题目描述:
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:

输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
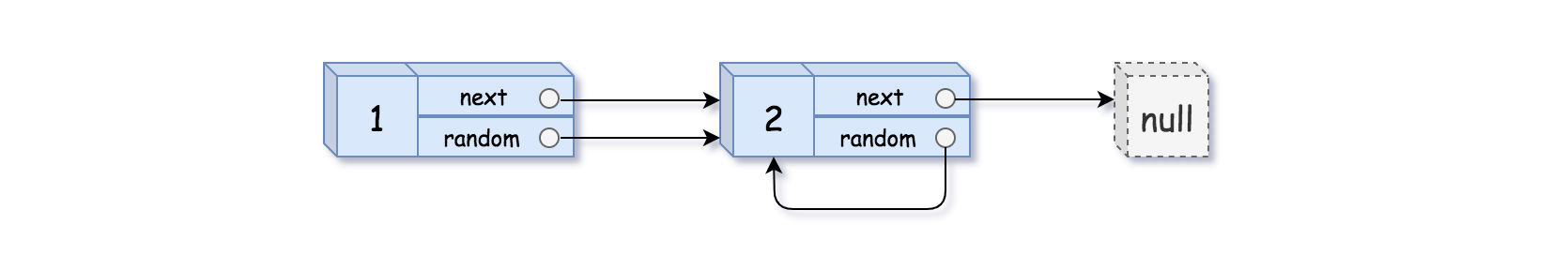
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:

输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
代码格式:
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
//write code here
}题解:
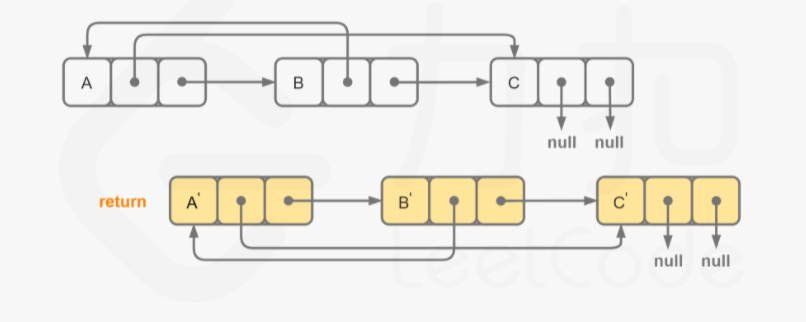
所谓穿插链表法,就是在原链表的基础上按需求插入新的节点构成新链表,然后再根据题目要求对新链表进行操作,包括拆分、排序等。
本题就可以利用穿插链表法,先在原链表每个节点后面插入一个新的拷贝节点,即其val和next的值都赋值的与原节点相同,然后通过迭代对每个拷贝节点的随机指针进行赋值,其值为指向原节点随即指针的新节点。最后分别断开为原链表和新链表即可。确实有点绕,不过下面有图,我相信你看一下就明白了。
先构造新链表:
例如对于链表 A→B→C,我们可以将其拆分为 A→A′→B→B′→C→C′
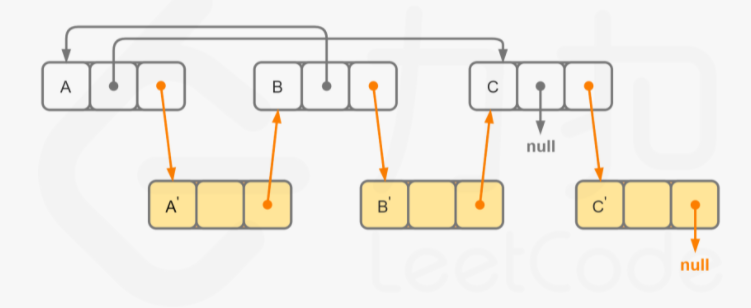
然后通过迭代赋值每个拷贝节点的随机指针。
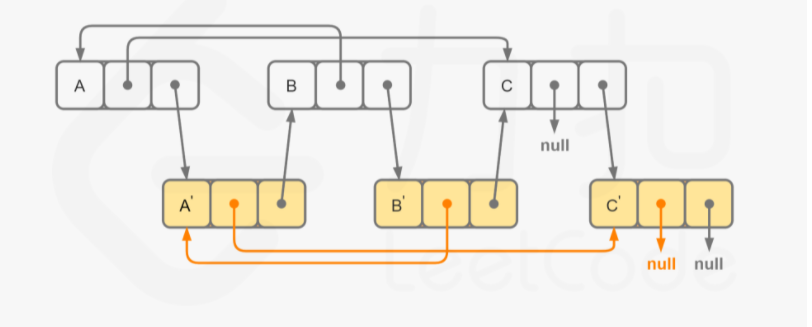
最后断开为原链表和新链表。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
//创建穿插链表
for(struct Node* cur=head;cur;cur=cur->next->next)
{
struct Node* newnode= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newnode->val=cur->val;
newnode->next=cur->next;
cur->next=newnode;
}
//给拷贝链表的random赋值
for(struct Node* cur=head;cur;cur=cur->next->next)
{
if(cur->random!=NULL)
cur->next->random=cur->random->next;
else
cur->next->random=NULL;
}
//切断穿插链表为原链表和新链表
struct Node* newhead = head->next;
for(struct Node* cur=head;cur;cur=cur->next)
{
struct Node* newnode = cur->next;//记录一下,以防丢失
cur->next=newnode->next;//先连接原链表
newnode->next=newnode->next!=NULL?newnode->next->next:NULL;
}
return newhead;
}




![[Linux]Linux项目自动化构建工具-make/Makefile](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5082d146f0734292bdf6d13eb197672f.png)