文章目录
- 翻转链表
- 找到链表的中间节点
- 返回倒数第k个节点
- 合并两个有序链表
- 判断链表是否回文
- 注意
翻转链表
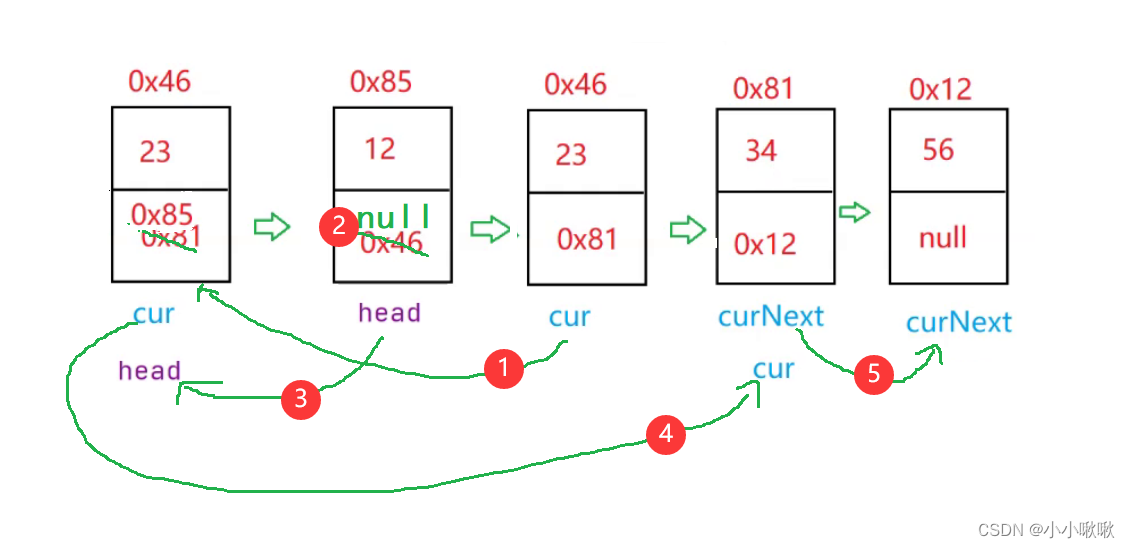
//反转链表
//实质上是把每一个节点头插法,原本第一个节点变成最后一个节点
public ListNode reverseList(){
//链表为空
if (head == null){
return null;
}
//链表只有一个节点
if (head.next == null ){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = this.head.next;//先定义cur的位置
this.head.next =null;//再把head.next置为空
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext =cur.next;//再定义curNext在cur后面
cur.next =this.head;//让cur的下一个等于头节点,就能把cur头插到head前面
head = cur;//head给到cur
cur = curNext;//cur再到curNext位置
}
return head;//返回头,就能返回一整个链表
}
}
找到链表的中间节点
方法1:链表长度除以2得到中间节点
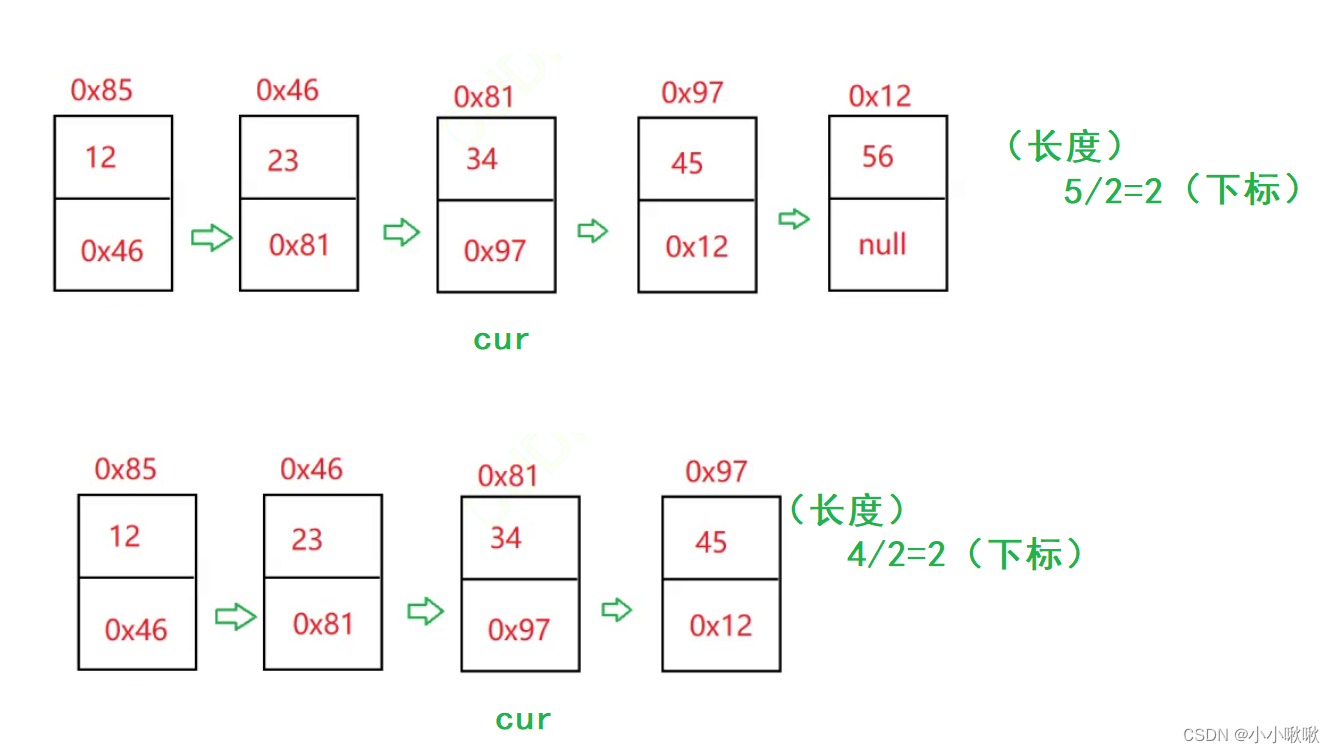
//求链表中间节点
//1.先求整个链表的长度
//2.再求长度/2 就找到这个节点了
public ListNode MiddleNode(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
int len = size();
//让cur走到中间节点
for (int i = 0; i < len/2; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
方法2:
优化代码:快慢指针的引用
- 当fast == null时,遍历结束
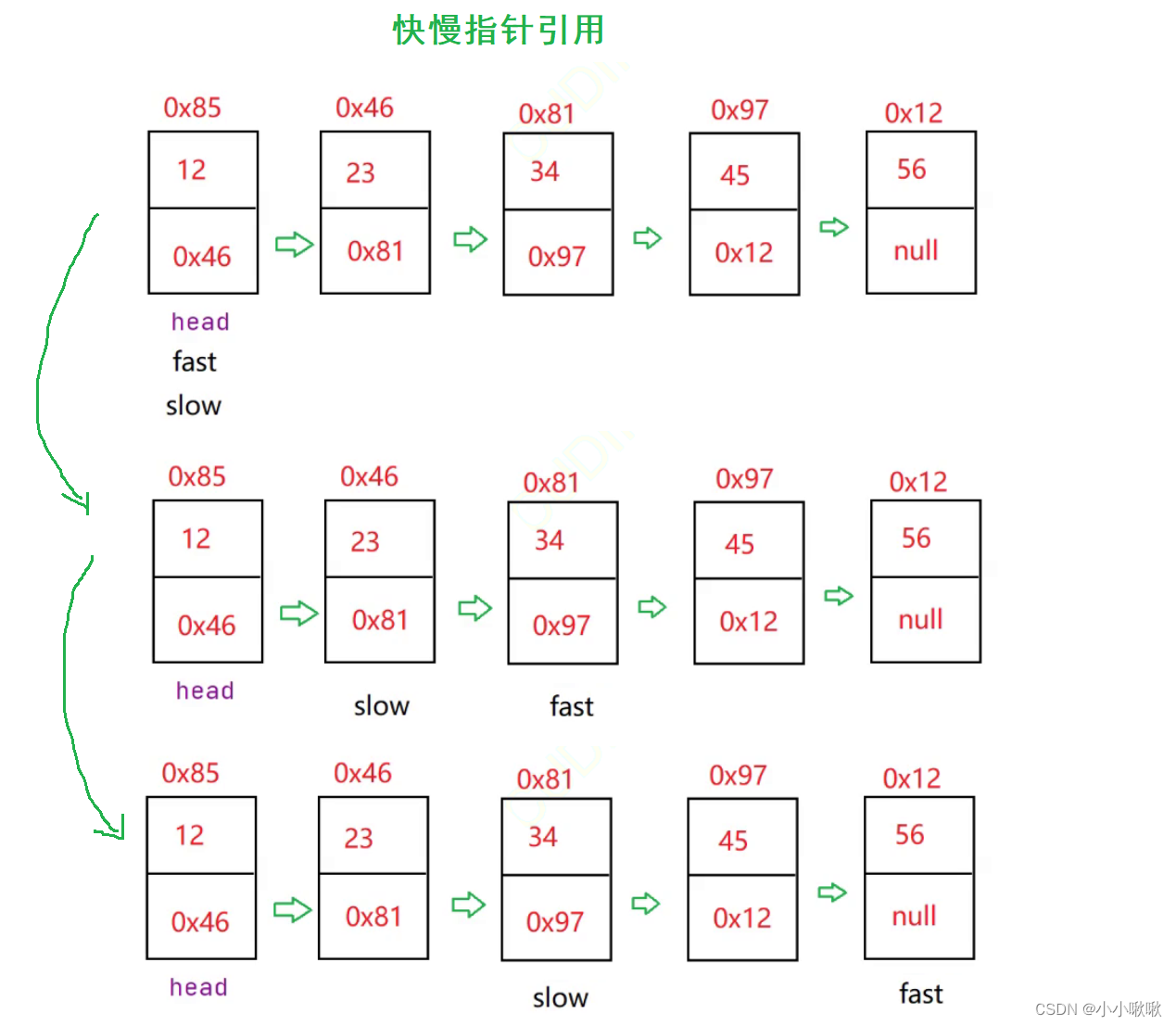
- 当fast.next == null时,遍历结束
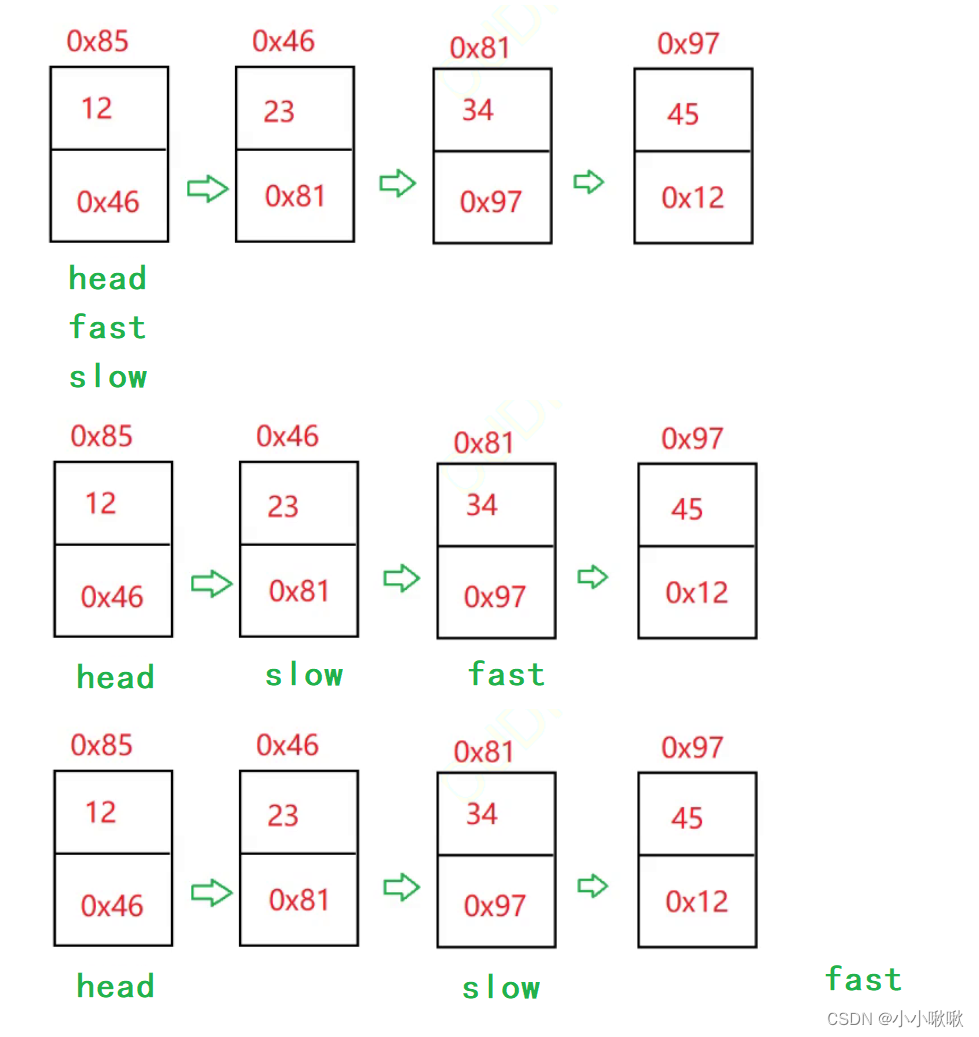
所以循环结束有两个条件:fast == null 或者 fast.next == null
public ListNode MiddleNode1(){
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
返回倒数第k个节点
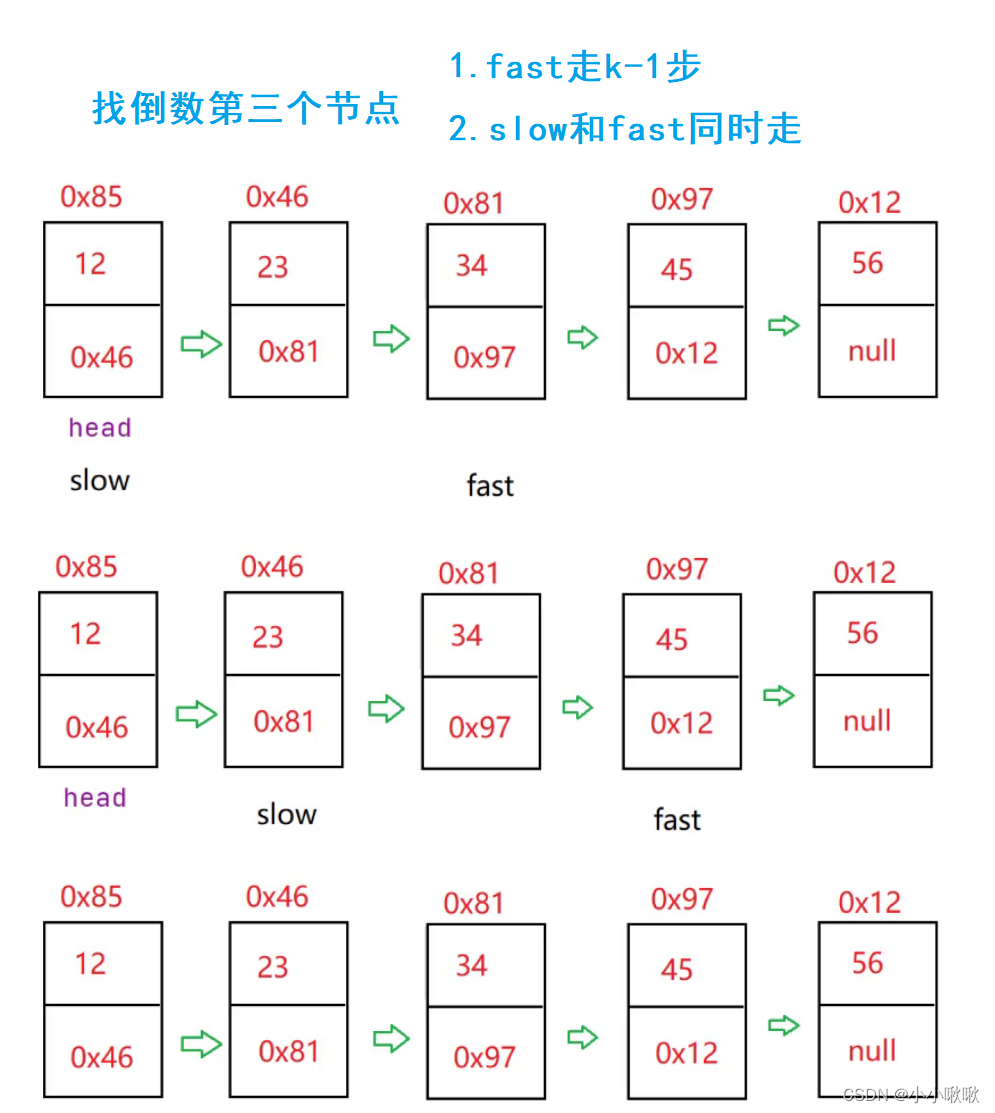
public ListNode findKthToTail(int k){
//判断k的合法性
if (k <= 0 || head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast =head;
ListNode slow =head;
//先让fast走k-1步
while(k-1 != 0){
fast = fast.next;
//如果k很大,这个判断可以让代码更高效
if (fast == null){
return null;
}
k--;
}
//slow和fast同时走
//当fast.next =null时,slow已经在倒数第k个节点了
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
合并两个有序链表
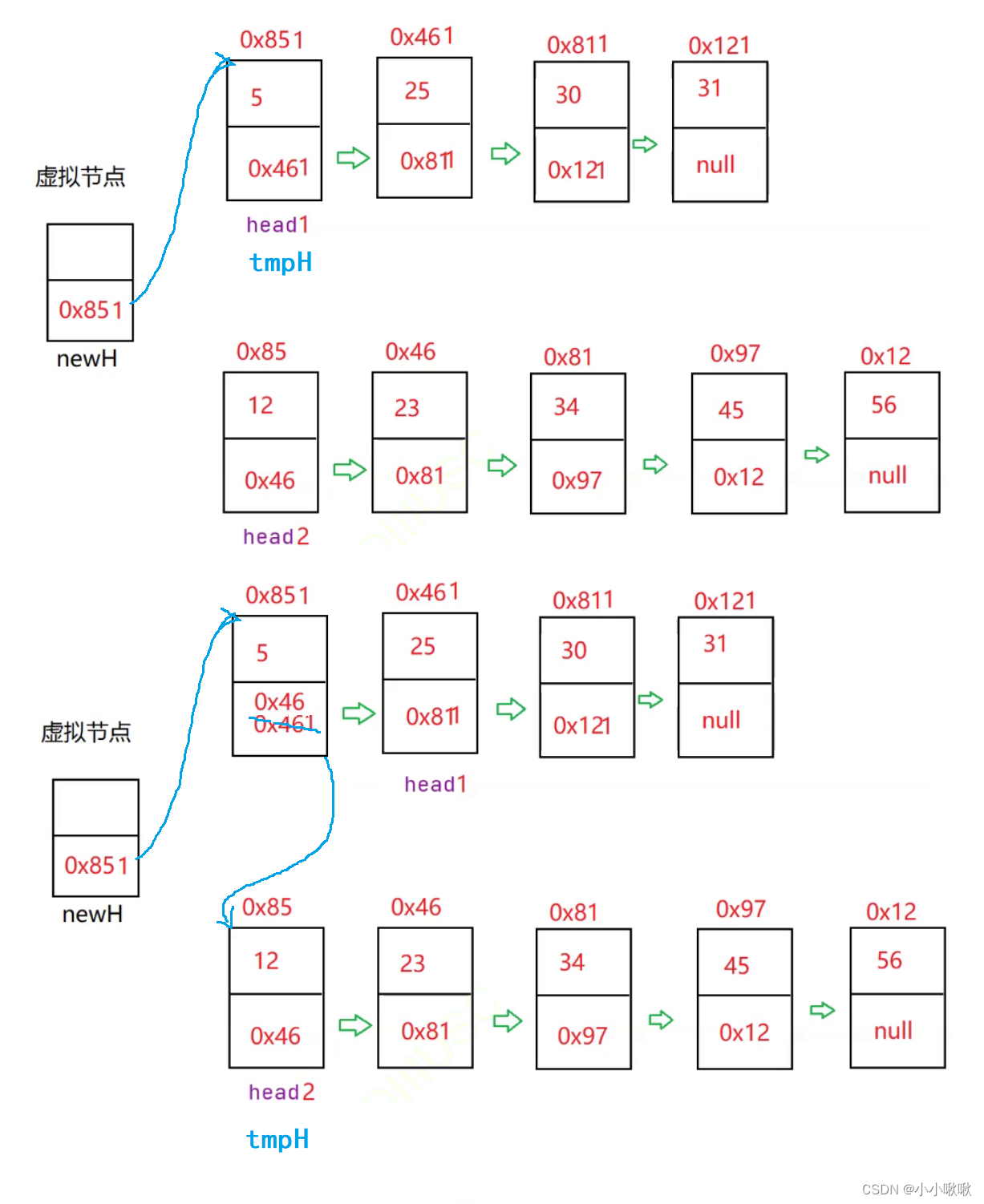
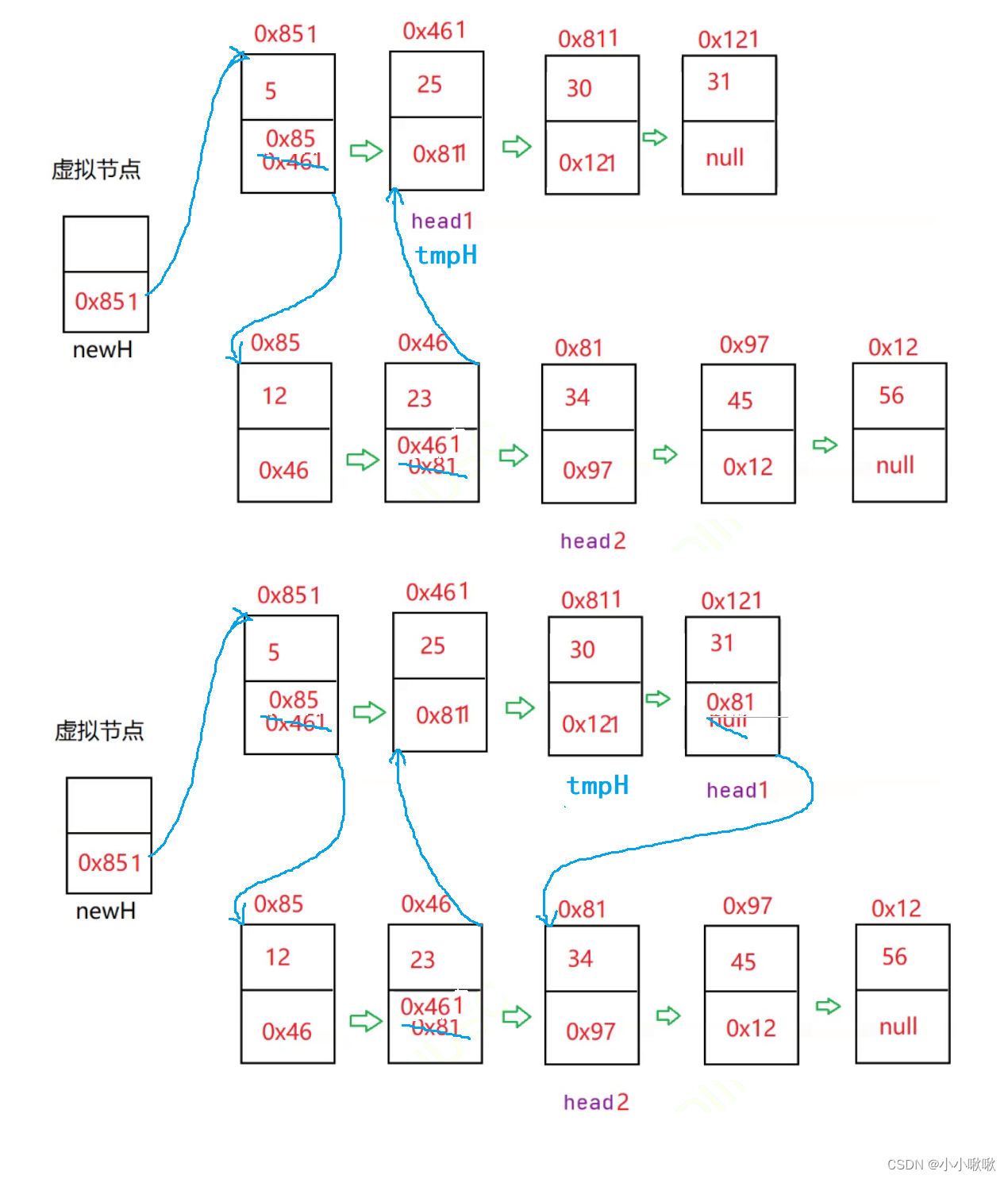
public class Test {
//定义两个链表
public static MySingleList.ListNode mergeTwoLists(MySingleList.ListNode head1, MySingleList.ListNode head2){
//定义一个虚拟节点,保存合并之后的新链表
MySingleList.ListNode newH = new MySingleList.ListNode(-1);
//newH节点是新链表的头节点,跟着记录串联之后的节点
MySingleList.ListNode tmpH = newH;
//当两个链表都不为空才能进入循环进行合并排序
while(head1 != null && head2 != null){
//当head1的值小于head2时,头节点tmpH的下一个节点就是连接小的那一个,然后head1再往后走一步
if (head1.val < head2.val){
tmpH.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
}else{
//当head2的值小于head1时,头节点tmpH的下一个节点就是连接小的那一个,然后head2再往后走一步
tmpH.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
//无论进入那个语句,tmp都会往后走一步
tmpH = tmpH.next;
}
//当head1没走完了,说明head2走完了,继续接着剩下的head1
if(head1 != null){
tmpH.next = head1;
}
//当head2没走完了,说明head1走完了,继续接着剩下的head2
if(head2 != null){
tmpH.next = head2;
}
//最后返回
return tmpH;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList();
mySingleList.addLast(12);
mySingleList.addLast(23);
mySingleList.addLast(34);
mySingleList.addLast(45);
mySingleList.display();//打印数组
MySingleList mySingleList2 = new MySingleList();
mySingleList2.addLast(15);
mySingleList2.addLast(24);
mySingleList2.addLast(37);
mySingleList2.addLast(166);
mySingleList2.display();
MySingleList.ListNode head = mergeTwoLists(mySingleList.head,mySingleList2.head);
mySingleList.display();
}
判断链表是否回文
1.先找到中间节点
2.翻转
3.前面往后走,后面往前走,值是否一样
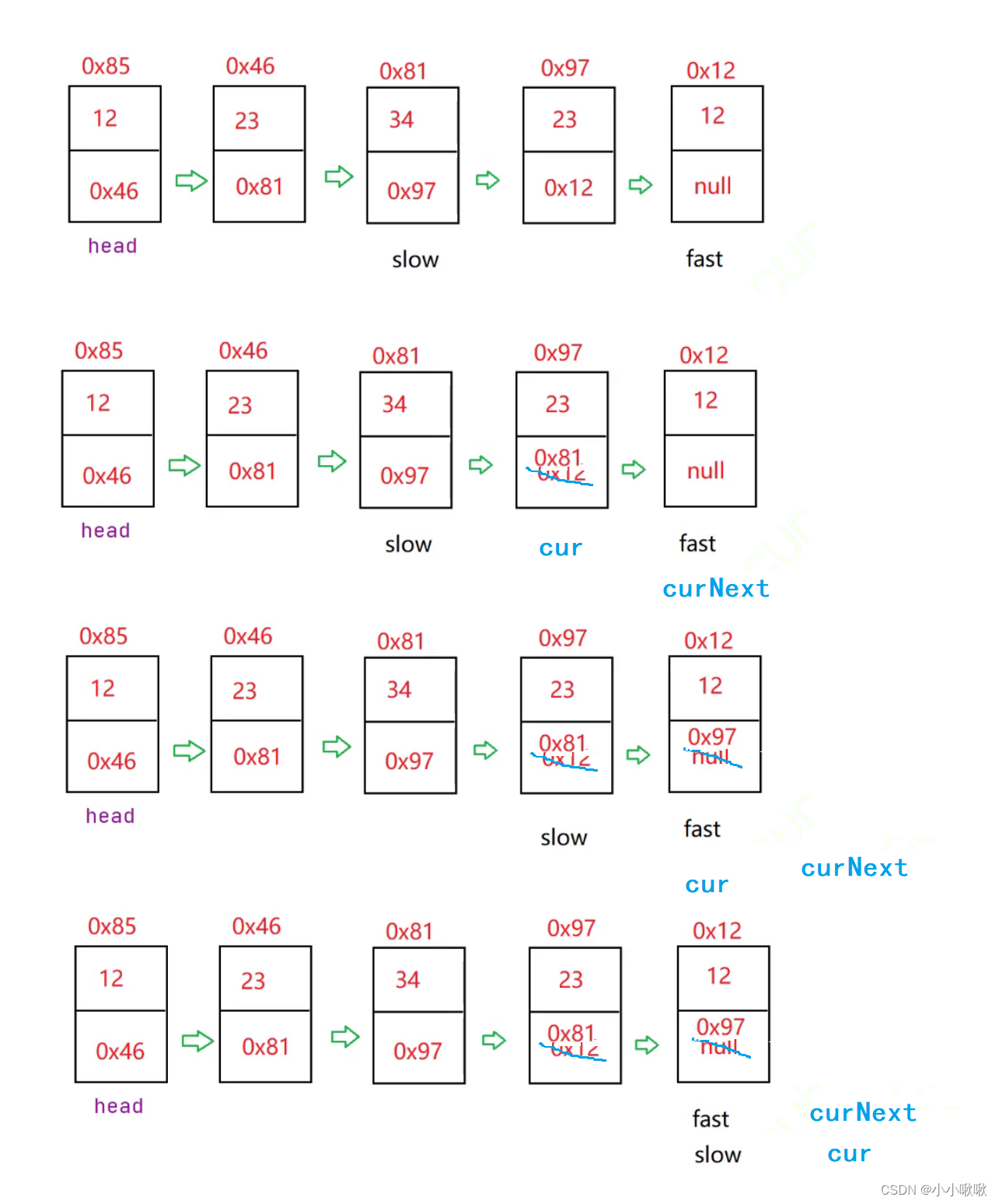
//判断是否回文
public boolean chkPalindrome(){
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int len = size()/2;//5/2=2
//1.找中间位置
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
//fast先走俩步,slow再走一步
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//2.翻转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//3.从前到后,从后到前
while(head != slow){
if (head.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
//考虑偶数链表
if (head.next == slow){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
注意
在写题过程中,我混淆了找中间节点和返回倒数第k个节点的方法
他们的区别其实是:
找中间节点 :fast永远是slow的二倍,slow走一步,fast就走两步。
返回倒数第k个节点 :fast和slow的关系不是固定的,fast走几步根据k-1得到,还有一个区别是,fast走了k-1步之后,slow走一步,fast也是走一步。