init进程学习:
文件路径system/core/init/init.cpp
- 解析init.rc配置文件,首先开启ServiceManager和MediaServer等关键进程
- init进程fork启动Zygote服务进程
- 处理子进程的终止(signal方式)
- 提供属性服务的功能
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//注释一:进行ueventd/watchdogd跳转及环境变量设置
//basename是C库中的一个函数,得到特定的路径中的最后一个'/'后面的内容,比如/sdcard/miui_recovery/backup,得到的结果是backup
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "watchdogd")) {
return watchdogd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (argc > 1 && !strcmp(argv[1], "subcontext")) {
InitKernelLogging(argv);
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
return SubcontextMain(argc, argv, &function_map);
}
//初始化重启系统的处理信号,通过sigaction注册新号并监听,源码位置:system/core/init/reboot_utils.cpp
//将各种信号量,如SIGABRT,SIGBUS等的行为设置为SA_RESTART,一旦监听到这些信号即执行重启系统
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
//之前准备工作时将INIT_SECOND_STAGE设置为true,已经不为nullptr,所以is_first_stage为false
bool is_first_stage = (getenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE") == nullptr);
//如果是第一次执行
if (is_first_stage) {
//系统时钟
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// Clear the umask.
umask(0);
clearenv();
setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1);
// Get the basic filesystem setup we need put together in the initramdisk
// on / and then we'll let the rc file figure out the rest.
// 注释二:创建和挂载启动所需要的文件目录
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
//一系列文件操作,linux下socket也是特殊文件,0755标记用户具有读/写/执行 权限,具体可查看相关命令
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC));
// Don't expose the raw commandline to unprivileged processes.
//CMD命令行
chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440);
gid_t groups[] = { AID_READPROC };
setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups);
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL);
mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11));
if constexpr (WORLD_WRITABLE_KMSG) {
mknod("/dev/kmsg_debug", S_IFCHR | 0622, makedev(1, 11));
}
mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8));
mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9));
// Mount staging areas for devices managed by vold
// See storage config details at http://source.android.com/devices/storage/
mount("tmpfs", "/mnt", "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=1000");
// /mnt/vendor is used to mount vendor-specific partitions that can not be
// part of the vendor partition, e.g. because they are mounted read-write.
mkdir("/mnt/vendor", 0755);
// Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev and we have /dev/kmsg, we can actually
// talk to the outside world...
// 注释三:初始化Kernel 的 Log,外界可获取 Kernel 的打印日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init first stage started!";
//挂载分区设备
if (!DoFirstStageMount()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to mount required partitions early ...";
}
SetInitAvbVersionInRecovery();
// Enable seccomp if global boot option was passed (otherwise it is enabled in zygote).
global_seccomp();
// Set up SELinux, loading the SELinux policy.
// 注释四:初始化selinux策略
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
SelinuxInitialize();
// We're in the kernel domain, so re-exec init to transition to the init domain now
// that the SELinux policy has been loaded.
//restorecon命令用来恢复SELinux文件属性即恢复文件的安全上下文
if (selinux_android_restorecon("/init", 0) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "restorecon failed of /init failed";
}
//设置环境变量
setenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE", "true", 1);
static constexpr uint32_t kNanosecondsPerMillisecond = 1e6;
uint64_t start_ms = start_time.time_since_epoch().count() / kNanosecondsPerMillisecond;
setenv("INIT_STARTED_AT", std::to_string(start_ms).c_str(), 1);
//重新执行main方法
char* path = argv[0];
char* args[] = { path, nullptr };
execv(path, args);
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never fall through this conditional.
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
}
/***************** 第二部分 ******************/
// At this point we're in the second stage of init. //初始化 kernel 日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
// Set up a session keyring that all processes will have access to. It
// will hold things like FBE encryption keys. No process should override
// its session keyring.
//初始化进程会话密钥 位置:/system/core/libkeyutils/Keyutils.cpp
keyctl_get_keyring_ID(KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
// Indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc.
//创建 /dev/.booting 文件,就是个标记,表示booting进行中
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
// 注释五:初始化属性系统,并从指定文件读取属性
property_init();
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
process_kernel_dt(); //处理DT属性
process_kernel_cmdline(); //处理命令行属性
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
export_kernel_boot_props(); //处理其他的一些属性
// Make the time that init started available for bootstat to log.
property_set("ro.boottime.init", getenv("INIT_STARTED_AT"));
property_set("ro.boottime.init.selinux", getenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK"));
// Set libavb version for Framework-only OTA match in Treble build.
const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
if (avb_version) property_set("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
// Clean up our environment.
//清空这些环境变量,因为之前都已经存入到系统属性中去了
unsetenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE");
unsetenv("INIT_STARTED_AT");
unsetenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK");
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
// Now set up SELinux for second stage.
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
SelabelInitialize(); // SElinux第二阶段
SelinuxRestoreContext(); // 恢复安全上下文
//注释六:创建 epoll 句柄
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
if (epoll_fd == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "epoll_create1 failed";
}
//类似java中的Handelr,如果子进程(比如 Zygote 进程)异常退出,init进程会调用到该函数中设定的信号处理函数来进行处理
sigchld_handler_init();
if (!IsRebootCapable()) {
// If init does not have the CAP_SYS_BOOT capability, it is running in a container.
// In that case, receiving SIGTERM will cause the system to shut down.
InstallSigtermHandler();
}
property_load_boot_defaults(); //从文件中加载一些属性,读取usb配置
export_oem_lock_status(); //设置ro.boot.flash.locked 属性
start_property_service(); //注释七:启动属性服务
set_usb_controller(); //设置sys.usb.controller 属性
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
Action::set_function_map(&function_map); //静态方法,将function_map放到Action中作为成员变量
subcontexts = InitializeSubcontexts();
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance(); //得到ActionManager对象
ServiceList& sm = ServiceList::GetInstance();
//注释八:解析init.rc 文件
LoadBootScripts(am, sm); //解析 init.rc 配置文件
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState();
//注释九:额外配置一些事件和Action
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
//注释十:监听新的事件
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
int epoll_timeout_ms = -1;
if (do_shutdown && !shutting_down) {
do_shutdown = false;
if (HandlePowerctlMessage(shutdown_command)) {
shutting_down = true;
}
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
if (!shutting_down) {
auto next_process_restart_time = RestartProcesses();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (next_process_restart_time) {
epoll_timeout_ms = std::chrono::ceil<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
*next_process_restart_time - boot_clock::now())
.count();
if (epoll_timeout_ms < 0) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
epoll_event ev;
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, epoll_timeout_ms));
if (nr == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_wait failed";
} else if (nr == 1) {
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
return 0;
}
1.1 注释一
1.1.1 ueventd_main 创建设备节点文件
Android 根文件系统的映像上不存在 /dev 目录,该目录是init进程启动后动态创建的,而init进程将创建设备节点文件的任务交给了 ueventd 子进程。
源码位置:\system\core\init\ueventd.cpp
int ueventd_main(int argc, char** argv) {
//...
DeviceHandler device_handler = CreateDeviceHandler();
//...
}
DeviceHandler CreateDeviceHandler() {
//... 创建dev目录
parser.AddSingleLineParser("/sys/",
std::bind(ParsePermissionsLine, _1, &sysfs_permissions, nullptr));
parser.AddSingleLineParser("/dev/",
std::bind(ParsePermissionsLine, _1, nullptr, &dev_permissions));
//...
}
ueventd 通过两种方式创建设备节点文件
1.冷插拔(Cold Plug)即以预先定义的设备信息统一创建设备节点文件,这一类设备节点文件也被称为静态节点文件
2.热插拔(Hot Plug)即在系统运行中,当有设备插入USB端口时,ueventd就会监听到这一时间,为插入的设备动态创建设备节点文件,这一类设备节点文件也被称为动态节点文件
1.1.2 watchdogd_main
看门狗本身是一个定时电路,内部会不断进行计时操作,有两个引脚与系统相连,正常运行时每隔一段时间计算机系统会通过一个引脚向看门狗发送信号,看门狗接收到信号后会将计时器清零并重新开始计时,若系统卡死,看门狗计时结束,就会通过另一个引脚向系统发动复位信号,让系统重启
位置:\system\core\init\watchdogd.cpp
int watchdogd_main(int argc, char **argv) {
InitKernelLogging(argv);
int interval = 10;
if (argc >= 2) interval = atoi(argv[1]); //字符串变数值
int margin = 10;
if (argc >= 3) margin = atoi(argv[2]);
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("ro.boot.watchdogd", prop, "0");
//...
LOG(INFO) << "watchdogd started (interval " << interval << ", margin " << margin << ")!";
int fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_RDWR|O_CLOEXEC); //打开/dev/watchdog文件
//...
int timeout = interval + margin;
int ret = ioctl(fd, WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT, &timeout); //设置WDIOC_SETTIMEOUT超时时间
if (ret) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to set timeout to " << timeout;
ret = ioctl(fd, WDIOC_GETTIMEOUT, &timeout);
//...
}
while (true) { //每隔一段时间文件中写入一个空字符
write(fd, "", 1);
sleep(interval);
}
}
1.2 注释二:第一部分 挂载文件系统并创建目录
因为是第一次执行main函数 is_first_stage 获得为null
bool is_first_stage = (getenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE") == nullptr);
if (is_first_stage) {
//系统时钟
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
mount是用来挂载文件系统的,非常熟悉了,用于挂载前面创建的节点文件,mknod用于创建Linux中的设备文件
init 初始化过程中,Android分别挂载了 tmpfs,devpts,proc,sysfs,selinuxfs 这5类文件系统
tmpfs:虚拟内存文件系统,会将所有的文件存储在虚拟内存中,既可以使用RAM,也可以使用交换分区,会根据实际需要改变大小,因为是驻留在RAM中,所以读取的速度非常快
- devpts:devpts文件系统为伪终端提供了一个标准的接口,标准节点是/dev/pts。只要pty的主复合设备/dev/ptmx被打开,就会在/dev/pts下动态的创建一个新的pty设备文件
- proc:虚拟文件系统,它可以看作是内核内部数据结构的接口,通过它我们可以获得系统的信息,同时也能够在运行时修改特定的内核参数
- sysfs:不占有任何磁盘空间的虚拟文件系统。它通常被挂接在/sys目录下。sysfs文件系统是Linux2.6内核引入的,它把连接在系统上的设备和总线组织成为一个分级的文件,使得它们可以在用户空间存取
- selinuxfs:通常挂载在/sys/fs/selinux目录下,用来存放SELinux安全策略文件
1.3 注释三:初始化日志输出,挂载分区设备
InitKernelLogging
位置:/system/core/init/log.cpp
Linux 万物皆文件,/sys/fs/selinux/null 相当于一个 null 对象
首先是将标准输入输出( 0、1、2)定向到 /sys/fs/selinux/null(null设备上)
void InitKernelLogging(char* argv[]) {
// Make stdin/stdout/stderr all point to /dev/null.
int fd = open("/sys/fs/selinux/null", O_RDWR); //打开文件
if (fd == -1) {
int saved_errno = errno;
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter);
errno = saved_errno;
PLOG(FATAL) << "Couldn't open /sys/fs/selinux/null";
}
dup2(fd, 0); //重定向stdin,dup2是复制文件描述符
dup2(fd, 1); //重定向stdout
dup2(fd, 2); //重定向stderr
if (fd > 2) close(fd);
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter); //初始化log
}
文件描述符 (file descriptor) 是内核为了高效管理已被打开的文件所创建的索引,其是一个非负整数(通常是小整数),用于指代被打开的文件,所有执行I/O操作的系统调用都通过文件描述符。
Linux 进程默认情况下会有3个缺省打开的文件描述符,分别是标准输入 0, 标准输出 1, 标准错误 2
InitLogging
位置:/system/core/base/logging.cpp
void SetLogger(LogFunction&& logger) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(LoggingLock());
Logger() = std::move(logger);
}
void SetAborter(AbortFunction&& aborter) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(LoggingLock());
Aborter() = std::move(aborter);
}
void InitLogging(char* argv[], LogFunction&& logger, AbortFunction&& aborter) {
SetLogger(std::forward<LogFunction>(logger)); //设置logger处理函数
SetAborter(std::forward<AbortFunction>(aborter)); //设置aborter处理函数
if (gInitialized) {
return;
}
gInitialized = true;
// Stash the command line for later use. We can use /proc/self/cmdline on
// Linux to recover this, but we don't have that luxury on the Mac/Windows,
// and there are a couple of argv[0] variants that are commonly used.
if (argv != nullptr) {
SetDefaultTag(basename(argv[0]));
}
const char* tags = getenv("ANDROID_LOG_TAGS"); //获得系统当前的日志等级
if (tags == nullptr) {
return;
}
std::vector<std::string> specs = Split(tags, " "); //将tags以空格拆分成数组,每个tag会表示不同的含义
for (size_t i = 0; i < specs.size(); ++i) {
// "tag-pattern:[vdiwefs]"
std::string spec(specs[i]);
if (spec.size() == 3 && StartsWith(spec, "*:")) { //以*:开头的3个字符
switch (spec[2]) { //第三个字符决定输出等级
case 'v':
gMinimumLogSeverity = VERBOSE;
continue;
case 'd':
gMinimumLogSeverity = DEBUG;
continue;
case 'i':
gMinimumLogSeverity = INFO;
continue;
case 'w':
gMinimumLogSeverity = WARNING;
continue;
case 'e':
gMinimumLogSeverity = ERROR;
continue;
case 'f':
gMinimumLogSeverity = FATAL_WITHOUT_ABORT;
continue;
// liblog will even suppress FATAL if you say 's' for silent, but that's
// crazy!
case 's':
gMinimumLogSeverity = FATAL_WITHOUT_ABORT;
continue;
}
}
LOG(FATAL) << "unsupported '" << spec << "' in ANDROID_LOG_TAGS (" << tags
<< ")";
}
}
DoFirstStageMount
位置:system/core/init/init_first_stage.cpp
主要作用是初始化特定设备并挂载
bool DoFirstStageMount() {
// Skips first stage mount if we're in recovery mode.
if (IsRecoveryMode()) { //刷机模式,直接跳过挂载
LOG(INFO) << "First stage mount skipped (recovery mode)";
return true;
}
// Firstly checks if device tree fstab entries are compatible.
//如果fastab/compatible的值不是android,fstab直接跳过
if (!is_android_dt_value_expected("fstab/compatible", "android,fstab")) {
LOG(INFO) << "First stage mount skipped (missing/incompatible fstab in device tree)";
return true;
}
std::unique_ptr<FirstStageMount> handle = FirstStageMount::Create(); //这里创建了一个FirstStageMount的类,然后第哦啊用了Create函数
if (!handle) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create FirstStageMount";
return false;
}
return handle->DoFirstStageMount(); //初始化特定设备并挂载
}
FirstStageMount::FirstStageMount()
: need_dm_verity_(false), device_tree_fstab_(fs_mgr_read_fstab_dt(), fs_mgr_free_fstab) {
if (!device_tree_fstab_) {
LOG(INFO) << "Failed to read fstab from device tree";
return;
}
// Stores device_tree_fstab_->recs[] into mount_fstab_recs_ (vector<fstab_rec*>)
// for easier manipulation later, e.g., range-base for loop.
for (int i = 0; i < device_tree_fstab_->num_entries; i++) {
mount_fstab_recs_.push_back(&device_tree_fstab_->recs[i]); //把挂载信息放入数组中存起来
}
auto boot_devices = fs_mgr_get_boot_devices();
device_handler_ =
std::make_unique<DeviceHandler>(std::vector<Permissions>{}, std::vector<SysfsPermissions>{},
std::vector<Subsystem>{}, std::move(boot_devices), false);
}
bool FirstStageMount::DoFirstStageMount() { //挂载设备
// Nothing to mount.
if (mount_fstab_recs_.empty()) return true;
if (!InitDevices()) return false;
if (!MountPartitions()) return false;
return true;
}
1.4 注释四:启用SELinux安全策略
位置:```\system\core\init\selinux.cpp``
void SelinuxInitialize() {
Timer t;
LOG(INFO) << "Loading SELinux policy";
if (!LoadPolicy()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Unable to load SELinux policy";
}
bool kernel_enforcing = (security_getenforce() == 1);
bool is_enforcing = IsEnforcing();
if (kernel_enforcing != is_enforcing) {
if (security_setenforce(is_enforcing)) { //设置selinux开启或关闭
PLOG(FATAL) << "security_setenforce(%s) failed" << (is_enforcing ? "true" : "false");
}
}
if (auto result = WriteFile("/sys/fs/selinux/checkreqprot", "0"); !result) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Unable to write to /sys/fs/selinux/checkreqprot: " << result.error();
}
// init's first stage can't set properties, so pass the time to the second stage.
setenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK", std::to_string(t.duration().count()).c_str(), 1);
}
1.5 注释五:第二部分 属性服务 property_init() 函数 和 start_property_service() 函数
启用SELinux安全策略后,会重新执行main函数,由于设置了INIT_SECOND_SRAGE 属性,所以第一部分执行的代码不会再执行
//设置环境变量
setenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE", "true", 1);
static constexpr uint32_t kNanosecondsPerMillisecond = 1e6;
uint64_t start_ms = start_time.time_since_epoch().count() / kNanosecondsPerMillisecond;
setenv("INIT_STARTED_AT", std::to_string(start_ms).c_str(), 1);
//重新执行main方法
char* path = argv[0];
char* args[] = { path, nullptr };
execv(path, args);
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never fall through this conditional.
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
位置:/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void property_init() {
mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH); //创建属性服务设备文件
CreateSerializedPropertyInfo(); //创建序列化过后的propertyInfo实体,主要是读取property_contexts文件,多个不同的文件
if (__system_property_area_init()) { //直接交给__system_property_area_init处理
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area";
}
if (!property_info_area.LoadDefaultPath()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load serialized property info file";
}
}
void CreateSerializedPropertyInfo() {
auto property_infos = std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>();
if (access("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts",
&property_infos)) {
return;
}
// Don't check for failure here, so we always have a sane list of properties.
// E.g. In case of recovery, the vendor partition will not have mounted and we
// still need the system / platform properties to function.
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts",
&property_infos)) {
// Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist.
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/nonplat_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
} else {
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
return;
}
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
// Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist.
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/nonplat_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
}
auto serialized_contexts = std::string();
auto error = std::string();
if (!BuildTrie(property_infos, "u:object_r:default_prop:s0", "string", &serialized_contexts,
&error)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to serialize property contexts: " << error;
return;
}
constexpr static const char kPropertyInfosPath[] = "/dev/__properties__/property_info";
if (!WriteStringToFile(serialized_contexts, kPropertyInfosPath, 0444, 0, 0, false)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write serialized property infos to file";
}
selinux_android_restorecon(kPropertyInfosPath, 0);
}
位置 /bionic/libc/bionic/system_property_api.cpp
int __system_property_area_init() {
bool fsetxattr_failed = false;
return system_properties.AreaInit(PROP_FILENAME, &fsetxattr_failed) && !fsetxattr_failed ? 0 : -1;
}
最终调用了system_properties中的AreaInit 方法 位置:/bionic/libc/system_properties/system_properties.cpp
主要完成的工作,清除缓存,主要清除几个链表以及在内存中的映射,新建property_fliename 目录(/dev/_properties)然后调用Initialize加载系统属性的类别信息,最后将加载的链表写入文件并映射到内存
bool SystemProperties::AreaInit(const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
if (strlen(filename) > PROP_FILENAME_MAX) {
return false;
}
strcpy(property_filename_, filename);
contexts_ = new (contexts_data_) ContextsSerialized();
if (!contexts_->Initialize(true, property_filename_, fsetxattr_failed)) {
return false;
}
initialized_ = true;
return true;
}
process_kernel_dt() 位置:/system/core/init/init.cpp
static void process_kernel_dt() {
//判断/proce/device-tree/firmware/android/compatible文件中值是否为android,firmware
if (!is_android_dt_value_expected("compatible", "android,firmware")) {
return;
}
//get_android_dt_dir()的值为/proc/device-tree/firmware/android
std::unique_ptr<DIR, int (*)(DIR*)> dir(opendir(get_android_dt_dir().c_str()), closedir);
if (!dir) return;
std::string dt_file;
struct dirent *dp;
while ((dp = readdir(dir.get())) != NULL) { //遍历dir文件夹中的文件
if (dp->d_type != DT_REG || !strcmp(dp->d_name, "compatible") || !strcmp(dp->d_name, "name")) {
continue;
}
std::string file_name = get_android_dt_dir() + dp->d_name;
android::base::ReadFileToString(file_name, &dt_file); //读取内容
std::replace(dt_file.begin(), dt_file.end(), ',', '.');
//将ro.boot.文件名 作为key,文件内同作为value设置进属性文件
property_set("ro.boot."s + dp->d_name, dt_file);
}
}
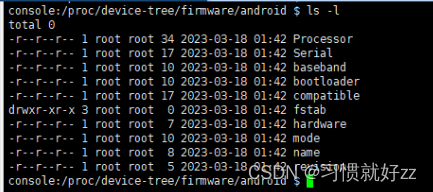
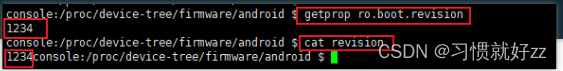
process_kernel_cmdline位置:/system/core/init/init.cpp
static void process_kernel_cmdline() {
// The first pass does the common stuff, and finds if we are in qemu.
// The second pass is only necessary for qemu to export all kernel params
// as properties.
import_kernel_cmdline(false, import_kernel_nv);
if (qemu[0]) import_kernel_cmdline(true, import_kernel_nv);
}
//"./system/core/init/util.cpp"
void import_kernel_cmdline(bool in_qemu,
const std::function<void(const std::string&, const std::string&, bool)>& fn) {
std::string cmdline;
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/cmdline", &cmdline);
//用空格为分隔符
for (const auto& entry : android::base::Split(android::base::Trim(cmdline), " ")) {
std::vector<std::string> pieces = android::base::Split(entry, "=");
if (pieces.size() == 2) {
fn(pieces[0], pieces[1], in_qemu);
}
}
}

1.6 注释六:新建epoll并初始化子进程终止信号处理函数
sigchld_handler_init() 位置:/system/core/init/signal_handler.cpp
这个函数的主要作用是注册 SIGCHLD 信号的处理函数,init是一个守护进程,为了防止init的子进程成为僵尸进程,需要init在子进程结束时获取子进程的结束码,通过结束码将程序表中的进程移除,防止僵尸进程占用程序表的空间(程序表空间达到上限时,系统不能再启动新的进程)
void sigchld_handler_init() {
// Create a signalling mechanism for SIGCHLD.
int s[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_NONBLOCK | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, s) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "socketpair failed in sigchld_handler_init";
}
signal_write_fd = s[0];
signal_read_fd = s[1];
// Write to signal_write_fd if we catch SIGCHLD.
struct sigaction act;
memset(&act, 0, sizeof(act));
act.sa_handler = SIGCHLD_handler;
act.sa_flags = SA_NOCLDSTOP;
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, 0);
ReapAnyOutstandingChildren();
register_epoll_handler(signal_read_fd, handle_signal);
}
//在system/core/init/init.cpp里设置了hadnle_signal函数的实现
void register_epoll_handler(int fd, void (*fn)()) {
epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN; //EPOLLIN表示fd中有数据可读
ev.data.ptr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(fn);
//epoll_fd增加了一个监听对象fd,fd上有数据来到时,调用对应的方法
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev) == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_ctl failed";
}
}
static void handle_signal() {
// Clear outstanding requests.
char buf[32];
read(signal_read_fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
//读取(清空)signal_read_fd的数据,然后调用相关函数处理
ReapAnyOutstandingChildren();
}
void ReapAnyOutstandingChildren() {
while (ReapOneProcess()) {
}
}
static bool ReapOneProcess() {
siginfo_t siginfo = {};
// This returns a zombie pid or informs us that there are no zombies left to be reaped.
// It does NOT reap the pid; that is done below.
// 如果不是0,说明没有僵尸进程
if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(waitid(P_ALL, 0, &siginfo, WEXITED | WNOHANG | WNOWAIT)) != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "waitid failed"; //用waitpid函数获取状态发生变化的子进程pid
return false;
}
auto pid = siginfo.si_pid;
if (pid == 0) return false;
// At this point we know we have a zombie pid, so we use this scopeguard to reap the pid
// whenever the function returns from this point forward.
// We do NOT want to reap the zombie earlier as in Service::Reap(), we kill(-pid, ...) and we
// want the pid to remain valid throughout that (and potentially future) usages.
auto reaper = make_scope_guard([pid] { TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(waitpid(pid, nullptr, WNOHANG)); });
std::string name;
std::string wait_string;
Service* service = nullptr;
if (PropertyChildReap(pid)) {
name = "Async property child";
} else if (SubcontextChildReap(pid)) {
name = "Subcontext";
} else {
//利用FindService找到pid对应的服务,轮询init.rc解析生成的service列表
service = ServiceList::GetInstance().FindService(pid, &Service::pid);
//找到服务的信息
if (service) {
name = StringPrintf("Service '%s' (pid %d)", service->name().c_str(), pid);
if (service->flags() & SVC_EXEC) {
auto exec_duration = boot_clock::now() - service->time_started();
auto exec_duration_ms =
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(exec_duration).count();
wait_string = StringPrintf(" waiting took %f seconds", exec_duration_ms / 1000.0f);
}
} else {
name = StringPrintf("Untracked pid %d", pid);
}
}
if (siginfo.si_code == CLD_EXITED) {
LOG(INFO) << name << " exited with status " << siginfo.si_status << wait_string;
} else {
LOG(INFO) << name << " received signal " << siginfo.si_status << wait_string;
}
//如果没有找到直接返回
if (!service) return true;
//清除子进程相关资料
service->Reap(siginfo);
//移除临时服务
if (service->flags() & SVC_TEMPORARY) {
ServiceList::GetInstance().RemoveService(*service);
}
return true;
}
1.7 注释七:start_property_service() 开启属性服务
start_property_service 位置:\system\core\init\property_service.cpp
之前都是通过property_set 可以轻松设置系统属性,但不是所有的进程都有权限可以随意修改系统属性,Android 将属性的设置统一交给init进程管理,其他进程不能直接修改属性,只能通过init进程来修改
void start_property_service() {
selinux_callback cb;
cb.func_audit = SelinuxAuditCallback;
selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_AUDIT, cb);
property_set("ro.property_service.version", "2");
//创建socket用于通信
property_set_fd = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
false, 0666, 0, 0, nullptr);
if (property_set_fd == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed";
}
//监听property_set_fd,设置最大的并发量为8
listen(property_set_fd, 8);
//注册epoll事件
register_epoll_handler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
}
static void handle_property_set_fd() {
static constexpr uint32_t kDefaultSocketTimeout = 2000; /* ms */
//等待客户端连接
int s = accept4(property_set_fd, nullptr, nullptr, SOCK_CLOEXEC);
if (s == -1) {
return;
}
ucred cr;
socklen_t cr_size = sizeof(cr);
//获取连接到此socket的进程的凭据
if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) {
close(s);
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: unable to get SO_PEERCRED";
return;
}
//建立socket连接
SocketConnection socket(s, cr);
uint32_t timeout_ms = kDefaultSocketTimeout;
uint32_t cmd = 0;
//读取socket中的操作信息
if (!socket.RecvUint32(&cmd, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: error while reading command from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_CMD);
return;
}
//根据操作信息,执行相对应的处理
switch (cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
const auto& cr = socket.cred();
std::string error;
uint32_t result = //通过HandlePropertySet去改变系统的属性值
HandlePropertySet(prop_name, prop_value, socket.source_context(), cr, &error);
if (result != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << prop_name << "' to '" << prop_value
<< "' from uid:" << cr.uid << " gid:" << cr.gid << " pid:" << cr.pid << ": "
<< error;
}
break;
}
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: {
std::string name;
std::string value;
if (!socket.RecvString(&name, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvString(&value, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP2): error while reading name/value from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_DATA);
return;
}
const auto& cr = socket.cred();
std::string error;
uint32_t result = HandlePropertySet(name, value, socket.source_context(), cr, &error);
if (result != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << name << "' to '" << value
<< "' from uid:" << cr.uid << " gid:" << cr.gid << " pid:" << cr.pid << ": "
<< error;
}
socket.SendUint32(result);
break;
}
default:
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: invalid command " << cmd;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_CMD);
break;
}
}
// This returns one of the enum of PROP_SUCCESS or PROP_ERROR*.
uint32_t HandlePropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value,
const std::string& source_context, const ucred& cr, std::string* error) {
//检测这个属性是否合法
if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) {
*error = "Illegal property name";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME;
}
//对ctl.开头的交给init去处理
if (StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {
if (!CheckControlPropertyPerms(name, value, source_context, cr)) { //权限检测
*error = StringPrintf("Invalid permissions to perform '%s' on '%s'", name.c_str() + 4,
value.c_str());
return PROP_ERROR_HANDLE_CONTROL_MESSAGE;
}
//调用HandleControlMessage函数来修改控制属性
HandleControlMessage(name.c_str() + 4, value, cr.pid);
return PROP_SUCCESS;
}
const char* target_context = nullptr;
const char* type = nullptr;
property_info_area->GetPropertyInfo(name.c_str(), &target_context, &type);
//SELinux安全检测有权限才进行处理
if (!CheckMacPerms(name, target_context, source_context.c_str(), cr)) {
*error = "SELinux permission check failed";
return PROP_ERROR_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
if (type == nullptr || !CheckType(type, value)) {
*error = StringPrintf("Property type check failed, value doesn't match expected type '%s'",
(type ?: "(null)"));
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
// sys.powerctl is a special property that is used to make the device reboot. We want to log
// any process that sets this property to be able to accurately blame the cause of a shutdown.
//名字为sys.powerctl的会做些特殊处理,控制重启关机
if (name == "sys.powerctl") {
std::string cmdline_path = StringPrintf("proc/%d/cmdline", cr.pid);
std::string process_cmdline;
std::string process_log_string;
if (ReadFileToString(cmdline_path, &process_cmdline)) {
// Since cmdline is null deliminated, .c_str() conveniently gives us just the process
// path.
process_log_string = StringPrintf(" (%s)", process_cmdline.c_str());
}
LOG(INFO) << "Received sys.powerctl='" << value << "' from pid: " << cr.pid
<< process_log_string;
}
//名字为selinux.restorecon_recursive的会做些特殊处理,其他的会调用PropertySet方法
if (name == "selinux.restorecon_recursive") {
return PropertySetAsync(name, value, RestoreconRecursiveAsync, error);
}
return PropertySet(name, value, error);
}
static uint32_t PropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value, std::string* error) {
size_t valuelen = value.size();
//属性是否符合命名规范
if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) {
*error = "Illegal property name";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME;
}
//判断长度是否符合规范,是否ro开头
if (valuelen >= PROP_VALUE_MAX && !StartsWith(name, "ro.")) {
*error = "Property value too long";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
//判断字符编码格式是否符合规范
if (mbstowcs(nullptr, value.data(), 0) == static_cast<std::size_t>(-1)) {
*error = "Value is not a UTF8 encoded string";
return PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE;
}
//检测属性是否存在
prop_info* pi = (prop_info*) __system_property_find(name.c_str());
if (pi != nullptr) {
// ro.* properties are actually "write-once".
//ro开头的属性只能赋值一次,如果是以ro.开头的直接返回read only
if (StartsWith(name, "ro.")) {
*error = "Read-only property was already set";
return PROP_ERROR_READ_ONLY_PROPERTY;
}
//存在更新属性的值
__system_property_update(pi, value.c_str(), valuelen);
} else {
//不存在就add一个属性值
int rc = __system_property_add(name.c_str(), name.size(), value.c_str(), valuelen);
if (rc < 0) {
*error = "__system_property_add failed";
return PROP_ERROR_SET_FAILED;
}
}
// Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default
// properties to prevent them from being overwritten by default values.
//persist开头的属性可以持久化属性是以persist.开头的特殊处理
if (persistent_properties_loaded && StartsWith(name, "persist.")) {
WritePersistentProperty(name, value);
}
//__system_property_update和__system_property_add并没有改变属性值,
//property_changed()方法采取更新这个值
property_changed(name, value);
return PROP_SUCCESS;
}
1.8 注释八:解析init.rc文件
位置:/system/core/init/parser.cpp
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
//创建Parser对象
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list);
//获得属性指定的rc文件
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
//首先解析根目录的init.rc
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
//解析/syste/etc/init目录
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")) {
//解析失败延迟解析
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/system/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/product/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/odm/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/vendor/etc/init");
}
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
}
}
//位置system/core/init/parser.cpp
bool Parser::ParseConfig(const std::string& path, size_t* parse_errors) {
*parse_errors = 0;
if (is_dir(path.c_str())) {
return ParseConfigDir(path, parse_errors); //解析配置目录
}
return ParseConfigFile(path, parse_errors); //解析配置文件
}
bool Parser::ParseConfigDir(const std::string& path, size_t* parse_errors) {
LOG(INFO) << "Parsing directory " << path << "...";
std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> config_dir(opendir(path.c_str()), closedir);
if (!config_dir) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not import directory '" << path << "'";
return false;
}
dirent* current_file;
std::vector<std::string> files;
while ((current_file = readdir(config_dir.get()))) { //读取目录下的内容,忽略子目录
// Ignore directories and only process regular files.
if (current_file->d_type == DT_REG) { //如果是文件则添加到待解析的集合中
std::string current_path =
android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%s", path.c_str(), current_file->d_name);
files.emplace_back(current_path);
}
}
// Sort first so we load files in a consistent order (bug 31996208)
std::sort(files.begin(), files.end());
for (const auto& file : files) { //遍历集合解析文件
if (!ParseConfigFile(file, parse_errors)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "could not import file '" << file << "'";
}
}
return true;
}
bool Parser::ParseConfigFile(const std::string& path, size_t* parse_errors) {
LOG(INFO) << "Parsing file " << path << "...";
android::base::Timer t;
auto config_contents = ReadFile(path); //读取文件内容到String,在system/core/init/util.cpp
if (!config_contents) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to read config file '" << path << "': " << config_contents.error();
return false;
}
config_contents->push_back('\n'); // TODO: fix parse_config.
ParseData(path, *config_contents, parse_errors); //解析脚本内容
for (const auto& [section_name, section_parser] : section_parsers_) {
section_parser->EndFile();
}
LOG(VERBOSE) << "(Parsing " << path << " took " << t << ".)";
return true;
}
解析数据的类:
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data, size_t* parse_errors) {
// TODO: Use a parser with const input and remove this copy
std::vector<char> data_copy(data.begin(), data.end());
data_copy.push_back('\0'); //添加一个结束符
parse_state state; //定义结构体
state.line = 0;
state.ptr = &data_copy[0];
state.nexttoken = 0;
SectionParser* section_parser = nullptr;
int section_start_line = -1;
std::vector<std::string> args;
auto end_section = [&] { //结束section的回调
if (section_parser == nullptr) return;
if (auto result = section_parser->EndSection(); !result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << section_start_line << ": " << result.error();
}
section_parser = nullptr;
section_start_line = -1;
};
for (;;) {
switch (next_token(&state)) {
case T_EOF: //文件结束
end_section();
return;
case T_NEWLINE: //检测到换行,解析当前行
state.line++;
if (args.empty()) break;
// If we have a line matching a prefix we recognize, call its callback and unset any
// current section parsers. This is meant for /sys/ and /dev/ line entries for
// uevent.
for (const auto& [prefix, callback] : line_callbacks_) {
if (android::base::StartsWith(args[0], prefix)) { //针对指定prefix的情况,比如/dev/
end_section();
if (auto result = callback(std::move(args)); !result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
}
break;
}
}
//如果第一个值能匹配到parser,section_parsers中只有三个值:on service import,之前AddSectionParser函数加入
if (section_parsers_.count(args[0])) {
end_section(); //结束之前
section_parser = section_parsers_[args[0]].get();
section_start_line = state.line;
if (auto result = //解析section
section_parser->ParseSection(std::move(args), filename, state.line);
!result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
section_parser = nullptr;
}
} else if (section_parser) { //使用当前parser解析一行,既不包含on service import则是command或iption
if (auto result = section_parser->ParseLineSection(std::move(args), state.line);
!result) {
(*parse_errors)++;
LOG(ERROR) << filename << ": " << state.line << ": " << result.error();
}
}
args.clear();
break;
case T_TEXT: //将读取的一行数据放到args中,args以空格或""为分隔符,将一行数据拆分成单词放进数组中
args.emplace_back(state.text);
break;
}
}
}
这里涉及到on service import 对应的三个解析器:ActionParser、ServiceParser、ImportParser,它们是之前加入到section_parsers_这个map中
//system/core/init/init.cpp
Parser CreateParser(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser;
parser.AddSectionParser("service", std::make_unique<ServiceParser>(&service_list, subcontexts));
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique<ActionParser>(&action_manager, subcontexts));
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique<ImportParser>(&parser));
return parser;
}
//./system/core/init/parser.cpp
void Parser::AddSectionParser(const std::string& name, std::unique_ptr<SectionParser> parser) {
section_parsers_[name] = std::move(parser);
}
它们都是SectionParser的子类,SectionParser中有三个虚函数和一个纯虚函数,只要包含纯虚函数的类就是抽象类,不能new,只能通过子类实现
class SectionParser {
public:
virtual ~SectionParser() {}
virtual Result<Success> ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args,
const std::string& filename, int line) = 0;
virtual Result<Success> ParseLineSection(std::vector<std::string>&&, int) { return Success(); };
virtual Result<Success> EndSection() { return Success(); };
virtual void EndFile(){};
};
ActionParser
位置:\system\core\init\action_parser.cpp
class ActionParser : public SectionParser {
public:
ActionParser(ActionManager* action_manager, std::vector<Subcontext>* subcontexts)
: action_manager_(action_manager), subcontexts_(subcontexts), action_(nullptr) {}
Result<Success> ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, const std::string& filename,
int line) override;
Result<Success> ParseLineSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, int line) override;
Result<Success> EndSection() override;
private:
ActionManager* action_manager_;
std::vector<Subcontext>* subcontexts_;
std::unique_ptr<Action> action_;
};
ParseSection 函数的作用就是构造了一个Action对象,将trigger条件记录到Action这个对象中,如果是event trigger 就赋值给event_trigger_,如果是property trigger就放到property_trigger_这个map中
Result<Success> ActionParser::ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args,
const std::string& filename, int line) {
std::vector<std::string> triggers(args.begin() + 1, args.end()); //将args复制到triggers中,去除下标0
if (triggers.size() < 1) {
return Error() << "Actions must have a trigger";
}
//...
std::string event_trigger;
std::map<std::string, std::string> property_triggers;
if (auto result = ParseTriggers(triggers, action_subcontext, &event_trigger, &property_triggers);
!result) {
return Error() << "ParseTriggers() failed: " << result.error();
}
auto action = std::make_unique<Action>(false, action_subcontext, filename, line, event_trigger,
property_triggers);
action_ = std::move(action);
return Success();
}
Result<Success> ParseTriggers(const std::vector<std::string>& args, Subcontext* subcontext,
std::string* event_trigger,
std::map<std::string, std::string>* property_triggers) {
const static std::string prop_str("property:"); //判断是否以property:开头
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < args.size(); ++i) {
if (args[i].empty()) {
return Error() << "empty trigger is not valid";
}
if (i % 2) {
if (args[i] != "&&") {
return Error() << "&& is the only symbol allowed to concatenate actions";
} else {
continue;
}
}
if (!args[i].compare(0, prop_str.length(), prop_str)) {
//如果是propert属性就调用ParsePropertyTrigger
if (auto result = ParsePropertyTrigger(args[i], subcontext, property_triggers);
!result) {
return result;
}
} else {
if (!event_trigger->empty()) {
return Error() << "multiple event triggers are not allowed";
}
//如果是args的参数属性就直接赋值给event_trigger_类型String
*event_trigger = args[i];
}
}
return Success();
}
Result<Success> ParsePropertyTrigger(const std::string& trigger, Subcontext* subcontext,
std::map<std::string, std::string>* property_triggers) {
const static std::string prop_str("property:");
std::string prop_name(trigger.substr(prop_str.length())); //截取property:后的内容
size_t equal_pos = prop_name.find('='); //获得等号的位置
if (equal_pos == std::string::npos) {
return Error() << "property trigger found without matching '='";
}
std::string prop_value(prop_name.substr(equal_pos + 1)); //取出value
prop_name.erase(equal_pos); //删除等号
if (!IsActionableProperty(subcontext, prop_name)) {
return Error() << "unexported property tigger found: " << prop_name;
}
//将name-value存放到map中
if (auto [it, inserted] = property_triggers->emplace(prop_name, prop_value); !inserted) {
return Error() << "multiple property triggers found for same property";
}
return Success();
}
ParseLineSection是直接调用Action对象的AddCommand函数,AddCommand看名字就大概知道是添加命令,其调用FindFunction查找命令对应的执行函数,最后将这些信息包装成Command对象存放到commands_数组中
Result<Success> ActionParser::ParseLineSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, int line) {
return action_ ? action_->AddCommand(std::move(args), line) : Success();
}
//位置:system\core\init\action.cpp
Result<Success> Action::AddCommand(const std::vector<std::string>& args, int line) {
//一个map记录命令和调用函数的对应关系
if (!function_map_) {
return Error() << "no function map available";
}
//查找指令对应执行的函数
auto function = function_map_->FindFunction(args);
//function_map_中没有定义的指令返回错误
if (!function) return Error() << function.error();
commands_.emplace_back(function->second, function->first, args, line);
return Success();
}
void Action::AddCommand(BuiltinFunction f, const std::vector<std::string>& args, int line) {
commands_.emplace_back(f, false, args, line); //commands相当于一个数组,emplace_back相当于add
}
//位置system/core/init/builtins.h
//这里对应上面个的function_map_
using KeywordFunctionMap = KeywordMap<std::pair<bool, BuiltinFunction>>;
class BuiltinFunctionMap : public KeywordFunctionMap {
public:
BuiltinFunctionMap() {}
private:
const Map& map() const override;
};
} // namespace init
} // namespace android
//位置system/core/init/keyword_map.h
const Result<Function> FindFunction(const std::vector<std::string>& args) const {
using android::base::StringPrintf;
if (args.empty()) return Error() << "Keyword needed, but not provided";
auto& keyword = args[0];
auto num_args = args.size() - 1;
auto function_info_it = map().find(keyword); //找到keyword对应的entry
if (function_info_it == map().end()) { //end表示最后一个元素,表示没找到
return Error() << StringPrintf("Invalid keyword '%s'", keyword.c_str());
}
auto function_info = function_info_it->second; //获取value值
auto min_args = std::get<0>(function_info); //获取参数数量最小值
auto max_args = std::get<1>(function_info); //获取参数数量最大值
if (min_args == max_args && num_args != min_args) { //将实际参数数量与最大最小值比较
return Error() << StringPrintf("%s requires %zu argument%s", keyword.c_str(), min_args,
(min_args > 1 || min_args == 0) ? "s" : "");
}
if (num_args < min_args || num_args > max_args) {
if (max_args == std::numeric_limits<decltype(max_args)>::max()) {
return Error() << StringPrintf("%s requires at least %zu argument%s",
keyword.c_str(), min_args, min_args > 1 ? "s" : "");
} else {
return Error() << StringPrintf("%s requires between %zu and %zu arguments",
keyword.c_str(), min_args, max_args);
}
}
return std::get<Function>(function_info); //返回命令对应的执行函数
}
//位置system\core\init\builtins.cpp
const BuiltinFunctionMap::Map& BuiltinFunctionMap::map() const {
constexpr std::size_t kMax = std::numeric_limits<std::size_t>::max();
// clang-format off
static const Map builtin_functions = {
{"bootchart", {1, 1, {false, do_bootchart}}},
{"chmod", {2, 2, {true, do_chmod}}}, //各种对应的函数
{"chown", {2, 3, {true, do_chown}}},
{"class_reset", {1, 1, {false, do_class_reset}}},
{"class_restart", {1, 1, {false, do_class_restart}}},
{"class_start", {1, 1, {false, do_class_start}}},
{"class_stop", {1, 1, {false, do_class_stop}}},
{"copy", {2, 2, {true, do_copy}}},
{"domainname", {1, 1, {true, do_domainname}}},
{"enable", {1, 1, {false, do_enable}}},
{"exec", {1, kMax, {false, do_exec}}},
{"exec_background", {1, kMax, {false, do_exec_background}}},
{"exec_start", {1, 1, {false, do_exec_start}}},
{"export", {2, 2, {false, do_export}}},
{"hostname", {1, 1, {true, do_hostname}}},
{"ifup", {1, 1, {true, do_ifup}}},
{"init_user0", {0, 0, {false, do_init_user0}}},
{"insmod", {1, kMax, {true, do_insmod}}},
{"installkey", {1, 1, {false, do_installkey}}},
{"load_persist_props", {0, 0, {false, do_load_persist_props}}},
{"load_system_props", {0, 0, {false, do_load_system_props}}},
{"loglevel", {1, 1, {false, do_loglevel}}},
{"mkdir", {1, 4, {true, do_mkdir}}},
// TODO: Do mount operations in vendor_init.
// mount_all is currently too complex to run in vendor_init as it queues action triggers,
// imports rc scripts, etc. It should be simplified and run in vendor_init context.
// mount and umount are run in the same context as mount_all for symmetry.
{"mount_all", {1, kMax, {false, do_mount_all}}},
{"mount", {3, kMax, {false, do_mount}}},
{"umount", {1, 1, {false, do_umount}}},
{"readahead", {1, 2, {true, do_readahead}}},
{"restart", {1, 1, {false, do_restart}}},
{"restorecon", {1, kMax, {true, do_restorecon}}},
{"restorecon_recursive", {1, kMax, {true, do_restorecon_recursive}}},
{"rm", {1, 1, {true, do_rm}}},
{"rmdir", {1, 1, {true, do_rmdir}}},
{"setprop", {2, 2, {true, do_setprop}}},
{"setrlimit", {3, 3, {false, do_setrlimit}}},
{"start", {1, 1, {false, do_start}}},
{"stop", {1, 1, {false, do_stop}}},
{"swapon_all", {1, 1, {false, do_swapon_all}}},
{"symlink", {2, 2, {true, do_symlink}}},
{"sysclktz", {1, 1, {false, do_sysclktz}}},
{"trigger", {1, 1, {false, do_trigger}}},
{"verity_load_state", {0, 0, {false, do_verity_load_state}}},
{"verity_update_state", {0, 0, {false, do_verity_update_state}}},
{"wait", {1, 2, {true, do_wait}}},
{"wait_for_prop", {2, 2, {false, do_wait_for_prop}}},
{"write", {2, 2, {true, do_write}}},
};
// clang-format on
return builtin_functions;
}
// Builtin-function-map end
FindFunction是通过命令查找对应的执行函数,比如.rc文件中定义chmod,那得在一个map中找到 chmod 具体去执行哪个函数,find相当于Java中的get,但是返回的是entry,可以通过entry ->first和entry ->second获取key-value。找到的value是一个结构体,里面有三个值,第一个是参数最小数目,第二个是参数最大数目,第三个就是执行函数,之后作了参数的数目检查,也就是说命令后的参数要在最小值和最大值之间。
这个BuiltinFunctionMap也比较简单,例如 {“chown”, {2, 3, {true, do_chown}}},表示
最小的参数为2,最大的参数为3,调用的方法为 do_chown(),ture表示 是否需要在vendor_init域的子进程中运行,SELinux相关
EndSection 直接是调用ActionManager::GetInstance().AddAction,将数据存放到 actions_ 数组中,EndFile是一个空实现
//位置system/core/init/action_parser.cpp
Result<Success> ActionParser::EndSection() {
if (action_ && action_->NumCommands() > 0) {
action_manager_->AddAction(std::move(action_)); //在ActionParser调用的就是父类的函数
}
return Success();
}
//位置./system/core/init/action_manager.cpp
void ActionManager::AddAction(std::unique_ptr<Action> action) {
actions_.emplace_back(std::move(action));
}
ServiceParser
位置:\system\core\init\service.cpp
class ServiceParser : public SectionParser {
public:
ServiceParser(ServiceList* service_list, std::vector<Subcontext>* subcontexts)
: service_list_(service_list), subcontexts_(subcontexts), service_(nullptr) {}
Result<Success> ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, const std::string& filename,
int line) override;
Result<Success> ParseLineSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, int line) override;
Result<Success> EndSection() override;
private:
bool IsValidName(const std::string& name) const;
ServiceList* service_list_;
std::vector<Subcontext>* subcontexts_;
std::unique_ptr<Service> service_;
};
一样是看ParseSection 、ParseLineSection方法
Result<Success> ServiceParser::ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args,
const std::string& filename, int line) {
if (args.size() < 3) { //传入的单词个数至少要三个,必须要有一个服务名称和执行文件
return Error() << "services must have a name and a program";
}
const std::string& name = args[1];
if (!IsValidName(name)) { //检查名称是否合法
return Error() << "invalid service name '" << name << "'";
}
Subcontext* restart_action_subcontext = nullptr;
if (subcontexts_) {
for (auto& subcontext : *subcontexts_) {
if (StartsWith(filename, subcontext.path_prefix())) {
restart_action_subcontext = &subcontext;
break;
}
}
}
std::vector<std::string> str_args(args.begin() + 2, args.end());
service_ = std::make_unique<Service>(name, restart_action_subcontext, str_args); //构造Service对象
return Success();
}
Result<Success> ServiceParser::ParseLineSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, int line) {
return service_ ? service_->ParseLine(std::move(args)) : Success();
}
Result<Success> Service::ParseLine(const std::vector<std::string>& args) {
static const OptionParserMap parser_map;
auto parser = parser_map.FindFunction(args); //还是调用了FindFunction方法,与Action一样
if (!parser) return parser.error();
return std::invoke(*parser, this, args);
}
const Service::OptionParserMap::Map& Service::OptionParserMap::map() const {
constexpr std::size_t kMax = std::numeric_limits<std::size_t>::max();
// clang-format off
static const Map option_parsers = {
{"capabilities",
{1, kMax, &Service::ParseCapabilities}},
{"class", {1, kMax, &Service::ParseClass}},
{"console", {0, 1, &Service::ParseConsole}},
{"critical", {0, 0, &Service::ParseCritical}},
{"disabled", {0, 0, &Service::ParseDisabled}},
{"enter_namespace",
{2, 2, &Service::ParseEnterNamespace}},
{"group", {1, NR_SVC_SUPP_GIDS + 1, &Service::ParseGroup}},
{"interface", {2, 2, &Service::ParseInterface}},
{"ioprio", {2, 2, &Service::ParseIoprio}},
{"priority", {1, 1, &Service::ParsePriority}},
{"keycodes", {1, kMax, &Service::ParseKeycodes}},
{"oneshot", {0, 0, &Service::ParseOneshot}},
{"onrestart", {1, kMax, &Service::ParseOnrestart}},
{"override", {0, 0, &Service::ParseOverride}},
{"oom_score_adjust",
{1, 1, &Service::ParseOomScoreAdjust}},
{"memcg.swappiness",
{1, 1, &Service::ParseMemcgSwappiness}},
{"memcg.soft_limit_in_bytes",
{1, 1, &Service::ParseMemcgSoftLimitInBytes}},
{"memcg.limit_in_bytes",
{1, 1, &Service::ParseMemcgLimitInBytes}},
{"namespace", {1, 2, &Service::ParseNamespace}},
{"rlimit", {3, 3, &Service::ParseProcessRlimit}},
{"seclabel", {1, 1, &Service::ParseSeclabel}},
{"setenv", {2, 2, &Service::ParseSetenv}},
{"shutdown", {1, 1, &Service::ParseShutdown}},
{"socket", {3, 6, &Service::ParseSocket}},
{"file", {2, 2, &Service::ParseFile}},
{"user", {1, 1, &Service::ParseUser}},
{"writepid", {1, kMax, &Service::ParseWritepid}},
};
// clang-format on
return option_parsers;
}
OptionParserMap也比较简单,例如 {“oneshot”, {0, 0, &Service::ParseOneshot}},表示
最小的参数为0,最大的参数为0,调用的方法为 Service 类中的 ParseOneshot() 方法
EndSection,直接调用ServiceManager的AddService函数,将数据存放到 services_ 数组中,EndFile依然是一个空实现
Result<Success> ServiceParser::EndSection() {
if (service_) {
Service* old_service = service_list_->FindService(service_->name());
if (old_service) { //服务是否已经启动
if (!service_->is_override()) {
return Error() << "ignored duplicate definition of service '" << service_->name()
<< "'";
}
service_list_->RemoveService(*old_service); //服务已经启动先移除旧服务
old_service = nullptr;
}
service_list_->AddService(std::move(service_)); //上面父类的函数
}
return Success();
}
ImportParser
位置:\system\core\init\import_parser.cpp
主要导入一些其他的rc文件进来,只实现了 ParseSection 和 EndFile ,因为它的语法比较单一
class ImportParser : public SectionParser {
public:
ImportParser(Parser* parser) : parser_(parser) {}
Result<Success> ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, const std::string& filename,
int line) override;
void EndFile() override;
private:
Parser* parser_;
// Store filename for later error reporting.
std::string filename_;
// Vector of imports and their line numbers for later error reporting.
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> imports_;
};
} // namespace init
} // namespace android
Result<Success> ImportParser::ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args,
const std::string& filename, int line) {
if (args.size() != 2) { //只能是两个参数
return Error() << "single argument needed for import\n";
}
std::string conf_file;
bool ret = expand_props(args[1], &conf_file); //处理第二个参数
if (!ret) {
return Error() << "error while expanding import";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Added '" << conf_file << "' to import list";
if (filename_.empty()) filename_ = filename;
imports_.emplace_back(std::move(conf_file), line); //存入数组
return Success();
}
void ImportParser::EndFile() {
auto current_imports = std::move(imports_);
imports_.clear();
for (const auto& [import, line_num] : current_imports) {
if (!parser_->ParseConfig(import)) { //重新调用解析.rc文件的方法
PLOG(ERROR) << filename_ << ": " << line_num << ": Could not import file '" << import
<< "'";
}
}
}
} // namespace init
} // namespace android
至此,解析init.rc语法的过程走完了,主要就是三个核心解析器:ActionParser、ServiceParser、ImportParser。而这几个解析器主要是实现ParseSection、ParseLineSection、EndSection、EndFile四个函数
1.9 注释九:其他事件和一些Action
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState(); //打印当前Parser信息
//注释九:额外配置一些事件和Action
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init"); //QueueEventTrigger用于触发Action,这里触发early-init时间
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done"); //添加Action
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init"); //触发init事件
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
注释十:监听新的事件
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
int epoll_timeout_ms = -1; //epoll超时事件,阻塞事件
if (do_shutdown && !shutting_down) {
do_shutdown = false;
if (HandlePowerctlMessage(shutdown_command)) {
shutting_down = true;
}
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
if (!shutting_down) {
auto next_process_restart_time = RestartProcesses(); //重启服务
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (next_process_restart_time) { //当有进程需要重启时,设置epoll_timeout_ms为重启等待时间
epoll_timeout_ms = std::chrono::ceil<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
*next_process_restart_time - boot_clock::now())
.count();
if (epoll_timeout_ms < 0) epoll_timeout_ms = 0; //还有命令要执行
}
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
epoll_event ev;
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, epoll_timeout_ms)); //epoll_wait用于等待时间的产生
if (nr == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_wait failed";
} else if (nr == 1) {
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
到这里 init 进程已经启动完成


![[H5动画制作系列]坐标转化问题一次搞清,一了百了](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/45839170544b4cf292e242a498fb82b3.png)