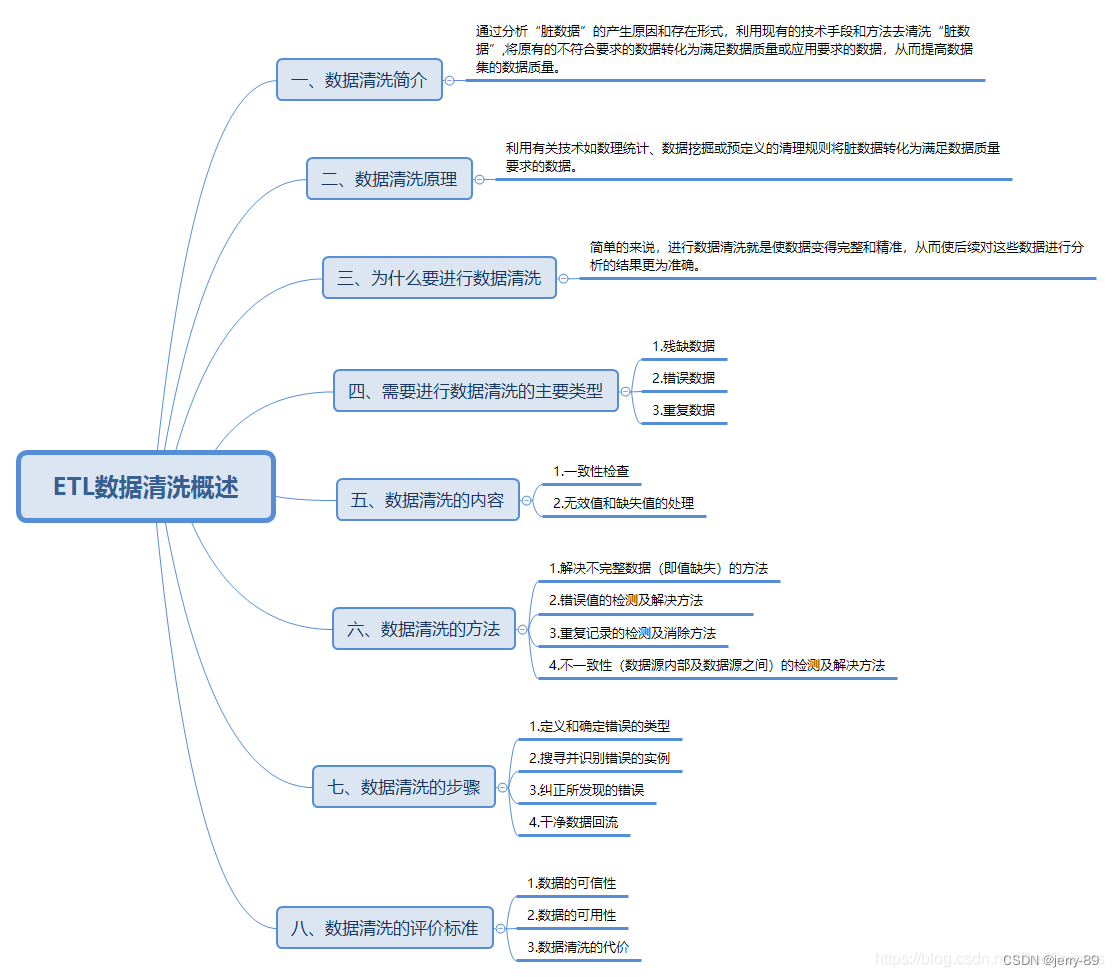
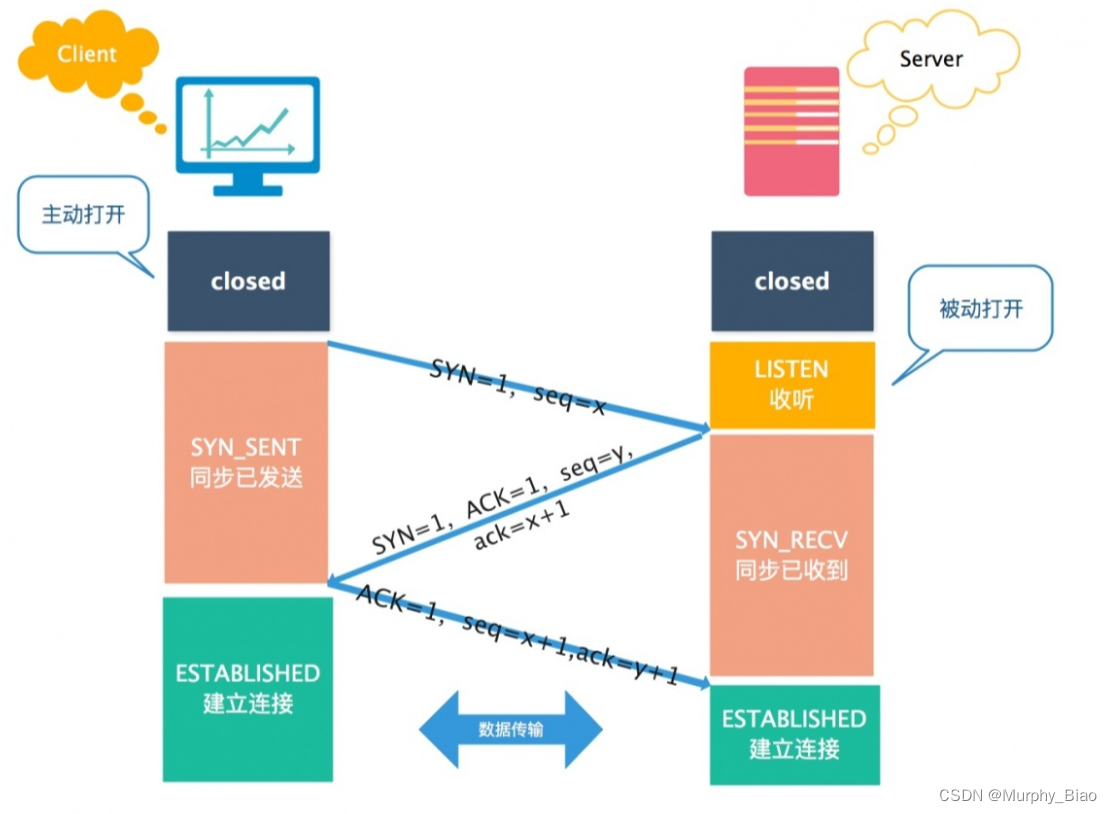
pause函数
该函数功能主要是暂停进程,它的返回值总是-1。
使用方式:
(1)首先使用signal函数提前注册一个中断函数,该函数用于将函数指针和信号做一个绑定;
(2)当程序进行执行pause,该进程暂停,等待处理信号,当任何信号到来时,程序将继续执行,不理会signal函数的响应。如果和signal中注册的信号相同,将会执行siganl中注册的函数,再继续执行后续代码;如果不同,将不会执行绑定的操作,直接退出。
以下是进程等待的信号表示:
| 信号表示 | 快捷键 | 该信号的意义 |
|---|---|---|
SIGINT | Ctrl+C | 进程中断 |
SIGTSTP | Ctrl+Z | 终端的停止信号 |
注意:
- 使用
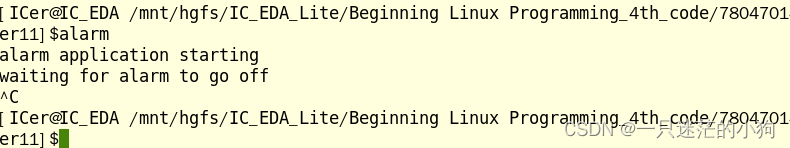
fork创建子进程之后,父子进程都可以接受到信号;/* In alarm.c, the first function, ding, simulates an alarm clock. */ #include <signal.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> static int alarm_fired = 0; void ding(int sig) { alarm_fired = 1; } /* In main, we tell the child process to wait for five seconds before sending a SIGALRM signal to its parent. */ int main() { pid_t pid; printf("alarm application starting\n"); pid = fork(); switch(pid) { case -1: /* Failure */ perror("fork failed"); exit(1); case 0: /* child */ sleep(5); kill(getppid(), SIGALRM); exit(0); } /* The parent process arranges to catch SIGALRM with a call to signal and then waits for the inevitable. */ printf("waiting for alarm to go off\n"); (void) signal(SIGALRM, ding); pause(); // if (alarm_fired) printf("Ding!\n"); printf("done\n"); exit(0); }父进程通过pid=fork()创建子进程后,子进程在休息5秒后向父进程发送ALARM信号。
此时父进程因为调用pause( )函数而被阻塞;
但是如果在5秒时间内父进程收到任何其他的信号,父进程将不会执行 (void) signal(SIGALRM, ding);语句,而是继续执行剩下的语句;
运行示例如下:在子进程向父进程发送ALARM信号时间内,通过终端向父进程发送Ctrl+C信号,此时父进程来不及接收子进程发送的ALARM,此时父进程的pause函数恢复执行。 -