1、说明
Sentinel主要用来流控,熔断降级保护目标资源用的,常用集成SCG,SpringBoot,SprinMVC这些,但底层本质没变,但是体现形式上会有差别。例如SCG底层是Netty 和 SpringWebFlux 采用Reactor Stream处理,SpringBoot内部通过AOP处理流控这些。
以网关形式展现Sentinel调用流程吧,网关Sentinel都会了,其它应用集成就更好理解了
2、准备
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel-gateway 适配包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-spring-cloud-gateway-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.8.1</version>
</dependency>
SCG集成Sentinel所需配置
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfiguration {
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public GatewayConfiguration(ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer) {
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler sentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler() {
// Register the block exception handler for Spring Cloud Gateway.
return new SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler(viewResolvers, serverCodecConfigurer);
}
@Bean
@Order(-1)
public GlobalFilter sentinelGatewayFilter() {
return new SentinelGatewayFilter();
}
}
往IOC容器中注入两个javaBean,SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler Sentinel异常处理器,SentinelGatewayFilter Sentinel流控过滤器
3、大致流程
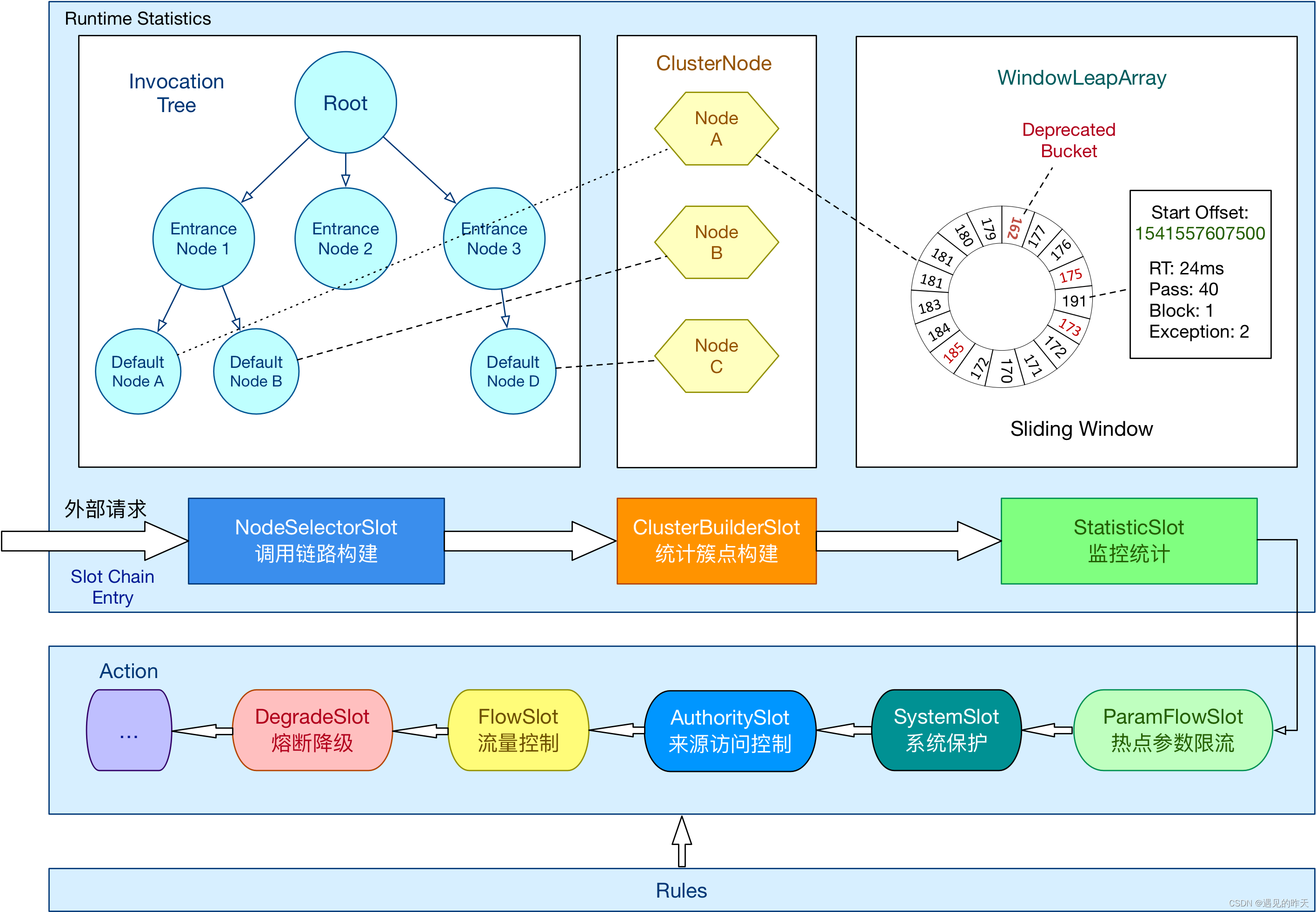
4、Sentinel执行流程
4.1、SentinelGlobalFilter
public class SentinelGatewayFilter implements GatewayFilter, GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private final int order;
// filterChain 中 filter执行优先级
public SentinelGatewayFilter() {
this(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
}
public SentinelGatewayFilter(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
private final GatewayParamParser<ServerWebExchange> paramParser = new GatewayParamParser<>(
new ServerWebExchangeItemParser());
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
// 获取当前路由
Route route = exchange.getAttribute(ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
Mono<Void> asyncResult = chain.filter(exchange);
if (route != null) {
String routeId = route.getId();
// 解析参数 以备参数流控
Object[] params = paramParser.parseParameterFor(routeId, exchange,
r -> r.getResourceMode() == SentinelGatewayConstants.RESOURCE_MODE_ROUTE_ID);
String origin = Optional.ofNullable(GatewayCallbackManager.getRequestOriginParser())
.map(f -> f.apply(exchange))
.orElse("");
// 定义流控发布者,准备流控/熔断
asyncResult = asyncResult.transform(
new SentinelReactorTransformer<>(new EntryConfig(routeId, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_API_GATEWAY,
EntryType.IN, 1, params, new ContextConfig(contextName(routeId), origin)))
);
}
Set<String> matchingApis = pickMatchingApiDefinitions(exchange);
for (String apiName : matchingApis) {
// 解析参数 以备参数流控
Object[] params = paramParser.parseParameterFor(apiName, exchange,
r -> r.getResourceMode() == SentinelGatewayConstants.RESOURCE_MODE_CUSTOM_API_NAME);
// 定义流控发布者,准备流控/熔断
asyncResult = asyncResult.transform(
new SentinelReactorTransformer<>(new EntryConfig(apiName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_API_GATEWAY,
EntryType.IN, 1, params))
);
}
return asyncResult;
}
private String contextName(String route) {
return SentinelGatewayConstants.GATEWAY_CONTEXT_ROUTE_PREFIX + route;
}
Set<String> pickMatchingApiDefinitions(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return GatewayApiMatcherManager.getApiMatcherMap().values()
.stream()
.filter(m -> m.test(exchange))
.map(WebExchangeApiMatcher::getApiName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return order;
}
}
SCG中只要匹配到route之后,通过FilteringWebHandler构建FiterChain,SentinelGlobalFilter会被执行。
4.2 EntryConfig
定义限流资源配置(Sentinel访问令牌配置)
new EntryConfig(routeId, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_API_GATEWAY, EntryType.IN, 1, params, new ContextConfig(contextName(routeId), origin))
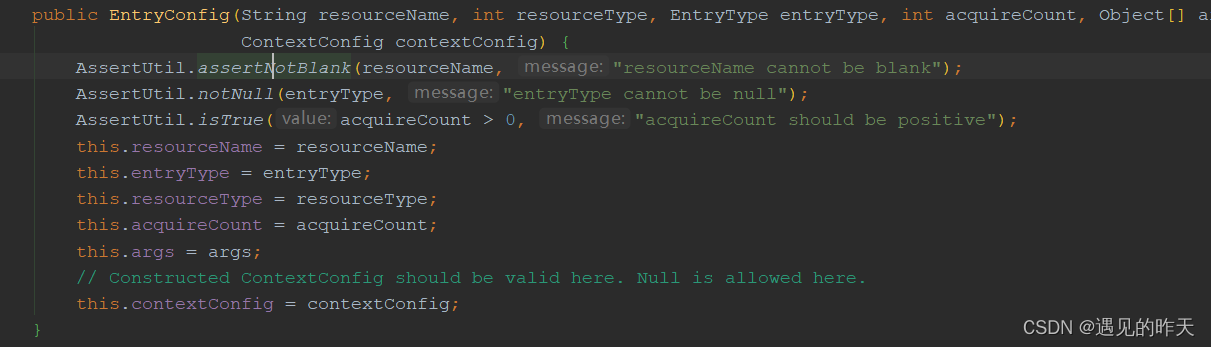
- resourceName:默认将路由id作为访问的资源名
- entryType:EntryType.IN
- resourceType:网关类型,集成在网关
- acquireCount:入口流量默认1
- args: 热点参数流控项
- contextConfig 上下文配置
4.3、SentinelReactorTransformer
SentinelReactorTransformer 主要用来将publisher发布者进行转换的
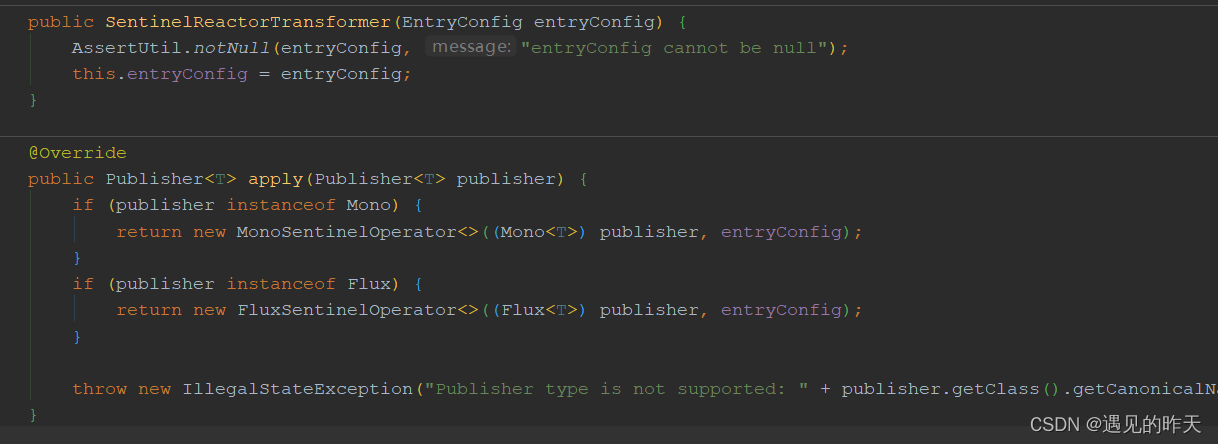
接收到EntryConfig之后,进行存储
@Override
public Publisher<T> apply(Publisher<T> publisher) {
if (publisher instanceof Mono) {
return new MonoSentinelOperator<>((Mono<T>) publisher, entryConfig);
}
if (publisher instanceof Flux) {
return new FluxSentinelOperator<>((Flux<T>) publisher, entryConfig);
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Publisher type is not supported: " + publisher.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
通过transfer调用apply封装
4.4 MonoSentinelOperator
流控发布者
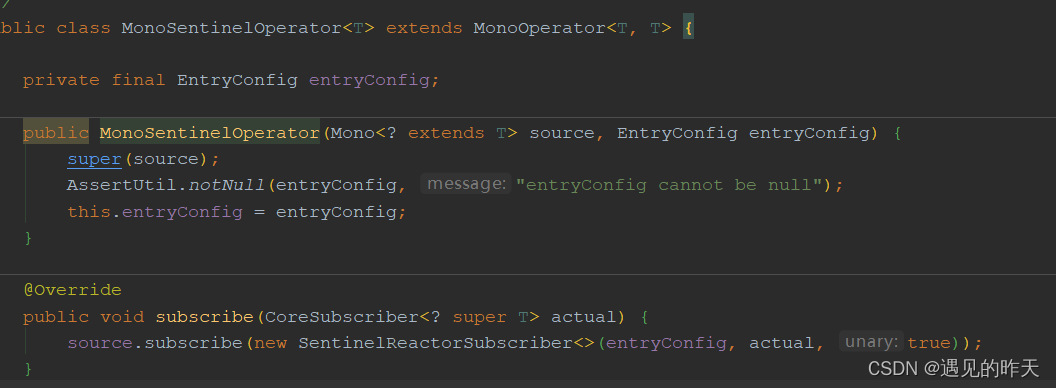
当请求进来的时候,消费者(subscriber)会订阅MonoSentinelOperator,FluxSentinelOperator,调用内部的subscribe方法,正式触发Sentinel流控
4.5 SentinelReactorSubscriber
订阅者负责处理请求,进行流控,SCG流控真正的入口
private void entryWhenSubscribed() {
// 获取上下文配置
ContextConfig sentinelContextConfig = entryConfig.getContextConfig();
if (sentinelContextConfig != null) {
// 一般情况下走不到这里,因为会自己创建ContextConfig
// If current we're already in a context, the context config won't work.
// 如果没有配置上下文,尝试获取上下文,并缓存
ContextUtil.enter(sentinelContextConfig.getContextName(), sentinelContextConfig.getOrigin());
}
try {
// 获取资源访问令牌
AsyncEntry entry = SphU.asyncEntry(entryConfig.getResourceName(), entryConfig.getResourceType(),
entryConfig.getEntryType(), entryConfig.getAcquireCount(), entryConfig.getArgs());
this.currentEntry = entry;
actual.onSubscribe(this);
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// Mark as completed (exited) explicitly.
entryExited.set(true);
// Signal cancel and propagate the {@code BlockException}.
cancel();
actual.onSubscribe(this);
// 派发异常信号
actual.onError(ex);
} finally {
// 清除线程上下文,SCG底层采用netty实现,io多路复用,
// 一个线程处理多个请求不清除上下文,会出现多个请求共用一个上下的问题
if (sentinelContextConfig != null) {
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}
}
1、一般情况下访问目标资源会创建上下文,什么意思?
在SCG网关中,一个访问资源route对应一个上下文,内部一般情况下只会存在一个调用链路,因为routeId既是资源访问者,又是受保护的资源。 是不是有点绕? 哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈。因为网关核心作用是转发请求到目标服务,以目标路由id,作为资源访问者,目标路由也是受保护的资源 。 资源访问者—》受保护资源 不就一条路径嘛?
只能是一个路由对应一个上下文嘛?不是的,可以修改源码自定义,例如将调用方AppKey作为上下文入口,访问目标路由a1,a2 不就是在一个上下文中存在两条调用链路嘛?
在SpringMVC中,请求者对应一个上下文,请求者访问不同的受限资源,会创建不同的调用链路
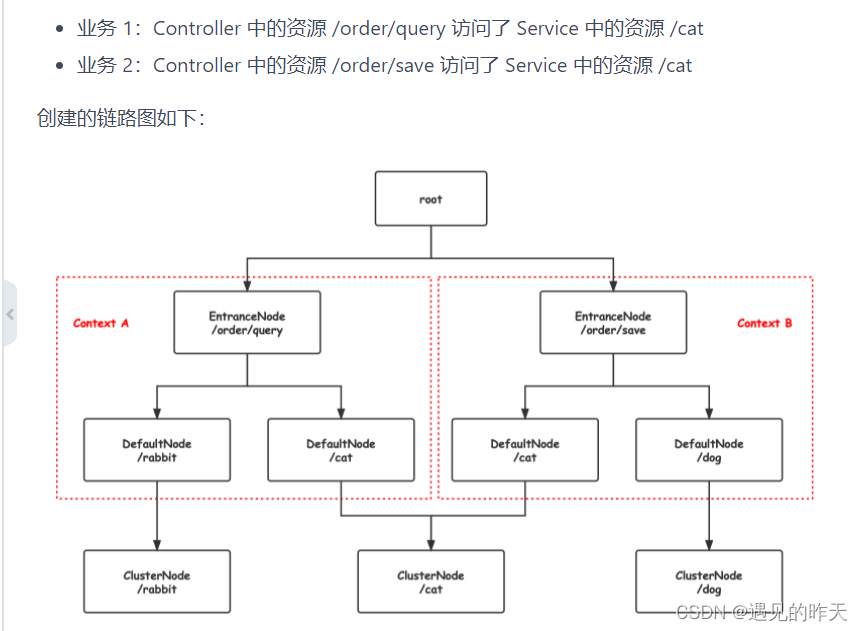
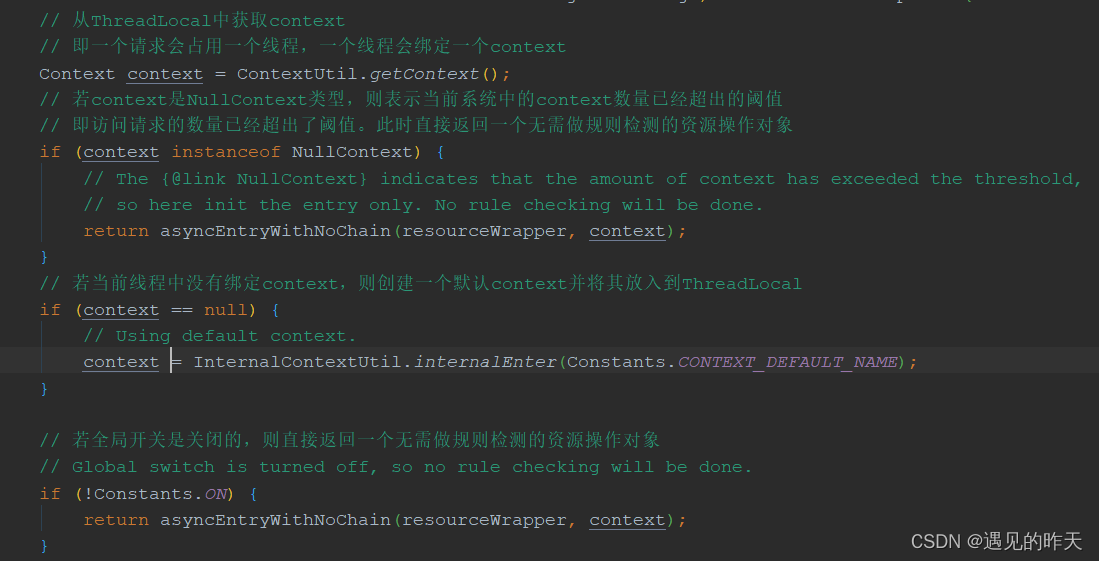
2、ContextUtil.enter(sentinelContextConfig.getContextName(), sentinelContextConfig.getOrigin()); 干什么?
从线程中获取context,没有就创建
public static Context enter(String name, String origin) {
if (Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME.equals(name)) {
throw new ContextNameDefineException(
"The " + Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME + " can't be permit to defined!");
}
return trueEnter(name, origin);
}
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
// 尝试着从ThreadLocal中获取Context
Context context = contextHolder.get();
// 若ThreadLocal中没有context,则尝试着从缓存map中获取
if (context == null) {
// 缓存map的key为context名称,value为EntranceNode
Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
// 获取EntranceNode——双重检测锁DCL——为了防止并发创建
DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
// 若缓存map的size 大于 context数量的最大阈值,则直接返回NULL_CONTEXT
if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
LOCK.lock();
try {
node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
// 创建一个EntranceNode
node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
// Add entrance node.将新建的node添加到ROOT
Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
// 将新建node写入到缓存map
// 为了防止“迭代稳定性问题”——iterate stable——对于共享集合的写操作
Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
newMap.put(name, node);
contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
// 将context的name与entranceNode封装为context
context = new Context(node, name);
// 初始化context的来源
context.setOrigin(origin);
// 将context写入到ThreadLocal
contextHolder.set(context);
}
return context;
}
3、AsyncEntry entry = SphU.asyncEntry(entryConfig.getResourceName(), entryConfig.getResourceType(),
entryConfig.getEntryType(), entryConfig.getAcquireCount(), entryConfig.getArgs()); 获取资源访问令牌
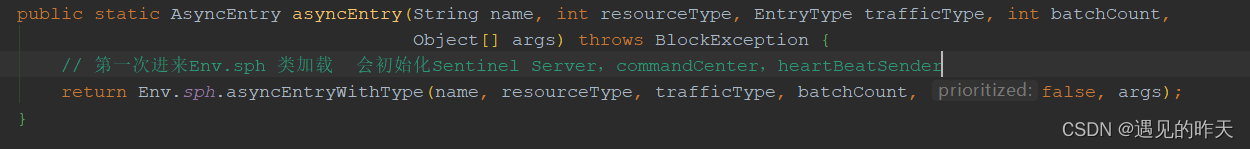
Sentinel初始化的源码分析,之前讲过,忘了可以看之前的文章
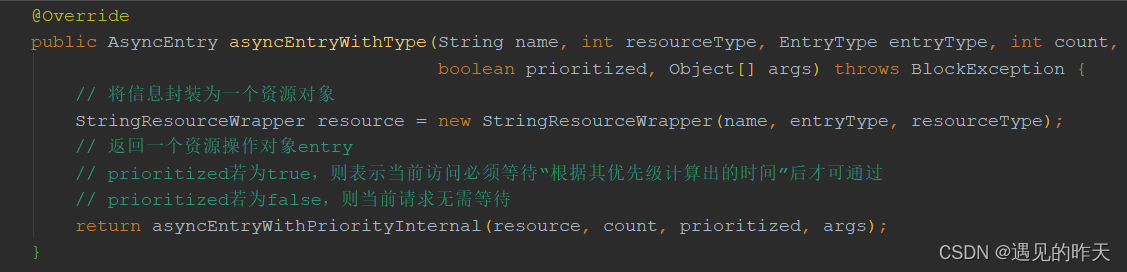
4.6、ProcessSlotChain
// 找到资源对应的 slotChain ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
// 从缓存map中获取当前资源的SlotChain
// 缓存map的key为资源,value为其相关的SlotChain
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
// DCL:double check lock
// 若缓存中没有相关的SlotChain,则创建一个并放入到缓存
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit.
// 缓存map的size >= chain数量最大阈值,则直接返回null,不再创建新的chain
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
return null;
}
// 创建新的chain
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
// 防止迭代稳定性问题 写时复制技术解决 线程读到脏数据的问题
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}
高并发情形下,使用DCL创建。这里的chainMap很重要避免一直SPI加载组件
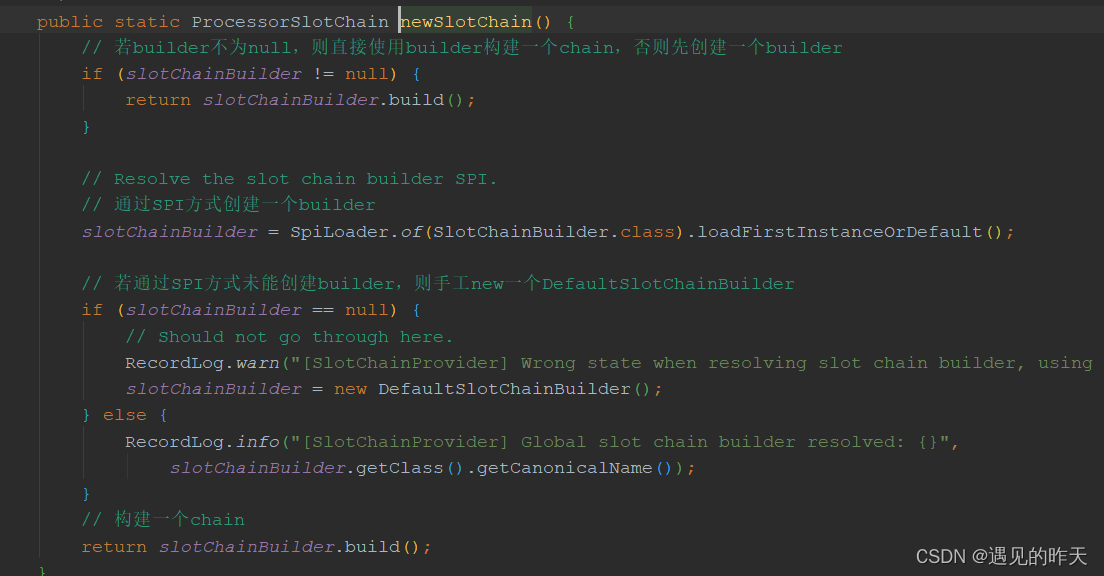
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain(); 通过SPI获取SlotChain,

DefaultProcessorSlotChain 主要用来构建责任链的
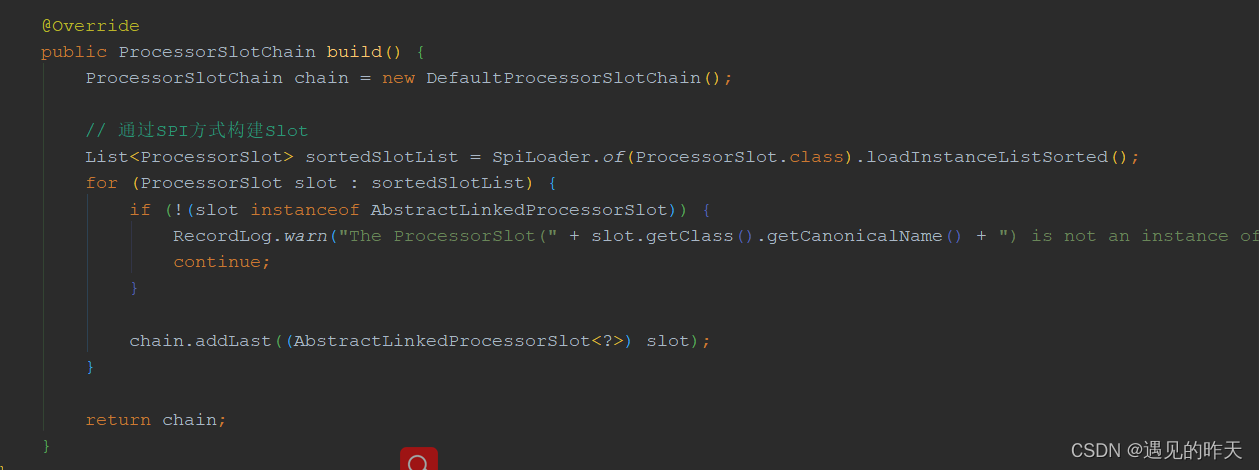
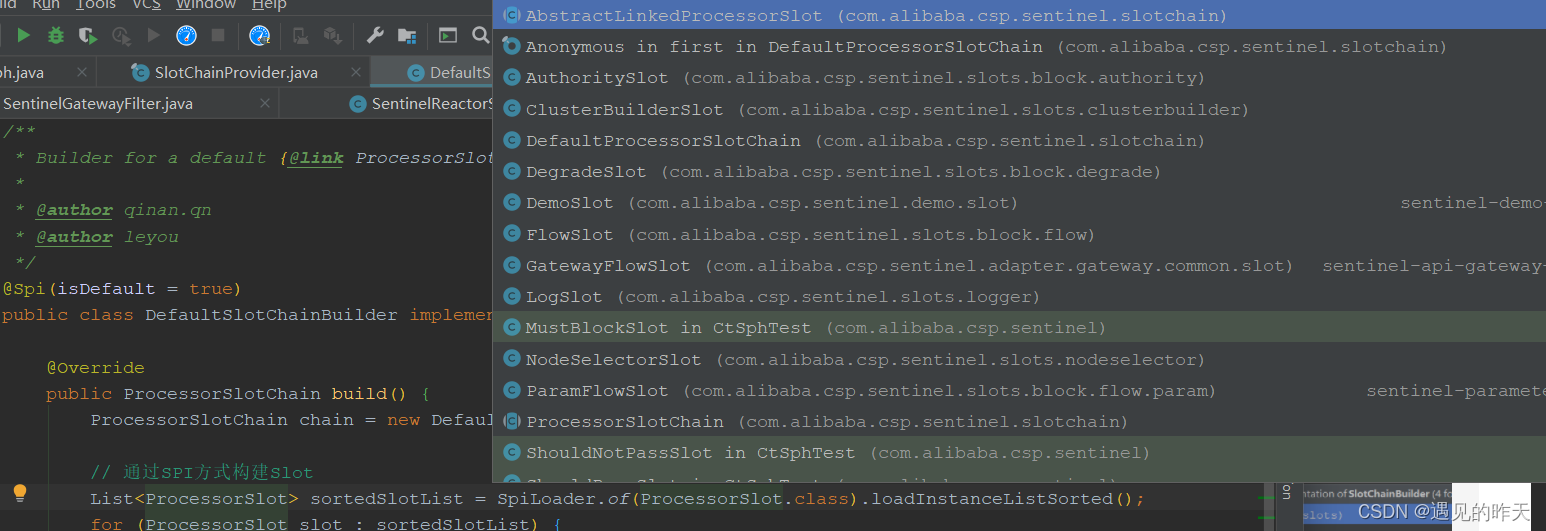
4.7、ProcessSlot
该接口的实现,就是Sentinel责任链中的组件,负责处理各自的任务,以前文章有讲
public interface ProcessorSlot<T> {
// 进入
void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, T param, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
// 进入完成
void fireEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
// 退出
void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
// 退出完成
void fireExit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
}
SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted(), 通过SPI按顺序优先级加载获取class

4.8、NodeSelectorSlot
负责构建上下文的调用链路
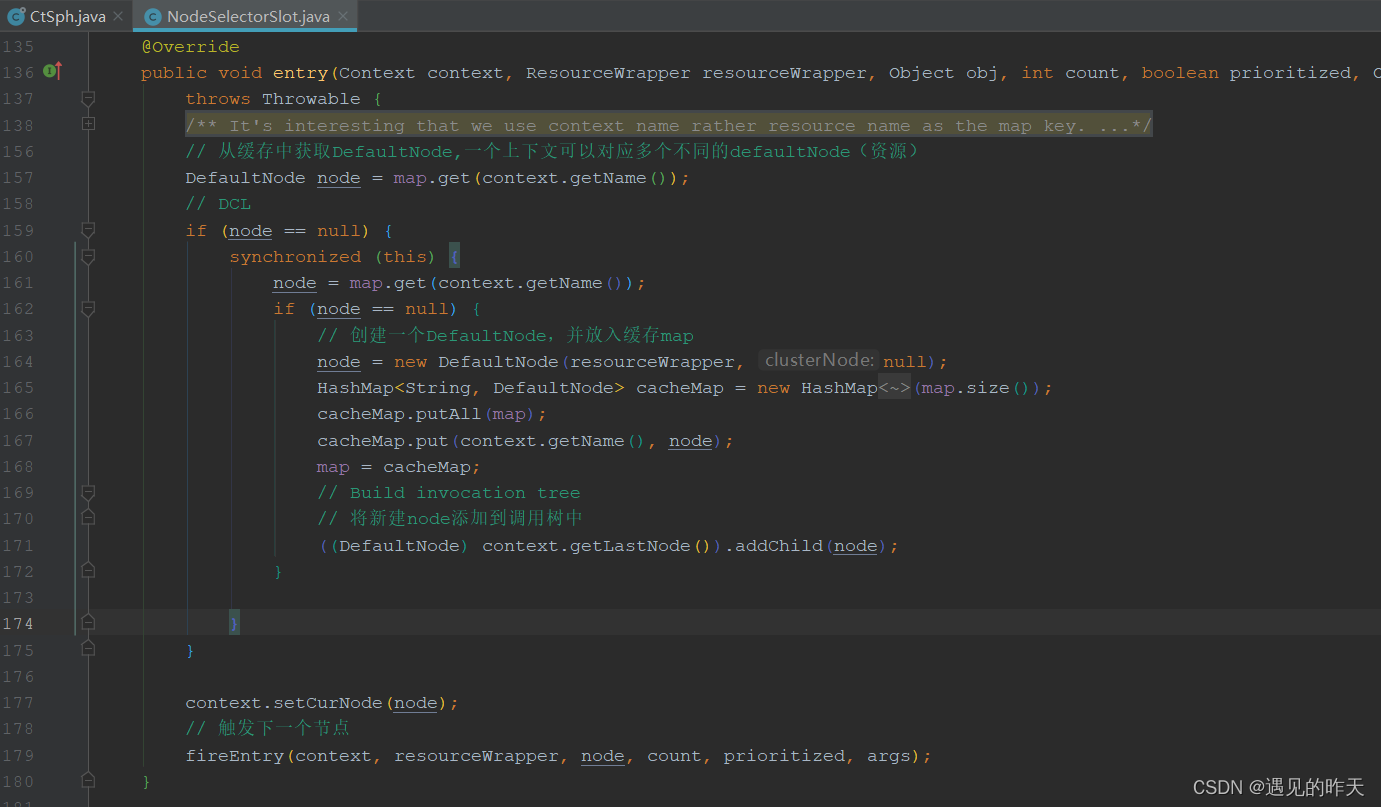
注意:DefalutNode,是资源统计节点,因为上级为StatisticNode。在网关中,默认情况下,资源访问者(entrenceNode)和受保护的资源(defaultNode)是相同的名字,且只有一条调用链路
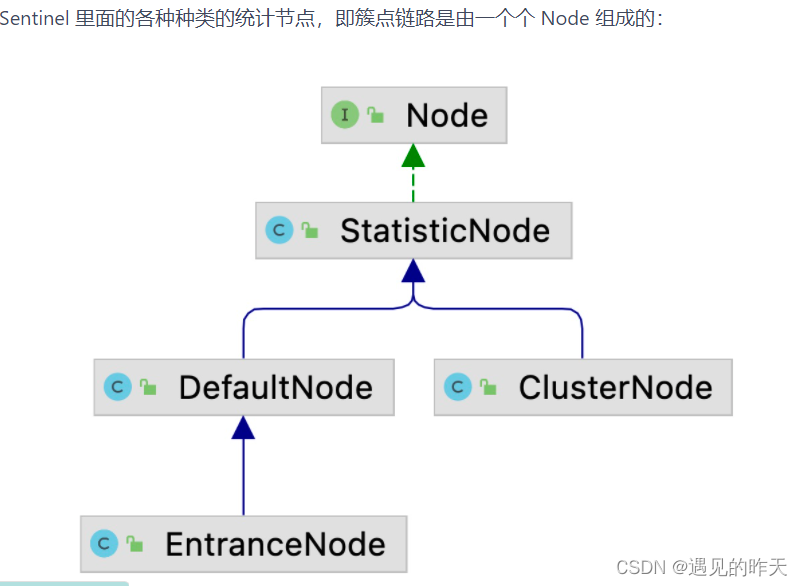
4.9、ClusterBuilderSlot
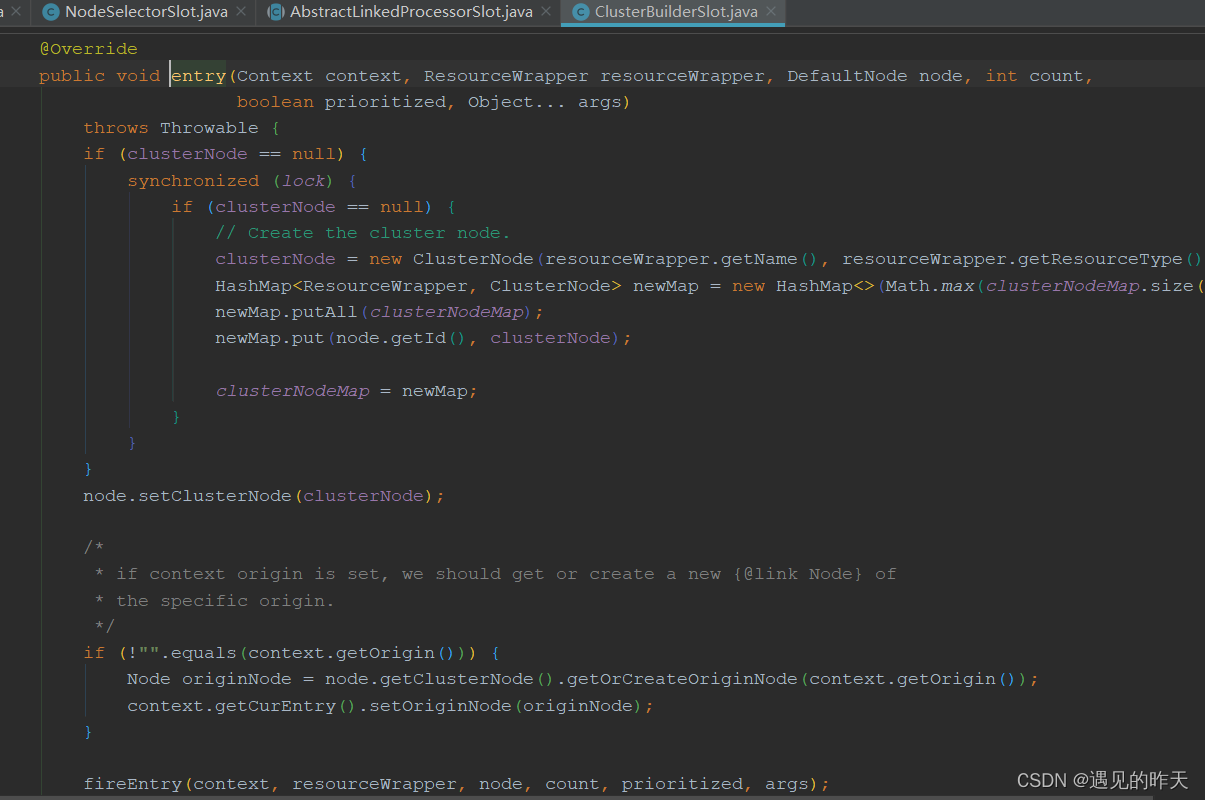
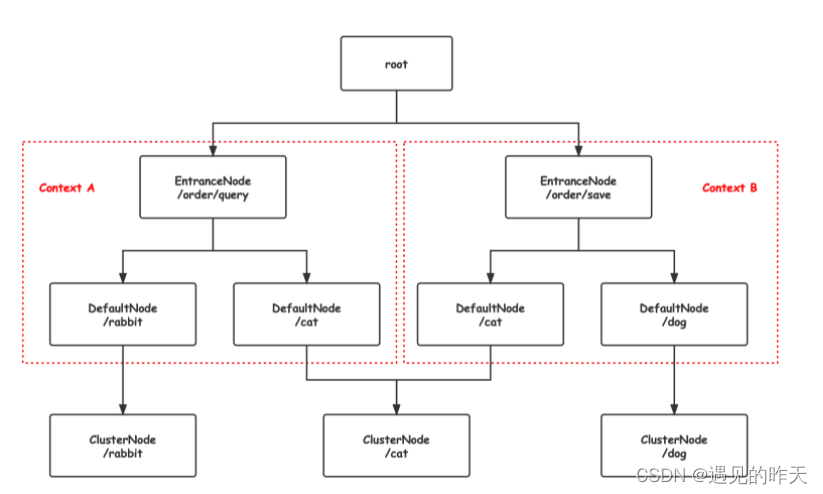
以上图为例,本质上对于不同上下文,对相同的受保护资源,进行数据统计
4.10、StatisticSlot
主要负责 数据统计
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Do some checking.
// 调用SlotChain中后续的所有Slot,完成所有规则检测
// 其在执行过程中可能会抛出异常,例如,规则检测未通过,抛出BlockException
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
// 代码能走到这里,说明前面所有规则检测全部通过,此时就可以将该请求统计到相应数据中了
// 增加线程数据
node.increaseThreadNum();
// 增加通过的请求数量
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
node.increaseThreadNum();
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setBlockError(e);
// Add block count.
node.increaseBlockQps(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count);
}
// Handle block event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
throw e;
}
}
这里直接调用fireEntry,先走完其它ProcessSlot,然后进行数据统计
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
// 代码能走到这里,说明前面所有规则检测全部通过,此时就可以将该请求统计到相应数据中了
// 增加线程数据
node.increaseThreadNum();
// 增加通过的请求数量
node.addPassRequest(count);
这里数据统计,都是获取到当前时间的时间窗口,进行数据统计,两个维度,一个通过数,一个线程数
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
// 增加当前入口的DefaultNode中的统计数据
super.addPassRequest(count);
// 增加当前资源的ClusterNode中的全局统计数据
this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}
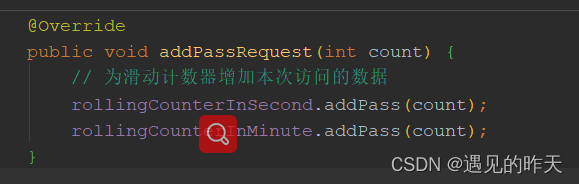
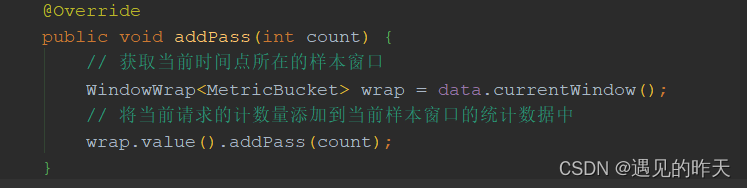
当前时间窗口怎么计算出来的?为什么要用滑动窗口算法?下篇文章讲
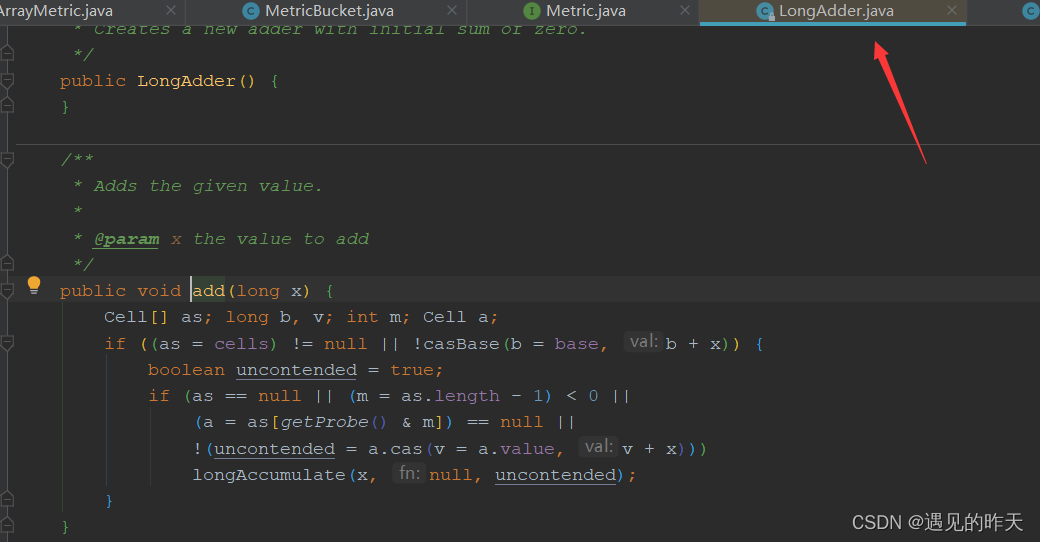
StatisticSlot计数,底层通过LongAdder实现,why?
1、LongAdder底层通过cas保证高并发情况下的线程安全
2、LongAdder底层通过add,decrement,sum这些现成的API可以使用
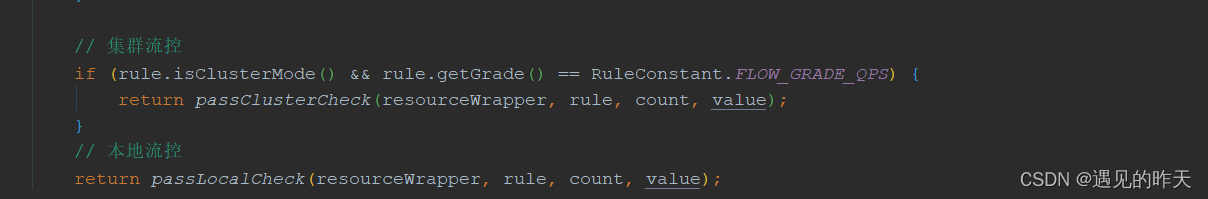
4.11、GatewayFlowSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resource, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 校验网关流控规则是否放行
checkGatewayParamFlow(resource, count, args);
fireEntry(context, resource, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
private void checkGatewayParamFlow(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args)
throws BlockException {
if (args == null) {
return;
}
// GatewayRuleManager通过资源名获取资源对应的所有流控规则
List<ParamFlowRule> rules = GatewayRuleManager.getConvertedParamRules(resourceWrapper.getName());
if (rules == null || rules.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 遍历流控规则
for (ParamFlowRule rule : rules) {
// Initialize the parameter metrics.
ParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule);
// 尝试判断当前请求是否通过流控规则
if (!ParamFlowChecker.passCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, args)) {
String triggeredParam = "";
if (args.length > rule.getParamIdx()) {
Object value = args[rule.getParamIdx()];
triggeredParam = String.valueOf(value);
}
// 不通过抛异常表示不放行
throw new ParamFlowException(resourceWrapper.getName(), triggeredParam, rule);
}
}
}
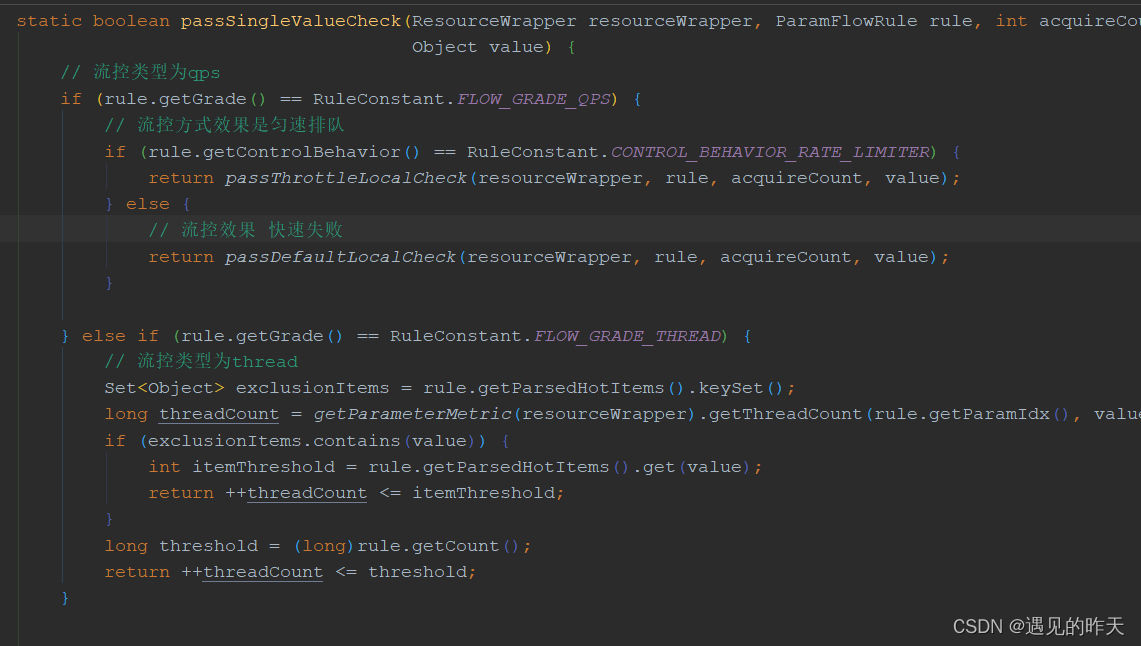
static boolean passDefaultLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount,
Object value) {
ParameterMetric metric = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper);
CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> tokenCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTokenCounter(rule);
CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> timeCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTimeCounter(rule);
if (tokenCounters == null || timeCounters == null) {
return true;
}
// Calculate max token count (threshold)
Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();
long tokenCount = (long)rule.getCount();
if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {
tokenCount = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);
}
if (tokenCount == 0) {
return false;
}
long maxCount = tokenCount + rule.getBurstCount();
if (acquireCount > maxCount) {
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
AtomicLong lastAddTokenTime = timeCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(currentTime));
if (lastAddTokenTime == null) {
// Token never added, just replenish the tokens and consume {@code acquireCount} immediately.
tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));
return true;
}
// Calculate the time duration since last token was added.
long passTime = currentTime - lastAddTokenTime.get();
// A simplified token bucket algorithm that will replenish the tokens only when statistic window has passed.
if (passTime > rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000) {
AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));
if (oldQps == null) {
// Might not be accurate here.
lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
} else {
long restQps = oldQps.get();
long toAddCount = (passTime * tokenCount) / (rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000);
long newQps = toAddCount + restQps > maxCount ? (maxCount - acquireCount)
: (restQps + toAddCount - acquireCount);
if (newQps < 0) {
return false;
}
if (oldQps.compareAndSet(restQps, newQps)) {
lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
}
Thread.yield();
}
} else {
AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.get(value);
if (oldQps != null) {
long oldQpsValue = oldQps.get();
if (oldQpsValue - acquireCount >= 0) {
if (oldQps.compareAndSet(oldQpsValue, oldQpsValue - acquireCount)) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
以上执行逻辑大概是 计算规则阈值(自定义值+burstValue),判断当前值是否大于小于阈值,大于返回false。判断当前时间是否超过间隔时间,如果没超过继续比较,满足条件位置。这一步感觉写复杂了。
4.12、ParamFlowSlot
参数流控
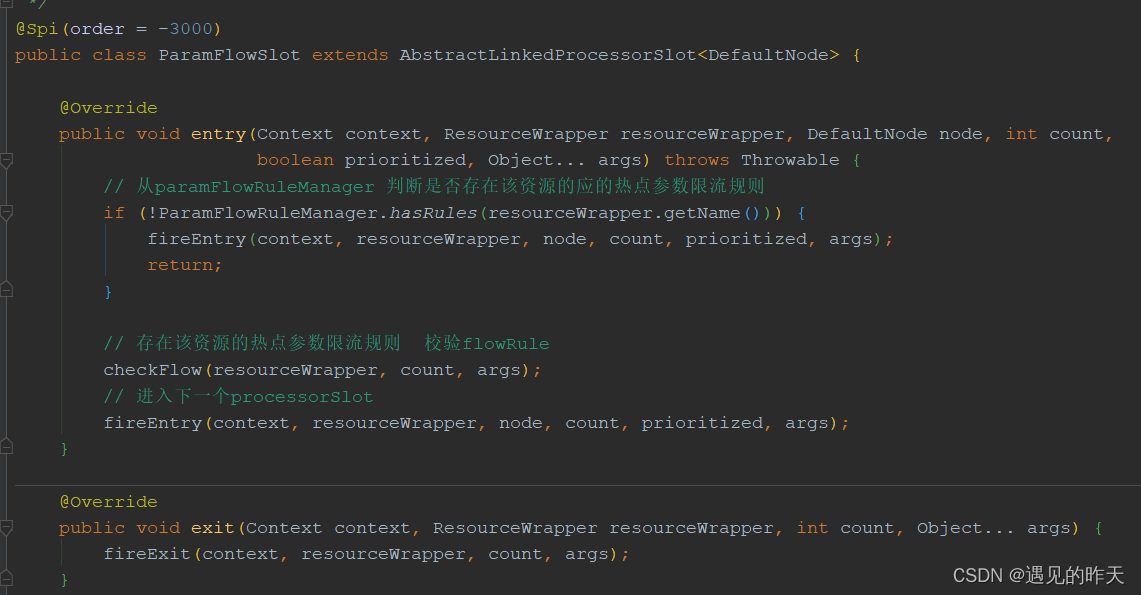
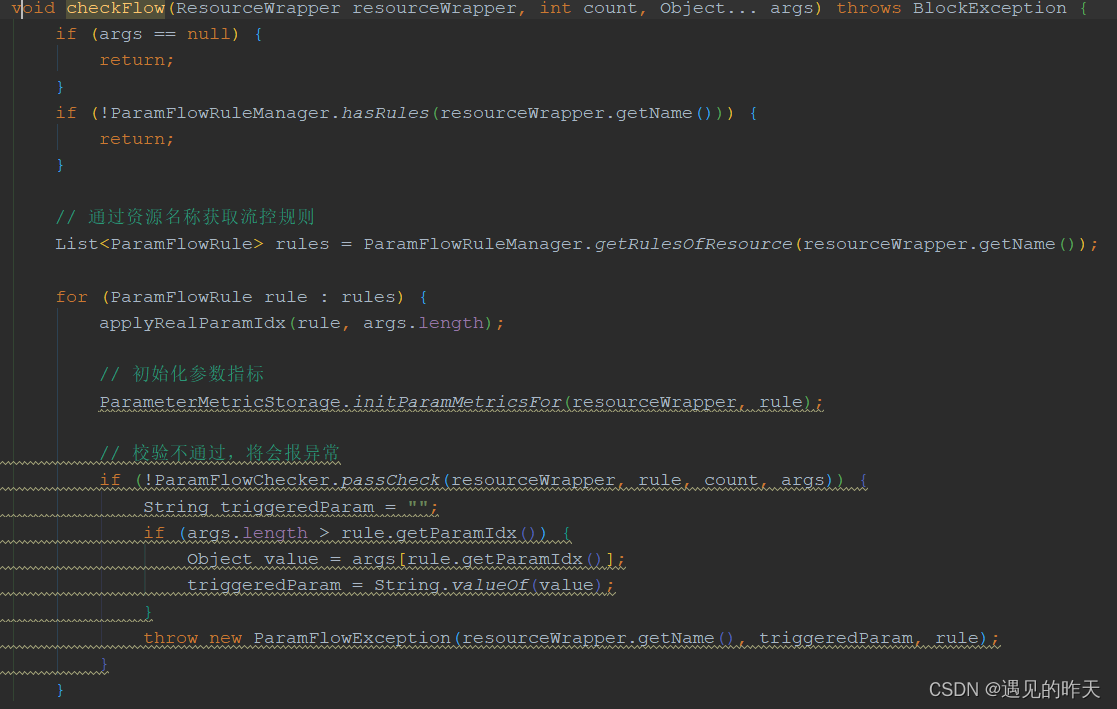
大概逻辑都类似,无非是判断是否满足规则而已,实现方式各有不同
4.13、FlowSlot
普通流控,SCG不会做处理,因为网关流控规则并不放在ruleProvider中,拿不到规则也就不会流控
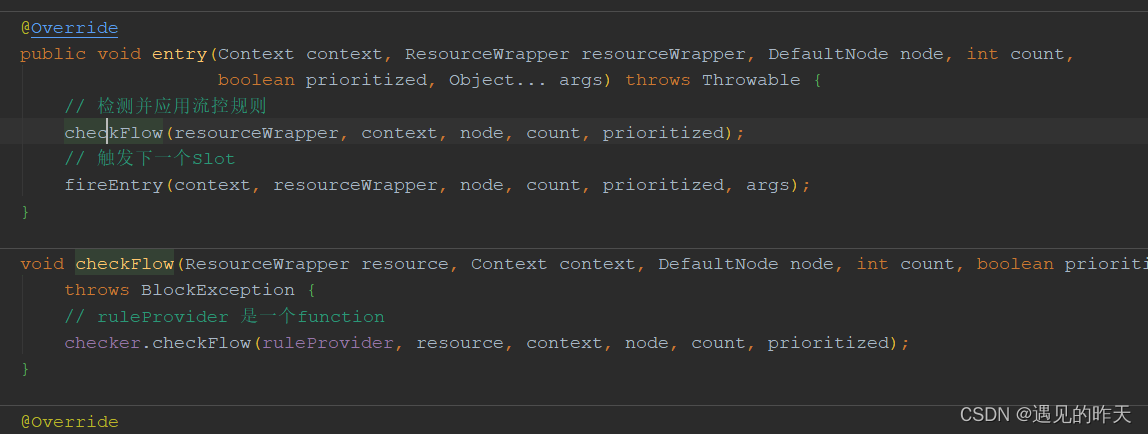


4.14、DegradeSlot
熔断降级处理器
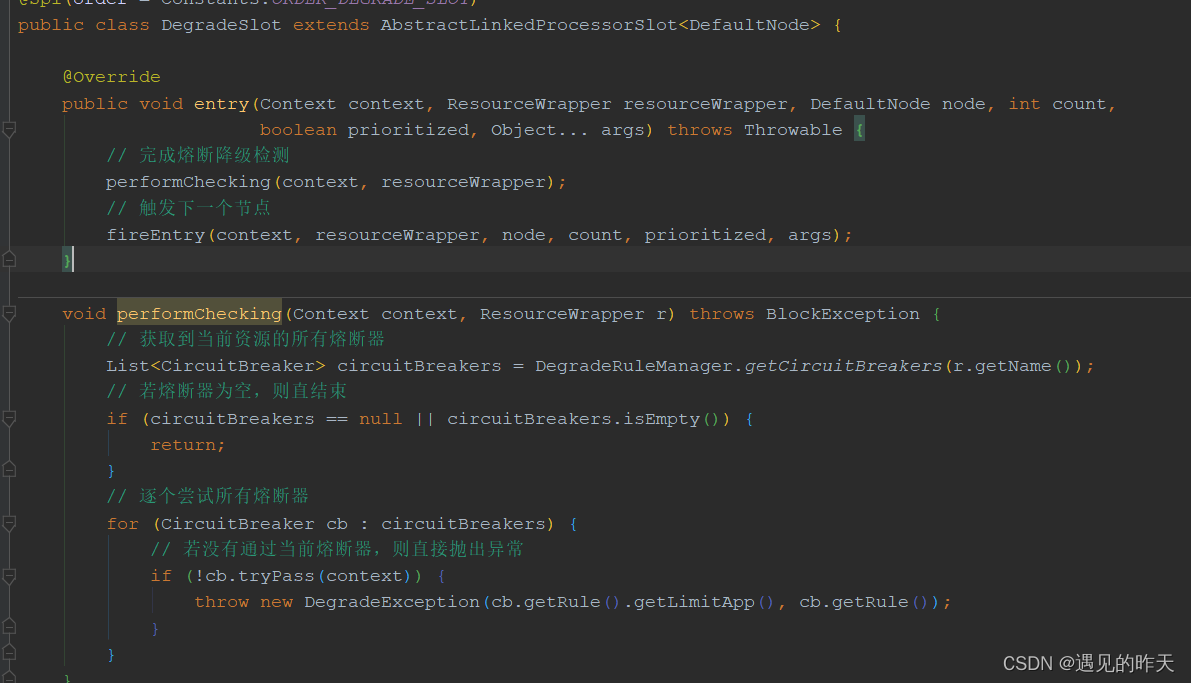
同理通过规则获取熔断器,遍历熔断器是否关闭,关闭放行,全开不放行,半开放行一次。
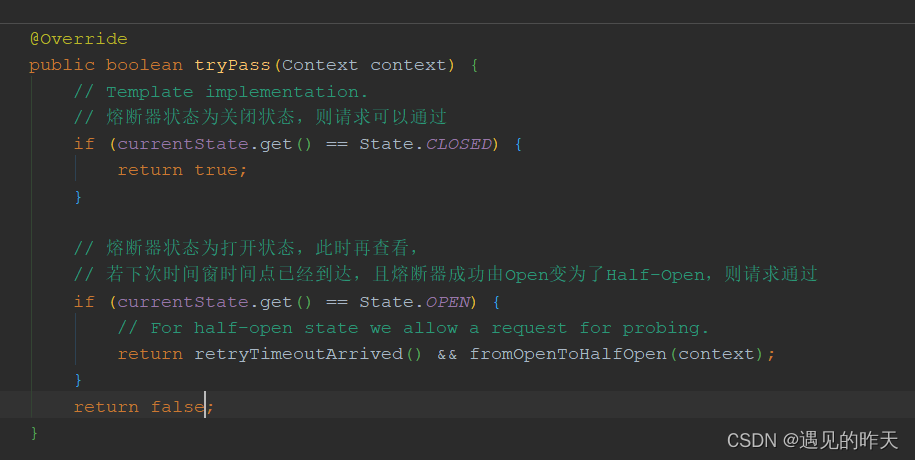
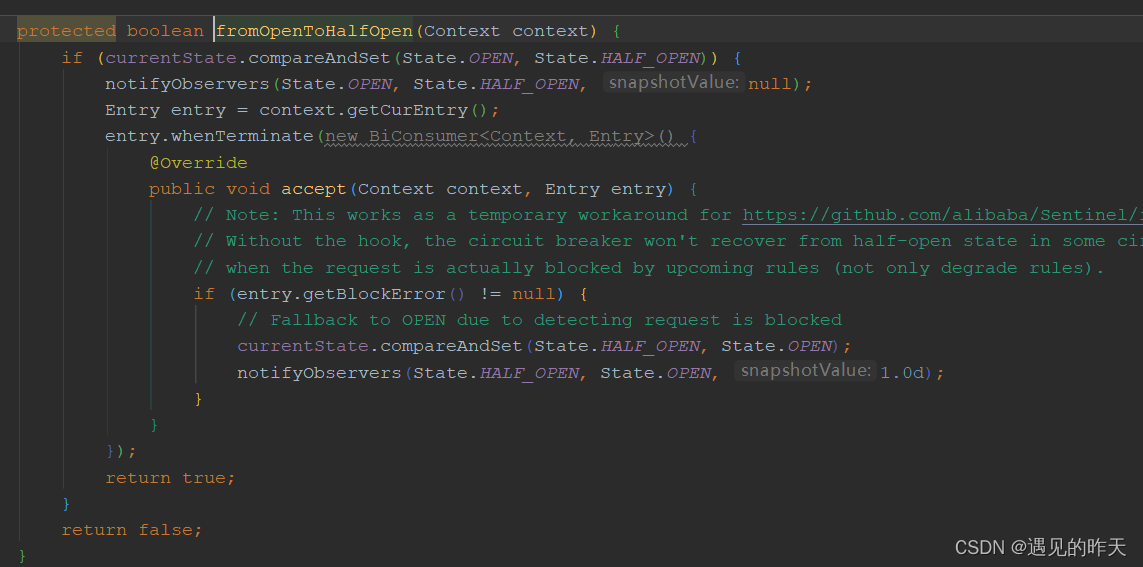
那熔断器在哪计数?对于网关而言派发错误信号,就会计数,实际统计在exit中执行
执行完DegradeSlot,接着执行StatisticSlot统计逻辑,责任链中,如果抛异常了也由这里处理
4.15、StatisticSlot后续处理
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Do some checking.
// 调用SlotChain中后续的所有Slot,完成所有规则检测
// 其在执行过程中可能会抛出异常,例如,规则检测未通过,抛出BlockException
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
// 代码能走到这里,说明前面所有规则检测全部通过,此时就可以将该请求统计到相应数据中了
// 增加线程数据
node.increaseThreadNum();
// 增加通过的请求数量
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
node.increaseThreadNum();
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setBlockError(e);
// Add block count.
node.increaseBlockQps(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count);
}
// Handle block event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
throw e;
}
}
向外层抛出异常,给订阅者ExceptionHandler处理,内部交由SentinelBlockExceptionHandler处理
5、总结
上述讲了SCG Sentinel执行流程,这里给一个SpringBoot集成Sentinel的执行流程,两则本质上执行流程一致

StatisticSlot计数,底层通过LongAdder实现,why?
1、LongAdder底层通过cas保证高并发情况下的线程安全
2、LongAdder底层通过add,decrement,sum这些现成的API可以使用
熔断器在哪计数?
下篇写
为什么要用滑动窗口算法?原理是什么? 怎么实现?
下篇写




![[发送AT指令配置a7670C模块上网]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b17882066b34406d933745ba4929b626.png)