一、引入
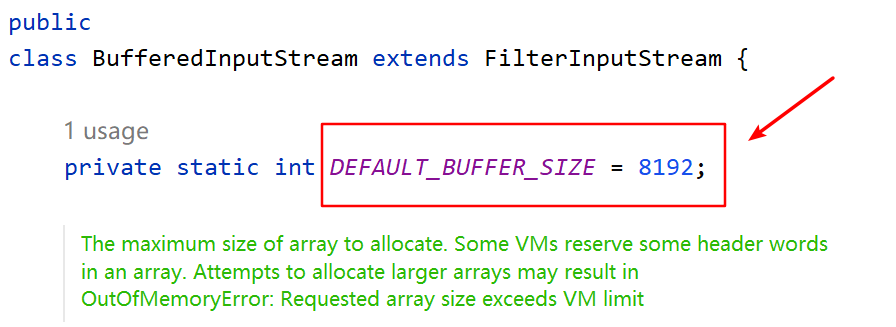
为了提高数据读写的速度,Java API提供了带缓冲功能的流类,在使用这些流类 时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组,缺省使用8192个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区。
二、缓冲流涉及到的类
字节输入流:BufferedInputStream
字节输出流BufferedOutputStream
字符输入流:BufferedReader
字符输出流:BufferedWrite
三、缓冲流的作用
1、提高节点流处理文件的效率。
2、提高读写效率的原因:内部提供了缓冲区。
四、缓冲流与节点流处理数据的效率对比
//封装一个缓冲流复制文件的方法
public void copyWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
//2.造流
//2.1造节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//2.2造缓冲流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.数据操作
byte[] cbuf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(cbuf)) != -1){
bos.write(cbuf,0,len);
// bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//关闭流资源
//要求:先关闭外层的流,在关闭内层的流
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//说明:在关闭外层的流后,会自动关闭内层的流。
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
@Test
public void testCopyWithBuffered(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\suxintai\\Desktop\\01-视频.mp4";
String destPath = "C:\\Users\\suxintai\\Desktop\\03-视频.mp4";
copyWithBuffered(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制视频花费的时间为" + (end-start));//605---156
}测试结果:复制相同视频缓冲流使用999毫秒,而根据上一章13_3、Java的IO流之节点流的使用 中字节流使用了4346毫秒。可见缓冲流在处理数据的效率要高于字节流。

![[ 常用工具篇 ] burpsuite_pro 安装配置详解(附安装包)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2e129eee05104753b9fa8e5bcf6a74bf.png)