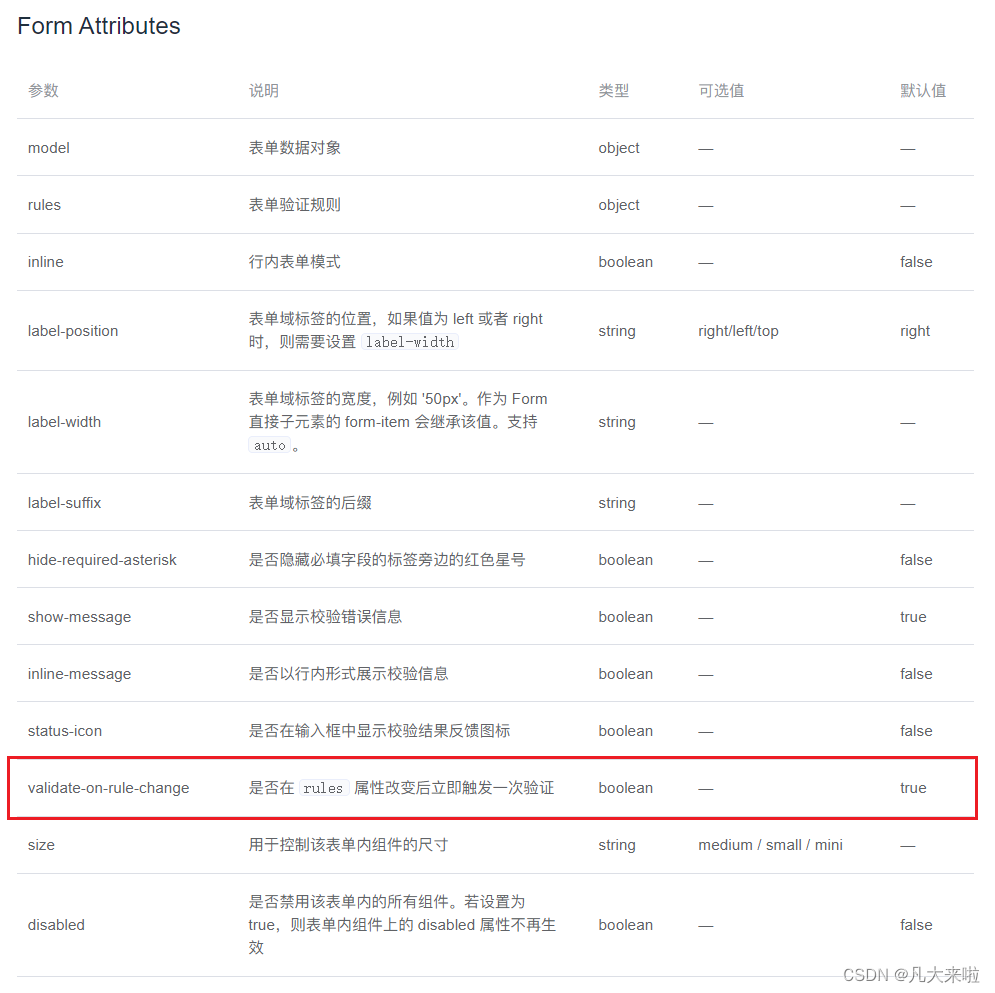
Himmelblau函数-优化问题的经典案例
前言
Himmelblau函数是一种常见的多元函数,它的形式为f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2。这个函数的名字来源于其发明者David Himmelblau,它在数学和工程领域中都有广泛的应用。
一、Himmelblau函数是什么?
形式为f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2的函数
二、优化小实例
1.引入库
代码如下(示例):
import numpy as np from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import torch import os
2.核心代码
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE"
def himmelblau(x):
return (x[0] ** 2 + x[1] - 11) ** 2 + (x[0] + x[1] ** 2 - 7) ** 2
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print('x,y range:', x.shape, y.shape)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print('X,Y maps:', X.shape, Y.shape)
Z = himmelblau([X, Y])
fig = plt.figure('himmelblau')
#ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') #原来的错误ax代码
ax = fig.add_axes(Axes3D(fig)) #改正后的ax代码
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
plt.show()
3.训练
x = torch.tensor([-4., 0.], requires_grad=True)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([x], lr=1e-3)
for step in range(20000):
pred = himmelblau(x)
optimizer.zero_grad()
pred.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step % 2000 == 0:
print ('step {}: x = {}, f(x) = {}'
.format(step, x.tolist(), pred.item()))
4.函数形状
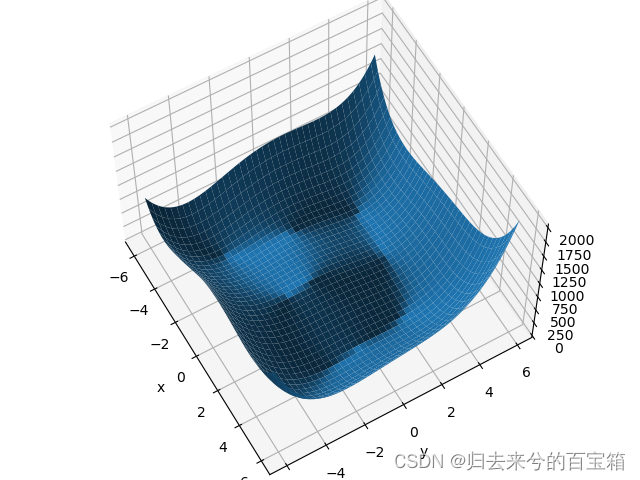
5.训练结果
x,y range: (120,) (120,)
X,Y maps: (120, 120) (120, 120)
step 0: x = [-3.999000072479248, -0.0009999999310821295], f(x) = 146.0
step 2000: x = [-3.526560068130493, -2.5002434253692627], f(x) = 19.450300216674805
step 4000: x = [-3.777446746826172, -3.2777843475341797], f(x) = 0.0012130826944485307
step 6000: x = [-3.7793045043945312, -3.283174753189087], f(x) = 5.636138666886836e-09
step 8000: x = [-3.779308319091797, -3.28318190574646], f(x) = 7.248672773130238e-10
step 10000: x = [-3.7793095111846924, -3.28318452835083], f(x) = 8.822098607197404e-11
step 12000: x = [-3.7793102264404297, -3.2831854820251465], f(x) = 8.185452315956354e-12
step 14000: x = [-3.7793102264404297, -3.2831859588623047], f(x) = 0.0
step 16000: x = [-3.7793102264404297, -3.2831859588623047], f(x) = 0.0
step 18000: x = [-3.7793102264404297, -3.2831859588623047], f(x) = 0.0