文章目录
- 1、等高虚拟列表
- 2、非等高虚拟列表
1、等高虚拟列表
参考文章1
参考文章2
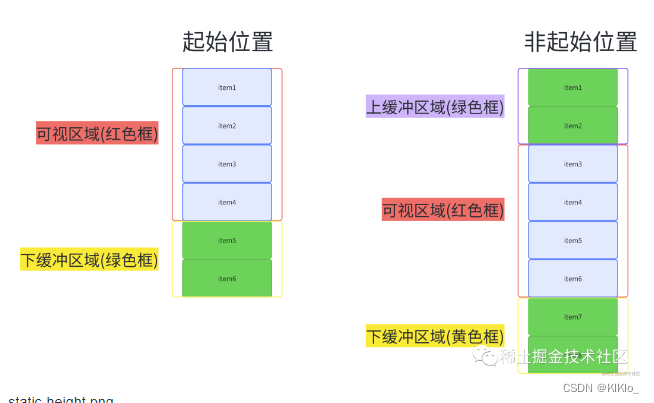
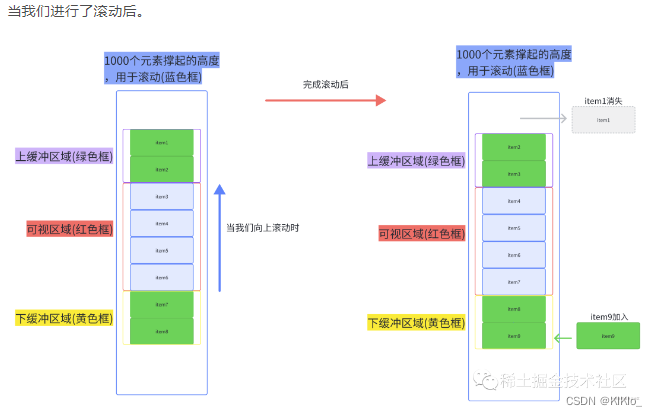
<!-- eslint-disable vue/multi-word-component-names -->
<template>
<div
class="waterfall-wrapper"
ref="waterfallWrapperRef"
@scroll="handleScroll"
>
<div :style="scrollStyle">
<div v-for="item in computedData.items" :key="item.userId">
{{ item.username }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, onMounted, ref } from "vue";
import { sameHighData } from "../data/index";
const itemHeight = 18; //每个item的高度
let itemCount = ref(500); // 设置总共长度为500
const scrollTop = ref(0); // 滚动的高度
const wrapperHeight = ref(0); // 滚动容器的高度
const waterfallWrapperRef = ref();
const list = ref([...sameHighData]);
const handleScroll = (e: any) => {
// 在content内容中距离content盒子的上部分的滚动距离
scrollTop.value = e.target.scrollTop;
// 判断是否接近底部,如果是则加载更多数据
if (e.target.scrollHeight - e.target.clientHeight - scrollTop.value < 100) {
getData();
}
};
const getData = () => {
list.value = list.value.concat(list.value);
itemCount.value = list.value.length;
// scrollBarRef.value.style.height = itemCount.value * itemHeight + "px";
console.log("发送网络请求", list.value.length);
};
const scrollStyle = computed(() => ({
height: `${
itemHeight * (list.value.length - computedData.value.startIndex)
}px`,
transform: `translateY(${itemHeight * computedData.value.startIndex}px)`,
}));
// 这里不使用方法的原因是以来了scrollTop 响应式数据来变更 所以使用computed更方便
const computedData = computed(() => {
// 可视区域的索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop.value / itemHeight);
// 设置上缓冲区为2 上缓冲区的索引
const finialStartIndex = Math.max(0, startIndex - 2);
// 可视区显示的数量 这里设置了item的高度为50
const numVisible = Math.floor(wrapperHeight.value / itemHeight);
// 设置下缓冲区的结束索引 上缓冲区也设置为2
const endIndex = Math.min(itemCount.value, startIndex + numVisible + 2);
// 将上缓冲区到下缓冲区的数据返回
const items: any = [];
// contentWrapRef.value!.style.height = finialStartIndex * itemHeight + "px";
for (let i = finialStartIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
const item = {
...list.value[i],
top: itemHeight * i + "px",
transform: `translateY(${itemHeight * i + "px"})`,
};
items.push(item);
}
console.log(startIndex);
return { items, startIndex };
});
onMounted(() => {
// 在页面一挂载就获取滚动区域的高度
if (waterfallWrapperRef.value) {
wrapperHeight.value = waterfallWrapperRef.value?.clientHeight;
}
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.waterfall-wrapper {
height: 500px;
overflow: hidden;
overflow-y: scroll;
position: relative;
.scroll-bar {
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
}
}
</style>
2、非等高虚拟列表
参考链接
非等高序列列表的实现逻辑并没有通过相对定位的方式,而是通过设置translateY来实现滚动
思路:
- 难点1:每个元素的高度不一样,没办法直接计算出容器的高度
-
- 容器高度的作用是足够大 可以让用户进行滚动,所以我们可以直接假设每一个元素的高度
需要保证预测的 item 高度尽量比真实的每一项 item 的高度要小或者接近所有 item 高度的平均值
- 容器高度的作用是足够大 可以让用户进行滚动,所以我们可以直接假设每一个元素的高度
- 难点2: 每个元素高度不一样,top值不能通过
count * index算出来 - 难点3: 每个元素高度不一样,不能通过
scrollTop * size计算出已经滚动的元素个数,很难获取可视区的起始索引 -
- 难度2和难度3的解决方案是先把数据渲染到页面上 之后再通过 获取正式dom的高度 来计算

- 难度2和难度3的解决方案是先把数据渲染到页面上 之后再通过 获取正式dom的高度 来计算
<template>
<div
class="waterfall-wrapper"
ref="waterfallWrapperRef"
@scroll="handleScroll"
>
<!-- 内容显示的区域 -->
<div ref="listRef" :style="scrollStyle">
<div v-for="(item, index) in computedData" :key="index">
{{ index }} {{ item.sentence }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
- 1、先确定预测的item高度和数据
- 2、获取滚动区域的高度且计算容器最大容量
onMounted(async () => {
// 在页面一挂载就获取滚动区域的高度
if (waterfallWrapperRef.value) {
wrapperHeight.value = waterfallWrapperRef.value?.clientHeight;
// 预测容器最多显示多少个元素
maxCount.value = Math.ceil(wrapperHeight.value / estimatedHeight) + 1;
await nextTick();
// 先把数据显示再页面上
initData();
setItemHeight();
}
});
- 3、引用一个新的变量来存放实际的dom和
预测结果和实际的偏差高度
interface IPosInfo {
// 当前pos对应的元素索引
index: number;
// 元素顶部所处位置
top: number;
// 元素底部所处位置
bottom: number;
// 元素高度
height: number;
// 自身对比高度差:判断是否需要更新
dHeight: number;
}
- 4、初始化预测的dom
参考逻辑
function initPosition() {
const pos: IPosInfo[] = [];
// 将获取到的数据全部进行初始化
for(let i = 0; i < props.dataSource.length; i++) {
pos.push({
index: item.id,
height: props.estimatedHeight, // 使用预测高度先填充 positions
top: item.id * props.estimatedHeight,
bottom: (item.id + 1) * props.estimatedHeight,
dHeight: 0,
})
}
positions.value = pos;
}
实际代码
// 初始化数据
const initData = () => {
const items: IPosInfo[] = [];
// 获取需要更新位置的dom长度 即新增加的数据
const len = list.value.length - preLen.value;
// 已经处理好位置的长度
const currentLen = initList.value.length;
// 可以用三元运算符是因为初始化的时候initList的数值是空的
const preTop = initList.value[currentLen - 1]
? initList.value[currentLen - 1].top
: 0;
const preBottom = initList.value[currentLen - 1]
? initList.value[currentLen - 1].bottom
: 0;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const currentIndex = preLen.value + i;
// 获取当前要初始化的item
const item: DiffHigh = list.value[currentIndex];
items.push({
id: item.id,
height: estimatedHeight, // 刚开始不知道他高度 所以暂时先设置为预置的高度
top: preTop
? preTop + i * estimatedHeight
: currentIndex * estimatedHeight,
// 元素底部所处位置 这里获取的是底部的位置 所以需要+1
bottom: preBottom
? preBottom + (i + 1) * estimatedHeight
: (currentIndex + 1) * estimatedHeight,
// 高度差:判断是否需要更新
dHeight: 0,
});
}
initList.value = [...initList.value, ...items];
preLen.value = list.value.length;
};
- 5、更新实际的数据,拿到实际的数据高度
-
- 通过 ref 获取到 list DOM,进而获取到它的 children
-
- 遍历 children,针对于每一个 DOM item 获取其高度信息,通过其 id 属性找到 positions 中对应的 item,更新该 item 信息
// 数据渲染之后更新item的真实高度
const setItemHeight = () => {
const nodes = listRef.value.children;
if (!nodes.length) return;
// Array.from(nodes): 使用 Array.from() 方法,其中 nodes 是一个类数组对象。
// [...nodes]: 使用数组解构语法,其中 nodes 是一个可迭代对象,例如 NodeList。
// 1、遍历节点并获取位置信息
// 2、更新节点高度和位置信息:
// 这里只更新了视图上的bottom 没有更新top的数值 而且只更新视图上面显示的,并没有更新整个列表,因为height发生了改变视图以外的数据也发生了变化 需要同步修改
[...nodes].forEach((node: Element, index: number) => {
const rect = node.getBoundingClientRect();
const item = initList.value[startIndex.value + index];
const dHeight = item?.height - rect?.height;
if (dHeight) {
item.height = rect.height;
item.bottom = item.bottom - dHeight;
item.dHeight = dHeight;
}
});
// 3、将当前 item 的 dHeight 进行累计,之后再重置为 0 (更新后就不再存在高度差了)
const len = initList.value.length;
let startHeight = initList.value[startIndex.value]?.dHeight;
if (startHeight) {
initList.value[startIndex.value].dHeight = 0;
}
// 从渲染视图的第二个开始处理
// 实际上第一项的 top 值为 0,bottom 值在上轮也更新过了,所以遍历的时候我们从第二项开始
for (let i = startIndex.value + 1; i < len; i++) {
const item = initList.value[i];
item.top = initList.value[i - 1].bottom;
item.bottom = item.bottom - startHeight;
if (item.dHeight !== 0) {
startHeight += item.dHeight;
item.dHeight = 0;
}
}
// 设置 list 高度
listHeight.value = initList.value[len - 1].bottom;
};
- 6、设置滚动
// 已经滚动的距离
const offsetDis = computed(() =>
startIndex.value > 0 ? initList.value[startIndex.value - 1]?.bottom : 0
);
const scrollStyle = computed(() => ({
height: `${listHeight.value - offsetDis.value}px`,
transform: `translateY(${offsetDis.value}px)`,
}));
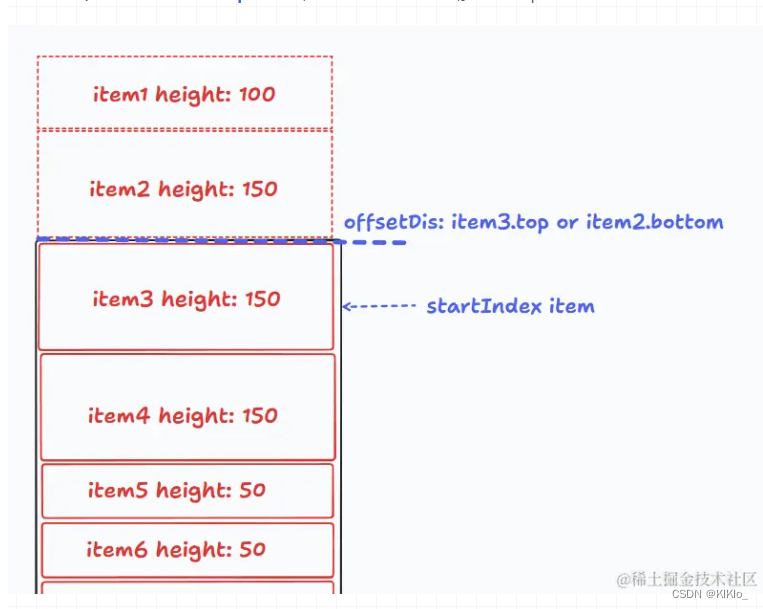
- 7、滚动事件和 startIndex 计算
-
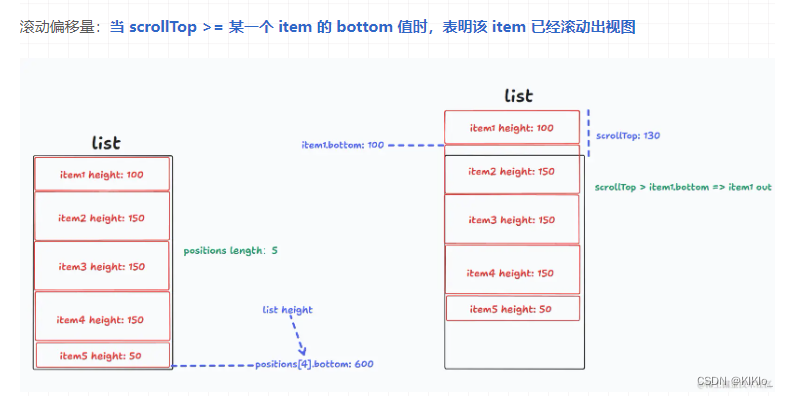
- 如何判断一个 item 滚出视图?这个问题在最早就提到过了,只需要看它的 bottom <= scrollTop
-
- 现在就好办了,我们可以遍历 positions 数组找到第一个 item.bottom >= scrollTop 的 item,它就是 startIndex 所对应的 item,那 startIndex 就拿到了
-
- 这里再补充一个细节,在 initList 数组中 item.bottom 一定是递增的,而我们现在想要做的是查找操作,有序递增 + 查找 = 二分查找
// 二分查找 找到可视区域的索引startIndex
const getStartIndex = (list: any, value: number) => {
let left = 0,
right = list.length - 1,
templateIndex = -1;
while (left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
const midValue = list[mid].bottom;
// 如果找到了就用找到的索引 + 1 作为 startIndex,因为找到的 item 是它的 bottom 与 scrollTop 相等,即该 item 已经滚出去了
if (midValue === value) return mid + 1;
else if (midValue < value) left = mid + 1;
else if (midValue > value) {
if (templateIndex == -1 || templateIndex > mid) {
templateIndex = mid;
}
right = mid;
}
}
return templateIndex;
};
- 8、每次 startIndex 改变,不仅会改变 renderList 的计算,我们还需要重新计算 item 信息
watch(
() => startIndex.value,
() => {
setItemHeight();
}
);
<!-- eslint-disable vue/multi-word-component-names -->
<template>
<div
class="waterfall-wrapper"
ref="waterfallWrapperRef"
@scroll="handleScroll"
>
<!-- 内容显示的区域 -->
<div ref="listRef" :style="scrollStyle">
<div v-for="(item, index) in computedData" :key="index">
{{ index }} {{ item.sentence }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, nextTick, onMounted, ref, watch } from "vue";
import { sameDiffData } from "../data/index";
interface IPosInfo {
// 当前pos对应的元素索引
id: number;
// 元素顶部所处位置
top: number;
// 元素底部所处位置
bottom: number;
// 元素高度
height: number;
// 高度差:判断是否需要更新
dHeight: number;
}
interface DiffHigh {
id: number;
sentence: string;
}
const waterfallWrapperRef = ref();
const listRef = ref();
const estimatedHeight = 60; // 设置预估的高度为100
let itemCount = ref(500); // 设置总共长度为500
const scrollTop = ref(0); // 滚动的高度
const wrapperHeight = ref(0); // 滚动容器的高度
const preLen = ref(0); // 因为每次处理数值的时候都需要处理全部数据 这个用来记录已经处理的数据
const list = ref<DiffHigh[]>([...sameDiffData]);
const initList = ref<IPosInfo[]>([]); // 用来存放已经处理好位置的数据
const listHeight = ref(0); // 列表的高度
const startIndex = ref(0);
const maxCount = ref(0);
const endIndex = computed(() =>
Math.min(list.value.length, startIndex.value + maxCount.value + 2)
);
const computedData = computed(() =>
list.value.slice(Math.max(0, startIndex.value - 2), endIndex.value)
);
// 已经滚动的距离
const offsetDis = computed(() =>
startIndex.value > 0 ? initList.value[startIndex.value - 1]?.bottom : 0
);
const scrollStyle = computed(() => ({
height: `${listHeight.value - offsetDis.value}px`,
transform: `translateY(${offsetDis.value}px)`,
}));
const handleScroll = (e: any) => {
scrollTop.value = e.target.scrollTop;
// 在content内容中距离content盒子的上部分的滚动距离
// 在开始滚动之后获取startIndex
startIndex.value = getStartIndex(initList.value, scrollTop.value);
console.log(startIndex.value, "-0-");
// 判断是否接近底部,如果是则加载更多数据
if (e.target.scrollHeight - e.target.clientHeight - scrollTop.value < 100) {
getMoreData();
}
};
watch(
() => startIndex.value,
() => {
setItemHeight();
}
);
const getMoreData = async () => {
list.value = list.value.concat(list.value);
await nextTick();
initData();
setItemHeight();
};
// 二分查找 找到可视区域的索引startIndex
const getStartIndex = (list: any, value: number) => {
let left = 0,
right = list.length - 1,
templateIndex = -1;
while (left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
const midValue = list[mid].bottom;
if (midValue === value) return mid + 1;
else if (midValue < value) left = mid + 1;
else if (midValue > value) {
if (templateIndex == -1 || templateIndex > mid) {
templateIndex = mid;
}
right = mid;
}
}
return templateIndex;
};
// 初始化数据
const initData = () => {
const items: IPosInfo[] = [];
// 获取需要更新位置的dom长度
const len = list.value.length - preLen.value;
// 已经处理好位置的长度
const currentLen = initList.value.length;
// 可以用三元运算符是因为初始化的时候initList的数值是空的
const preTop = initList.value[currentLen - 1]
? initList.value[currentLen - 1].top
: 0;
const preBottom = initList.value[currentLen - 1]
? initList.value[currentLen - 1].bottom
: 0;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const currentIndex = preLen.value + i;
// 获取当前要初始化的item
const item: DiffHigh = list.value[currentIndex];
items.push({
id: item.id,
height: estimatedHeight, // 刚开始不知道他高度 所以暂时先设置为预置的高度
top: preTop
? preTop + i * estimatedHeight
: currentIndex * estimatedHeight,
// 元素底部所处位置 这里获取的是底部的位置 所以需要+1
bottom: preBottom
? preBottom + (i + 1) * estimatedHeight
: (currentIndex + 1) * estimatedHeight,
// 高度差:判断是否需要更新
dHeight: 0,
});
}
initList.value = [...initList.value, ...items];
preLen.value = list.value.length;
};
// 数据渲染之后更新item的真实高度
const setItemHeight = () => {
const nodes = listRef.value.children;
if (!nodes.length) return;
// Array.from(nodes): 使用 Array.from() 方法,其中 nodes 是一个类数组对象。
// [...nodes]: 使用数组解构语法,其中 nodes 是一个可迭代对象,例如 NodeList。
// 1、遍历节点并获取位置信息
// 2、更新节点高度和位置信息:
[...nodes].forEach((node: Element, index: number) => {
const rect = node.getBoundingClientRect();
const item = initList.value[startIndex.value + index];
const dHeight = item?.height - rect?.height;
if (dHeight) {
item.height = rect.height;
item.bottom = item.bottom - dHeight;
item.dHeight = dHeight;
}
});
// 3、将当前 item 的 dHeight 进行累计,之后再重置为 0 (更新后就不再存在高度差了)
const len = initList.value.length;
let startHeight = initList.value[startIndex.value]?.dHeight;
if (startHeight) {
initList.value[startIndex.value].dHeight = 0;
}
for (let i = startIndex.value + 1; i < len; i++) {
const item = initList.value[i];
item.top = initList.value[i - 1].bottom;
item.bottom = item.bottom - startHeight;
if (item.dHeight !== 0) {
startHeight += item.dHeight;
item.dHeight = 0;
}
}
// 设置 list 高度
listHeight.value = initList.value[len - 1].bottom;
};
onMounted(async () => {
// 在页面一挂载就获取滚动区域的高度
if (waterfallWrapperRef.value) {
wrapperHeight.value = waterfallWrapperRef.value?.clientHeight;
// 预测容器最多显示多少个元素
maxCount.value = Math.ceil(wrapperHeight.value / estimatedHeight) + 1;
await nextTick();
// 先把数据显示再页面上
initData();
setItemHeight();
}
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.waterfall-wrapper {
height: 300px;
/* overflow: hidden; */
overflow-y: scroll;
/* position: relative; */
.scroll-bar {
width: 100%;
}
}
</style>


![猫头虎分享已解决Bug || RuntimeError: size mismatch, m1: [32 x 100], m2: [500 x 10]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/aa86eef0d81e4f279688a772e92ea3bc.webp#pic_center)