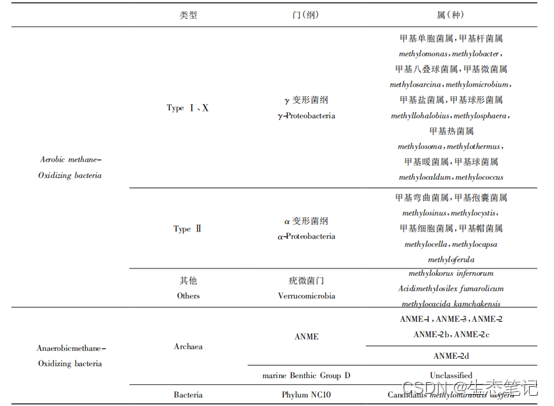
散列表
完整可编译运行代码:Github:Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_22hash/
定义
字典的另一种表示方法是散列(hashing)。它用一个散列函数(也称哈希函数)把字典的数对映射到一个散列表(也称哈希表)的具体位置。如果数对p的关键字是k,散列函数为f,那么在理想情况下,p 在散列表中的位置为f(k)。暂时假定散列表的每一个位置最多能够存储一个记录。为了搜索关键字为 k 的数对,先要计算f(k),然后查看在散列表的f(k)处是否已有一个数对。如果有,便找到了该数对。如果没有,字典就不包含该数对。在前一种情况下,可以删除该数对,为此只需使散列表的f(k)位置为空。在后一种情况下,可以把该数对插在f(k)的位置。
初始化一个空字典需要的时间为 O(b)(b 为散列表拥有的位置数),查找、插入、删除操作的时间均为0(1)。
散列函数和散列表
桶和起始桶
当关键字的范围太大,不能用理想方法表示时,可以采用并不理想的散列表和散列函数:散列表位置的数量比关键字的个数少,散列函数把若干个不同的关键字映射到散列表的同一个位置。散列表的每一个位置叫一个桶(bucket);对关键字为 k的数对,f(k)是起始桶(home bucket);桶的数量等于散列表的长度或大小。因为散列函数可以把若干个关键字映射到同一个桶,所以桶要能够容纳多个数对。本章我们考虑两种极端情况。第一种情况是每一个桶只能存储一个数对。第二种情况是每一个桶都是一个可以容纳全部数对的线性表。
除法散列函数
f ( k ) = k % D ( 10 − 2 ) f(k)=k\%D (10-2) f(k)=k%D(10−2)
其中 k 是关键字,D 是散列表的长度(即桶的数量),%为求模操作符。散列表的位置索引从0到D-1。当D=11时,与关键字3、22、27、40、80和96分别对应的起始桶是f(3)=3,f(22)=0,f(27)=5,f(40)=7,f(80)=3 和f(96)=8。
冲突和溢出
散列表有 11 个桶,序号从 0 到 10,而且每一个桶可以存储一个数对。除数D为11。因为80%11=3,则 80 的位置为3,40的位置为40%11=7,65的位置为65%11=10。每个数对都在相应的起始桶中。散列表余下的桶为空。
现在假设要插入 58。58 的起始桶为f(58)=58%11=3。这个桶已被另一个关键字占用。这时就发生了冲突。**当两个不同的关键字所对应的起始桶相同时,就是冲突(collision)发生了。**因为一个桶可以存储多个数对,因此发生碰撞也没什么了不起。只要起始桶足够大,所有对应同一个起始桶的数对都可存储在一起。如果存储桶没有空间存储一个新数对,就是溢出(overflow)发生了。
我需要一个好的散列函数
当映射到散列表中任何一个桶里的关键字数量大致相等时,冲突和溢出的平均数最少。**均匀散列函数(uniform hash function)**便是这样的函数。
在实际应用中,关键字不是从关键字范围内均匀选择的,因此有的均匀散列函数表现好一点,有一些就差一些。那些在实际应用中性能表现好的均匀散列函数被称为良好散列函数(good hash function)。
对于除法散列函数,假设 D 是偶数。当 k是偶数时,f(k)是偶数;当k 是奇数时,f(k)是奇数。例如 k%20,当k是偶数时为偶数,当k是奇数时为奇数。如果你的应用以偶数关键字为主,那么大部分关键字都被映射到序号为偶数的起始桶里。如果你的应用以奇数关键字为主,那么大部分关键字都被映射到序号为奇数的起始桶里。因此,选择D为偶数,得到的是不良散列函数。
当 D 可以被诸如 3、5 和 7 这样的小奇数整除时,不会产生良好散列函数。因此,要使除法散列函数成为良好散列函数,你要选择的除数D应该既不是偶数又不能被小的奇数整除。理想的D是一个素数。当你不能用心算找到一个接近散列表长度的素数时,你应该选择不能被2和19之间的数整除的D。
因为在实际应用的字典中,关键字是相互关联的,所以你所选择的均匀散列函数,其值应该依赖关键字的所有位(而不是仅仅取决于前几位,或后几位,或中间几位)。当D既是素数又不能被小于20的数整除,就能得到良好散列函数。
除法和非整型关键字
为使用除法散列函数,在计算f(k)之前,需要把关键字转换为非负整数。
需要将串数据、结构和算法转换为整数。
冲突和溢出的解决方案
线性探查
- 插入元素
散列表有 11 个桶,序号从 0 到 10,而且每一个桶可以存储一个数对。除数D为11。因为80%11=3,则 80 的位置为3,40的位置为40%11=7,65的位置为65%11=10。每个数对都在相应的起始桶中。散列表余下的桶为空。
现在假设要插入 58。58 的起始桶为f(58)=58%11=3。这个桶已被另一个关键字占用。这时就发生了冲突。
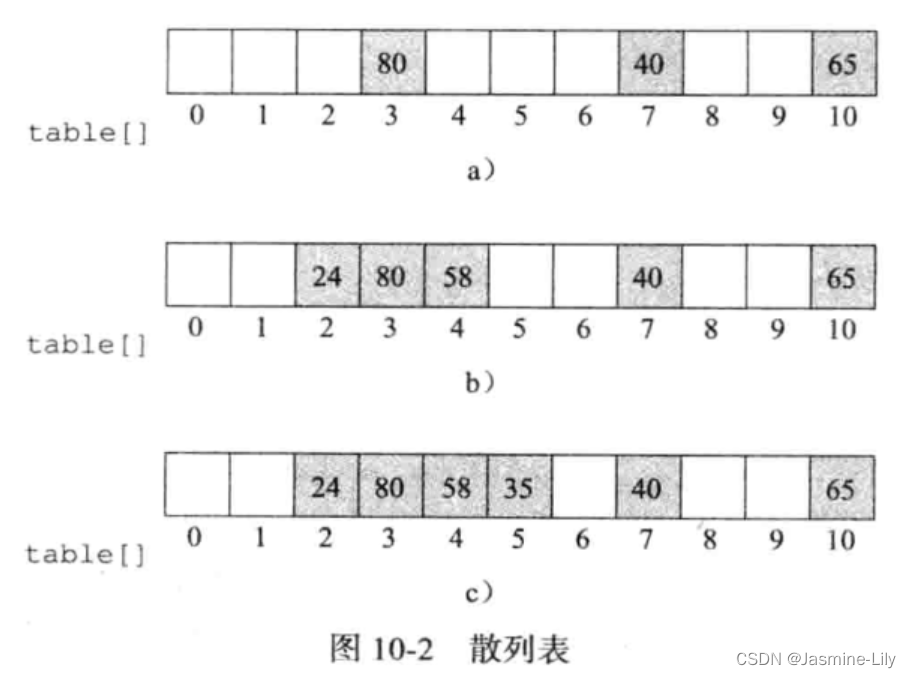
要在图 10-2a 的散列表中把 58放进去,最简单方法是找到下一个可用的桶。这种解决溢出的方法叫作线性探查(Linear Probing)。
58 因此被存储在 4 号桶。假设下一个要插入的数对关键字为 24,24%11=2,2 号桶为空,于是把24放入2号桶。这时的散列表如图 10-2b所示。现在要插入35。35的起始桶2已满。用线性探查,结果如图 10-2c 所示。最后一例,插入 98。它的起始桶 10已满,而下一个可用桶是 0 号桶,于是 98 被插入在此。由此看来,在寻找下一个可用桶时,散列表被视为环形表。
- 查找元素
假设要查找关键字为k的数对,首先搜索起始桶f(k),然后把散列表当做环表继续搜索下一个桶,直到以下情况之一发生为止:
1)存有关键字 k 的桶已找到,即找到了要查找的数对;
2)到达一个空桶;
3)又回到起始桶f(k)。
后两种情况说明关键字为k的数对不存在。
- 删除一个元素
删除一个记录要保证上述的搜索过程可以正常进行。若在图 10-2c 中删除了关键字 58,不能仅仅把4号桶置为空,否则就无法找到关键字为35的数对。删除需要移动若干个数对。从删除位置的下一个桶开始,逐个检查每个桶,以确定要移动的元素,直至到达一个空桶或回到删除位置为止。在做删除移动时,一定要注意,不要把一个数对移到它的起始桶之前,否则,对这个数对的查找就可能失败。
实现删除的另一个策略是为每个桶增加一个域 neverUsed。在散列表初始化时,这个域被置为true。当一个数对存入一个桶中时,neverUsed域被置为false。现在,搜索的结束条件2)变成:桶的 neverUsed域为 true。不过在删除时,只是把表的相应位置置为空。一个新元素被插入在其对应的起始桶之后所找到的第一个空桶中。注意,在这种方案中,neverUsed不会重新置为true。用不了多长时间,所有(或几乎所有)桶的neverUsed域都等于false,这时搜索是否失败,只有检查所有的桶之后才可以确定。为了提高性能,当很多空桶的neverUsed域等于false时,必须重新组织这个散列表。例如,可把所有余下的数对都插到一个空的散列表中。这种方案不太可行
- 性能分析
我们只分析时间复杂度。设b为散列表的桶数,D为散列函数的除数,且b=D。散列表初始化的时间为0(b)。当表中有n个记录时,最坏情况下的插入和查找时间均为0(n)。当所有关键字都对应同一个起始桶时,便是最坏情况。把字典的散列在最坏情况下的复杂度与线性表在最坏情况下的复杂度相比较,二者完全相同。
然而,就平均性能而言,散列远远优于线性表。令
U
n
U_n
Un,和
S
n
S_n
Sn,分别表示在一次成功搜索和不成功搜索中平均搜索的桶数,其中 n是很大的值。这个平均值是由插入的 n个关键字计算得来的。对于线性探查,有如下近似公式:
U
n
≈
1
2
(
1
+
1
(
1
−
α
)
2
)
(
10
−
3
)
U_n\approx\frac{1}{2}\left(1 + \frac{1}{(1-\alpha)^2}\right)(10-3)
Un≈21(1+(1−α)21)(10−3)
S n ≈ 1 2 ( 1 + 1 1 − α ) ( 10 − 4 ) S_n\approx\frac{1}{2}\left(1 + \frac{1}{1-\alpha}\right)(10-4) Sn≈21(1+1−α1)(10−4)
其中 α \alpha α=n/b为负载因子(loading factor)。
从上述公式可以证明,当 α \alpha α=0.5时,一次不成功的搜索将平均查找2.5 个桶,一次成功的搜索将平均查找 1.5 个桶。当 α \alpha α=0.9时,这些数字分别为 50.5 和 5.5。当然,这时假定 n 比 51 大得多。当负载因子比较小时,使用线性探查,散列的平均性能比线性表的平均性能要优越许多。一般情况下都是 α \alpha α<0.75。可以根据 α \alpha α和n的值确定b的值,从什么样的 α \alpha α能接受上考虑。
随机探查分析
用随机数生成器产生一个桶的搜索序列,然后用这个序列去确定插入位置。
理 10-1 设p 是某一事件发生的概率。为了该事件发生,独立试验的期望次数是 1/p。
U
n
U_n
Un,公式按如下方式导出:当装载因子是a时,一个桶有数对的概率是a,没有数对的概率为 p=1-a。在随机探查中,使用一个独立试验序列进行搜索,一次失败的搜索是找到一个空桶,为此,我们期望搜索的桶数是:
U
n
≈
a
p
=
1
1
−
α
(
10
−
5
)
U_n\approx\frac{a}{p}=\frac{1}{1-\alpha}(10-5)
Un≈pa=1−α1(10−5)
S
n
S_n
Sn,公式可以从
U
n
U_n
Un公式推导出来。按照插入顺序,给散列表的 n个记录编号为1,2,…,n。当插入第i个数对时,首先通过一次不成功的搜索找到一个空桶,然后把该数对插到这个空桶里。在插入第i个数对时,装载因子是(i-1)/b,其中b是桶数。从公式(10-5)得出,在搜索第i个桶时,查看的期望桶数是:
a
1
−
i
−
1
b
\frac{a}{1-\frac{i-1}{b}}
1−bi−1a
假设每一个数对搜索的概率是相等的,由此可得:
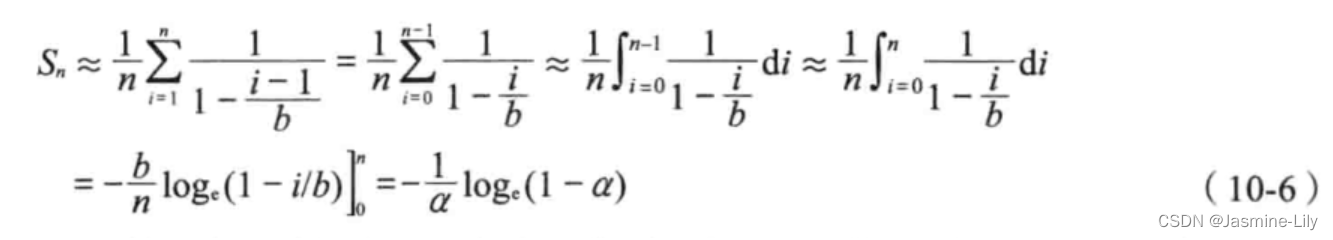
就需要查看的桶数而言,线性探查的性能不如随机探查。例如,当a=0.9时,使用线性探查进行一次不成功的搜索而期望查看的桶数是50.5,而用随机探查时,这个数降到10。
为什么不使用随机探查?
- 真正影响运行时间的不是要查看的桶数。计算一个随机数比查看若干个桶更需要时间。
- 随机探查是用随机方式搜索散列表,高速缓存使运行时间增大。因此,尽管随机探查需要查看的桶数要比线性探查少,但是它实际使用的时间很多,除非装载因子接近1。
链式散列
如果散列表的每一个桶可以容纳无限多个记录,那么溢出问题就不存在了。实现这个目标的一个方法是给散列表的每一个位置配置一个线性表。这时,每一个数对可以存储在它的起始桶线性表中。
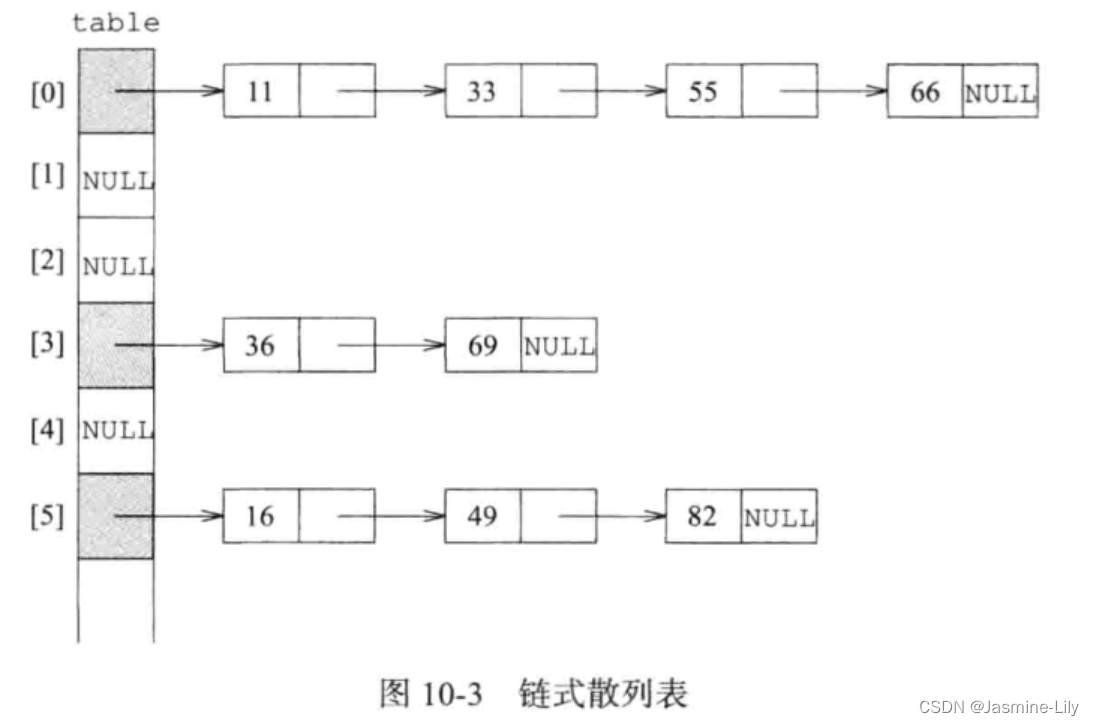
为搜索关键字值为 k的记录,首先计算其起始桶,k%D,然后搜索该桶所对应的链表。为插入一个记录,首先要保证散列表没有一个记录与该记录的关键字相同,为此而进行的搜索仅限于该记录的起始桶所对应的链表。要删除一个关键字为k的记录,我们要搜索它所对应的起始桶链表,找到该记录,然后删除。
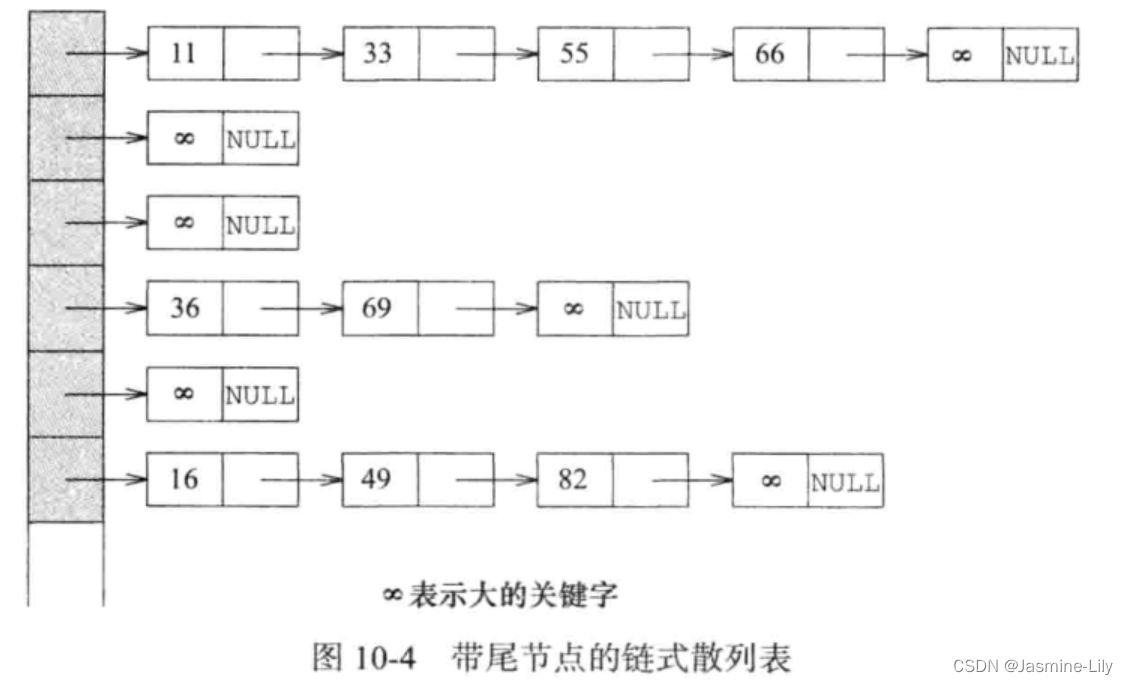
在图 10-4的每个链表上增加一个尾节点,可以改进一些程序的性能。尾节点的关键字值最起码要比插入的所有数对的关键字都大。在图10-4中,尾节点的关键字用正无穷来表示。在实际应用中,当关键字为整数时,可以用limits.h文件中定义的INT_MAX常量来替代。有了尾节点,就可以省去在sortedChain的方法中出现的大部分对空指针的检验操作。注意,在图 10-4 中,每个链表都有不同的尾节点,而实际上,所有链表可共用一个尾节点。
链式散列与线性探查相比:
线性探查占用的空间小于链式散列的空间,因为链式散列需要存储一些指针。
使用链表时要检查的节点数比使用线性和随机探查时要检查的桶数少。(详细证明见《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》原书第二版链式散列介绍中 与线性探查比较 公式详细介绍)
链式散列与跳表相比:
通过使用随机过程,跳表和散列操作的平均复杂度分别是对数级和常数级。跳表方法的最坏时间复杂度为O(n+maxLevel),而散列的最坏时间复杂度为O(n)。跳表中指针平均占用的空间约为maxLevel+n/(1-p);最坏情况需要maxLevel*(n+1)个指针空间。就最坏情况下的空间需求而言,跳表远远大于链式散列。链式散列需要的指针空间为D+n。
不过,跳表比散列更灵活。例如,只需简单地沿着 0 级链就可以在线性时间内按关键字升序输出所有的元素。使用链式散列时,需要O(D)时间去搜索最多D个非空链表,另外需要O(nlogD)时间把有序链表按关键字升序合并。合并过程如下:
1)把链表放到一个队列中;
2)从队列中提取一对链表,把它们合并为一个有序链表,然后放入队列;
3)重复步骤2),直至队列中仅剩一个链表。其他的操作,如查找或删除其关键字最大或最小的数对,使用散列也要花费更多的时间(仅考虑平均复杂度)。
代码测试
main.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: main()函数,控制运行所有的测试函数
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "_25hashTable.h"
#include "_26hashChains.h"
int main()
{
hashTableTest();
hashChainsTest();
return 0;
}
_25hash.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈希---散列函数(将type K转换为非负整数)
// functions to convert from type K to nonnegative integer
// derived from similar classes in SGI STL
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _HASH_H_
#define _HASH_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/*之前名称时hash,实例化hash一直报错,然后我就各种找原因*/
/*后来发现原因可能是 C++STL源文件定义了hash类,所以我后面定义的模板就不作数,所以一直报错*/
/*因此解决方案就是:将类名称hash改为hashNode*/
template <class K>
class hashNode
{
public:
size_t operator()(const int theKey) const
{
return size_t(theKey);
}
};
/*这是一个实例化*/
template<>
class hashNode<string>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const string theKey) const
{// Convert theKey to a nonnegative integer.
unsigned long hashNodeValue = 0;
int length = (int)theKey.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
hashNodeValue = 5 * hashNodeValue + theKey.at(i);
return size_t(hashNodeValue);
}
};
/*这是一个实例化*/
template<>
class hashNode<int>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const int theKey) const
{
return size_t(theKey);
}
};
/*这是一个实例化*/
template<>
class hashNode<long>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const long theKey) const
{
return size_t(theKey);
}
};
#endif
_25hashTable.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈希表(数组存储)---使用线性探查的头文件---是无序的
// hash table using linear open addressing and division
// implements dictionary methods other than erase
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _HASHTABLE_H_
#define _HASHTABLE_H_
#include <iostream>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_25hash.h" // mapping functions from K to nonnegative integer
using namespace std;
/*测试函数*/
void hashTableTest();
template<class K, class E>
class hashTable
{
public:
hashTable(int theDivisor = 11);
~hashTable() { delete[] table; }
bool empty() const { return dSize == 0; }
int size() const { return dSize; }
pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const;
void insert(const pair<const K, E>&);
void erase(const K theKey);
/*友元函数*/
/*输入字典*/
istream& input(istream& in);
// friend istream& operator>> <K, E>(istream& in, hashTable<K, E>& m);
/*输出字典*/
ostream& output(ostream& out) const;
// friend ostream& operator<< <K, E>(ostream& out, const hashTable<K, E>& m);
protected:
int search(const K&) const;
pair<const K, E>** table; // hash table
hashNode<K> hashNode; // maps type K to nonnegative integer
int dSize; // number of pairs in dictionary
int divisor; // hash function divisor
};
/*输入字典*/
template<class K, class E>
istream& hashTable<K, E>::input(istream& in)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
while (!(in >> numberOfElement))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
}
K first;
E second;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
while (!(in >> first >> second))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
}
const pair<const K, E> element(first, second);
insert(element);
}
return in;
}
template<class K, class E>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, hashTable<K, E>& m){
m.input(in);
return in;
}
/*输出字典*/
template<class K, class E>
ostream& hashTable<K, E>::output(ostream& out) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < divisor; i++)
if (table[i] == nullptr)
cout << "nullptr" << " ";
else
cout << "(" << table[i]->first << "," << table[i]->second << ")" << " ";
cout << endl;
return out;
}
template<class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const hashTable<K, E>& m){
m.output(out);
return out;
}
template<class K, class E>
hashTable<K, E>::hashTable(int theDivisor)
{
divisor = theDivisor;
dSize = 0;
// allocate and initialize hash table array
table = new pair<const K, E>*[divisor];
for (int i = 0; i < divisor; i++)
table[i] = nullptr;
}
template<class K, class E>
int hashTable<K, E>::search(const K& theKey) const
{// Search an open addressed hash table for a pair with key theKey.
// Return location of matching pair if found, otherwise return
// location where a pair with key theKey may be inserted
// provided the hash table is not full.
int i = (int)hashNode(theKey) % divisor; // home bucket
int j = i; // start at home bucket
do
{
if (table[j] == nullptr || table[j]->first == theKey)
return j;
j = (j + 1) % divisor; // next bucket
} while (j != i); // returned to home bucket?
return j; // table full
}
template<class K, class E>
pair<const K, E>* hashTable<K, E>::find(const K& theKey) const
{// Return pointer to matching pair.
// Return nullptr if no matching pair.
// search the table
int b = search(theKey);
// see if a match was found at table[b]
if (table[b] == nullptr || table[b]->first != theKey)
return nullptr; // no match
return table[b]; // matching pair
}
template<class K, class E>
void hashTable<K, E>::insert(const pair<const K, E>& thePair)
{// Insert thePair into the dictionary. Overwrite existing
// pair, if any, with same key.
// Throw hashTableFull exception in case table is full.
// search the table for a matching pair
int b = search(thePair.first);
// check if matching pair found
if (table[b] == nullptr)
{
// no matching pair and table not full
table[b] = new pair<const K, E>(thePair);
dSize++;
}
else
{// check if duplicate or table full
if (table[b]->first == thePair.first)
{// duplicate, change table[b]->second
table[b]->second = thePair.second;
}
else // table is full
throw hashTableFull();
}
}
/*删除关键字为theKey的元素*/
template<class K, class E>
void hashTable<K, E>::erase(const K theKey)
{
int i = (int)hashNode(theKey) % divisor;
int j = i;
/*从起始桶开始寻找关键字为theKey的元素*/
while (table[j] != nullptr && table[j]->first != theKey)
{
j = (++j) % divisor;
/*如果找完了所有桶都没找到以theKey为关键字的数对,说明该数对不存在,抛出异常*/
if (j == i)
throw illegalParameterValue("The key is not exist");
}
if(table[j] == nullptr)
throw illegalParameterValue("The key is not exist");
/*能到这里说明已经找到以theKey为关键字的数对了*/
i = j;//使用i记录该数对的位置
delete table[i];//将该数对删除
table[i] = nullptr;
j++;//找到下一个数对
/*将后面的数对前移*/
/*不是空桶不是起始桶不是原始桶*/
while (table[j] != nullptr && (int)hashNode(table[j]->first) % divisor != j && j != i)
{
table[j - 1] = table[j];//移动后面的元素
j = (++j) % divisor;
}
}
#endif
_25hashTable.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈希表(数组存储)---使用线性探查的cpp文件
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "_25hashTable.h"
using namespace std;
void hashTableTest()
{
cout << endl << "*********************************hashTableTest()函数开始**************************************" << endl;
hashTable<int, int> a;
//测试输入和输出
cout << endl << "测试友元函数*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "输入输出************************" << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "hashTable a is:" << a;
cout << endl << "测试成员函数*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "empty()*************************" << endl;
cout << "a.empty() = " << a.empty() << endl;
cout << "size()**************************" << endl;
cout << "a.size() = " << a.size() << endl;
cout << "find()**************************" << endl;
cout << "a.find(1)->second = " << a.find(1)->second << endl;
cout << "insert()************************" << endl;
pair<const int, int> insertData(3, 4);
a.insert(insertData);
cout << "hashTable a is:" << a;
cout << "erase()*************************" << endl;
a.erase(2);
cout << "hashTable a is:" << a;
cout << "*********************************hashTableTest()函数结束**************************************" << endl;
}
_23dictionary.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月22日09点17分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 字典的抽象类
*/
/*
pair:
介绍:是将2个数据组合成一组数据,是一个结构体,主要的两个成员变量first和second,分别存储两个数据.
使用:使用std命名空间引入对组std::pair
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _DICTIONARY_H_
#define _DICTIONARY_H_
using namespace std;
template<class K,class E>
class dictionary
{
public:
virtual ~dictionary() {}
/*返回为true,当且仅当字典为空*/
virtual bool empty() const = 0;
/*返回字典中数对的数目*/
virtual int size() const = 0;
/*返回匹配数对的指针*/
virtual pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const = 0;
/*删除匹配的数对*/
virtual void erase(const K&) = 0;
/*往字典中插入一个数对*/
virtual void insert(const pair<const K, E>&) = 0;
};
#endif
_23pairNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月22日09点17分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 是字典的一个节点
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _PAIRNODE_H_
#define _PAIRNODE_H_
using namespace std;
template <class K, class E>
struct pairNode
{
typedef pair<const K, E> pairType;
pairType element;
pairNode<K, E>* next;
pairNode(const pairType& thePair) :element(thePair) {}
pairNode(const pairType& thePair, pairNode<K, E>* theNext)
:element(thePair) {
next = theNext;
}
};
#endif
_23dictionaryChain.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月22日09点17分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 使用链表实现的字典的头文件---是有序的
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _DICTIONARY_CHAIN_H_
#define _DICTIONARY_CHAIN_H_
#include <iostream>
#include "_23pairNode.h"
#include "_23dictionary.h"
using namespace std;
/*测试函数*/
void dictionaryChainTest();
template<class K, class E>
class dictionaryChain : public dictionary<K, E>
{
public:
/*成员函数*/
/*构造函数和析构函数*/
dictionaryChain() { firstNode = nullptr; dSize = 0; }
~dictionaryChain();
/*其他成员函数*/
bool empty() const { return dSize == 0; }
int size() const { return dSize; }
pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const;
void erase(const K&);
void insert(const pair<const K, E>&);
/*友元函数*/
/*输入字典*/
istream& input(istream& in);
// friend istream& operator>> <K,E>(istream& in, dictionaryChain<K,E>& m);
/*输出字典*/
ostream& output(ostream& out) const;
// friend ostream& operator<< <K,E>(ostream& out, const dictionaryChain<K,E>& m);
protected:
pairNode<K, E>* firstNode; // pointer to first node in chain
int dSize; // number of elements in dictionary
};
/*输入字典*/
template<class K, class E>
istream& dictionaryChain<K, E>::input(istream& in)
//istream& operator>>(istream& in, dictionaryChain<K,E>& m)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
while (!(in >> numberOfElement))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
}
pair<K, E> element;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
while (!(in >> element.first >> element.second))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
}
insert(element);
}
return in;
}
template<class K, class E>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, dictionaryChain<K,E>& m){
m.input(in);
return in;
}
/*输出字典*/
template<class K, class E>
ostream& dictionaryChain<K, E>::output(ostream& out) const
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const dictionaryChain<K,E>& m)
{
pairNode<K, E>* currentNode = firstNode;
while (currentNode != nullptr)
{
out << "(" << currentNode->element.first << " ," << currentNode->element.second << ")" << " ";
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
cout << endl;
return out;
}
template<class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const dictionaryChain<K,E>& m){
m.output(out);
return out;
}
/*析构函数*/
template<class K,class E>
dictionaryChain<K,E>::~dictionaryChain()
{
pairNode<K, E>* nextNode;
while (firstNode != nullptr)
{
nextNode = firstNode->next;
delete firstNode;
firstNode = nextNode;
}
}
/*寻找关键字为key的数对并返回*/
template<class K, class E>
pair<const K, E>* dictionaryChain<K, E>::find(const K& key) const
{
//返回匹配的数对的指针
//如果不存在匹配的数对,则返回nullptr
pairNode<K, E>* currentNode = firstNode;
while (currentNode != nullptr && currentNode->element.first != key)
currentNode = currentNode->next;
if (currentNode != nullptr && currentNode->element.first == key)
return ¤tNode->element;
return nullptr;//如果没找到就返回nullptr
}
/*删除关键字为key的数对*/
template<class K, class E>
void dictionaryChain<K, E>::erase(const K& key)
{
//删除关键字为key的数对
pairNode<K, E>* p = firstNode;//存储的是插入元素之后的位置
pairNode<K, E>* tp = nullptr;//存储的是插入元素之前的位置
//搜索关键字为key的数对
while (p != nullptr && p->element.first < key)
{
tp = p;
p = p->next;
}
//确定是否匹配
if (p != nullptr && p->element.first == key)
if (tp == nullptr) firstNode = p->next;//p是第一个节点
else tp->next = p->next;
delete p;
dSize--;
}
/*往字典中插入data,覆盖已经存在的匹配的数对*/
template<class K,class E>
void dictionaryChain<K, E>::insert(const pair<const K, E>& data)
{
pairNode<K, E>* p = firstNode;//存储的是插入元素之后的位置
pairNode<K, E>* tp = nullptr;//存储的是插入元素之前的位置
while (p != nullptr && p->element.first < data.first)
{
tp = p;
p = p->next;
}
//检查是否有匹配的数对
if (p != nullptr && p->element.first == data.first)
{
p->element.second = data.second;
return;
}
//无匹配的数对,为thePair建立新节点
pairNode<K, E>* newNode = new pairNode<K, E>(data, p);
//在tp之后插入新节点
if (tp == nullptr) firstNode = newNode;
else tp->next = newNode;
dSize++;
return;
}
#endif
_26hashChains.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月24日11点16分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈希表---链式散列(链表存储)---头文件---是无序的
// hash table using sorted chains and division
// implements all dictionary methods
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _HASHCHAINDS_H_
#define _HASHCHAINDS_H_
#include <iostream>
#include "_23dictionary.h"
#include "_23dictionaryChain.h"
#include "_25hash.h"
using namespace std;
/*测试函数*/
void hashChainsTest();
template<class K, class E>
class hashChains : public dictionary<K, E>
{
public:
hashChains(int theDivisor = 11)
{
divisor = theDivisor;
dSize = 0;
// allocate and initialize hash table array
table = new dictionaryChain<K, E>[divisor];
}
~hashChains() { delete[] table; }
bool empty() const { return dSize == 0; }
int size() const { return dSize; }
pair<const K, E>* find(const K& theKey) const
{
return table[hashNode(theKey) % divisor].find(theKey);
}
void insert(const pair<const K, E>& thePair)
{
int homeBucket = (int)hashNode(thePair.first) % divisor;
int homeSize = table[homeBucket].size();
table[homeBucket].insert(thePair);
if (table[homeBucket].size() > homeSize)
dSize++;
}
void erase(const K& theKey)
{
table[hashNode(theKey) % divisor].erase(theKey);
}
/*友元函数*/
/*输入字典*/
istream& input(istream& in);
// friend istream& operator>> <K, E>(istream& in, hashChains<K, E>& m);
/*输出字典*/
ostream& output(ostream& out) const;
// friend ostream& operator<< <K, E>(ostream& out, const hashChains<K, E>& m);
protected:
dictionaryChain<K, E>* table; // hash table
hashNode<K> hashNode; // maps type K to nonnegative integer
int dSize; // number of elements in list
int divisor; // hash function divisor
};
/*输入字典*/
template<class K, class E>
istream& hashChains<K, E>::input(istream& in)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
while (!(in >> numberOfElement))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
}
K first;
E second;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
while (!(in >> first >> second))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
}
const pair<const K, E> element(first, second);
cout << element.first << endl;
cout << element.second << endl;
insert(element);
}
return in;
}
template<class K, class E>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, hashChains<K, E>& m){
m.input(in);
return in;
}
/*输出字典*/
template<class K, class E>
ostream& hashChains<K, E>::output(ostream& out) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < divisor; i++)
{
if (table[i].size() == 0)
cout << "nullptr" << endl;
else
cout << table[i] << " ";
}
return out;
}
template<class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const hashChains<K, E>& m){
m.output(out);
return out;
}
#endif
_26hashChains.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月24日11点16分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈希表---链式散列(链表存储)---cpp文件
// hash table using sorted chains and division
// implements all dictionary methods
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "_26hashChains.h"
using namespace std;
void hashChainsTest()
{
cout << endl << "*********************************hashChainsTest()函数开始*************************************" << endl;
hashChains<int, int> a;
//测试输入和输出
cout << endl << "测试友元函数*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "输入输出************************" << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "hashChains a is:" << a;
cout << endl << "测试成员函数*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "empty()*************************" << endl;
cout << "a.empty() = " << a.empty() << endl;
cout << "size()**************************" << endl;
cout << "a.size() = " << a.size() << endl;
cout << "find()**************************" << endl;
cout << "a.find(1)->second = " << a.find(1)->second << endl;
cout << "insert()************************" << endl;
pair<const int, int> insertData(3, 4);
a.insert(insertData);
cout << "hashChains a is:" << a;
cout << "erase()*************************" << endl;
a.erase(1);
cout << "hashChains a is:" << a;
cout << "*********************************hashChainsTest()函数结束*************************************" << endl;
}
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:
illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:
illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:
matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:
matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:
stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:
queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:
hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:
undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:
undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_22hash\cmake-build-debug\_22hash.exe"
*********************************hashTableTest()函数开始**************************************
测试友元函数*******************************************
输入输出************************
Please enter the number of element:3
Please enter the element 1:1 2
Please enter the element 2:2 4
Please enter the element 3:5 6
hashTable a is:nullptr (1,2) (2,4) nullptr nullptr (5,6) nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr
测试成员函数*******************************************
empty()*************************
a.empty() = 0
size()**************************
a.size() = 3
find()**************************
a.find(1)->second = 2
insert()************************
hashTable a is:nullptr (1,2) (2,4) (3,4) nullptr (5,6) nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr
erase()*************************
hashTable a is:nullptr (1,2) nullptr (3,4) nullptr (5,6) nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr nullptr
*********************************hashTableTest()函数结束**************************************
*********************************hashChainsTest()函数开始*************************************
测试友元函数*******************************************
输入输出************************
Please enter the number of element:3
Please enter the element 1:1 2
1
2
Please enter the element 2:3 5
3
5
Please enter the element 3:6 9
6
9
hashChains a is:nullptr
(1 ,2)
nullptr
(3 ,5)
nullptr
nullptr
(6 ,9)
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
测试成员函数*******************************************
empty()*************************
a.empty() = 0
size()**************************
a.size() = 3
find()**************************
a.find(1)->second = 2
insert()************************
hashChains a is:nullptr
(1 ,2)
nullptr
(3 ,4)
nullptr
nullptr
(6 ,9)
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
erase()*************************
hashChains a is:nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
(3 ,4)
nullptr
nullptr
(6 ,9)
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
nullptr
*********************************hashChainsTest()函数结束*************************************
Process finished with exit code 0