文件的基础
-
概念:一组相关数据的有序集合
-
文件的类型:
常规文件-r
目录文件-d
字符设备文件-c:键盘
块设备文件-b:U盘 磁盘
管道文件-p
套接字文件-s
符号链接文件-I:快捷方式
标准I/O 流
-
file
标准IO用一个结构体类型来保存打开的文件的相关信息
标准的IO操作都是围绕file来进行的 -
流(stream)
file有被称为流(stream)
文本流/二进制流
文本流/二进制流
-
window :
二进制流:换行符 ‘/n’
文本流:换行符:‘/r’ ‘/n’ -
linux:
换行符:‘/n’
流的缓冲的类型
- 全缓冲:缓冲区写满再将数据写入磁盘
- 行缓冲:当行结束时,将数据写入磁盘
- 无缓冲:直接读写磁盘
- 标准的输入流
- 标准的输出流
- 标准的错误流
文件的打开和关闭
-
打开:占用资源
-
关闭:释放资源
-
打开函数:FILE *fopen (const char *path, const char *mode);
-
- Path:普通文件当前路径不需要加目录,其他要使用完整的路径
-
- Mode:
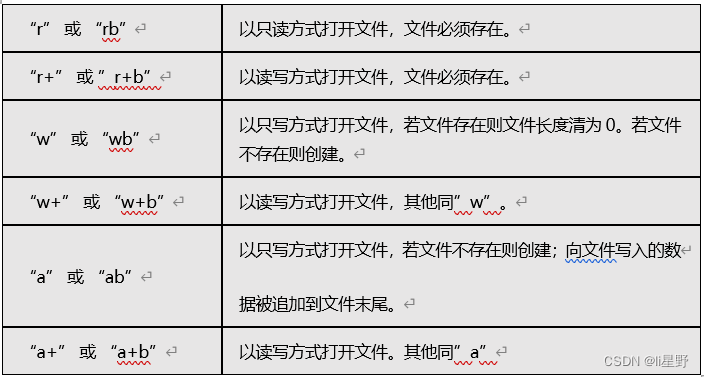
- Mode:
-
- 返回值:出现错误返回NULL,使用必须判断是否为空
文件的关闭
函数:int fclose(FILE *stream)
- fclose()调用成功返回0,失败返回EOF(-1),并设置errno
- fclose()函数的入参stream必须保证为非空,否则出现断错误。
打开关闭练习
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
int ret;
fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (fp = NULL) {
perror("fopen");
printf("fopen:%s\n", strerror(errno));
} else {
printf("Open file success\n");
}
ret = fclose(fp);
if (ret == 0) {
printf("file close sucess\n");
} else {
perror("fclose");
printf("fclose:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return 0;
}
字符的输入
读单个字符
- int fgetc(FILE *stream);
- int getc(FILE *stream); //宏
- int getchar(void);
成功时返回读取的字符;若到文件末尾或出错时返回EOF(-1),
getchar()等同于fgetc(stdin)
getc和fgetc区别是一个是宏一个是函数
读取整个行
- char *gets(char *s); 读取标准输入到缓冲区s
- char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);
成功时返回s,到文件末尾或出错时返回NULL
遇到’\n’或已输入size-1个字符时返回,总是包含’\0’
字符的输出
写单个字符
- int fputc(int c, FILE *stream);
- int putc(int c, FILE *stream);
- int putchar(int c);
成功时返回写入的字符;出错时返回EOF
putchar©等同于fputc(c, stdout)
读取整个行
- int puts(const char *s);
- int fputs(const char *s, FILE *stream);
成功时返回非负整数;出错时返回EOF
puts将缓冲区s中的字符串输出到stdout,并追加’\n’
fputs将缓冲区s中的字符串输出到stream,不追加 ‘\n’
二进制读写
文本文件和二进制的区别:
存储的格式不同:文本文件只能存储文本。
二进制读写函数格式:
-
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE *fp);
void *ptr 读取内容放的位置指针
size_t size 读取的块大小
size_t n 读取的个数
FILE *fp 读取的文件指针 -
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE *fp);
void *ptr 写文件的内容的位置指针
size_t size 写的块大小
size_t n 写的个数
FILE *fp 要写的文件指针
流的刷新
int fflush(FILE *fp);
成功时返回0;出错时返回EOF
将流缓冲区中的数据写入实际的文件
Linux下只能刷新输出缓冲区,输入缓冲区丢弃
如果输出到屏幕使用fflush(stdout)
流的定位:
long ftell(FILE *stream);
long fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence);
void rewind(FILE *stream);
fseek 参数whence参数:SEEK_SET/SEEK_CUR/SEEK_END
SEEK_SET 从距文件开头 offset 位移量为新的读写位置
SEEK_CUR:以目前的读写位置往后增加 offset 个位移量
SEEK_END:将读写位置指向文件尾后再增加 offset 个位移量
offset参数:偏移量,可正可负
注意事项:
1.文件的打开使用a模式 fseek无效
2.rewind(fp) 相当于 fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET);
3.这三个函数只适用2G以下的文件
格式化输出(重要)
int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *fmt, …);
int sprintf(char *s, const char *fmt, …);
成功时返回输出的字符个数;出错时返回EOF
格式化输入
int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, …);
int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format, …);
文件IO的API
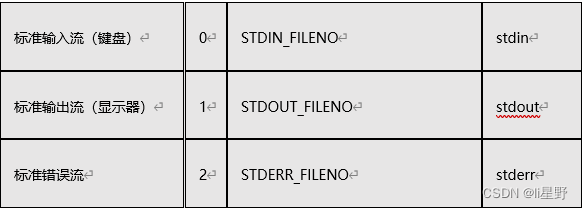
文件描述符概念:
英文:缩写fd(file descriptor)
是0-1023的数字,表示文件。
0, 1, 2 的含义 标准输入,标准输出,错误
- 文件IO 打开 open
int open(const char *pathname, int flags); 不创建文件
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); 创建文件,不能创建设备文件
成功时返回文件描述符;出错时返回EOF
文件IO和标准的模式对应关系:
r—— O_RDONLY
r+—— O_RDWR
w —— O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664
w+ —— O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664
a —— O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0664
a+ —— O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0664
- umask概念:
umask 用来设定文件或目录的初始权限 - 文件的关闭
int close(int fd)
关闭后文件描述符不能代表文件
对目录的操作
打开目录
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd); 使用文件描述符,要配合open函数使用
DIR是用来描述一个打开的目录文件的结构体类型
成功时返回目录流指针;出错时返回NULL
读取目录
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
struct dirent是用来描述目录流中一个目录项的结构体类型
包含成员char d_name[256] 参考帮助文档
成功时返回目录流dirp中下一个目录项;
出错或到末尾时时返回NULL
关闭目录
closedir函数用来关闭一个目录文件:
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
成功时返回0;出错时返回EOF
修改文件权限
chmod/fchmod函数用来修改文件的访问权限:
#include <sys/stat.h>
int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
成功时返回0;出错时返回EOF
获取文件属性
#include <sys/stat.h>
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
成功时返回0;出错时返回EOF
如果path是符号链接stat获取的是目标文件的属性;而lstat获取的是链接文件的属性
练习:使用文件IO实现“每隔1秒向文件1.txt写入当前系统时间,行号递增”
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int fd;
int ret;
time_t ctime;
struct tm *ctimestr;
int linecount = 0;
char rbuf[32];
char wbuf[32];
fd = open("1.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0666);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open");
return 0;
}
while (1) {
memset(rbuf, 0, sizeof(rbuf));
ret = read(fd, rbuf, sizeof(rbuf)); //写入字符串长度 "\0结束"
if (ret < 0) {
perror("write");
ret = close(fd);
return 0;
}
if (ret == 0) {
break;
}
if (strcmp(rbuf, "\n")) {
linecount++;
}
}
while (1) {
ctime = time(NULL); //获取当前时间
ctimestr = localtime(&ctime); //转换为结构体格式
sprintf(wbuf, "%d, %04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", linecount,
ctimestr->tm_year + 1900, ctimestr->tm_mon + 1, ctimestr->tm_mday,
ctimestr->tm_hour, ctimestr->tm_min, ctimestr->tm_sec);
printf("wbuf:%s", wbuf);
ret = write(fd, wbuf, sizeof(wbuf));
if (ret < 0) {
perror("write");
ret = close(fd);
return 0;
}
linecount++;
sleep(1);
}
ret = close(fd);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("close");
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
练习:遍历一个文件夹下所有文件,并打印文件权限、大小和日期
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define FILENAME "./day5_1"
int main() {
DIR *dp;
struct dirent *dt;
struct stat buf;
int ret;
struct tm *t;
dp = opendir(FILENAME);
if (dp < 0) {
perror("opendir");
return 0;
}
while ((dt = readdir(dp)) != NULL) {
if (strcmp(dt->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(dt->d_name, "..") == 0) {
continue;
}
// printf("%s\n", dt->d_name);
char name[64] = {0};
memset(name, 0, sizeof(name));
memcpy(name, FILENAME, sizeof(FILENAME));
strcat(name, "/");
strcat(name, dt->d_name);
// printf("%s\n", name);
ret = stat(name, &buf);
if (ret < 0) {
perror("stat");
return 0;
}
if (S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("-");
}
if (S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("d");
}
if (S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("c");
}
if (S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("b");
}
if (S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("p");
}
if (S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode)) {
printf("s");
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if (buf.st_mode & (1 << i)) {
switch (i % 3) {
case 2:
printf("r");
break;
case 1:
printf("w");
break;
case 0:
printf("x");
break;
}
} else {
printf("-");
}
}
printf(" %d", (int)buf.st_size);
t = localtime(&buf.st_ctime);
printf(" %d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d", t->tm_year + 1900, t->tm_mon + 1, t->tm_mday,
t->tm_hour+8, t->tm_min, t->tm_sec);//小时+8北京时间
printf(" %s\n", dt->d_name);
}
closedir(dp);
return 0;
}