文章目录
- 一、Spring通过命名空间整合第三方框架
- 1. Dubbo 命名空间
- 2. Context 命名空间
- 二、Spring自定义命名空间原理解析
- 三、手写自定义命名空间标签与Spring整合
一、Spring通过命名空间整合第三方框架
1. Dubbo 命名空间
Spring 整合其他组件时就不像MyBatis这么简单了,例如Dubbo框架在与Spring进行整合时,要使用Dubbo提供的命名空间的扩展方式,自定义了一些Dubbo的标签,Dubbo框架再去解析自己的Dubbo标签
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
<!--引入dubbo命名空间-->
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
<!--引入dubbo对应的schema映射地址-->
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!--配置应用名称-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo1-consumer"/>
<!--配置注册中心地址-->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://localhost:2181"/>
<!--扫描dubbo的注解-->
<dubbo:annotation package="com.itheima.controller"/>
<!--消费者配置-->
<dubbo:consumer check="false" timeout="1000" retries="0"/>
</beans>
2. Context 命名空间
为了降低我们此处的学习成本,不再引入Dubbo第三方框架了,以Spring的 context 命名空间去进行讲解,该方式也是命名空间扩展方式。
需求:加载外部properties文件jdbc.properties,将键值对存储在Spring容器中
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
引入context命名空间,再使用context命名空间的标签,使用SpEL表达式在xml或注解中根据key获得value
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--加载properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<beans>
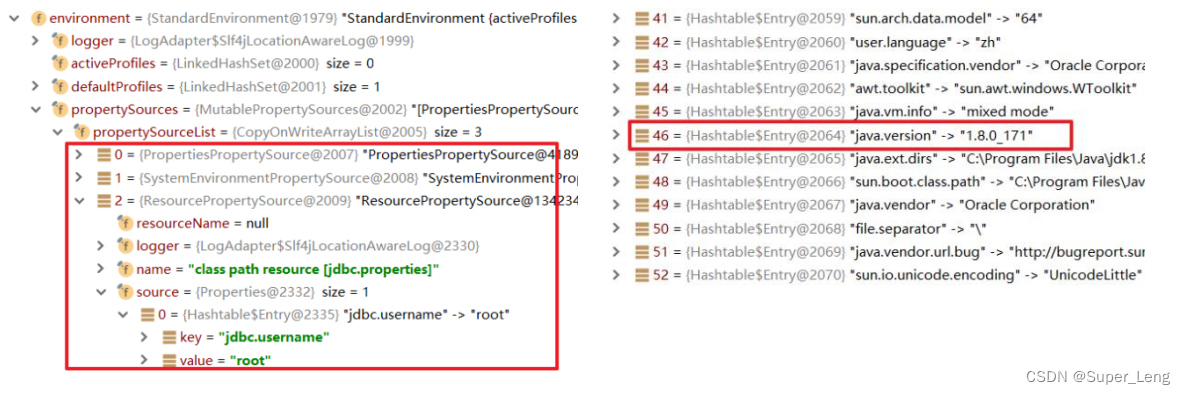
其实,加载的properties文件中的属性最终通过Spring解析后会被存储到了Spring容器的environment中去,不仅自己定义的属性会进行存储,Spring也会把环境相关的一些属性进行存储
二、Spring自定义命名空间原理解析
首先从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext入手,进入spring容器入口refresh()方法
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
...
// 将beanDefinition定义信息填充到beanDefinitionMap中
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
...
}
}
}
接着调用AbstractApplicationContext类中的obtainFreshBeanFactory方法
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
}
接着执行AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类中的refreshBeanFactory方法
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
...
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
...
}
}
最终会通过loadBeanDefinitions方法->doLoadBeanDefinitions方法->registerBeanDefinitions方法->doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法->parseBeanDefinitions方法
public class DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader implements BeanDefinitionDocumentReader {
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
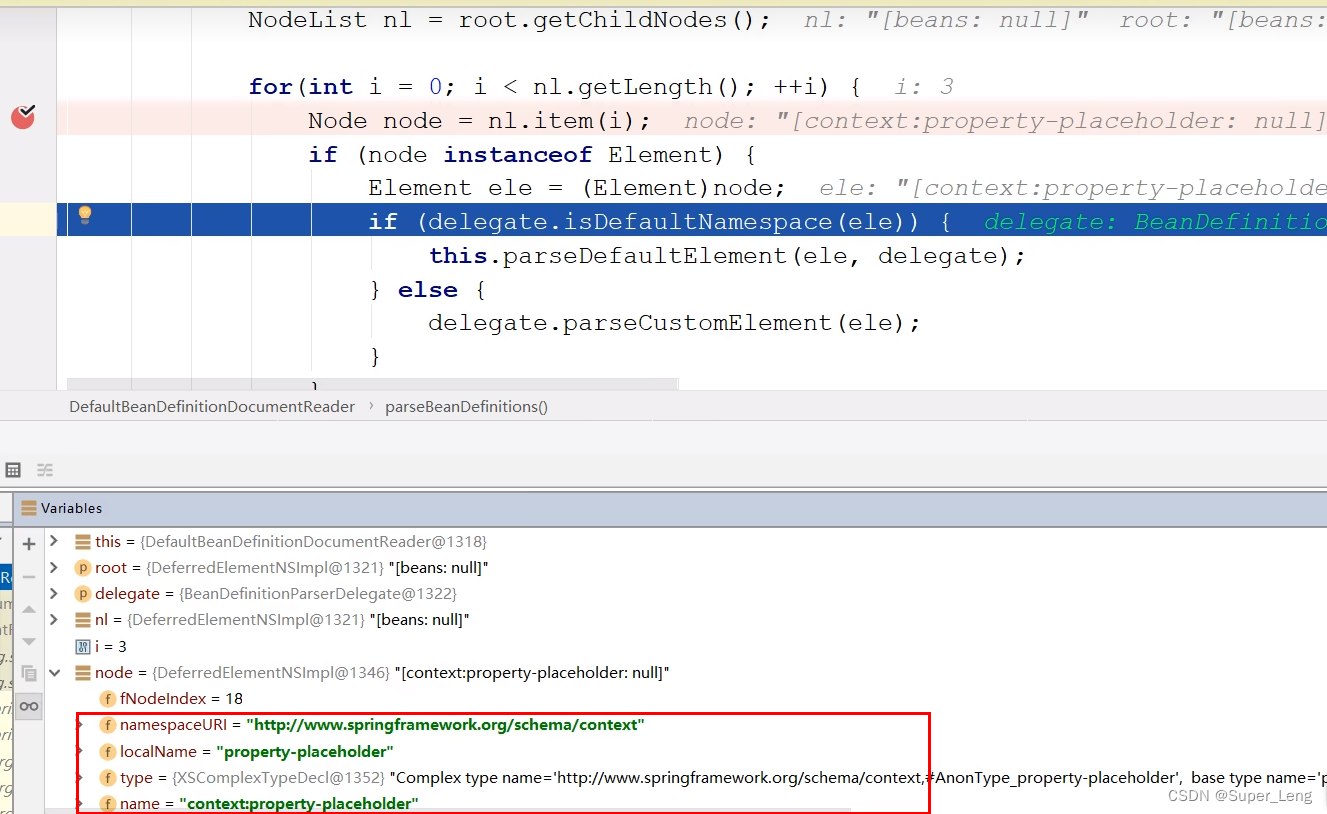
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
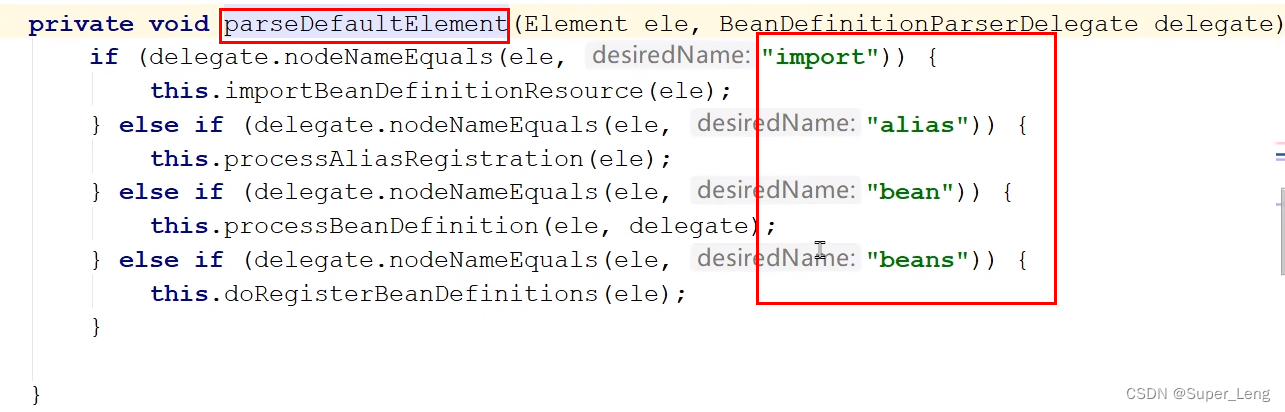
// 默认命名空间的标签有import、alias、bean、beans
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
} else {
// 解析自定义命名空间的标签
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
}
默认命名空间的标签有import、alias、bean、beans
由于context是自定义命名空间的标签,所以会执行delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);方法
public class BeanDefinitionParserDelegate {
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
// 这里的namespaceUri对应的是xml中的"http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
// 根据命名空间uri获取命名空间处理器
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
// 执行命名空间处理器的parse方法,解析执行的标签
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
}
根据命名空间uri获取命名空间处理器
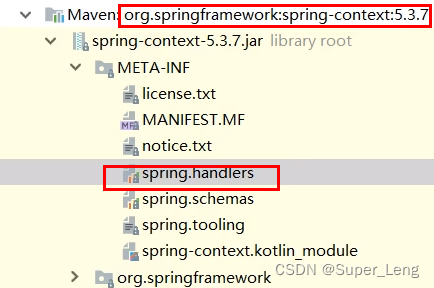
public class DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver implements NamespaceHandlerResolver {
// 通过构造方法创建DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver时,会将"META-INF/spring.handlers"中配置的命名空间处理器加载到handlerMappings中
public DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver() {
this(null, "META-INF/spring.handlers");
}
// 在执行resovle方法时,就是从Map<String, Object> handlerMappings中根据命名空间名称获得对应的处理器对象,此处是ContextNamespaceHandler,最终执行NamespaceHandler的parse方法
@Override
@Nullable
public NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri) {
// key是命名空间uri,value是命名空间处理器
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = getHandlerMappings();
...
String className = handlerMappings.get(namespaceUri);
Class<?> handlerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, this.classLoader);
// 此时这里的命名空间处理器就是ContextNamespaceHandler
NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler = (NamespaceHandler) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass);
// 执行ContextNamespaceHandler的init方法
namespaceHandler.init();
handlerMappings.put(namespaceUri, namespaceHandler);
return namespaceHandler;
...
}
}
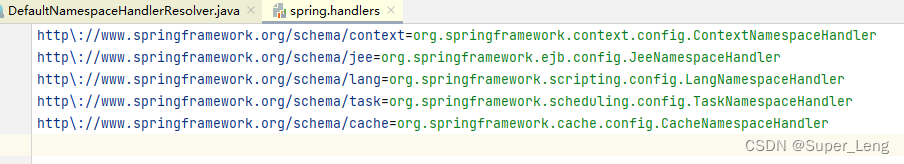
执行ContextNamespaceHandler的init方法
ContextNamespaceHandler源码如下,间接实现了NamespaceHandler接口,初始化方法init会被自动调用。由于context命名空间下有多个标签,所以每个标签又单独注册了对应的解析器,注册到了其父类NamespaceHandlerSupport的Map<String, BeanDefinitionParser> parsers中去了
public class ContextNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
// 注入解析器,不同的标签有不同的解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
注入解析器后,再去执行命名空间处理器ContextNamespaceHandler的parse方法,该parse方法具体流程是再去调每个自定义标签解析器的parse方法,例如上面"property-placeholder"标签,会执行PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser解析器的parse方法,parse方法主要作用就是解析标签的beanDefinition定义信息注册到容器中,Spring再根据对应的beanDefinition定义信息创建对象
public abstract class NamespaceHandlerSupport implements NamespaceHandler {
@Override
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
BeanDefinitionParser parser = findParserForElement(element, parserContext);
return (parser != null ? parser.parse(element, parserContext) : null);
}
}
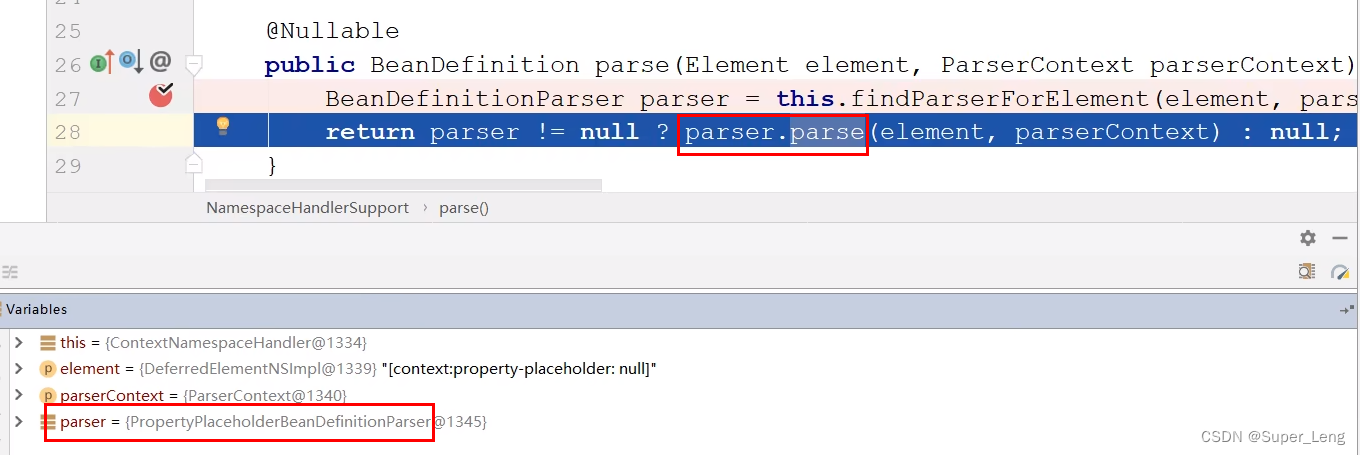
通过上述分析,我们清楚的了解了外部命名空间标签的执行流程,如下:
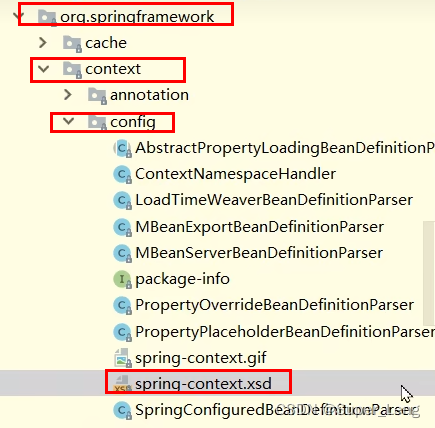
⚫ 将自定义标签的约束:物理约束文件与网络约束名称的约束 以键值对形式存储到一个spring.schemas文件里,该文件存储在类加载路径的 META-INF里,Spring会自动加载到;
⚫ 将自定义命名空间的名称 与 自定义命名空间的处理器映射关系 以键值对形式存在到一个叫spring.handlers文件里,该文件存储在类加载路径的 META-INF里,Spring会自动加载到;
⚫ 准备好NamespaceHandler,如果命名空间只有一个标签,那么直接在parse方法中进行解析即可,一般解析结果就是注册该标签对应的BeanDefinition。如果命名空间里有多个标签,那么可以在init方法中为每个标签都注册一个BeanDefinitionParser,在执行NamespaceHandler的parse方法时再分流给不同的BeanDefinitionParser进行解析(重写doParse方法即可)。
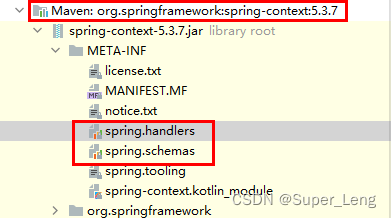

http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd=org/springframework/context/config/spring-context.xsd
约束文件http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd对应真实的路径是org/springframework/context/config/spring-context.xsd
三、手写自定义命名空间标签与Spring整合
设想自己是一名架构师,进行某一个框架与Spring的集成开发,效果是通过一个指示标签,向Spring容器中自动注入一个BeanPostProcessor,这样可以在创建bean的生命周期中对自定义框架中的bean进行增强处理
步骤分析:
- 确定命名空间名称、schema虚拟路径、标签名称;
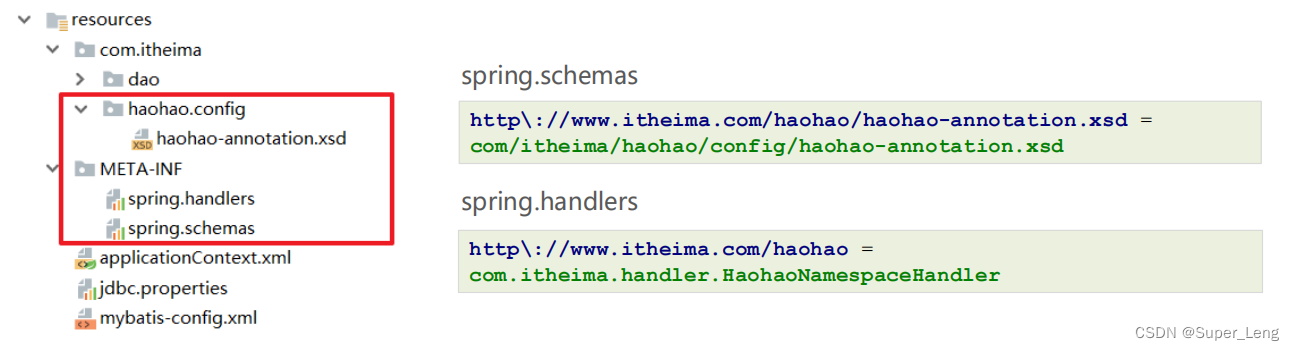
- 编写schema约束文件haohao-annotation.xsd
- 在类加载路径下创建META目录,编写约束映射文件spring.schemas和处理器映射文件spring.handlers
- 编写命名空间处理器 HaohaoNamespaceHandler,在init方法中注册HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser
- 编写标签的解析器 HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser,在parse方法中注册HaohaoBeanPostProcessor
- 编写HaohaoBeanPostProcessor
========== 以上五步是框架开发者写的,以下是框架使用者写的===========- 在applicationContext.xml配置文件中引入命名空间
- 在applicationContext.xml配置文件中使用自定义的标签
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlSchema-instance"
xmlns:haohao="http://www.itheima.com/haohao"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.itheima.com/haohao
http://www.itheima.com/haohao/haohao-annotation.xsd">
<haohao:annotation-driven/>
</beans>
编写schema约束文件haohao-annotation.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.itheima.com/haohao"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.itheima.com/haohao">
<xsd:element name="annotation-driven"></xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>
在类加载路径下创建META目录,编写约束映射文件spring.schemas和处理器映射文件spring.handlers
编写命名空间处理器 HaohaoNamespaceHandler,在init方法中注册HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser
public class HaohaoNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
编写标签的解析器 HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser,在parse方法中注册HaohaoBeanPostProcessor
public class HaohaoBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 创建HaohaoBeanPostProcessor的BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(HaohaoBeanPostProcessor.class);
// 注册HaohaoBeanPostProcessor
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition("haohaoBeanPostProcessor", beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
}
编写HaohaoBeanPostProcessor
public class HaohaoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("创建bean时,可以在此进行增强处理...");
return bean;
}
}











![[数据结构]什么是树?什么是二叉树?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/71f60028d0c14282b604ae1fa49ba39c.png)