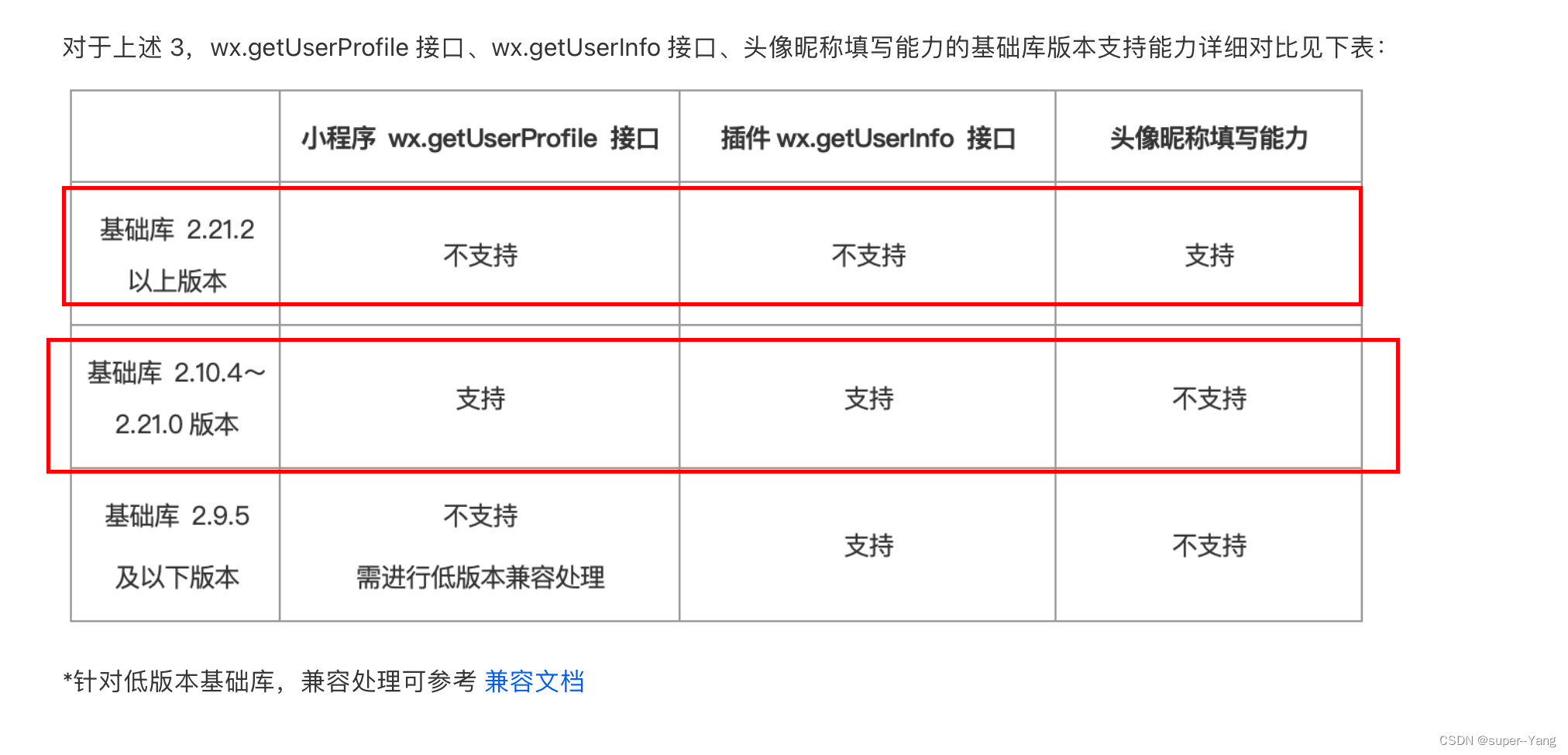
模拟
模拟加法运算,设置进位数 t t t , t = ( l 1 t=(l1 t=(l1-> v a l + l 2 val+l2 val+l2-> v a l + t ) % 10 val+t)\%10 val+t)%10 即为当前位上的数, t / 10 t/10 t/10 即是进位数。
设置哑结点,便于操作头结点。
模拟上述操作,最后返回哑结点的后继。
代码展示
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
int t = 0;//进位
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
auto cur = dummy;
while(l1||l2){
if(l1) t+=l1->val,l1 = l1->next;
if(l2) t+=l2->val,l2 = l2->next;
cur->next = new ListNode(t%10);//当前位的数
cur = cur->next;
t/=10;//进位数
}
if(t) cur->next = new ListNode(t);
return dummy->next;
}
};
//同时遍历两个链表
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
struct ListNode* cur = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));//声明一个链表,存储答案
struct ListNode* dummyhead = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));//哑结点,用于存储cur的值
dummyhead = cur;
int next = 0;//是否进位
while (l1 && l2) {
int sum = l1->val + l2->val + next;
cur->next = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur->next->val = sum % 10;
if (sum >= 10) {
next = 1;
}
else {
next = 0;
}
cur = cur->next;
l2 = l2->next, l1 = l1->next;//所有链表后移一位
}
while (l2) {//遍历结束,l2非空
int sum = l2->val + next;
cur->next = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur->next->val = sum % 10;
if (sum >= 10) {
next = 1;
}
else {
next = 0;
}
cur = cur->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
while (l1) {//遍历结束,l2非空
int sum = l1->val + next;
cur->next = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur->next->val = sum % 10;
if (sum >= 10) {
next = 1;
}
else {
next = 0;
}
cur = cur->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if(next){
cur->next = (struct ListNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur->next->val = 1;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
博主致语
理解思路很重要!
欢迎读者在评论区留言,作为日更博主,看到就会回复的。
AC

复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( m a x ( m , n ) ) O(max(m,n)) O(max(m,n)), n n n 是 l 1 l1 l1 的长度, m m m 是 l 2 l2 l2 的长度,同时遍历 l 1 , l 2 l1,l2 l1,l2 , 一次遍历得到答案。
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),除去保存答案所用空间,没有使用额外的线性空间。