Java 集合学习笔记:HashMap - 迭代器
- iterators
- HashIterator
- hasNext
- nextNode
- remove
- KeyIterator
- ValueIterator
- EntryIterator
- spliterators
- HashMapSpliterator
- getFence 获取拆分器的右边界
- estimateSize 估计剩余元素的个数
- KeySpliterator
- 1. trySplit 尝试拆分
- 2. forEachRemaining 遍历剩余元素
- 3. tryAdvance 如果还有元素就消费一个
- 4. characteristics 返回特征
- ValueSpliterator
- EntrySpliterator
- 内部类
- KeySet
- Values
- EntrySet
- contains 是否包含给定对象
- remove 移除给定对象
- spliterator 返回可拆分迭代器
- forEach 遍历元素
- 参考资料
iterators
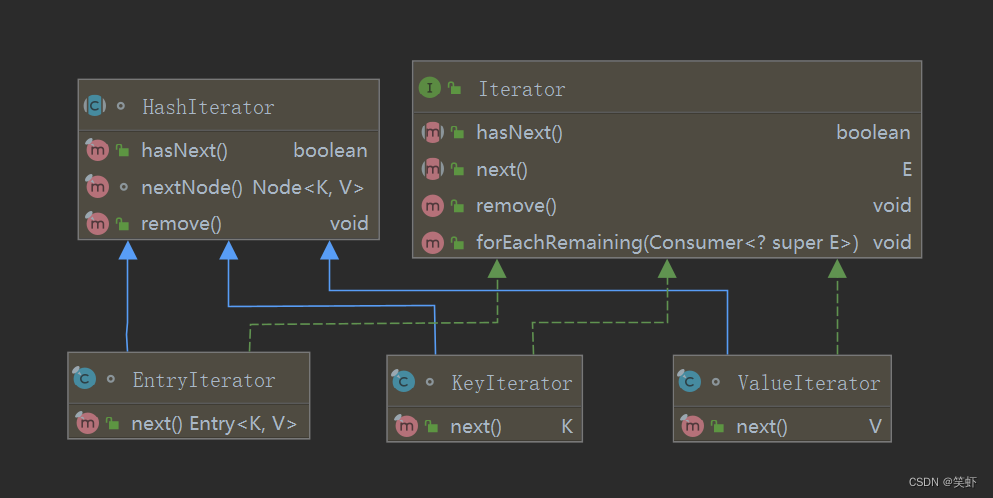
HashIterator 自己实现了 hasNext、nextNode、remove 三个方法。(它没有实现 Iterator )
因为是个抽象类,无法实例化,所以只能作为其他类的公共部分。
三个子类 KeyIterator、ValueIterator、EntryIterator 继承 HashIterator 并各自己实现自己的 next。
共同实现了 Iterator 接口中的所有方法。
HashIterator
这段源码中亮点应该就是通过 if + do while 实现遍历的部分了吧。
abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // 下一次调用 nextNode 会返回的结点
Node<K,V> current; // 当前结点
int expectedModCount; // 预期修改次数。用于检测并发冲突
int index; // 当前索引
// 初始化迭代器
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount; // 缓存修改次数
Node<K,V>[] t = table; // 缓存哈希表
current = next = null; // 当前、下一次将要返回的 entry 都置空
index = 0; // 当前所在位置的索引放到 0
// 如果哈希表不为空,先来到第一个结点
// do-while 遍历哈希表,找到第一个结点,给 next。(它也是所在桶的第一个节点)
if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
}
hasNext
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
nextNode
final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
Node<K,V> e = next;
// 检测并发冲突
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 检测将要返回的结点如果为空就抛锅。因为调用 nextNode() 前,我们通常是检测过 hasNext()的。
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 1. 用即将返回的 e 更新 current 指针。
// 2. if 这句就是在遍历链表
// 2.1. 取出当前结点 current 的下一个结点给 next 指针。
// 2.2. 如果 next 为 null 说明链表遍历完了。要是哈希表不为空,就继续遍历哈希表,找下一个桶。
// 3. do-while 是遍历哈希表
// 3.1. index 还没走到头,就一直取下一个索引对应的值来判断。找到非空的,就是 next 指针该有的值了。
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
remove
// remove 与 nextNode 成对调用。移除后 current 会被置 null
public final void remove() {
// 拿到当前对象,并检测。如果为空抛锅。
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
// 并发冲突检测
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// current 被置 null,在下次调用 nextNode 前都无法再使用 remove
current = null;
// 拿到 key 调用底层 removeNode 方法
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
// 同步修改次数
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
KeyIterator
继承 HashIterator 重写 next 方法,返回具体的 key 值。
final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
}
ValueIterator
继承 HashIterator 重写 next 方法,返回具体的 value 值。
final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
EntryIterator
继承 HashIterator 重写 next 方法,原样返回结点 Node,只不过返回类型改为接口 Map.Entry 。
Node 是 Map.Entry 的实现类:static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {...}
final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
spliterators
- 可拆分迭代器的区间定义是
[左边界索引, 右边界索引)右闭右开。 - 初始时如:
[0, arr.length]
HashMapSpliterator
作为其他几个可拆分迭代器的基类,实现了公用的方法。
static class HashMapSpliterator<K,V> {
final HashMap<K,V> map; // 临时变量缓存将被拆分的 HashMap m
Node<K,V> current; // 当前结点(下一次将要处理的结点)
int index; // 左边界[包含] current 的索引, 在 advance/split 中被更改
int fence; // 右边界(不包含)
int est; // 元素个数(不是精确值,是个估值)
int expectedModCount; // 预期修改次数。用于检测并发冲突
// (map, 0, -1, 0, 0);
HashMapSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin,
int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
this.map = m;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence; // 初始化 -1
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
getFence 获取拆分器的右边界
获取拆分器的右边界。(如果还没有就先获取)
- 将一堆临时变量初始化赋值。(只有第一次调用时才会进入 if )
- 算出并返回右边界。
final int getFence() {
int hi;
// fence 初始化 -1,所以第一次调用此方法是会进入 if
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
HashMap<K,V> m = map; // 取hashmap实例
est = m.size; // 获取元素个数
expectedModCount = m.modCount; // 同步计数:预期修改次数 = 修改次数
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table; // 缓存哈希表
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length; // 哈希表不为空返回长度。
}
return hi;
}
estimateSize 估计剩余元素的个数
public final long estimateSize() {
getFence(); // 初始化
return (long) est;
}
}
KeySpliterator
static final class KeySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<K> {
/**
* @param m 将要被拆分的 HashMap
* @param origin 左边界
* @param fence 右边界
* @param est 剩余元素个数
* @param expectedModCount 预期修改次数
*/
KeySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est, int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
}
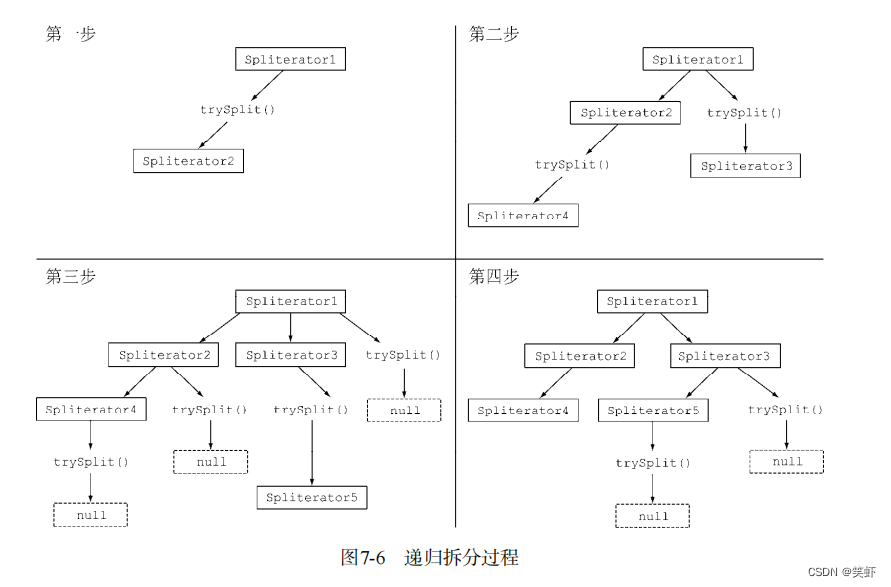
1. trySplit 尝试拆分
尝试拆分,如果可拆分,创建一个新的拆分器并返回。
注意:是按哈希表拆分,并不理会桶中结点的个数。
除非每个桶中都平均分配元素,否则 est >>>= 1 算出来的元素个数,肯定是不准确的。
- 算出左、中、右三个位置的索引。
- 判断如果还能拆分,就劈成两半,用左半边
[左,中)创建一个新拆分器返回。 - 当前
拆分器更新一下左边界,新范围[中,右)
public KeySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
// 获取右、左边界 hi 和 lo,算出中间位置 = (左 + 右) / 2
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
// 1. 左边界 >= 中间,表示已无可再分了。
// 2. 正常情况下 current 为空,原因见 tryAdvance 部分。
// 3. 新拆分器的范围[左,中),当前拆分器的左更新为中[中,右)
// new 的同时更新当前拆分器 index,est
// est >>>= 1 位运算结果作为参数。一步搞定当前和新拆分器的 size
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null
: new KeySpliterator<>(
map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1, expectedModCount
);
}
2. forEachRemaining 遍历剩余元素
遍历每个剩余元素依次执行给定的操作 action,直到所有元素都处理完毕或该操作抛出异常。如果该Spliterator为ORDERED,则按遇到顺序执行操作。动作抛出的异常被传递给调用者。
- 准备工作:声明临时变量。检测并发冲突。初始化。
- 哈希表有内容就进去遍历。消费每一个元素的 key
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
// i 临时变量用于缓存当前桶索引
// hi 临时变量用于缓存右边界
// mc 临时变量用于缓存预期修改次数
int i, hi, mc;
// 传进来的 Lambda 为空,直接抛锅。是个 null 让我怎么执行?
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map; // 临时变量缓存将被拆分的 HashMap。下面会用它来取 table、modCount
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table; // 临时变量缓存此 hashmap 中的哈希表
// 确保第一次调用时进入if。
// 道理与 getFence 中 if ((hi = fence) < 0) 一样。
// 对比一下就能发现,这里是个简化了的 getFence()
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
// 同步三个层级的:缓存预期修改次数
// 当前方法的 = 迭代器的 = hashMap的
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
// 符合条件就执行遍历
// 1. 哈希表不为空,且长度 >= 右边界 (如果哈希表都没东西,就没必要遍历了)
// 2. 左边界 >= 0 (索引值不可能 < 0)
// 3. 当前索引 < 右边界 || 当前结点非空
// (没有右边界,可以继续找剩余的桶,当前结点非空,可以消费之)
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
// 真正开始遍历工作
do {
// 如果结点 p 为null,说明链表走到头了,去下一个桶。
// 否则:先消费一下 key,再继续下一个结点。
// 继续条件:
// p != null 表示当前有结,可以继续。
// i < hi 表示还未到达右边界,可以继续。
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.key);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
// 检测并发冲突
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
3. tryAdvance 如果还有元素就消费一个
如果存在剩余元素,则对其执行给定操作 action,返回true;否则返回false。
如果该Spliterator为ORDERED,则操作将按遇到顺序对下一个元素执行。
action 抛出的异常被传递给调用者。
注意:只有 current == null,的情况下,才可以才分。因为它不为空,说明调用过 n 次 tryAdvance current 走到了链表中的某个结点。此时不允许拆分,只有处理完当前桶中所有节点,current 为 null 后才能拆分。
- 准备工作:声明临时变量。检测并发冲突。初始化。
- 哈希表非空,且长度 >= 右边界,且当前索引 >=0 遍历结点
- 找到下一个结果,找到就消费它。
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int hi;
// 传进来的 Lambda 为空,直接抛锅。是个 null 让我怎么执行?
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 如果前面没报错,这里再声明临时变量拿哈希表。免得浪费资源。
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
// 1. 哈希表不为空,且长度大于当前拆分器的右边界,且当前索引 >= 0
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
// current 不为空,则继续消费它。
// index < hi,表示当前还未走到右边界,可以继续。
while (current != null || index < hi) {
// 如果 current 结点为 null,说明链表走到头了,去下一个桶看看。
// 否则,当前结点不为空继续遍历链表。
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++]; // 取下一个桶的首结点。(同时还更新了index)
else {
K k = current.key; // 取出当前结点的 key
current = current.next; // 遍历到下一个结点。
action.accept(k); // 消费 key
// 检测并发冲突
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true; // 消费成功返回 true
}
}
}
return false;
}
4. characteristics 返回特征
返回该Spliterator及其元素的一组特征。
这里用的是位运算|,8个特性每个特性占一位,可以组合。参考:《Java8实战》读书笔记06:Parallel Stream 并行流 - 表7-2 Spliterator的特性
在给定的分割器上重复调用characteristics(),在调用trySplit之前或中间,应该总是返回相同的结果。否则不能保证使用该Spliterator进行的任何计算。
public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
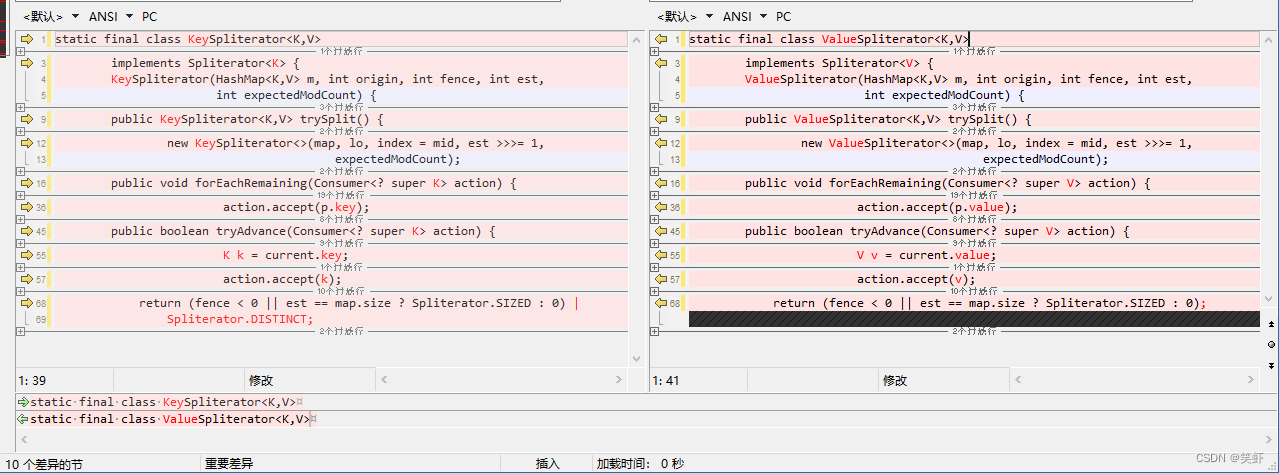
ValueSpliterator
逻辑与 KeySpliterator 基本相同,只是把消费对象从 key 改为了 value。
static final class ValueSpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<V>
{
ValueSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est, int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
}
public ValueSpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new ValueSpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.value);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
V v = current.value;
current = current.next;
action.accept(v);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0);
}
}
EntrySpliterator
逻辑与 KeySpliterator 基本相同,只是把消费对象从 key 改为了 entry。

static final class EntrySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntrySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est, int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
}
public EntrySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new EntrySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
Node<K,V> e = current;
current = current.next;
action.accept(e);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
}
内部类
KeySet
final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<K> iterator() { return new KeyIterator(); }
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); }
public final boolean remove(Object key) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;
}
// 返回 key可拆分迭代器
public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
return new KeySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
// 遍历整个集合,对每个key 执行 action
// size > 0 且哈希表为不为空就遍历集合。
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
// 外层 i 是索引,没到哈希表的尽头就继续
// 内层 当前结点 e 不为空就继续 e = e.next
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.key); // 对 key 执行 action
}
// 检测并发冲突
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
Values
final class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<V> iterator() { return new ValueIterator(); }
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsValue(o); }
public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() {
return new ValueSpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.value);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
EntrySet
final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
...
}
contains 是否包含给定对象
- 首先检测指定对象类型是否
Map.Entry实例。不事就肯定 false 了 - 类型对的上,强转为
Map.Entry<?,?>方便接下来的操作。 - 从给定对象中取出
key,再用这个key从 hashmap 中取结点(Entry)出来。 - 如果取到 Entry,且
equals相等,说明找到目标。返回true。
public final boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
remove 移除给定对象
- 检测给定对象,类型符合就取出
key、value - 调用
removeNode移除结点。要求key、value都匹配才移除。 removeNode会返回被移除的结点,如果不为空,说明移除成功。
public final boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Object value = e.getValue();
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
return false;
}
spliterator 返回可拆分迭代器
public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
forEach 遍历元素
逻辑跟 KeySet 一样。就强调一个关键部分:
- 两层 for 外层走索引,遍历数组。
- 内层走 next 遍历链表。
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
参考资料
笑虾:Java 集合学习笔记:HashMap
笑虾:《Java8实战》读书笔记06:Parallel Stream 并行流 - 表7-2 Spliterator的特性
笑虾:《Java8实战》读书笔记06:Parallel Stream 并行流 - 7.3 Spliterator 可分迭代器