目录
项目MVC层级设计规范
工程项目模块设计
设计规约
Java编码规范
参考《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》,见文末参考文档
OOP 面向对象设计 & 面向接口编程
Lombok工具包依赖
Guava、Hutool 等脚手架工具包(三方包使用其一即可)
日志打印的标准格式
异常日志
业务日志
枚举Enum的使用场景
状态单例
枚举嵌套模式
简单属性标识
Constant 常量规范
涉及到如金融数据,数据类型需利用java.math.BigDecimal类型及其Api 保证精度问题
集合使用规范、Java8 Lambda表达式、 Optional 姿势要用对
线程池的使用规范
并发编程处理规范
ThreadLocal的正确使用规范
URL规范设计 尽量保持RESTful风格
了解设计模式、设计原则(接口单一原则、依赖倒置原则等),工厂模式、单例枚举等
多If else 等场景,可借鉴策略模式、Switch Case等
Controller 标准式举例
ServiceImpl 标准式举例
Dao 标准式举例 同interface 及其Impl 略写
Mapper 标准式举例
配置项规范
数据库设计规范
Redis 使用规范
参考文档
项目MVC层级设计规范
-
Controller 层 不进行业务逻辑处理,最多只进行入参校验。
-
Service 层 实现业务接口,必须通过ServiceImpl 实现类完成(面向接口编程)
-
ServiceImpl 层禁止直接调用Mapper层,需通过DAO穿透,解耦
-
DAO 层、Mapper层、Manager层 第三方调用隔离
-
Manager RESTful层 包括:微服务下第三方接口调用(类似防腐层)、MQ生产者,消费者模块、定时任务调度、ElasticSearch 增删改查模块等
-
通用逻辑处理层,如Log Aspect、工具类统一封装(尽量少定义工具方法,多利用业内标准“脚手架”)、RestTemplete、RedisTemplete等模板类自定义业务异常类等
-
包命名规范、类命名规范、接口命名规范、方法命名规范、参数属性命名规范
-
全局驼峰命名规范:
定义JSON 驼峰格式:spring.jackson.property-naming-strategy=LOWER_CAMEL_CASE
-
领域模型命名规约:
-
1)数据对象:xxxDO/xxxEntity,xxx 即为数据表名。
2)数据传输对象:xxxDTO,xxx 为业务领域相关的名称。
3)展示对象:xxxVO,xxx 一般为网页名称。
4)存储对象:xxxPO,xxx 一般为数据库实体名称,一般情况下PO 与Entity互通
4)POJO 是 DO / DTO / BO / VO/PO 的统称,禁止命名成 xxxPOJO。
-
限定符使用规范,public、protect、private、final、abstract、default等
工程项目模块设计
-
应用模块解耦、内聚逻辑标准。pom.xml 设置root module举例如:
<modules> <!-- 模块1功能 --> <module>xxxx-manage</module> <!-- 模块2功能 --> <module>xxxx-notify</module> <!-- 模块3功能 --> <module>xxxx-dispatch</module> <module>xxx-common</module> </modules> -
分模式设计、分层次设计
-
公共二方库依赖
设计规约
-
领域驱动设计(DDD)
-
面向对象设计、模块化解耦设计
-
面向未来设计、 可拓展能力设计
Java编码规范
-
参考《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》,见文末参考文档
-
OOP 面向对象设计 & 面向接口编程
1.【强制】避免通过一个类的对象引用访问此类的静态变量或静态方法,无谓增加编译器解析成本,直接用类名来访问即可。
2.【强制】所有的覆写方法,必须加 @Override 注解。 增强编译期代码校验。
3.【强制】相同参数类型,相同业务含义,才可以使用的可变参数,参数类型避免定义为 Object。
说明:可变参数必须放置在参数列表的最后。(但强烈建议开发者尽量不用可变参数编程)
正例但不建议使用:public List<User> listUsers(String type, Long... ids) {...}
4.【强制】外部正在调用的接口或者二方库依赖的接口,不允许修改方法签名,避免对接口调用方产生影响。接口过时必须加 @Deprecated 注解。
5.【强制】Object 的 equals 方法容易抛空指针异常,应使用常量或确定有值的对象来调用 equals。
正例:"test".equals(param);
反例:param.equals("test");
说明:推荐使用 JDK7 引入的工具类 java.util.Objects#equals(Object a, Object b)
6.【强制】任何货币金额,有关金融金额的数值问题 强烈建议使用BigDecimal类型,并利用其api实现增减乘除等运算。注意小数位的截断精度问题处理。涉及到金额的,强烈注意精度问题。
}
7.【强制】BigDecimal 的等值比较应使用 compareTo() 方法,而不是 equals() 方法。
说明:equals() 方法会比较值和精度(1.0 与 1.00 返回结果为 false),而 compareTo() 则会忽略精度。
8.根据实际需要操作字符串拼接方式
StringBuilder 非线程安全
StringBuffer (Synchronized append)线程安全
9.深拷贝与浅拷贝问题
【推荐】慎用 Object 的 clone 方法来拷贝对象。
说明:对象 clone 方法默认是浅拷贝,若想实现深拷贝需覆写 clone 方法实现域对象的深度遍历式拷贝。
10.SimpleDateFormat 是线程不安全的类
【强制】SimpleDateFormat 是线程不安全的类,一般不要定义为 static 变量,如果定义为 static,必须加锁synchronized 关键字实现锁,或者使用 DateUtils 工具类。
正例:注意线程安全,使用 DateUtils。亦推荐如下处理:
private static final ThreadLocal<DateFormat> dateStyle = new ThreadLocal<DateFormat>() {
@Override
protected DateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
}
};
或者如ThreadLocal 保障SimpleDateFormat 线程安全
private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> DATE_FORMATTER = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat(DATE_FORMAT));
private static long getDate(String date) {
try {
if (date.length() == DATE_TIME_FORMAT.length()) {
return DATE_TIME_FORMATTER.get().parse(date).getTime();
} else if (date.length() == DATE_FORMAT.length()) {
return DATE_FORMATTER.get().parse(date).getTime();
} else {
log.error("the date format is invalid,date value:{}", date);
return 0;
}
} catch (ParseException e) {
log.error("the date format is invalid,date value:{}", date);
return 0;
}
}
说明:如果是 JDK8 的应用,可以使用 Instant 代替 Date,LocalDateTime 代替 Calendar,DateTimeFormatter 代替 SimpleDateFormat,官方给出的解释:simple beautiful strong immutable thread-safe。
11. Random
【推荐】避免 Random 实例被多线程使用,虽然共享该实例是线程安全的,但会因竞争同一 seed 导致的性能下降。
说明:Random 实例包括 java.util.Random 的实例或者 Math.random() 的方式。
正例:在 JDK7 之后,可以直接使用 API ThreadLocalRandom,而在 JDK7 之前,需要编码保证每个线程持有一个单独的 Random 实例。
12 switch
【强制】在一个 switch 块内,每个 case 要么通过 continue / break / return 等来终止,要么注释说明程序将继续执行到哪一个 case 为止;在一个 switch 块内,都必须包含一个 default 语句并且放在最后,即使它什么代码也没有。
说明:注意 break 是退出 switch 语句块,而 return 是退出方法体。
举例说明break方式如下
switch (messageMode) {
case REALTIME:
rabbitBinding = new RabbitRealTimeQueueBinding(rabbitAdmin, registerInfo, name, tags, existRealtimeQueueRoutingKeys);
break;
case DELAY:
rabbitBinding = new RabbitDelayQueueBinding(rabbitAdmin, registerInfo, name, tags, existRealtimeQueueRoutingKeys, existDelayQueueRoutingKeys);
break;
case TIMING:
rabbitBinding = new RabbitTimingQueueBinding(rabbitAdmin, registerInfo, name, tags, existRealtimeQueueRoutingKeys, existDelayQueueRoutingKeys);
break;
default:
throw new MessageBusException("invalid message mode " + messageMode);
}
rabbitBinding.build();
或者 return 方式的
public static BaseRabbitListener createWrapper(String queueName) {
switch (queueName) {
case STORAGE_QUEUE_NAME:
return new RabbitMessageListenerWrapper1();
case TRACING_QUEUE_NAME:
return new RabbitTracingListenerWrapper2();
default:
throw new MessageBusException("invalid queue name " + queueName);
}
}-
Lombok工具包依赖
@Slf4j、@Data、@Getter、@NoArgsConstructor、@Accessors(chain = true)、@Builder等常用注解 -
Guava、Hutool 等脚手架工具包(三方包使用其一即可)
maven参考依赖: <dependency> <groupId>cn.hutool</groupId> <artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId> <version>5.8.0.M4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>22.0</version> </dependency> -
日志打印的标准格式
异常日志
- Error级别
- 异常暴露方法 及业务操作关键信息
- 完全异常栈信息
-
举例如下
日志标准化格式: log.error("webhook happens Exception . alertname={}, url={}, params={}, exceptionMsg:", alertname, url, params, e); 业务异常-状态码设计 枚举统一定义 code-statusMsg 模式业务日志
-
Info、Debug级别
-
业务操作关键信息
-
举例如下
日志标准化格式: log.info("AlertManagerWatchDogService started. watchDogKey:{},envServerName:{}", watchDogKey, this.getEnvServerName()); -
枚举Enum的使用场景
状态单例
模式说明
常见场景如表示某些类型、状态、种类、标签等通用模式。
代码举例
/**
* 订单状态 枚举
*/
@Getter
public enum OrderStateEnum {
CHECKING(1, "待审核"),
NOT_PASSED_CHECK(2, "审核未通过"),
PASSED_CHECK(3, "审核通过"),
PARTIAL_DELIVERY(4, "部分发货"),
ALL_DELIVERY(5, "全部发货"),
FINISHED(6, "已完成"),
CANCELED(7, "已取消");
private static final Map<Integer, OrderStateEnum> VALUE_MAP = new HashMap<>(OrderStateEnum.values().length);
static {
for (OrderStateEnum orderStateEnum : OrderStateEnum.values()) {
VALUE_MAP.put(orderStateEnum.getType(), orderStateEnum);
}
}
private Integer type;
private String desc;
OrderStateEnum(Integer type, String desc) {
this.type = type;
this.desc = desc;
}
public static OrderStateEnum getOrderStateEnumByType(Integer type) {
if (!VALUE_MAP.containsKey(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未定义的枚举类型值:" + type);
}
return VALUE_MAP.get(type);
}
}枚举嵌套模式
模式说明
枚举内包含其他枚举类型,如例子中的WorkOrderSubStatusEnum 包含嵌套WorkOrderStatusEnum类型。
代码举例
public enum WorkOrderSubStatusEnum {
/**
* 待派单
*/
UNALLOCATED(WorkOrderStatusEnum.UNALLOCATED, "UNALLOCATED", "待派单(评估师)"),
/**
* 待上门
*/
UNVISITED(WorkOrderStatusEnum.UNINSPECTED, "UNVISITED", "待上门"),
/**
* 重联系
*/
RECONTACT(WorkOrderStatusEnum.UNINSPECTED, "RECONTACT", "重联系"),
/**
* 验车中
*/
INSPECTING(WorkOrderStatusEnum.INSPECTING, "INSPECTING", "验车中"),
/**
* 审核未通过
*/
RETURNED(WorkOrderStatusEnum.INSPECTING, "RETURNED", "审核未通过"),
/**
* 待补充资料
*/
REPLENISH(WorkOrderStatusEnum.INSPECTING, "REPLENISH", "待补充资料"),
/**
* 关闭
*/
CLOSED(WorkOrderStatusEnum.CLOSED, "CLOSED", "关闭"),
/**
* 已验收
*/
INSPECTED(WorkOrderStatusEnum.INSPECTED, "INSPECTED", "已验收");
public WorkOrderStatusEnum getParentStatus() {
return parentStatus;
}
private WorkOrderStatusEnum parentStatus;
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public String getStatusDesc() {
return statusDesc;
}
private String status;
private String statusDesc;
WorkOrderSubStatusEnum(WorkOrderStatusEnum parentStatus, String status, String statusDesc) {
this.parentStatus = parentStatus;
this.status = status;
this.statusDesc = statusDesc;
}
}简单属性标识
模式说明
常用于标识特定简单对立属性,比如是/否。好/坏。方便代码中直接区分“true/false”等相反逻辑。
代码举例
public enum WhetherEnum {
NO(0, "否"), YES(1, "是");
private Integer code;
private String desc;
WhetherEnum(Integer code, String desc) {
this.code = code;
this.desc = desc;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public static String getDesc(Integer code) {
for (WhetherEnum e: values()) {
if (e.getCode().equals(code)) {
return e.getDesc();
}
}
return null;
}
}-
Constant 常量规范
-
不要使用一个常量类维护所有常量,要按常量功能进行归类,分开维护。但建议在同一common包下维护。
-
常量名称定义规范,尽量保持大写。多结构关联用下划线‘_’。举例如:private static final String MY_NAME="hello world"。
-
long 或 Long 赋值时,数值后使用大写 L,不能是小写 l,小写容易跟数字混淆,造成误解。
-
浮点数类型的数值后缀统一为大写的 D 或 F。
-
有些常量类内属性 也可以通过在interface 、enum等定义实现,可灵活掌握。
-
涉及到如金融数据,数据类型需利用java.math.BigDecimal类型及其Api 保证精度问题
BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend) // 加法操作 BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend) // 减法操作 BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplieand) // 乘法操作 BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor,int scale,int roundingMode ) // 除法操作 new BigDecimal(0).setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));//保留2位小数模式名称 说明 BigDecimal.ROUND_UP 商的最后一位如果大于 0,则向前进位,正负数都如此 BigDecimal.ROUND_DOWN 商的最后一位无论是什么数字都省略 BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING 商如果是正数,按照 ROUND_UP 模式处理;如果是负数,按照 ROUND_DOWN
模式处理BigDecimal.ROUND_FLOOR 与 ROUND_CELING 模式相反,商如果是正数,按照 ROUND_DOWN 模式处理;
如果是负数,按照 ROUND_UP 模式处理BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_ DOWN 对商进行五舍六入操作。如果商最后一位小于等于 5,则做舍弃操作,否则对最后
一位进行进位操作BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP 对商进行四舍五入操作。如果商最后一位小于 5,则做舍弃操作,否则对最后一位
进行进位操作BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_EVEN 如果商的倒数第二位是奇数,则按照 ROUND_HALF_UP 处理;如果是偶数,则按
照 ROUND_HALF_DOWN 处理
-
集合使用规范、Java8 Lambda表达式、 Optional 姿势要用对
1.多线程并发环境,集合类需使用J.U.C包下的线程安全集合类。如常见的ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArrayList等。 2.List、Set的区别。HashMap、ArrayList、LinkedList、TreeSet、TreeMap等。 3.集合的使用 必须用泛型强制约束对象类型,不建议用Object、JSONObject等弱类型。 正例如: List<CirclePictureVo> result = new ArrayList<>(); Map<Integer, UserEntity> users = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, UserEntity>(); 4.java8 使用lambda表达式对象转map时重复key Duplicate key xxxx 常规解决方案 我们需要使用toMap的另外一个重载的方法! Collectors.toMap(keyMapper, valueMapper, mergeFunction) 举例如: 若不允许重复key 且需覆盖上一个老值的情况 Map<String, String> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student :: getClassName, Student :: getStudentName, (value1, value2)-> value2)); 若不允许重复key 则按默认处理 无需覆盖,存在则抛异常来中断流程。 如Map<String, DataCenter> dataCenterMap = dataCenterList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(DataCenter::generateTenantId, Function.identity())); 5.集合的判空 【强制】org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils#sEmpty 或者org.apache.commons.collections.MapUtils#isEmpty 【禁止】map.isEmpty()、list.isEmpty()等方式,因为map、list等可能为null NPE等问题 字符串判空 org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isBlank org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isEmpty 6. 【强制】不要在 foreach 循环里进行元素的 remove / add 操作。remove 元素请使用 iterator 方式, 如果并发操作,需要对 iterator 对象加锁。//集合的fail-fast快速失败检测机制,并发检查异常ConcurrentModificationExceptionJAVA的Stream流相关操作举例
Java8 Optional 使用方法详解
-
线程池的使用规范
Java并发编程:线程池的使用
正确使用java线程池
public class ThreadFactoryBuilder { private String nameFormat = null; //利用自定义线程工厂 指定线程名称 private Boolean daemon = null; private Integer priority = null; private Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler = null; private ThreadFactory backingThreadFactory = null; public ThreadFactoryBuilder() { } public ThreadFactoryBuilder setNameFormat(String nameFormat) { String.format(nameFormat, 0); this.nameFormat = nameFormat; return this; } public ThreadFactoryBuilder setDaemon(boolean daemon) { this.daemon = daemon; return this; } public ThreadFactoryBuilder setPriority(int priority) { if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("Thread priority (%s) must be >= %s", priority, Thread.MIN_PRIORITY)); } if (priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("Thread priority (%s) must be <= %s", priority, Thread.MAX_PRIORITY)); } this.priority = priority; return this; } public ThreadFactoryBuilder setUncaughtExceptionHandler(Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler) { if (null == uncaughtExceptionHandler) { throw new NullPointerException(); } this.uncaughtExceptionHandler = uncaughtExceptionHandler; return this; } public ThreadFactoryBuilder setThreadFactory(ThreadFactory backingThreadFactory) { if (null == backingThreadFactory) { throw new NullPointerException(); } this.backingThreadFactory = backingThreadFactory; return this; } public ThreadFactory build() { return build(this); } private static ThreadFactory build(ThreadFactoryBuilder builder) { final String nameFormat = builder.nameFormat; final Boolean daemon = builder.daemon; final Integer priority = builder.priority; final Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler uncaughtExceptionHandler = builder.uncaughtExceptionHandler; final ThreadFactory backingThreadFactory = (builder.backingThreadFactory != null) ? builder.backingThreadFactory : Executors.defaultThreadFactory(); final AtomicLong count = (nameFormat != null) ? new AtomicLong(0) : null; return runnable -> { Thread thread = backingThreadFactory.newThread(runnable); if (nameFormat != null) { thread.setName(String.format(nameFormat, count.getAndIncrement())); } if (daemon != null) { thread.setDaemon(daemon); } if (priority != null) { thread.setPriority(priority); } if (uncaughtExceptionHandler != null) { thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(uncaughtExceptionHandler); } return thread; }; } } --使用姿势举例1 Runnable-- ThreadFactory producerProcessorThreadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder() .setNameFormat("producer-processor-pool-executor-%d") .setUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) -> log.error("Thread " + t.getName() + " throws uncaught exception", e)) .build(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 10, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(40), producerProcessorThreadFactory ); //核心线程数、最大线程数等参数可通过配置读取 threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> { //业务逻辑 }); --使用姿势举例2 Future Callable方式-- List<CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto> carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDtoList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>(carDetailRequestDtos.size())); List<Future<CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto>> futureList = new ArrayList();// 创建多个有返回值的任务 carDetailRequestDtos.forEach(carDetailRequestDto -> { Callable callable = new CarWarrantyInfoCallable(carDetailRequestDto); Future future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(callable);// 执行任务并获取Future对象 futureList.add(future); }); for (Future<CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto> future : futureList) { carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDtoList.add(future.get()); // 从Future对象上获取任务的返回值 } return carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDtoList; class CarWarrantyInfoCallable implements Callable<CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto> { private CarDetailRequestDto carDetailRequestDto; CarWarrantyInfoCallable(CarDetailRequestDto carDetailRequestDto) { this.carDetailRequestDto = carDetailRequestDto; } @Override public CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto call() throws Exception { CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto = doCall(carDetailRequestDto); return carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto; } CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto doCall(CarDetailRequestDto carDetailRequestDto) { CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto = new CarDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto(); //业务逻辑 return carDetailSimpleV1ResponseDto; } }【强制】线程池不允许使用Executors去创建,而是通过ThreadPoolExecutor的方式, 这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。 说明:Executors各个方法的弊端: 1)newFixedThreadPool和newSingleThreadExecutor: 主要问题是堆积的请求处理队列可能会耗费非常大的内存,甚至OOM。 2)newCachedThreadPool和newScheduledThreadPool: 主要问题是线程数最大数是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建数量非常多的线程,甚至OOM。 -
并发编程处理规范
【强制】高并发时,同步调用应该去考量锁的性能损耗。能用无锁数据结构,就不要用锁;能锁区块,就 不要锁整个方法体;能用对象锁,就不要用类锁。
说明:尽可能使加锁的代码块工作量尽可能的小,避免在锁代码块中调用 RPC 方法。
-
ThreadLocal的正确使用规范
线程池场景下的线程变量传递问题 解决方案:ThreadLocal、InheritableThreadLocal、TransmittableThreadLocal
ThreadLocal的垃圾对象内存释放问题,防止OOM问题。
【强制】必须回收自定义的 ThreadLocal 变量,如果不正确清理自定义的 ThreadLocal 变量,可能会影响后续业务逻辑和造成内存泄露等问题。所以尽量在代理中使用
try-finally 块进行回收。
正例如下
正例:
objectThreadLocal.set(userInfo);
try {
// ...
} finally {
objectThreadLocal.remove();
} -
URL规范设计 尽量保持RESTful风格
RESTful风格的接口命名规范
-
了解设计模式、设计原则(接口单一原则、依赖倒置原则等),工厂模式、单例枚举等
23 种设计模式(Java代码演示版)
-
多If else 等场景,可借鉴策略模式、Switch Case等
设计模式之策略模式(场景说明)
设计模式之策略模式(常规版&Lambda Function版)
-
Controller 标准式举例
//入参 多参数需封装Req DTO。入参参数校验 利用@Validated 、@NotBlank、@NotNull等
//抛异常的正确姿势 禁用 e.getMessage(),防止异常栈信息打印不全
//返回结果 data有实际含义。error/success标准化。业务状态码规范约束(标准枚举化)
禁止Map/JSONObject等弱类型 入参、返回值
定义结构化统一通用返回体如下:Response、构造器模式ResponseBuilder//通用返回体Demo
public class Response<T> {
private int version = 0;
private int status = 0;
private String errMsg = "";
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
private String errorMsg = "";
private long ts = System.currentTimeMillis();
private T data;
public Response() {
}
public static <T> ResponseBuilder<T> builder() {
return new ResponseBuilder();
}
public static <T> Response<T> ok() {
return ok((Object)null);
}
public static <T> Response<T> ok(T data) {
return ok(0, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> ok(int version, T data) {
return ok(version, System.currentTimeMillis(), data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> ok(int version, long ts, T data) {
return of(ErrorCode.OK, version, ts, "ok", data);
}
public void setErrorCode(ErrorCode code) {
this.setErrorCode(code, code.getMsg());
}
public void setErrorCode(ErrorCode code, String msg) {
if (null != code) {
this.status = code.getCode();
this.errMsg = msg;
this.errorMsg = msg;
}
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code) {
return of(code, code.getMsg());
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code, T data) {
return of(code, (String)null, data);
}
public static Response<String> error(String data, ErrorCode code) {
return of(code, (String)null, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code, String msg) {
return of(code, msg, (Object)null);
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code, String msg, T data) {
return of(code, 0, msg, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code, int version, String msg, T data) {
return of(code, version, System.currentTimeMillis(), msg, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> error(ErrorCode code, int version, long ts, String msg, T data) {
return of(code, version, ts, msg, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code) {
return of(code, code.getMsg());
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code, T data) {
return of(code, (String)null, data);
}
public static Response<String> of(String data, ErrorCode code) {
return of(code, (String)null, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code, String msg) {
return of(code, msg, (Object)null);
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code, String msg, T data) {
return of(code, 0, msg, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code, int version, String msg, T data) {
return of(code, version, System.currentTimeMillis(), msg, data);
}
public static <T> Response<T> of(ErrorCode code, int version, long ts, String msg, T data) {
Response<T> resp = new Response();
resp.setErrorCode(code);
resp.setData(data);
if (null != msg) {
resp.setErrMsg(msg);
}
resp.setVersion(version);
resp.setTs(ts);
return resp;
}
public int getStatus() {
return this.status;
}
public void setStatus(int status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getErrMsg() {
return this.errMsg;
}
public void setErrMsg(String errMsg) {
this.errMsg = errMsg;
this.errorMsg = errMsg;
}
public T getData() {
return this.data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public String getErrorMsg() {
return this.errorMsg;
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public void setErrorMsg(String errorMsg) {
this.errMsg = errorMsg;
this.errorMsg = errorMsg;
}
public int getVersion() {
return this.version;
}
public void setVersion(int version) {
this.version = version;
}
public long getTs() {
return this.ts;
}
public void setTs(long ts) {
this.ts = ts;
}
public String toString() {
return "Response{version=" + this.version + ", status=" + this.status + ", errMsg='" + this.errMsg + '\'' + ", errorMsg='" + this.errorMsg + '\'' + ", ts=" + this.ts + ", data=" + this.data + '}';
}
}
public final class ResponseBuilder<T> {
private Response<T> response = new Response();
public ResponseBuilder() {
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> version(int version) {
this.response.setVersion(version);
return this;
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> timestamp(long timestamp) {
this.response.setTs(timestamp);
return this;
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> status(int status) {
this.response.setStatus(status);
return this;
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> message(String message) {
this.response.setErrMsg(message);
return this;
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> code(ErrorCode code) {
this.response.setErrorCode(code);
return this;
}
public ResponseBuilder<T> data(T data) {
this.response.setData(data);
return this;
}
public Response<T> build() {
return this.response;
}
}-
ServiceImpl 标准式举例
//单一方法,逻辑聚合。不建议同一方法实现多个不相干的业务逻辑,可定义对应业务的Impl //方法体过大、逻辑过于复杂。建议 进行方法的原子拆分、方法的抽象、继承 禁止嵌套循环、循环调用DAO等 -
Dao 标准式举例 同interface 及其Impl 略写
-
Mapper 标准式举例
尽量避免多表关联查询、Concat函数拼接等,尽量降低mysql等数据库的SQL计算压力 不允许物理删除(delete)、建议逻辑删除 deleted=1 尽量避免 select * 。模糊字段情况 -
配置项规范
根据逻辑规范化 建立对应文件夹、特性.yml配置项 基于Property 实体配置项对象读取配置。禁止直接通过 @Value 分散配置项 yml 规范化 缩进两个字符 定义@Configuration、@PropertySource 的bean demo举例如下 @Data @Slf4j @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "grade") @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:grade/grade-config-${spring.profiles.active}.yml", "file:${spring.config.location}/grade/grade-config-${spring.profiles.active}.yml"}, ignoreResourceNotFound = true, factory = YamlPropertyLoaderFactory.class ) public class GradeConfig { /** * 打电话功能开关 false 关闭打电话功能 true 开启打电话功能 */ private boolean phoneSwitch; } -
不允许项目中利用分散、散落的数字表示 判断状态、类型等逻辑
-
不允许基于异常 做业务逻辑
-
自定义注解 实现切面逻辑
@Target({ ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyCustomizeAnnotation { } @Component @Aspect public class CustomizeAspect { //使用@annotation配置匹配所有还有指定自定义注解的方法 @Pointcut("@annotation(com.st.dk.demo7.annotations.MyCustomizeAnnotation)") private void pointCut1() { } //定义一个前置通知 @Before("pointCut1()") private static void before() { System.out.println("---前置通知---"); //切面实现的逻辑code } @Pointcut("execution(public * com.business.*.controller.*..*.*(..))") public void myPointCut() { } @Around("myPointCut()") public Object businessMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { //切面实现的逻辑code } } -
日期和时间规范:如利用json property注解 @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
-
注释规范
-
前后端数据传递规约
-
其他
-
数据库设计规范
-
建表规约
-
Sql demo:
CREATE TABLE `test_demo_table` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id|作者名|2022-12-07', `demo_column_code` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '编码|作者名|2022-12-07', `demo_column_id` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'id|作者名|2022-12-07', `demo_column_name` varchar(128) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '名称|作者名|2022-12-07', `demo_column_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT 'xxx时间|作者名|2022-12-07', `demo_column_value` varchar(128) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'xxx 字段值|刘超|2022-12-07', `create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间|作者名|2022-12-07', `update_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间|作者名|2022-12-07', `deleted` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '逻辑删除', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) , KEY `idx_create_time` (`create_time`) USING BTREE, KEY `idx_update_time` (`update_time`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_general_ci COMMENT = '表定义的说明描述'; -
索引规约
主键索引
唯一索引
-
SQL规约
--增加字段-- alter table demoTableName add demo_columnName varchar(255) null comment '字段名称说明'; --删除字段-- alter table demoTableName drop column demo_columnName; --修改字段-- alter table demoTableName modify demo_columnName varchar(255) null comment '字段名称说明'; --插入sql-- INSERT INTO demoTableName (id, label, value, menu_id, create_by, update_by) VALUES (1, '门店及人员管理', '门店及人员管理', 2097, null, null); -
ORM映射
-
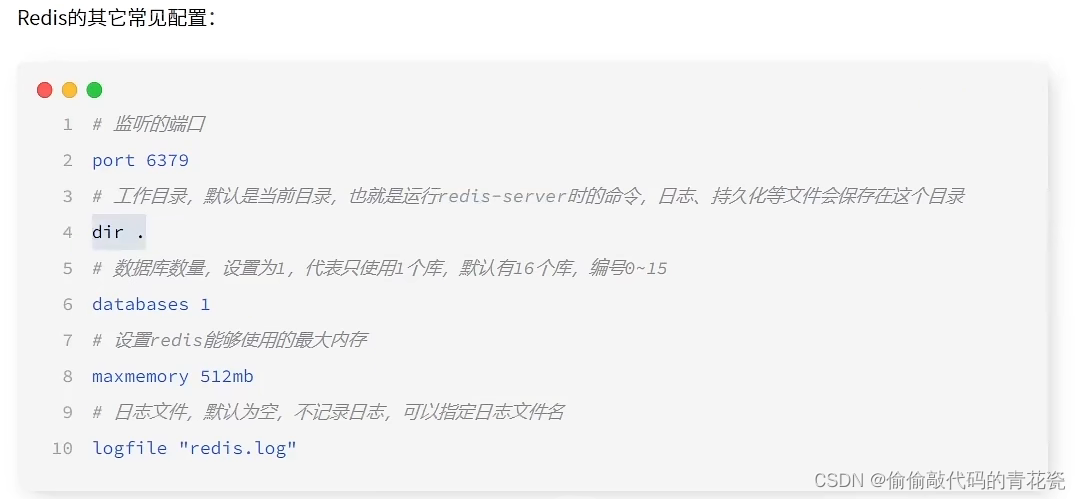
Redis 使用规范
-
各数据类型的常规使用场景
-
可利用RedisTemplate 模板类实现统一通用调度api
-
Big Key、Keys * 问题
-
Key 定义格式标准:可以区分业务逻辑,加相应的prefix 前缀
-
Value 存储,String 、Hash 类型 序列化
-
可利用ObjectMapper 实现JSON序列化 如
@Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); // 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class); ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper); // 设置value的序列化规则和 key的序列化规则 redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } -
TTL 约定
-
设置的key过期时间需要合理、满足业务要求
-
参考文档
-
《阿里巴巴Java开发手册.pdf》
-
RichardGeek CSDN 整理博客
 https://blog.csdn.net/CoderTnT
https://blog.csdn.net/CoderTnT