🕺作者: 主页
我的专栏 C语言从0到1 探秘C++ 数据结构从0到1 探秘Linux 😘欢迎关注:👍点赞🙌收藏✍️留言
🏇码字不易,你的👍点赞🙌收藏❤️关注对我真的很重要,有问题可在评论区提出,感谢支持!!!
文章目录
- 实验八
- 实验目的
- 实验准备
- 编译内核模块
- 加载内核模块
- 查看和操作文件内容
- 卸载内核模块
实验八
实验目的
通过加载内核模块,为/proc文件系统创建以下内容:
- 一个名叫proc_test的子目录。
- 一个名叫current的文件,只读,读出的内容是读它的进程的情况。
- 一个名叫current_too的链接,指向current。
- 一个名叫hello的文件,可读可写。读出的内容是上次写的内容前面加两句话。
实验准备
- 复制文件到工作目录:
- 使用将 proc_test.c 文件复制到工作目录。

- 进入工作目录:
- 进入工作目录。

编译内核模块
- 编译 proc_test.c 模块:
- 编写proc_test.c代码
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/init_task.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#define MAX_LENGTH 1024
static char hello_content[MAX_LENGTH] = "hello world\n"; // 初始化一个长度为 1024 的字符数组,并赋值 "hello world\n"
//用于处理对 /proc/proc_test/hello 文件的写操作。它从用户空间接收数据并将其复制到内核空间的 hello_content 数组中,偏移量为12。如果写入的字符数超过了数组长度,会返回错误。
static ssize_t hello_proc_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *pos) {
if (count > MAX_LENGTH - 1) // 如果写入的字符数大于 MAX_LENGTH - 1,则返回错误
return -EINVAL;
if (copy_from_user(hello_content + 12, buffer, count)) // 将用户空间的数据复制到内核空间的 hello_content 数组中,偏移量为 12
return -EFAULT;
hello_content[count + 12] = '\0'; // 在 hello_content 数组中写入字符串结束符'\0'
return count; // 返回成功写入的字符数
}
//用于处理对 /proc/proc_test/hello 文件的读操作。它将 hello_content 的内容输出到 seq_file 结构体中,从而在读取文件时显示出来。
static int hello_proc_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v) {
seq_printf(m, "%s", hello_content); // 将 hello_content 的内容输出到 seq_file 结构体 m 中
return 0;
}
//用于打开 /proc/proc_test/hello 文件。它调用 single_open 函数来打开文件,并指定 hello_proc_show 函数来显示文件内容。
static int hello_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
return single_open(file, hello_proc_show, NULL); // 打开 proc 文件,调用 hello_proc_show 函数来显示内容
}
//定义了对 /proc/proc_test/hello 文件的操作集合,包括打开、读取、写入、定位和释放文件。
static const struct proc_ops hello_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = hello_proc_open, // 打开文件操作
.proc_read = seq_read, // 读取文件操作
.proc_write = hello_proc_write, // 写文件操作
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek, // 文件定位操作
.proc_release = single_release, // 释放文件操作
};
//用于处理对 /proc/proc_test/current 文件的读操作。它输出当前进程的相关信息,如进程ID、优先级、进程名等。
static int current_proc_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v) {
struct task_struct *cur = current;
seq_printf(m, "进程ID: %d\n", cur->pid); // 输出进程ID
seq_printf(m, "优先级: %d\n", cur->prio); // 输出进程优先级
seq_printf(m, "静态优先级: %d\n", cur->static_prio); // 输出静态优先级
seq_printf(m, "正常优先级: %d\n", cur->normal_prio); // 输出正常优先级
seq_printf(m, "策略: %d\n", cur->policy); // 输出进程调度策略
seq_printf(m, "进程名: %s\n", cur->comm); // 输出进程名
return 0;
}
//用于打开 /proc/proc_test/current 文件。它调用 single_open 函数来打开文件,并指定 current_proc_show 函数来显示文件内容。
static int current_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
return single_open(file, current_proc_show, NULL); // 打开 proc 文件,调用 current_proc_show 函数来显示内容
}
// 定义了对 /proc/proc_test/current 文件的操作集合,包括打开、读取、定位和释放文件。
static const struct proc_ops current_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = current_proc_open, // 打开文件操作
.proc_read = seq_read, // 读取文件操作
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek, // 文件定位操作
.proc_release = single_release, // 释放文件操作
};
//模块的初始化函数,它在内核加载模块时被调用。它创建了一个名为 /proc/proc_test 的目录,并在其中创建了文件 current、current_too 和 hello。
static int __init proc_test_init(void) {
struct proc_dir_entry *test_dir;
test_dir = proc_mkdir("proc_test", NULL); // 创建一个目录 /proc/proc_test
proc_create("current", 0, test_dir, ¤t_proc_ops); // 在 /proc/proc_test 目录下创建一个名为 "current" 的文件
proc_symlink("current_too", test_dir, "current"); // 在 /proc/proc_test 目录下创建一个名为 "current_too" 的符号链接,指向 "current"
proc_create("hello", 0666, test_dir, &hello_proc_ops); // 在 /proc/proc_test 目录下创建一个名为 "hello" 的文件,可读可写权限为 0666
return 0;
}
//模块的退出函数,它在内核卸载模块时被调用。它移除了之前创建的 /proc/proc_test 目录及其下的文件。
static void __exit proc_test_exit(void) {
remove_proc_entry("proc_test/current", NULL); // 移除 /proc/proc_test 目录下的文件 "current"
remove_proc_entry("proc_test/current_too", NULL); // 移除 /proc/proc_test 目录下的文件 "current_too"
remove_proc_entry("proc_test/hello", NULL); // 移除 /proc/proc_test 目录下的文件 "hello"
remove_proc_entry("proc_test", NULL); // 移除 /proc/proc_test 目录
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); // 指定模块的许可证为 GPL
module_init(proc_test_init); // 指定模块的初始化函数
module_exit(proc_test_exit); // 指定模块的退出函数
- 使用makefile文件编译内核模块。
obj-m:=proc_test.o
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
- 使用make命令编译
make

加载内核模块
- 加载编译后的模块:
- 使用insmod加载模块。
insmod proc_test.ko

- 检查是否加载成功:
- 使用lsmod命令检查模块是否加载。
lsmod | grep proc_test

- 检查是否创建了 /proc/proc_test 目录:
- 进入/proc目录查看。
cd /proc
ls
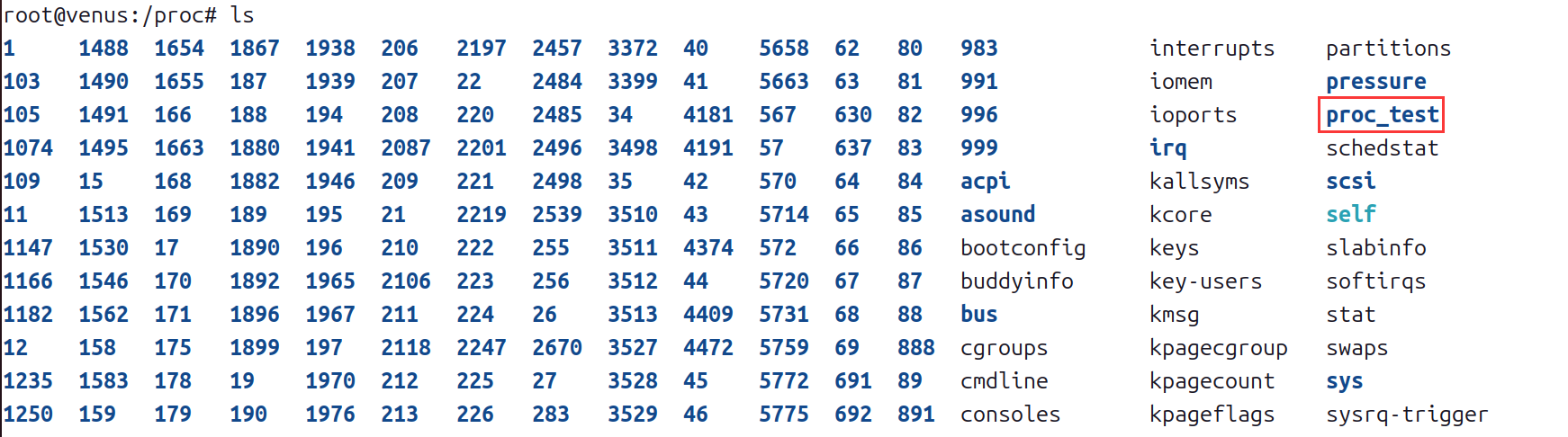
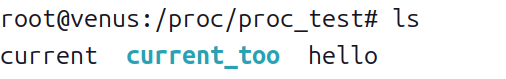
- 检查 /proc/proc_test 目录下是否创建了三个文件:
- current、current_too 和 hello。
cd /proc/proc_test
ls
查看和操作文件内容
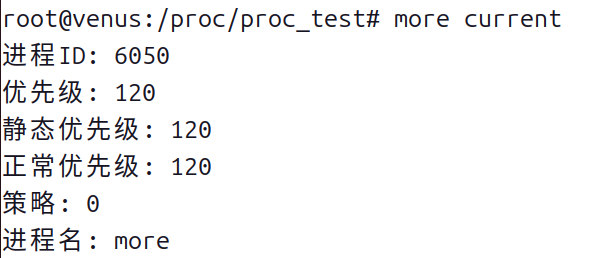
- 查看 current 文件的内容:
- 使用more命令查看。
more current
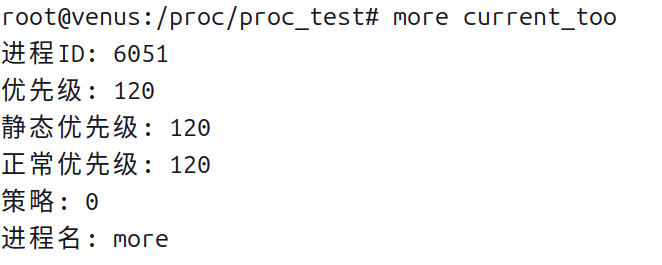
- 查看 current_too 文件的内容:
- 使用more命令查看。
more current_too
- 查看 hello 文件的内容:
- 使用more命令查看。
more hello

- 写入 hello 文件:
- 使用echo命令将数据输入到hello文件。

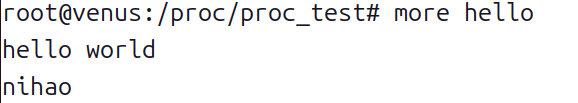
- 再次查看 hello 文件的内容:
- 使用more命令查看。
more hello
卸载内核模块
- 卸载加载的内核模块:
- 使用rmmod卸载模块。
rmmod proc_test

- 检查是否卸载成功:
- 使用lsmod命令检查模块是否卸载。
lsmod | grep proc_test