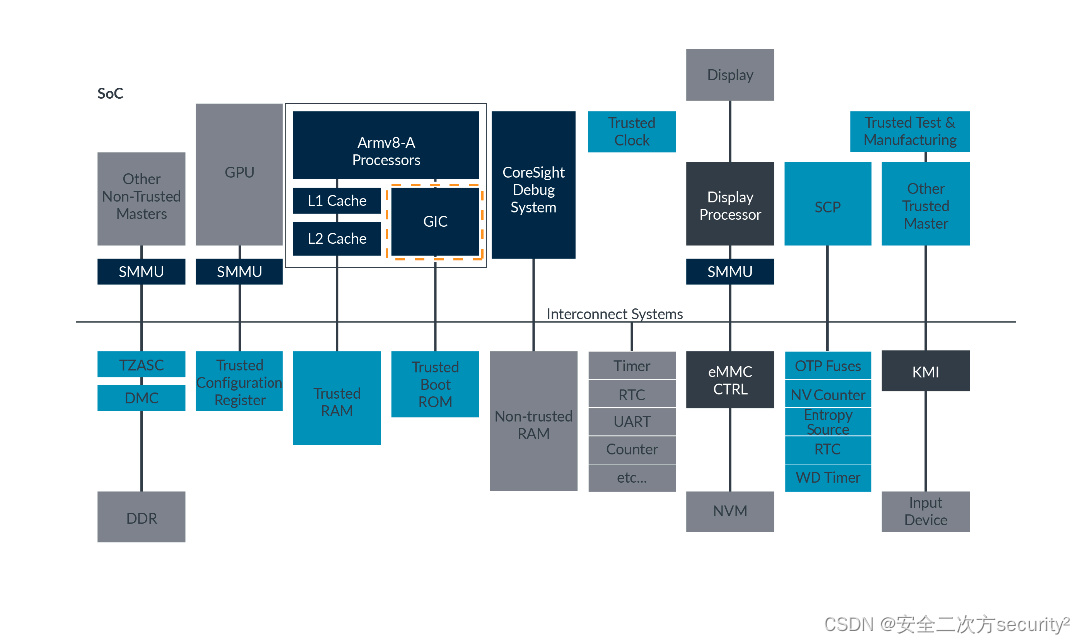
1 Bean创建的生命周期
Spring bean是Spring运行时管理的对象。Spring Bean的生命周期指的是Bean从创建到初始化再到销毁的过程,这个过程由IOC容器管理。
IOC即控制反转,是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,通过依赖注入(DI)、依赖查找的方式实现对象之间的松耦合关系。
BeanFactory为IoC容器,ApplicationContext为应用上下文,ApplicationContext容器包括BeanFactory容器的所有功能。
1)创建bean的三种方式
- 基于XML配置文件
- 基于注解,@Component、 @Repository、@Service、@Controller;@Component可以代替@Repository、@Service、@Controller。
- 基于Java类的bean定义,需要提供setter方法
@Bean
public Student student(){
return new Student();;
}
public class Student{
private String name;
public void SetName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}2)bean对象

对象不一定是bean,bean一定是对象,bean对象都放在一个MAP里。
![]()
获取对象的方式可以使用构造方法去创建对象,上面的UserService就存在一个默认的构造方法。(如果程序中没有显式定义任何构造方法,那么java语言将自动提供一个隐含的默认构造方法。
spring扫描到@Component等注解时,就会认为这是定义的bean,就会使用此类构造方法获取对象。然后Spring去检查哪些对象存在@Autowired,就给自动进行依赖注入,进行赋值。
UserServie.class--->构造方法--->普通对象--->依赖注入--->放入Map<beanName,Bean对象>
spring会继续去检查哪些方法存在@PostConstruct方法,然后主动执行方法里的内容。
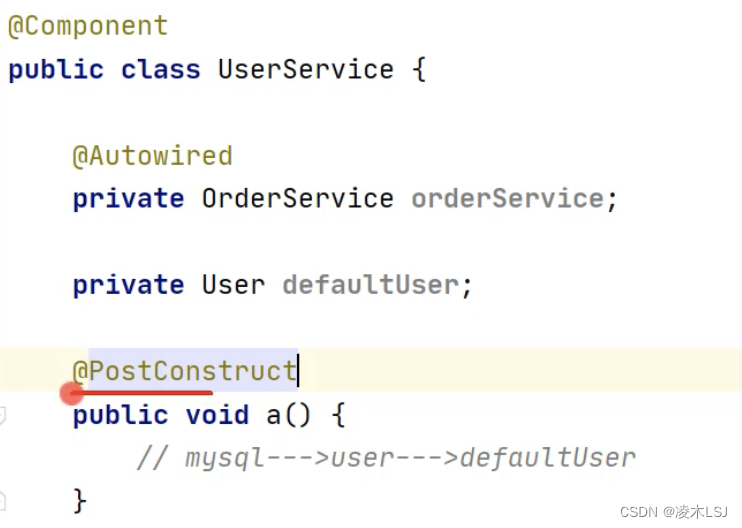
实现逻辑如下:

当然也可以实现InitializingBean接口,用写afterPropertiesSet()方式实现

((InitializingBean)对象).afterPropertiesSet();
UserServie.class--->推断构造方法--->普通对象--->依赖注入--->初始化前(@PostConstruct)--->初始化(InitializingBean)--->初始化后(AOP)--->代理对象--->放入Map<beanName,Bean对象>
推断构造方法:
@Service
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
}写了无参构造,则默认使用无参构造依赖注入;
不写无参构造,写多个有参构造,会报错No Default Construct;必须使用@Autowired指定默认是是哪个;
不写无参构造,只写一个有参构造,则会直接使用这个有参构造进行依赖注入;
依赖注入完成属性赋值,spring会依据入参的类型、名字去spring IOC容器里的Bean MAP<beanname,bean对象>里寻找bean对象。

1.1 依赖注入
在Java中,DI的实现方式主要有以下几种:
● 构造器注入
● Setter方法注入
● 接口注入
● 注解注入
1)构造器注入(spring框架中在构造方法上添加@Autowired注解)
@Component 标准一个普通的spring Bean类; @Repository标注一个DAO组件类; @Service标注一个业务逻辑组件类。 @Component可以代替@Repository、@Service、@Controller,因为这三个注解是被@Component标注的。
@Service
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
public User getUserById(int id) {
return userRepository.getUserById(id);
}
}2)setter方法注入(在setter方法上添加@Autowired注解)
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public void setUserRepository(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
public User getUserById(int id) {
return userRepository.getUserById(id);
}
}3)接口注入
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public void setUserRepositorySetter(UserRepositorySetter userRepositorySetter) {
userRepositorySetter.setUserRepository(userRepository);
}
public User getUserById(int id) {
return userRepository.getUserById(id);
}
}实现对应的接口
public interface UserRepositorySetter {
void setUserRepository(UserRepository userRepository);
}
@Repository
public class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserRepository, UserRepositorySetter {
@Override
public User getUserById(int id) {
// 实现代码
}
@Override
public void setUserRepository(UserRepository userRepository) {
// 实现代码
}
}4)注解注入
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public User getUserById(int id) {
return userRepository.getUserById(id);
}
}依赖注入如何寻找是哪个 userRepository?过程如下,从by type 到 by name:
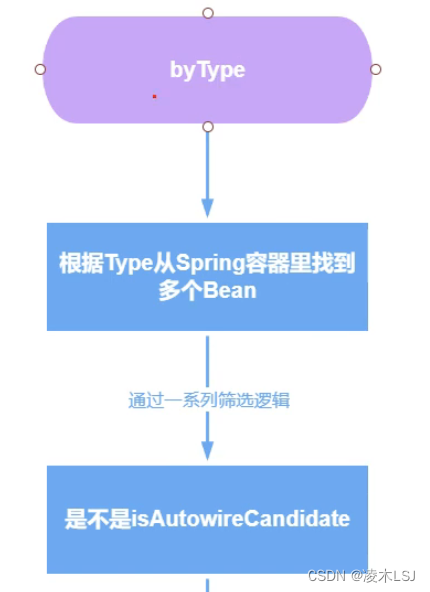


1.2 AOP
认识AOP
AOP 是 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,译为面向切向编程。
设计一个日志打印模块:
- 按 OOP 思想,我们会设计一个打印日志 LogUtils 类,然后在需要打印的地方引用即可。
- 按AOP思想,声明哪些地方需要打印日志,这个地方就是一个切面,AOP 会在适当的时机为你把打印语句插进切面。
AOP实现的关键在于AOP框架自动创建的AOP代理,以AspectJ为代表的静态代理,以Spring AOP为代表的动态代理。Spring AOP中的动态代理主要有两种方式:JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理。
Spring AOP通过在代理类中包裹切面,Spring在运行期把切面织入到Spring管理的bean中。代理类封装了目标类,并拦截被通知方法的调用,再把调用转发给真正的目标bean(目标对象)。
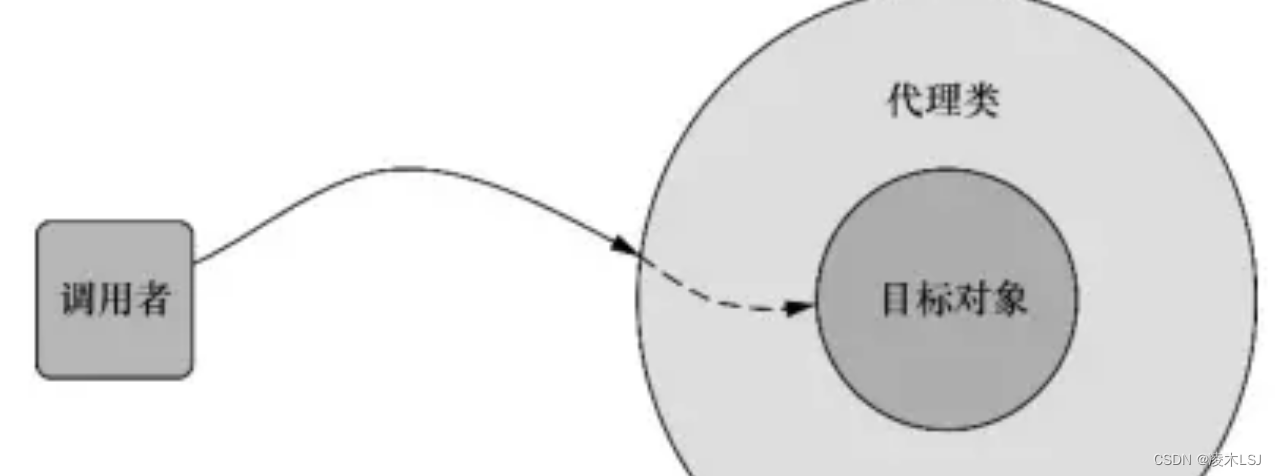
AOP实现技术由APT、AspetJ等,如下:

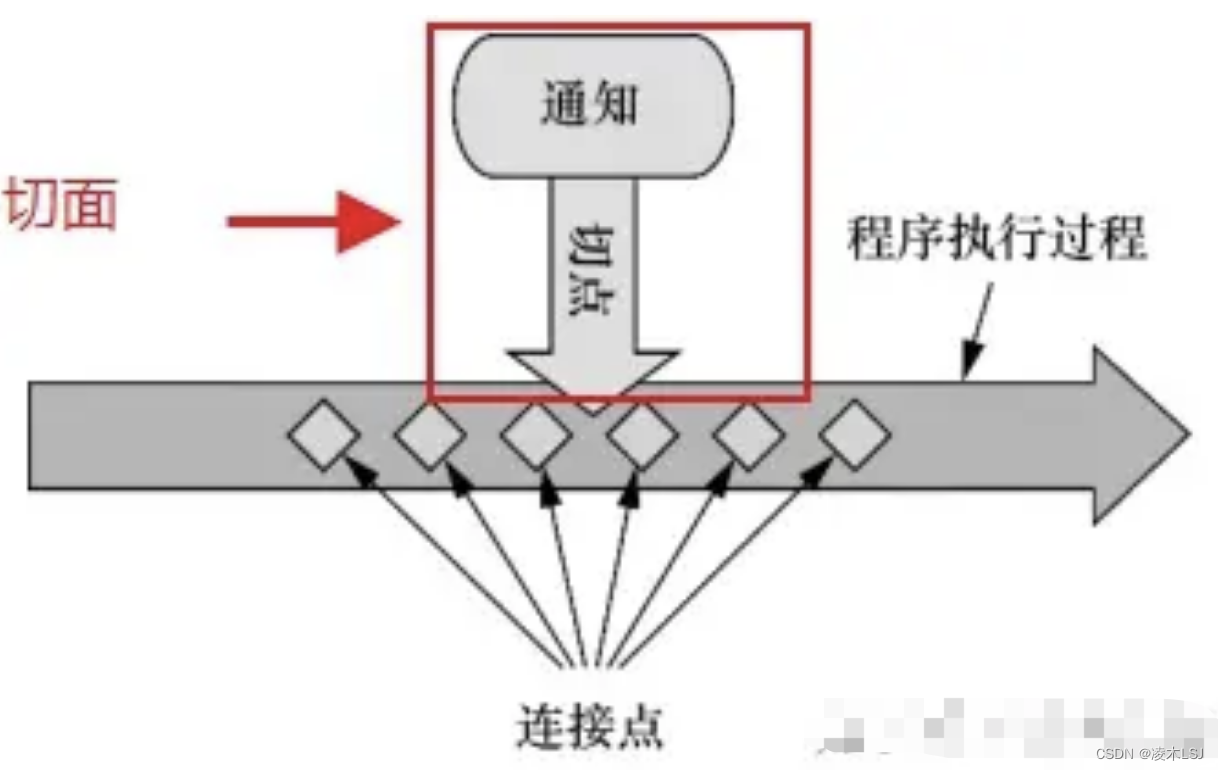
1)横切关注点
跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能,如日志、安全、缓存、事务等等。
2)连接点
连接点是在应用执行中能够插入切面的一个点。即程序执行过程中能够应用通知的所有点。
3)通知
切面的工作被称为通知,Spring切面可以应用5种类型的通知:
- 前置通知(Before):在目标方法被调用之前调用通知功能。
- 后置通知(After):在目标方法完成之后调用通知,此时不会关心方法的输出是什么。
- 返回通知(After-returning):在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知。
- 异常通知(After-throwing)):在目标方法抛出异常后调用通知。
- 环绕通知(Around) :通知包裹了被通知的方法,在被通知的方法调用之前和调用之后执行自定义的行为。
1.3 SpringBoot AOP
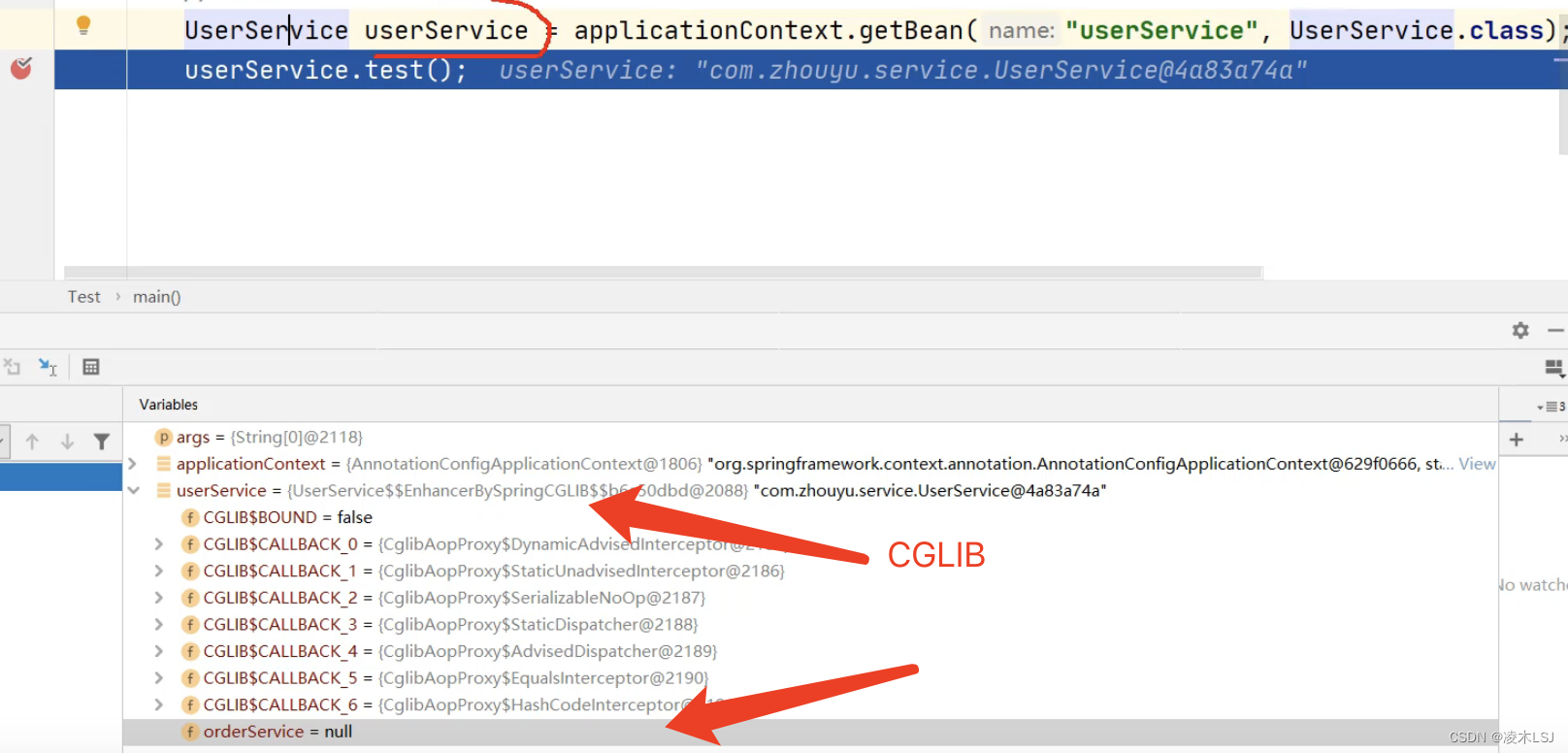
orderService为空?
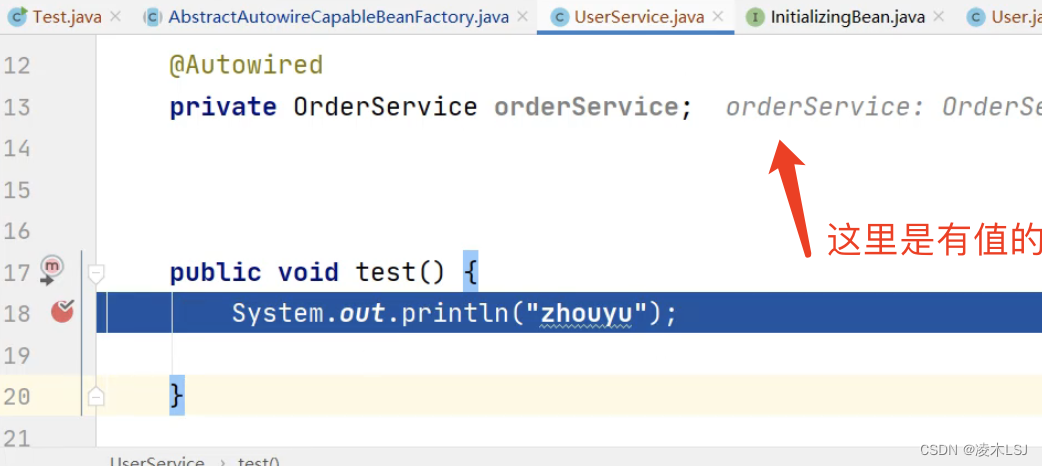
进入test之前,orderServcie是有值的!
1)Spring首先要判断这个对象要不要执行AOP
2)生成一个子类代理类,继承UserService,重写UserService里的test方法
3)子类代理类(代理对象)执行test方法时,先执行切面逻辑,然后执行业务逻辑
4)执行 代理对象.target.test()方法
代理对象.target对象 = 被代理对象 = 普通对象 = 已经经过了依赖注入 = 对象已经属性有值;
但是代理对象没有依赖注入,没有值;他只是为了执行切面逻辑,所以不需要必须去用对象的属性。


切面逻辑中可以通过获取这个target对象,来获取普通对象

AOP基本使用:
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
代码
@Aspect // 使用@Aspect注解声明一个切面
@Component
public class SysLogAspect {
@Autowired
private SysLogService sysLogService;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.lmlsj.SysLog)")
public void logPointCut() {}
@Before("execution(* com.lmlsj.SysLog.*(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("MyAspect: 前置增强.....");
}
}
配置
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
}正常流程:【环绕通知-前】-> 【前置通知】-> 【返回通知】-> 【后置通知】->【环绕通知-后】。
2 事物
1)事物执行逻辑
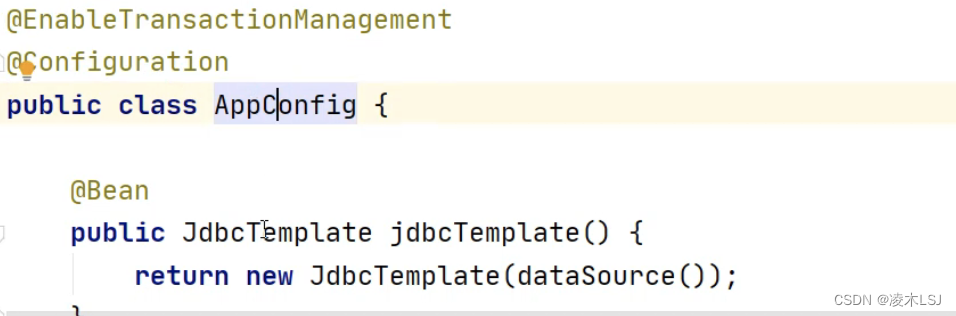


2)普通对象调用,事物失效

这里a()方法是普通对象的,直接执行a()里面的语句,不会去走切面逻辑判断是否有@Transactional注解,事物失效。
3)代理对象调用才会去走切面逻辑
自己注入自己,使用代理对象实现事物正常执行

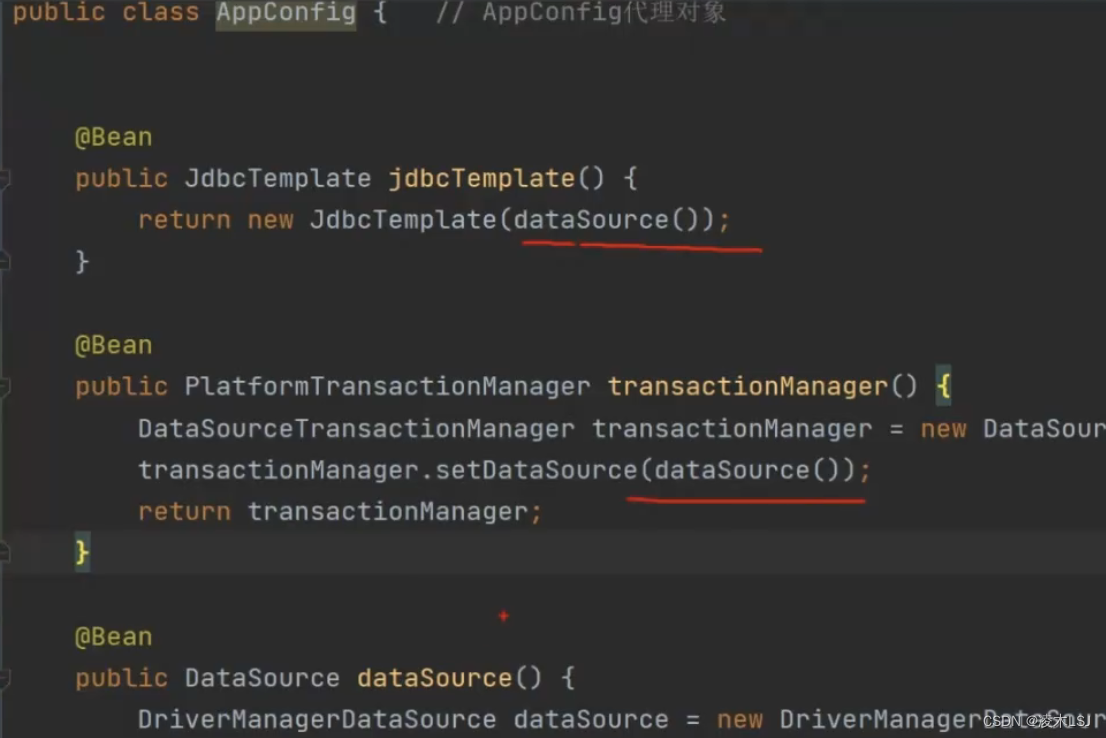
4)@Configuration
加上@Configuration后,Appconfig就是代理对象,才能保证下图两处的dataSource()是同一个对象,才能执行事务。
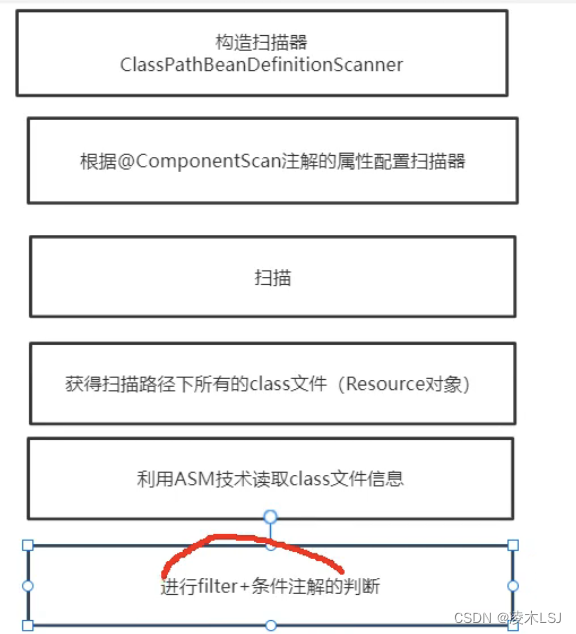
3 扫描
Spring扫描首先Spring根据注解去寻找bean类,非懒加载的bean在Spring容器启动时就创建好,懒加载的bean是用到时再创建。如何寻找注解的实现思路:
1)反射方式:AA.class.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)
2)ASM技术(Spring使用):编辑CLASS字节码
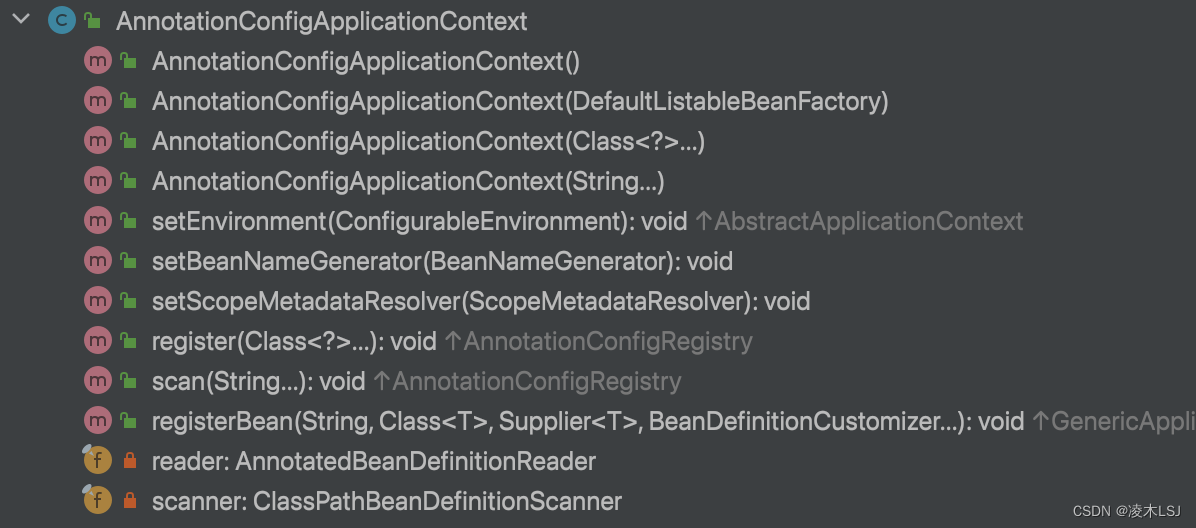
扫描类的寻找:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.java

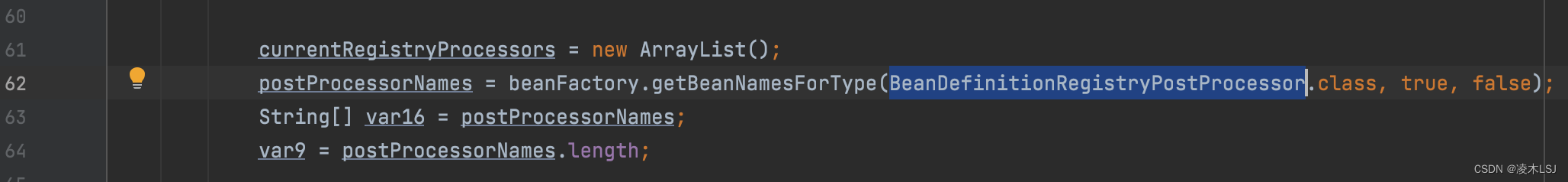





1)处理配置类
(1)判断Component注解
ConfigurationClassParser.java doProcessConfigurationClass(*)
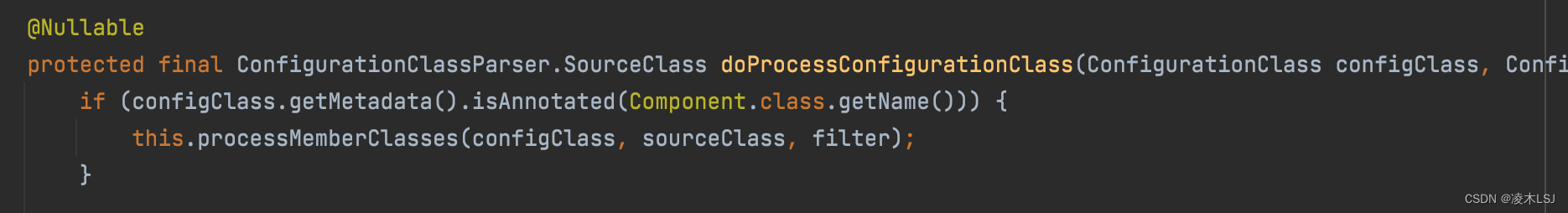
(2)检查是不是配置类的地方
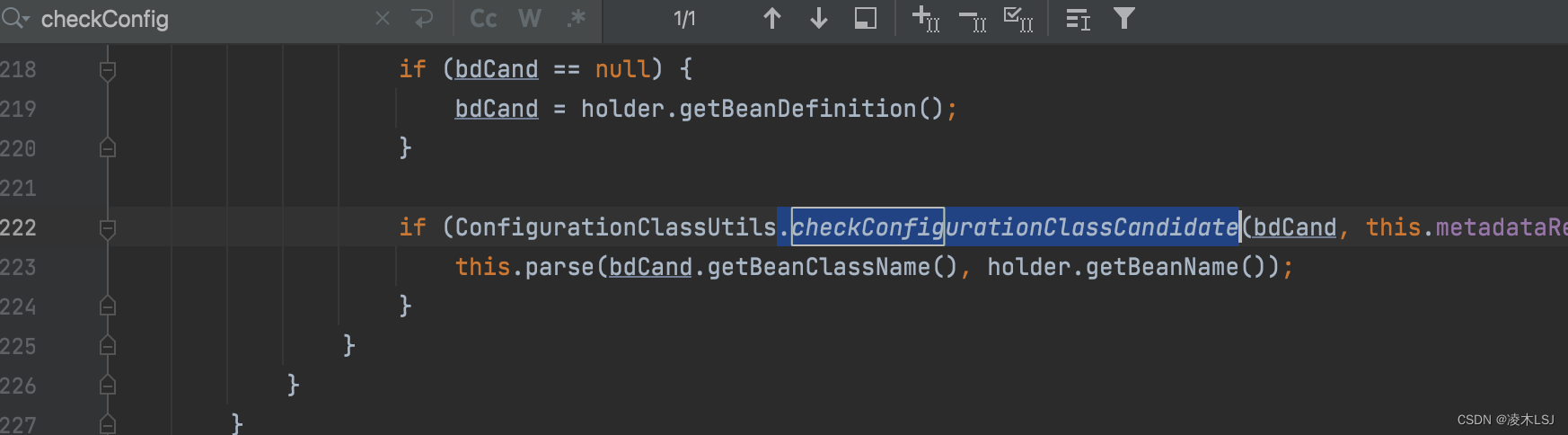

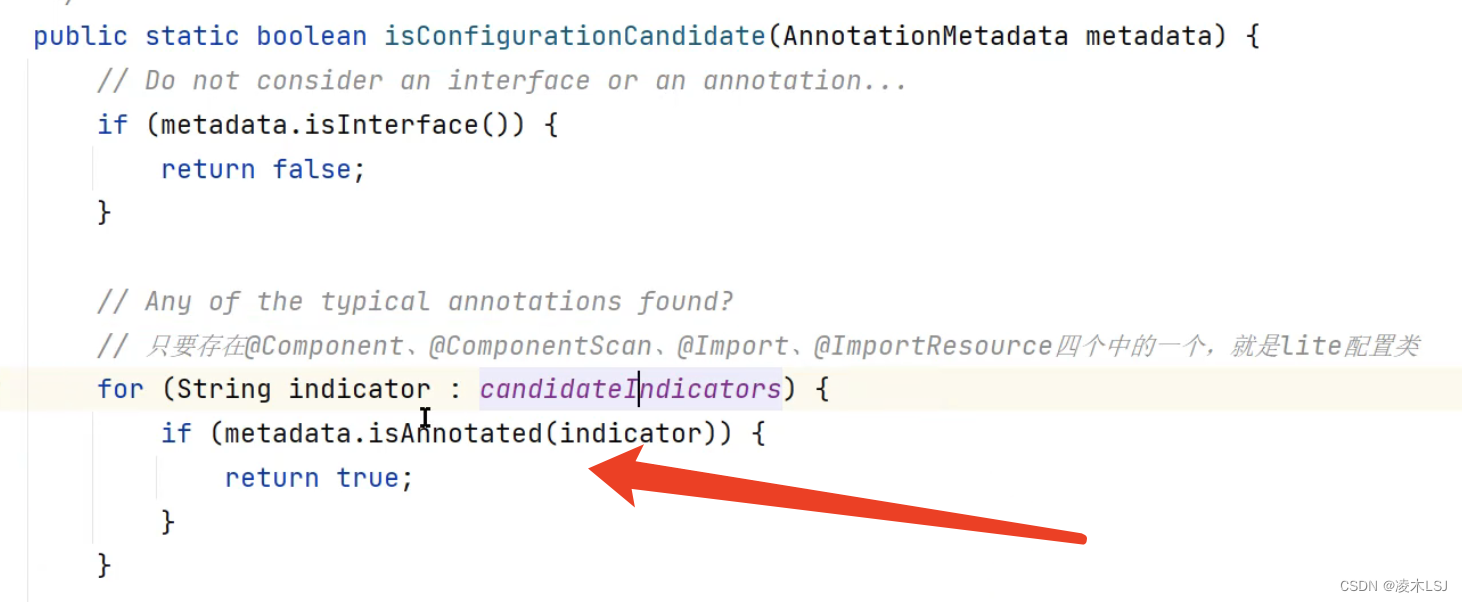

2)ComponentScan
parse解析得到BeanDefinition集合,然后去遍历BeanDefinition这些对象是不是有什么注解、配置

3)parse属性解析过程
ComponentScanAnnotationParser类

this.registry是Spring IOC容器
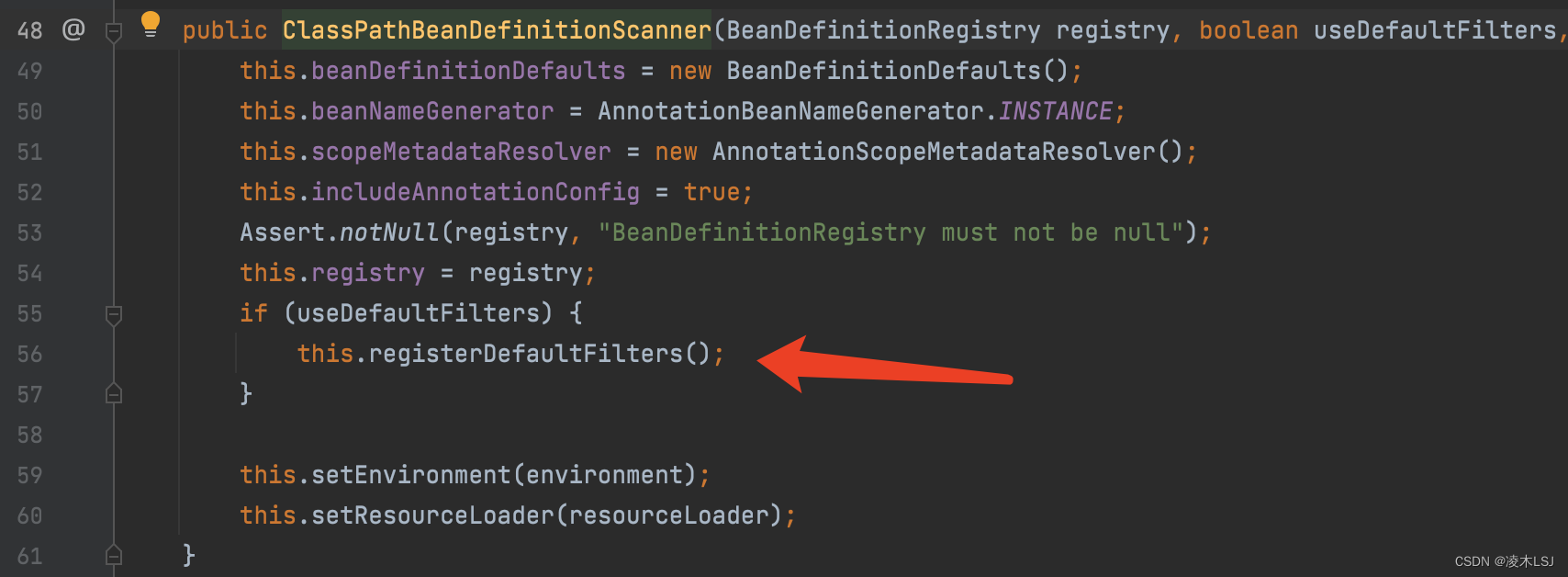
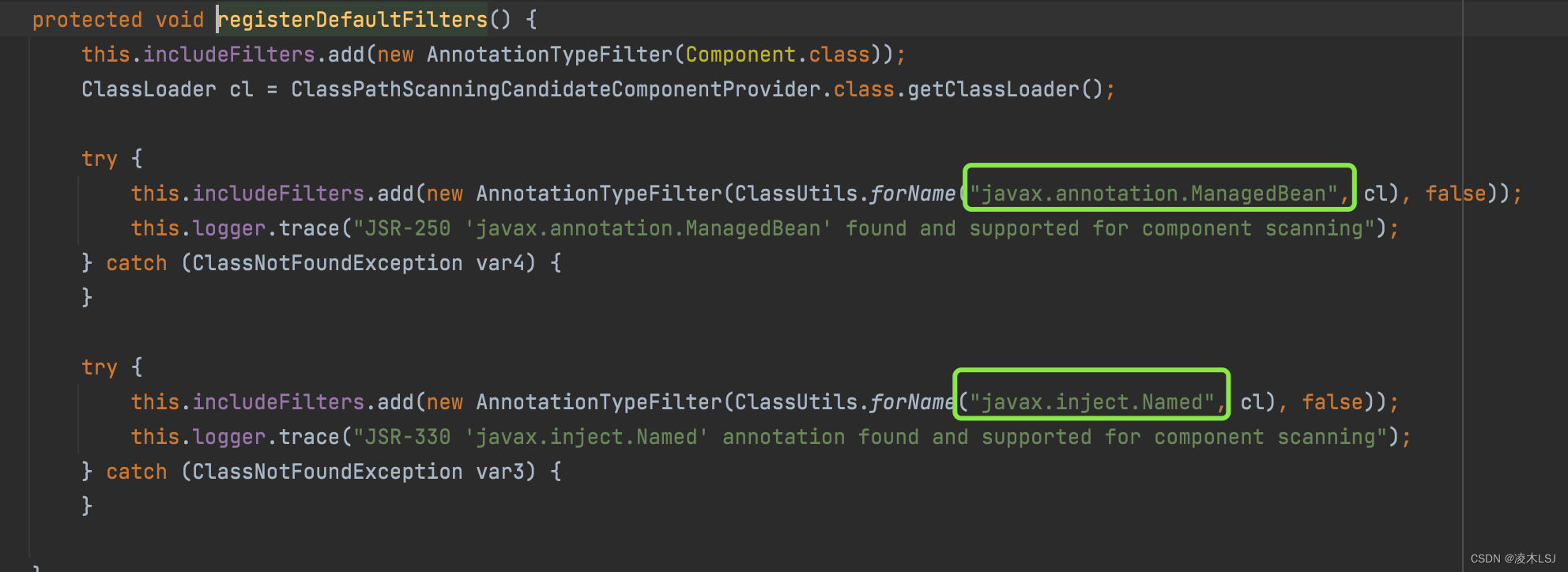
(1) useDefaultFilters属性,注册一些默认的过滤器
(2)ComponentScan的nameGenerator属性
generatorClass是nameGenerator属性的管理,没有设置该属性就使用默认值。
补充:可以根据@Component的value设置bean的名字,没有设置就根据类名进行设置。

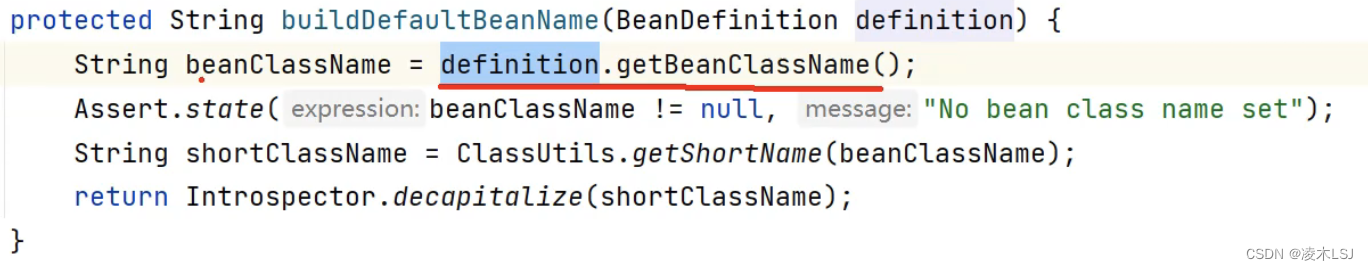
前两个字符都是大写,就直接返回;不符合就将第一个字符,设置为小写。

(3)scopeProxy属性设置

作用域在类上设置,在收到请求时再创建bean

同时可以指定代理对象的生成方式


(4)resourcePattern、includeFilters、excludeFilters属性

excludeFilters可以设置某个类不是一个bean,type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE是根据类class来过滤
@ComponentScan(value = "com.lmlsj", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {MyService.class})})
(5)懒加载

(6)扫描路径属性
根据属性值配置扫描路径,或者根据@ComponentScan注解配置扫描路径
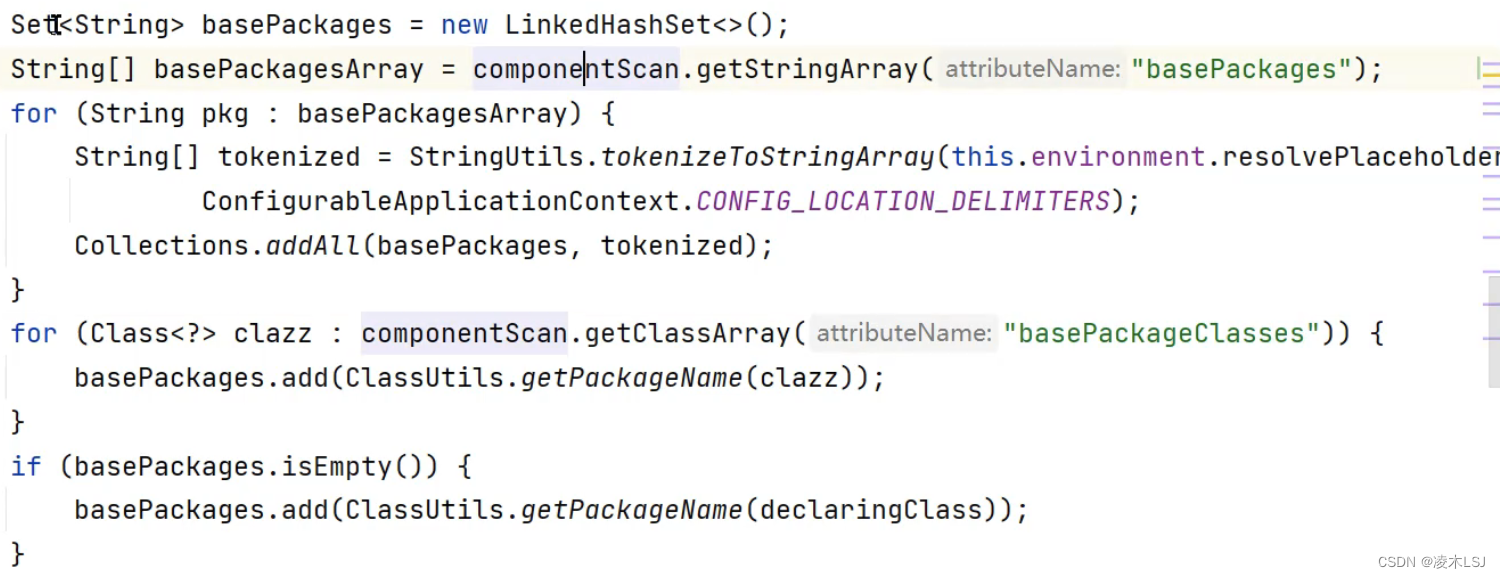
排除器,排除已经设置成bean的类

最后就是doScan真正的扫描开始。
4)doScan扫描
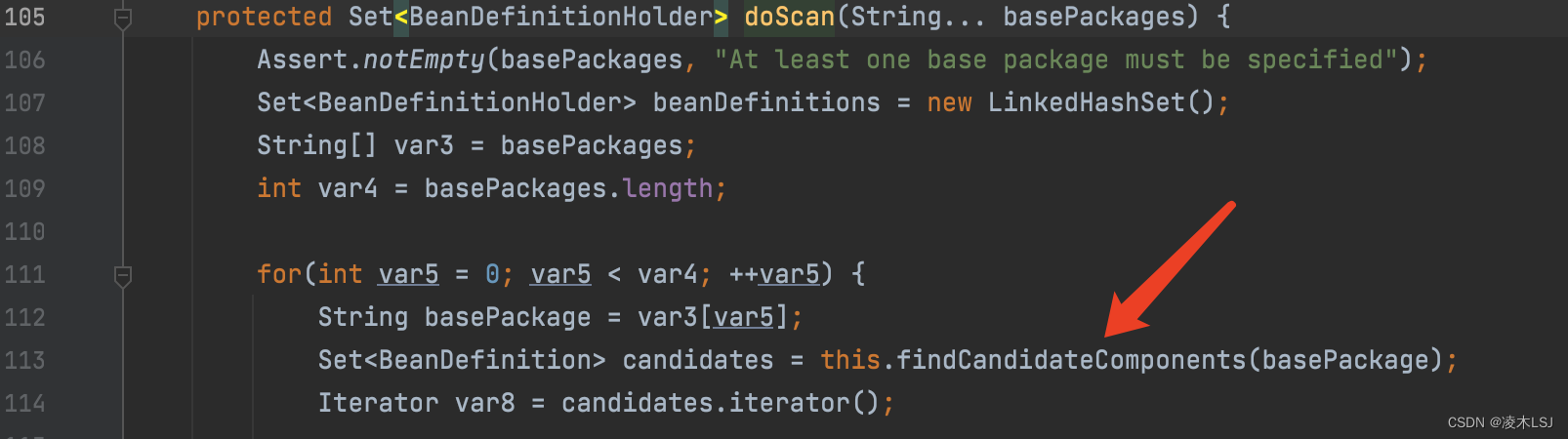
扫描包路径
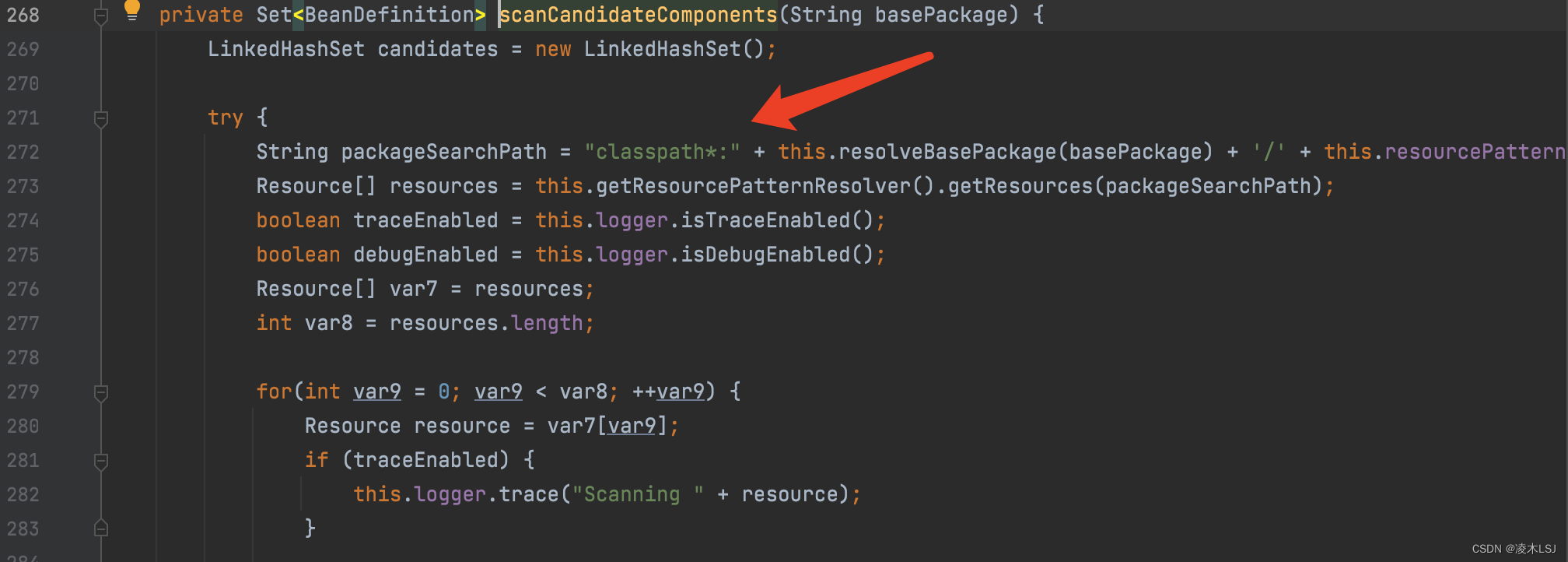
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
return this.componentsIndex != null && this.indexSupportsIncludeFilters()
?
this.addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this.componentsIndex, basePackage) :
this.scanCandidateComponents(basePackage);
}

检查是否在过滤器里
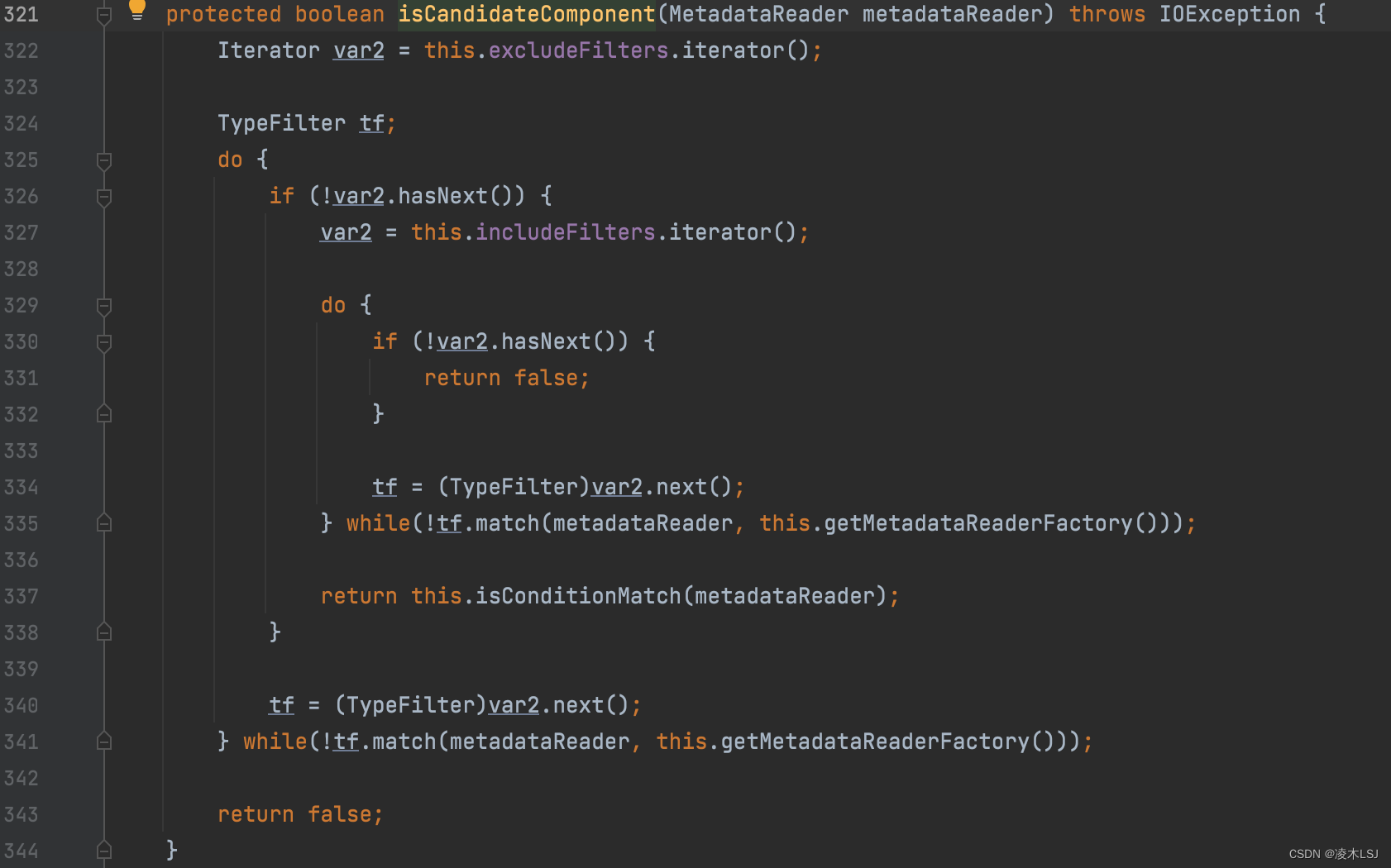
4 Spring启动demo
1)SpringApplicationContex
public class SpringApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
private Map<String,BeanDefination> beanDefinationMap = new HashMap<>();
private Map<String,Object> singletonObjects = new HashMap<>(); //单例池
private List<BeanPostProcess> beanPostProcessorList = new ArrayList<>();
public SpringApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
scan(configClass); //解析传进来的配置类,生成beanDefination
preInstantiateSingletons(); //单例bean初始化
}
private void preInstantiateSingletons() {
for(Map.Entry<String,BeanDefination> entry : beanDefinationMap.entrySet()){
BeanDefination beanDefination = entry.getValue();
if(beanDefination.getScope().equals("singleton")){
Object bean = createBean(entry.getKey(), beanDefination);
singletonObjects.put(entry.getKey(), bean); //单例bean
}
}
}
public Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefination beanDefination){
Class clazz = beanDefination.getClazz();
Object instance = null;
try {
// 1 对象实例化
instance = clazz.newInstance();
// 2 依赖注入 属性赋值
for(Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()){
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(LmAutowired.class)){
String name = field.getName(); // field.getType() ,by name/ by type
Object bean = getBean(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance,bean);
}
}
// 4 初始化前
for (BeanPostProcess beanPostProcess : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcess.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance,beanName);
}
// 3 spring初始化数值
if(instance instanceof InitializingBean){
try {
((InitializingBean)instance).afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 5 初始化后
for (BeanPostProcess beanPostProcess : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcess.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance,beanName);
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return instance;
}
public void scan(Class configClass){
// 1 解析配置类
if(configClass.isAnnotationPresent(LmComponentScan.class)){
LmComponentScan componentScan = (LmComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(LmComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScan.value();
System.out.println("配置路径: " + path);
path = path.replace(".","/");
//2 扫描配置路径下有LmComponent注解的类
ClassLoader classLoader = SpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader(); //app
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
File file = new File(resource.getFile()); //获取对应文件夹
File[] files = file.listFiles();//文件夹下所有的文件
for (File f : files) {
String fileName = f.getAbsolutePath();
if(fileName.endsWith(".class")){
String className = fileName.substring(fileName.indexOf("com"),fileName.indexOf(".class"));
className = className.replace("/",".");
try {
Class clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className);
//spring是使用ASM去解析字节码文件的,这里简单实现一下
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(LmComponent.class)){
//beanPostProcessorList初始化
if(BeanPostProcess.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)){
try {
BeanPostProcess beanPostProcess = (BeanPostProcess) clazz.newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcess);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
LmComponent annotation = (LmComponent) clazz.getAnnotation(LmComponent.class);
String beanName = annotation.value();
//3 生成beanDefination对象
BeanDefination beanDefination = new BeanDefination();
beanDefination.setClazz(clazz);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scope = (Scope) clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefination.setScope(scope.value());
}else{
beanDefination.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinationMap.put(beanName,beanDefination);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}else {
System.out.println("没有LmComponentScan注解");
}
}
public Object getBean(String beanName){
//1 判断是否已存在bean
if(beanDefinationMap.containsKey(beanName)){
BeanDefination beanDefination = beanDefinationMap.get(beanName);
//2 判断是不是单例bean
if(beanDefination.getScope().equals("singleton")){
Object o = singletonObjects.get(beanName);
return o;
}else{
//多例bean
Object bean = createBean(beanName,beanDefination);
return bean;
}
}else {
System.out.println("没有找到" + beanName);
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
}
2)BeanDefination
public class BeanDefination {
private Class clazz;
private String scope;
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
}3)BeanPostProcess
public interface BeanPostProcess {
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean,String beanName);
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean,String beanName);
}4)InitializingBean
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}5)注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface LmAutowired {
String value() default ""; //属性
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface LmComponent {
String value() default ""; //属性
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface LmComponentScan {
String value() default ""; //属性
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {
String value() default ""; //属性
}6)测试类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
//用spring 包里自己写的代码
SpringApplicationContext springApplicationContext = new SpringApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//多例bean
UserService userService = (UserService)springApplicationContext.getBean("userService");
UserService userService2 = (UserService)springApplicationContext.getBean("userService");
UserService userService3 = (UserService)springApplicationContext.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService2);
System.out.println(userService3);
userService.test();
System.out.println("_____________________");
//单例bean
OrderService orderService = (OrderService)springApplicationContext.getBean("orderService");
OrderService orderService2 = (OrderService)springApplicationContext.getBean("orderService");
OrderService orderService3 = (OrderService)springApplicationContext.getBean("orderService");
System.out.println(orderService);
System.out.println(orderService2);
System.out.println(orderService3);
}
}
7)BeanPostProcesorImpl
@LmComponent
public class BeanPostProcesorImpl implements BeanPostProcess {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if(beanName.equals("orderService")){
System.out.println("初始化之前");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
//代理AOP在此实现
return bean;
}
}8)AppConfig
@LmComponentScan("com.lmlsj.test")
public class AppConfig {
}9)其他类
@LmComponent("orderService")
public class OrderService {
}
@LmComponent("userDao")
public class UserDao {
}
@LmComponent("userService")
@Scope("prototype")
public class UserService implements InitializingBean {
@LmAutowired
private UserDao userDao;
private User defaultUser;
public void test(){
System.out.println(userDao);
System.out.println(defaultUser.getName() + ":" + defaultUser.getPass());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
defaultUser = new User("default","123456");
}
}
10)测试结果