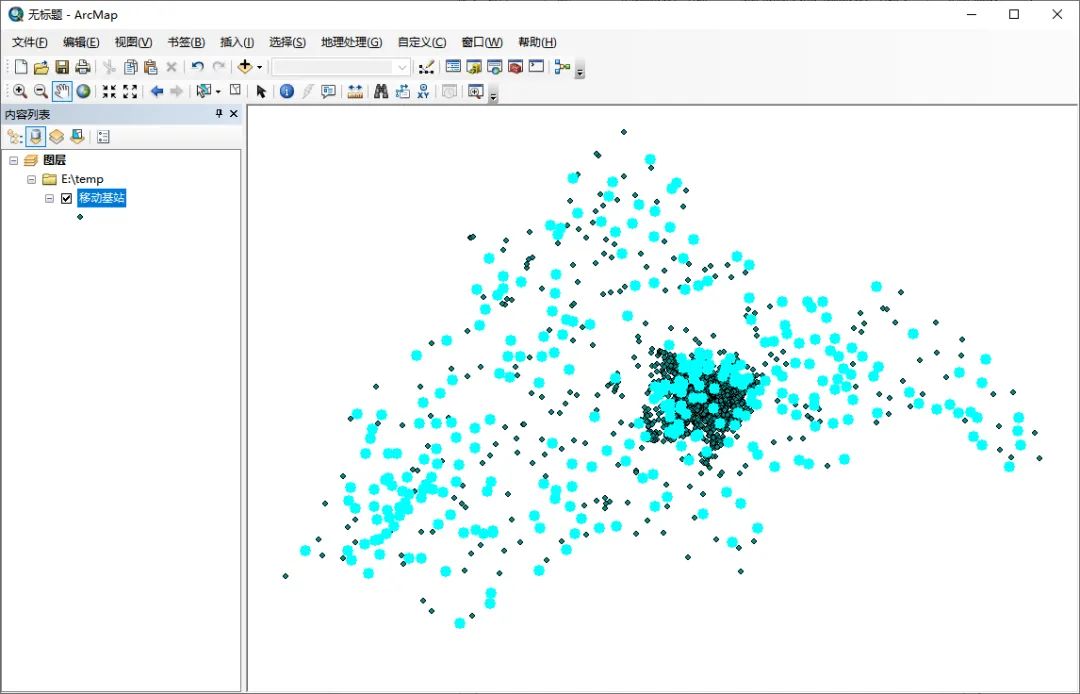
前言
对于学习STL而言,最重要的手段之一就是亲手模拟实现一个自己的容器。string存储只为char类型,且操作上并没有很难的操作。因此对于初学者而言,string是一个很好的练手项目。
一、确定思路
虽说相对适合初学者模拟实现,但是string的规模也并不小,粗略也需要 300+ 行代码实现。因此在开始模拟实现之前一个完善的思维导图必不可少。下方给出一个简单的思维导图以及一个大体的框架

namespace hty {
class string {
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const hty::string& s);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, hty::string& s);
private:
char* _str;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
const static size_t _npos = -1;
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
public:
string(const char* str = "")
string(const string& s)
string& operator=(const string& s)
~string()
//
// iterator
iterator begin()
iterator end()
const iterator begin()const
const iterator end()const
/
// modify
void push_back(char c)
void append(const char* str)
string& operator+=(char c)
string& operator+=(const char* str)
void clear()
void swap(string& s)
const char* c_str()const
/
// capacity
size_t size()const
size_t capacity()const
bool empty()const
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
void reserve(size_t n)
/
// access
char& operator[](size_t index)
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
/
//relational operators
bool operator<(const string& s)
bool operator>(const string& s)
bool operator==(const string& s)
bool operator<=(const string& s)
bool operator>=(const string& s)
bool operator!=(const string& s)
// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const
// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str
string& insert(size_t pos, char c)
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = _npos)
};
};
二、实现过程
对于模拟实现,详细讲每个函数的实现过程显得冗杂,因此我将提出自己对于模拟实现的一些看法和实用性方法。
2.1 查阅文档
对于第一次模拟实现库来说,要学会多查阅文档,了解一个函数的返回值、功能是什么。同时了解该函数还能接受那些类型的传参,进行了哪些重载等,都十分重要。
2.2 验证正确性
在上面我们已经说到,模拟string库对于初学者来说也算一个不小的工作,因此在模拟过程中,必要的正确性验证是少不了的。每当我们完成一个或者多个功能相近的函数之后,我们首先要对这几个函数的正确性进行验证,而不是等到所有完成之后在验证。
过程中验证一方面能提高我们的动力,看到自己逐步实现的过程;另一方面有助于我们完成调试工作。等到所有函数完成之后,许多函数可能存在复用关系等,这样一来出现错误便不易定位,增大了调试的工作量。
2.3 测试案例
验证正确性过程中需要自己创建若干测试案例。对于测试案例的选取也是有很多要求的,要保证一些可能出现 bug 的位置也要测试到位。例如常见的对首元素、尾元素操作,对空字符串操作,对很大的字符串操作等。
三、完整代码
以下给出我的实现,如有错误欢迎指正:
namespace hty {
class string {
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const hty::string& s);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, hty::string& s);
private:
char* _str;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
const static size_t _npos = -1;
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
public:
string(const char* str = "") {
_size = strlen(str);
_str = new char[_size + 1];
_capacity = _size;
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string(const string& s) {
_size = s.size();
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_size + 1];
strcpy(_str, s.c_str());
}
string& operator=(const string& s) {
if (this != &s) {
resize(s.size());
strcpy(_str, s.c_str());
}
return *this;
}
~string() {
_size = _capacity = 0;
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
//
// iterator
iterator begin() {
return _str;
}
iterator end() {
return _str + _size;
}
const iterator begin()const {
return _str;
}
const iterator end()const {
return _str + _size;
}
/
// modify
void push_back(char c) {
if (_size == _capacity) {
size_t new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
_str[_size] = c;
_str[_size + 1] = 0;
++_size;
}
void append(const char* str) {
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
reserve(_capacity + len);
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(char c) {
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str) {
append(str);
return *this;
}
void clear() {
_str[0] = 0;
_size = 0;
}
void swap(string& s) {
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
const char* c_str()const {
return _str;
}
/
// capacity
size_t size()const {
return _size;
}
size_t capacity()const {
return _capacity;
}
bool empty()const {
return _size == 0;
}
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0') {
if (n > _capacity)
reserve(n);
if (n > _size) {
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
_str[i] = c;
}
_str[n] = 0;
_size = n;
}
void reserve(size_t n) {
if (n > _capacity) {
_capacity = n;
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
}
}
/
// access
char& operator[](size_t index) {
assert(index >= 0 && index <= _size);
return _str[index];
}
const char& operator[](size_t index)const {
assert(index >= 0 && index <= _size);
return _str[index];
}
/
//relational operators
bool operator<(const string& s) {
size_t len = max(s.size(), _size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (_str[i] < s[i] || (_str[i] == 0 && s[i] != 0))
return true;
else if (s[i] == 0)
return false;
}
return false;
}
bool operator>(const string& s) {
size_t len = max(s.size(), _size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (_str[i] > s[i] || (s[i] == 0 && s[i] != 0))
return true;
else if (_str[i] == 0)
return false;
}
return false;
}
bool operator==(const string& s) {
size_t len = max(s.size(), _size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (_str[i] != s[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s) {
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool operator>=(const string& s) {
return *this > s || *this == s;
}
bool operator!=(const string& s) {
return !(*this == s);
}
// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const {
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++) {
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return _npos;
}
// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const {
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < _size);
const char* ret = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (ret)
return (ret - _str);
else
return _npos;
}
// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str,并返回该字符的位置
string& insert(size_t pos, char c) {
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity) {
size_t new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
for (size_t i = _size + 1; i > pos; i--)
_str[i] = _str[i - 1];
_str[pos] = c;
_size++;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str) {
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity) {
size_t new_capacity = _size + len;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
for (size_t i = _size + len; i > pos; i--)
_str[i] = _str[i - len];
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = _npos) {
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < _size);
if (len == _npos || pos + len >= _size) {
_str[pos] = 0;
_size = pos;
return *this;
}
for (size_t i = pos; i <= _size - len; i++)
_str[i] = _str[i + len];
_size -= len;
return *this;
}
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const hty::string& s) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
_cout << s[i];
}
return _cout;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, hty::string& s) {
char ch = '0', buff[128] = { 0 };
s.clear();
int i = 0;
while (ch = _cin.get()) {
if (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n') {
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127){
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
}
else {
buff[i] = 0;
s += buff;
break;
}
}
return _cin;
}
};