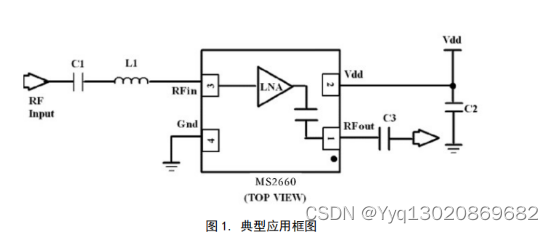
一、基本概念
1、程序是一段静态代码;进程是正在运行的程序;线程则是程序内部的执行路径。
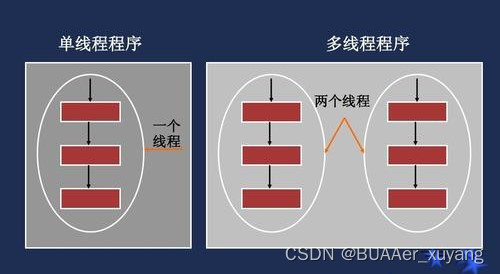
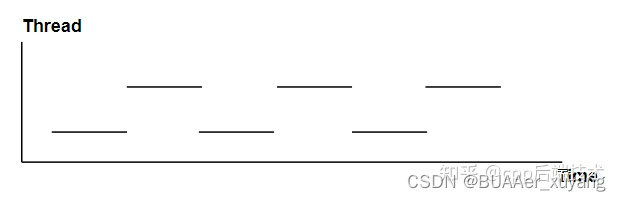
上面这张图就解释了线程和多线程的意义。
2、若一个程序在同一时间执行多个线程,便是支持多线程的。一个进程中的多个线程共享相同的内存单元/内存地址空间。
二、两种形式的多线程
1、单CPU内核的多线程
单个CPU以极高的频率轮流执行多个线程的运算,各个线程雨露均沾。
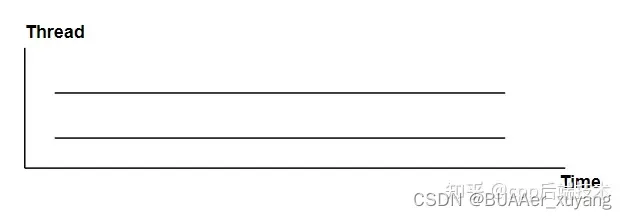
2、多CPU内核的多线程
可以做到真正的并行运算
所以,现在我们所说的软件意义上的线程和硬件意义上的线程(如我的i7就是4核心8线程)并不是同一个概念。单个CPU内核也可以模拟出多个线程。对于一般的家用电脑,运行大约100个线程是可行的。
三、Cpp的多线程
在C++11标准之前,C++多线程需要借助操作系统提供的API,如Linux的pthread.h库和Windows的<windows.h>库。C++11提供了语言层面上的多线程,包含在头文件<thread>中。它解决了跨平台的问题。以下的各个库均为C++11标准为多线程所设计的:
- thread
- mutex
- atomic
- condition_variable
- future
四、创建线程
创建线程时,必须把需要分开执行的程序封装在不同的代码块里,也就是函数里。对于线程,C++用类来描述,创建了一个Thread类的对象,即是新增了一个线程。
比如说我要分别执行两个冒泡排序,我便先写了一个冒泡排序的函数。
void bubblesort(int* array,int len)
{
for(int i=1;i<len;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len-i;j++)
{
if (array[j]>array[j+1])
{
int temp=array[j];
array[j]=array[j+1];
array[j+1]=array[j];
}
}
}
}有下面两种创建线程的方法:
std::thread thread1(bubblesort,array1,LEN);
thread1.join();1、创建线程thread1,运行函数bubblesort。对于thread构造函数,其第一个参数为所执行函数的名称(可能是引用),后面的参数则为所执行函数的参数。
std::thread (bubblesort,array1,LEN).join();2、直接创建线程(无名称),并以规定的方式运行程序。
下面给出创建线程运行的例子,以及单线程运行的对比程序。两程序输出结果均为排序算法运行时间。读者可以自行验证,多线程的效率确实大有优势!
多线程:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#define LEN 100000
void bubblesort(int* array,int len);
int main(void)
{
int* array1;
int* array2;
array1=new int[LEN];
array2=new int[LEN];
srand(time(0));
for (int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
{
array1[i]=(rand()%10000)*(rand()%10000);
array2[i]=(rand()%10000)*(rand()%10000);
}
clock_t start_time=clock();
std::thread thread1(bubblesort,array1,LEN);
std::thread thread2(bubblesort,array2,LEN);
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
clock_t stop_time=clock();
std::cout<<1.0*(stop_time-start_time)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
}
void bubblesort(int* array,int len)
{
for(int i=1;i<len;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len-i;j++)
{
if (array[j]>array[j+1])
{
int temp=array[j];
array[j]=array[j+1];
array[j+1]=array[j];
}
}
}
}单线程:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#define LEN 100000
void bubblesort(int* array,int len);
int main(void)
{
int* array1;
int* array2;
array1=new int[LEN];
array2=new int[LEN];
srand(time(0));
for (int i=0;i<LEN;i++)
{
array1[i]=(rand()%10000)*(rand()%10000);
array2[i]=(rand()%10000)*(rand()%10000);
}
clock_t start_time=clock();
bubblesort(array1,LEN);
bubblesort(array2,LEN);
clock_t stop_time=clock();
std::cout<<1.0*(stop_time-start_time)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
}
void bubblesort(int* array,int len)
{
for(int i=1;i<len;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len-i;j++)
{
if (array[j]>array[j+1])
{
int temp=array[j];
array[j]=array[j+1];
array[j+1]=array[j];
}
}
}
}五、是否循环等待 detach和join
- detach方式,启动的线程自主在后台运行,当前的代码继续往下执行,不等待新线程结束。
- join方式,等待启动的线程完成,才会继续往下执行。
1、直接一个小实验分析join的用法
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
//func1和func2这两个函数,分别打印对应内容10次
void func1()
{
int count=0;
while(count<=10)
{
std::cout<<"thread1 working"<<std::endl;
Sleep(1000);
count++;
}
}
void func2()
{
int count=0;
while(count<=10)
{
std::cout<<"thread2 working"<<std::endl;
Sleep(1000);
count++;
}
}
int main(void)
{
std::cout<<"one"<<std::endl;
std::thread thread1(func1);
std::thread thread2(func2);
std::cout<<"two"<<std::endl;
//这里使用了join,程序会一直循环等待
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
std::cout<<"three";
}程序的输出结果是:
one
two
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 workingthread2 workingthread2 working
thread1 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
three
可以看出,位于join之前的one和two还是可以被打印的,而three要等到thread1和thread2执行完毕,才被打印。可以把join理解为循环等待函数。在thread1和thread2执行完毕前,主程序一直卡在里面不继续执行,知道两个线程结束,主程序才继续执行。
(此外,由于两线程一同占用输出流,可以看到thread1的某个换行符被吞掉了,我想这是两线程占用资源冲突造成的)
2、把join改为detach重复实验
int main(void)
{
std::cout<<"one"<<std::endl;
std::thread thread1(func1);
std::thread thread2(func2);
std::cout<<"two"<<std::endl;
//这里使用了detach,主线程继续运行
thread1.detach();
thread2.detach();
std::cout<<"three";
}one
two
thread1 working
thread2 working
three
可以看到thread1和thread2中的函数只执行了一次打印,主线程就结束了。那么子线程也结束了。
3、只改一个join呢?
int main(void)
{
std::cout<<"one"<<std::endl;
std::thread thread1(func1);
std::thread thread2(func2);
std::cout<<"two"<<std::endl;
//这里使用了join,程序会一直循环等待
thread1.join();
thread2.detach();
std::cout<<"three";
}one
two
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 workingthread2 workingthread1 workingthread2 working
thread1 workingthread2 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread1 workingthread2 workingthread1 working
thread2 working
thread1 working
thread2 working
three
这印证了我们对join的理解,它的的确确就是一个循环等待函数一般的存在(像arduino里和ROS里面一样)
上面这个例子,我们可以说吗,托thread1的福,thread2也得以运行完毕,但是如果thread2运行得慢一点,那么thread2依旧无法执行完毕。
4、继续做一些操作呢?
int main(void)
{
std::cout<<"one"<<std::endl;
std::thread thread1(func1);
std::thread thread2(func2);
std::cout<<"two"<<std::endl;
thread1.detach();
std::cout<<"three"<<std::endl;
thread2.join();
std::cout<<"four";
}我把代码改成了这样,读者可以自行验证输出结果,非常有意思!
参考资料:
多线程的学习_多线程学习-CSDN博客
C++多线程详解(全网最全) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)