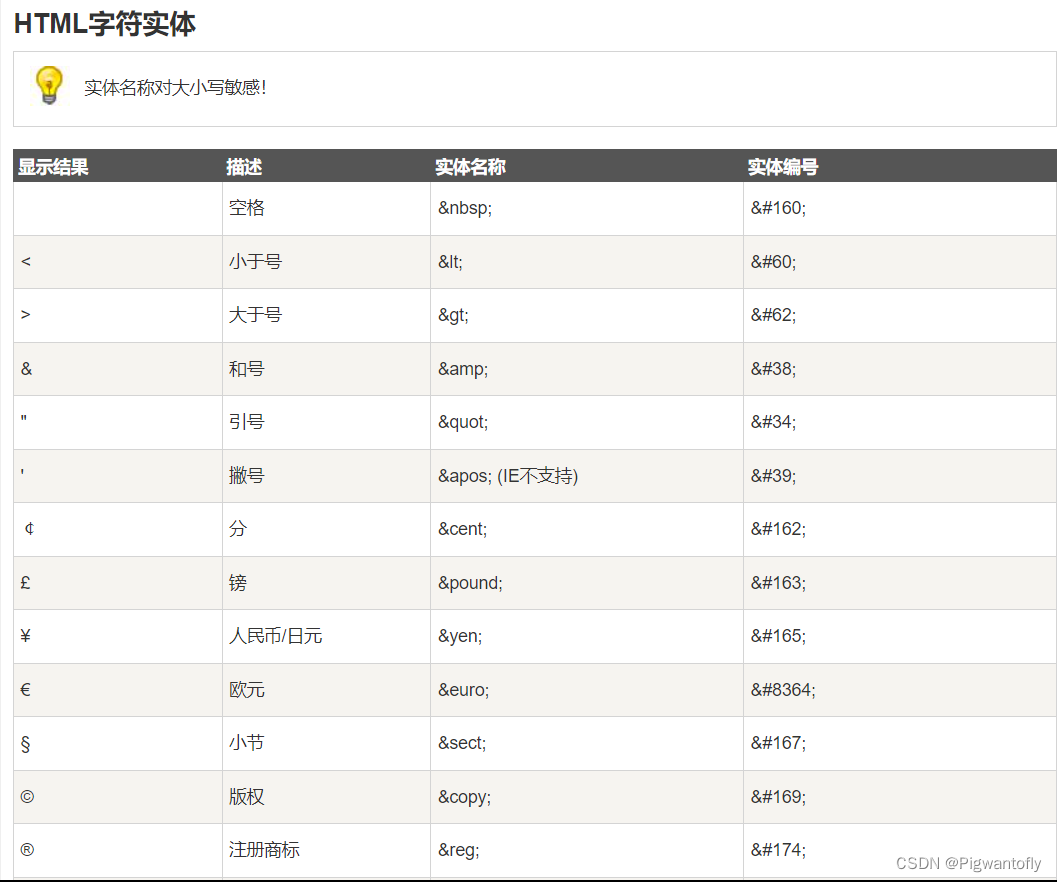
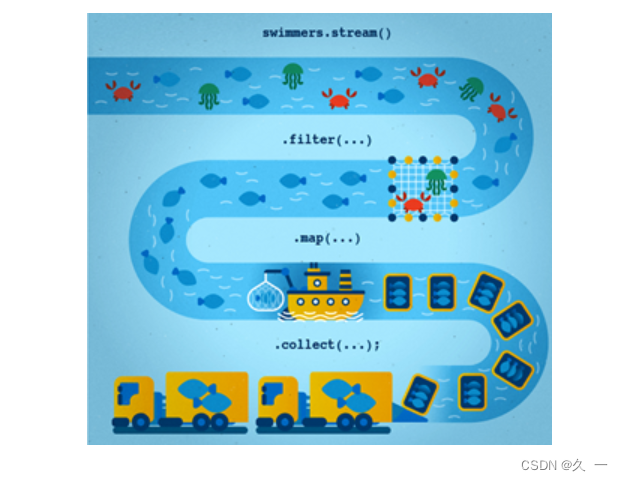
文章目录
- HashSet判断是否两次add都能加入成功
- HashSet编码
- 遍历HashMap
- 判断输出中是否有"abc"
HashSet判断是否两次add都能加入成功
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add(new String("hsp"));
set.add(new String("hsp"));
第一次可以,第二次不能。因为hashset 的底层源码决定,如果equals能够度量并确定两个对象相同(String可以使用equals直接判断两个串是否相同),所以检测到两个String对象相同时无法重复加入hashset。
HashSet编码

hashCode 是 Object 类中的一个方法,它返回对象的哈希码。其默认实现在 Object 类中是基于对象的内存地址的,这就意味着不同对象(即使是同一个类)通常会有不同的哈希码。
【ps:在课堂上,老师为了让同一个类的对象聚集到hashset中的同一个key下,重写同一个类的hashcode使之返回相同的值。但由于equals比较的结果是不同的对象(即使是同一个类)而返回false,所以不会被判为相同而无法加入hashset】
下面重写equals和hashCode方法,如果name 和 age 值相同,则返回相同的hash值,保证映射到hashset的相同键值下;equals返回true,从而在同一键值的链表比较中,防止拥有相同name 和 age 值的两个对象重复(equals返回true则插入失败)。IDEA快捷键:alt+insert
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan", 18));//ok
hashSet.add(new Employee("smith", 28));//ok
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan", 18));//加入不成功.
}
}
//创建Employee
class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//如果name 和 age 值相同,则返回相同的hash值:
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age &&
Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
遍历HashMap

考察遍历的HashMap的熟练使用。
另外,Object的toString方法被其他类重写时,即使编译类型是Object类,还是能够在输出类时调用被重写的toString方法。
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Exercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
Employee a = new Employee("a", 19000, "1");
Employee b = new Employee("b", 18000, "2");
Employee c = new Employee("c", 19000, "3");
hashMap.put(a.getId(), a);
hashMap.put(b.getId(), b);
hashMap.put(c.getId(), c);
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
for (Object key :set) {
Employee e = (Employee) hashMap.get(key);
if (e.getSal() > 18000)
System.out.println(e); // 根据key输出value
// PS:
// System.out.println(hashMap.get(key))输出的是Employee中重写的toString方法,
// 因为此时Object的toString方法被Employee重写,
// 但Employee中独有的方法不能被调用,需要先转成Employee类
}
System.out.println("========");
Set set1 = hashMap.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = set1.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry next = (Map.Entry) iterator.next();
Employee e = (Employee) next.getValue();
if (e.getSal() > 18000)
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
class Employee {
private String name;
private double sal;
private String id;
public Employee(String name, double sal, String id) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", id='" + id + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
}
判断输出中是否有"abc"
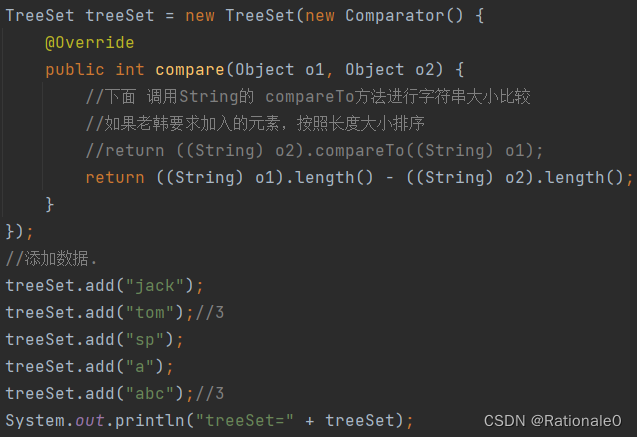
没有。因为按照长度大小进行比较,根据底层源码,两个String由于长度相同,加上匿名类中重写的比较方法以长度作为唯一度量标准,所以长度相同的就被认为是相同对象而不能加入treeset。