
this.residenceMap = residenceMap;
this.aliasSet = aliasSet;
this.array = array;
}
/**
* 使用Setter方法注入,提供默认无参数的构造方法,并为注入的属性提供Setter方法
*/
public ComplexUser() {
super();
}
public void setUname(String uname) {
this.uname = uname;
}
public void setHobbyList(List<String> hobbyList) {
this.hobbyList = hobbyList;
}
public void setResidenceMap(Map<String, String> residenceMap) {
this.residenceMap = residenceMap;
}
public void setAliasSet(Set<String> aliasSet) {
this.aliasSet = aliasSet;
}
public void setArray(String[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ComplexUser [uname=" + uname + ", hobbyList=" + hobbyList + ", residenceMap=" + residenceMap
+ ", aliasSet=" + aliasSet + ", array=" + Arrays.toString(array) + "]";
}
}
创建Spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml,在配置文件中使用实现类ComplexUser配置bean的两个实例。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 使用构造方法注入方式装配ComplexUser实例 user1-->
<bean id="user1" class="assemble.ComplexUser">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="chenheng1"/>
<constructor-arg index="1">
<list>
<value>唱歌</value>
<value>跳舞</value>
<value>爬山</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2">
<map>
<entry key="dalian" value="大连"/>
<entry key="beijing" value="北京"/>
<entry key="shanghai" value="上海"/>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="3">
<set>
<value>陈100</value>
<value>陈101</value>
<value>陈102</value>
</set>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="4">
<array>
<value>aaaaa</value>
<value>bbbbb</value>
</array>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 使用Setter方法注入方式装配 ComplexUser实例user2 -->
<bean id="user2" class="assemble.ComplexUser">
<property name="uname" value="chenheng2"/>
<property name="hobbyList">
<list>
<value>看书</value>
<value>学习Spring</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="residenceMap">
<map>
<entry key="shenzhen" value="深圳"/>
<entry key="gaungzhou" value="广州"/>
<entry key="tianjin" value="天津"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="aliasSet">
<set>
<value>陈103</value>
<value>陈104</value>
<value>陈105</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>cccccc</value>
<value>dddddd</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
创建一个名为test的包,并在该包中创建测试类TestAssemble:
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import assemble.ComplexUser;
public class TestAssemble {
private static ApplicationContext appCon;
public static void main(String[] args) {
appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//构造方法装配测试
ComplexUser u1 = (ComplexUser)appCon.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(u1);
//setter方法装配测试
ComplexUser u2 = (ComplexUser)appCon.getBean("user2");
System.out.println(u2);
}
}
3.5.2 基于注解的装配
需要注意的是,基于注解的装配需要使用<context:component-scan>元素或@ComponentScan注解定义包(注解所在的包)扫描的规则,然后根据定义的规则找出哪些类(bean)需要自动装配到Spring容器中,然后交由Spring进行统一管理。
Spring框架基于AOP编程(面向切面编程)实现注解解析,因此,在使用注解编程时,需要导入spring-aop-6.0.0.jar包。
1.声明Bean的注解
1)@Component
该注解是一个泛化的概念,仅仅表示一个组件对象(bean),可以作用在任何层次上。
演示@Component()注解的用法:
1.创建名为annotation的包,并在该包中创建bean的实现类AnnotationUser。在类AnnotationUser中使用@Component()注解声明一个bean对象,同时使用@Value注解注入属性值。
package annotation;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component()
/**相当于@Component("annotationUser")
* 或@Component(value = "annotationUser"),
* annotationUser为bean的id,默认为首字母小写的类名
**/
public class AnnotationUser {
@Value("chenheng")
private String uname;
@Value("#{{'0411': '大连', '010': '北京'}}")
private Map<String, String> cities;
@Value("{'篮球','足球','排球','乒乓球'}")
private List<String> hobbyList;
@Value("22")
private int age;
public String getUname() {
return uname;
}
public Map<String, String> getCities() {
return cities;
}
public List<String> getHobbyList() {
return hobbyList;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setUname(String uname) {
this.uname = uname;
}
public void setCities(Map<String, String> cities) {
this.cities = cities;
}
public void setHobbyList(List<String> hobbyList) {
this.hobbyList = hobbyList;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AnnotationUser [uname=" + uname + ", cities=" + cities + ", hobbyList=" + hobbyList + ", age=" + age
+ "]";
}
}
2.现在有了bean的实现类,但还不能使用bean对象,因为Spring容器并不知道去哪里扫描bean对象。需要在配置文件中,使用<context:component-scan>元素配置注解。
<!-- 通过component-scan扫描指定包annotation及其子包下所有基于注解的bean实现,进行注解解析 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="annotation"/>
3.创建名为test的包,并在该包中创建测试类TestAnnotation,测试上述基于注解的bean。
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import annotation.AnnotationUser;
public class TestAnnotation {
private static ApplicationContext appCon;
public static void main(String[] args) {
appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("annotationContext.xml");
AnnotationUser au = (AnnotationUser)appCon.getBean("annotationUser");
System.out.println(au);
}
}
2)@Repository
该注解用于将数据访问层(DAO)的类标识为bean,即注解数据访问层bean,其功能与@Component()相同。
3)@Service
该注解用于标注一个业务逻辑组件类(Service层),其功能与@Component()相同。
4)@Controller
该注解用于标注一个控制器组件类(Spring MVC的Controller),其功能与@Component()相同。
2.注入Bean的注解
1)@Autowired
该注解可以对类的成员变量、方法及构造方法进行标注,完成自动装配的工作。通过 @Autowired的使用来消除Setter和Getter方法。默认按照bean的类型进行装配。
2)@Resource
该注解与@Autowired功能一样。区别在于,该注解默认是按照名称来装配注入的,只有当找不到与名称匹配的bean才会按照类型来装配注入;而@Autowired默认按照bean的类型进行装配,如果想按照名称来装配注入,则需要结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。
@Resource注解有两个属性:name和type。name属性指定bean的实例名称,即按照名称来装配注入;type属性指定bean类型,即按照bean的类型进行装配。
3)@Qualifier
该注解与@Autowired注解配合使用。当@Autowired注解需要按照名称来装配注入,则需要结合该注解一起使用,bean的实例名称由@Qualifier注解的参数指定。
基于注解的依赖注入的使用过程:虽然@Repository、@Service和 @Controller等注解的功能与@Component()相同,但为了使标注类的用途更加清晰(层次化),在实际开发中推荐使用@Repository标注数据访问层(DAO层)、使用@Service标注业务逻辑层(Service层)以及使用@Controller标注控制器层(控制层)。