文章目录
- 一、图的概述
- 1.1 图论的作用
- 1.2 图的分类
- 1.2.1 无向图
- 1.2.2 有向图
- 1.2.3 无权图
- 1.2.4 有劝图
- 1.3 图的基本概念
- 二、树的基本表示
- 2.1 邻接矩阵
- 2.1.1 邻接矩阵 表示图
- 2.1.2 邻接矩阵的复杂度
- 2.2 邻接表
- 2.2.1 邻接表的复杂度
- 2.2.2 邻接表By哈希表
- 三、图的深度优先遍历
- 3.1 图深度遍历过程
- 3.2 图遍历改进
- 3.3 先中后
- 3.4 复杂度
- 四、深度遍历的应用
- 4.1 求联通分量
- 4.2 单源路径问题
- 4.3 检测无向图中的环
- 4.4 二分图检测
- 五、图的广度优先遍历
- 六、图论问题的建模
- 七、图论和AI
- 十一、最小生成树
- 11.1 带权图
- 十二、最短路径
- 12.1 迪杰斯特拉算法
- 12.1.1 Dijkstra原理
一、图的概述
1.1 图论的作用






1.2 图的分类


1.2.1 无向图

1.2.2 有向图
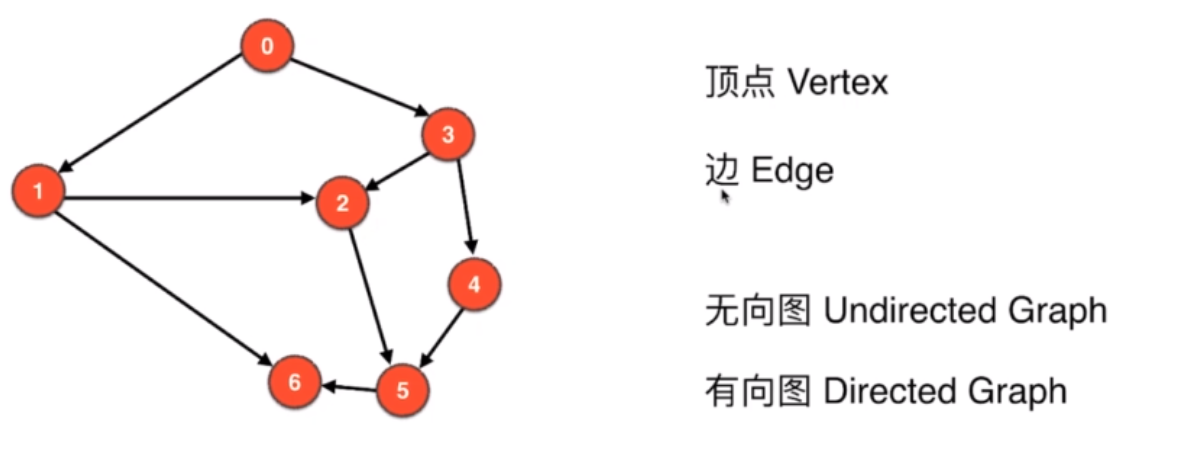
1.2.3 无权图

1.2.4 有劝图

1.3 图的基本概念
- 两点相邻
- 点的邻边
- 路径Path,从一个点到另一个点走过的路
- 环Loop,多个点围城一个圈
- 自环边,自己和自己形成环
- 平行边,重复的边

-
联通分量
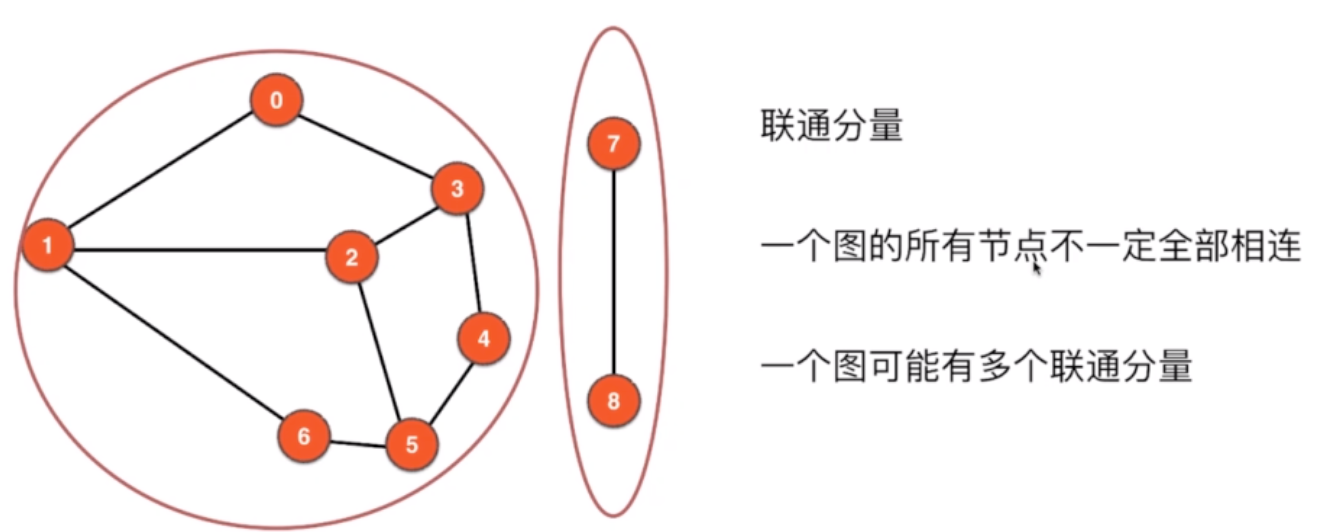
-
无环图

树是一种无环图,一个联通的无环图(一个联通分量)就是树 -
连通图的 生成树

V:顶点数

10) 顶点的度degree
顶点相邻的边数

二、树的基本表示
2.1 邻接矩阵
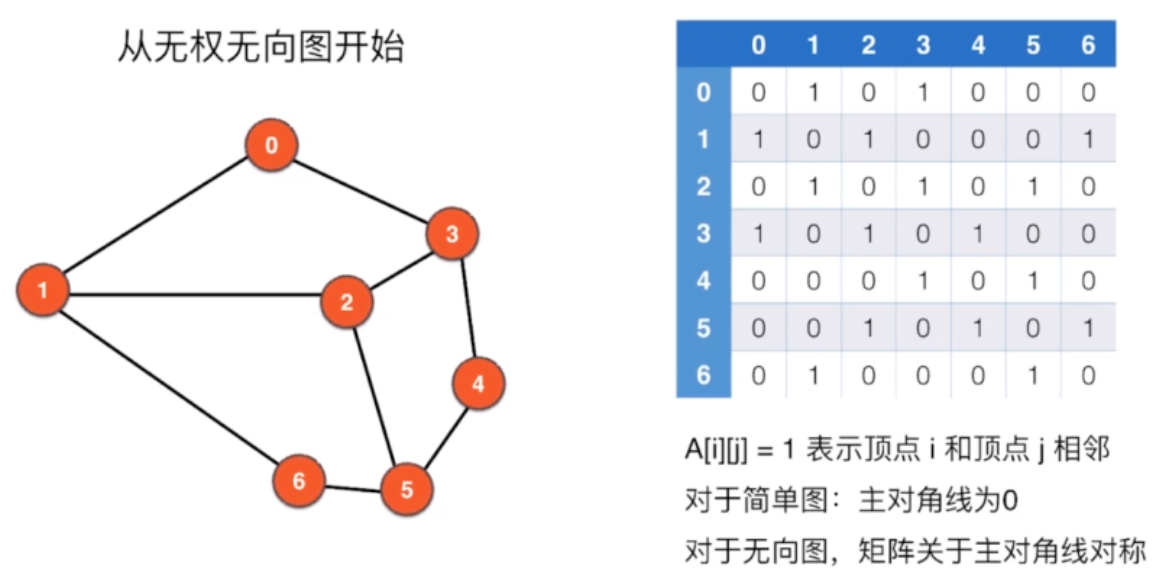

V:顶点数,E:边数
2.1.1 邻接矩阵 表示图
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjMatrix {
private int V;
private int E;
private int[][] adj;
public AdjMatrix(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
adj = new int[V][V];
E = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
adj[a][b] = 1;
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++){
for(int j = 0; j < V; j ++)
sb.append(String.format("%d ", adj[i][j]));
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjMatrix adjMatrix = new AdjMatrix("src/main/java/hGraph/base/file/g.txt");
System.out.print(adjMatrix);
}
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
//判断是否有边,两顶点是否相邻
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v][w] == 1;
}
//查找和顶点v相连的顶点
public ArrayList<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)
if(adj[v][i] == 1)
res.add(i);
return res;
}
//查找顶点的度
public int degree(int v){
return adj(v).size();
}
2.1.2 邻接矩阵的复杂度

空间复杂度 可以优化,
求一个点的相邻结点 可以优化
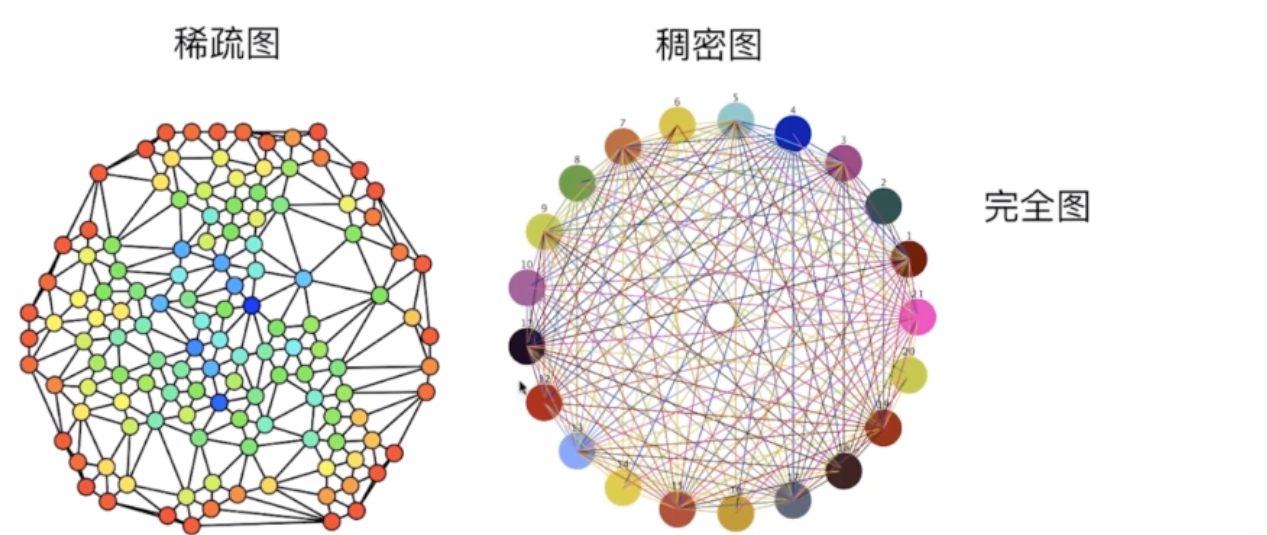
稀疏图&稠密图
根据边的多少
完全图 每个顶点都连接
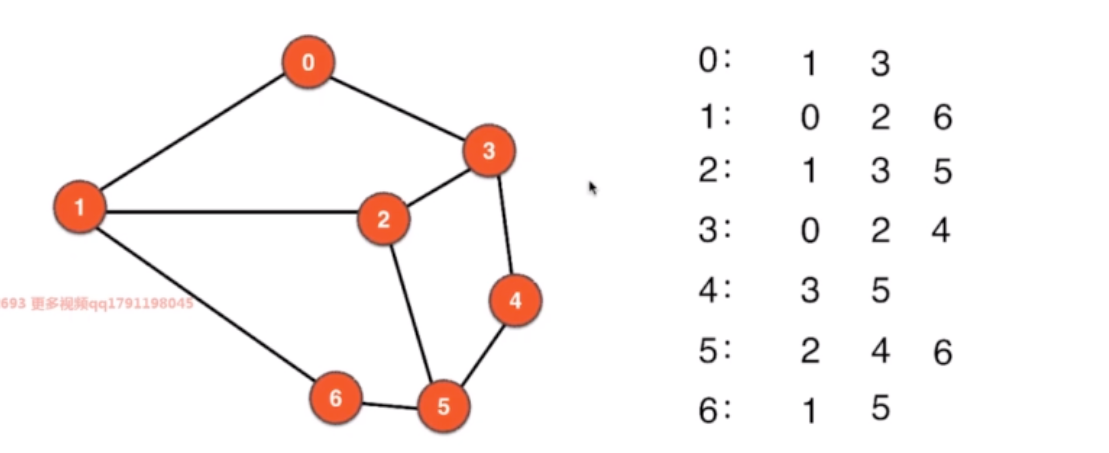
2.2 邻接表
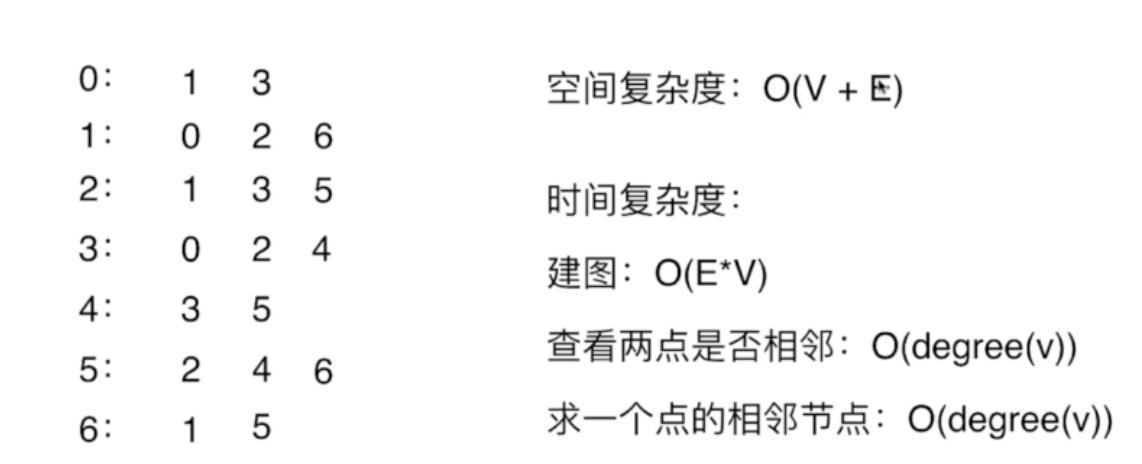
2.2.1 邻接表的复杂度

2.2.2 邻接表By哈希表

用红黑树实现图
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjSet {
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjSet(String pathStr){
File file = new File(pathStr);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeSet[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)
adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){
// public TreeSet<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for(int w : adj[v])
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjSet adjSet = new AdjSet("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjSet);
}
}
三、图的深度优先遍历
3.1 图深度遍历过程
之前描述过树的遍历
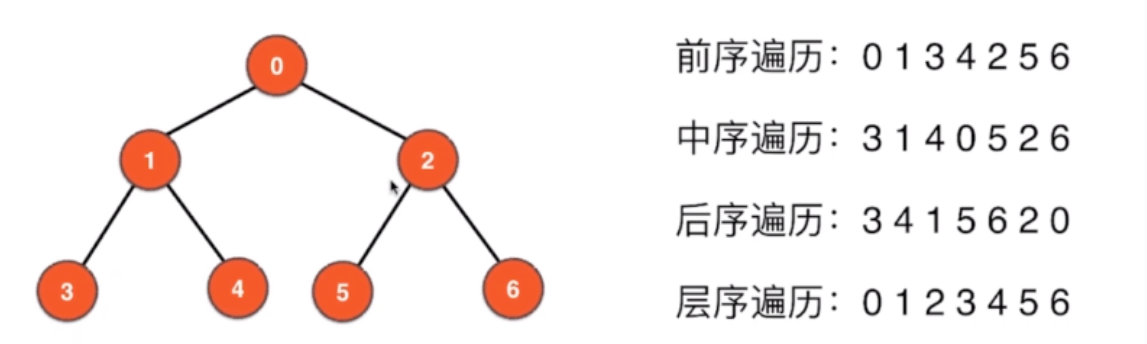
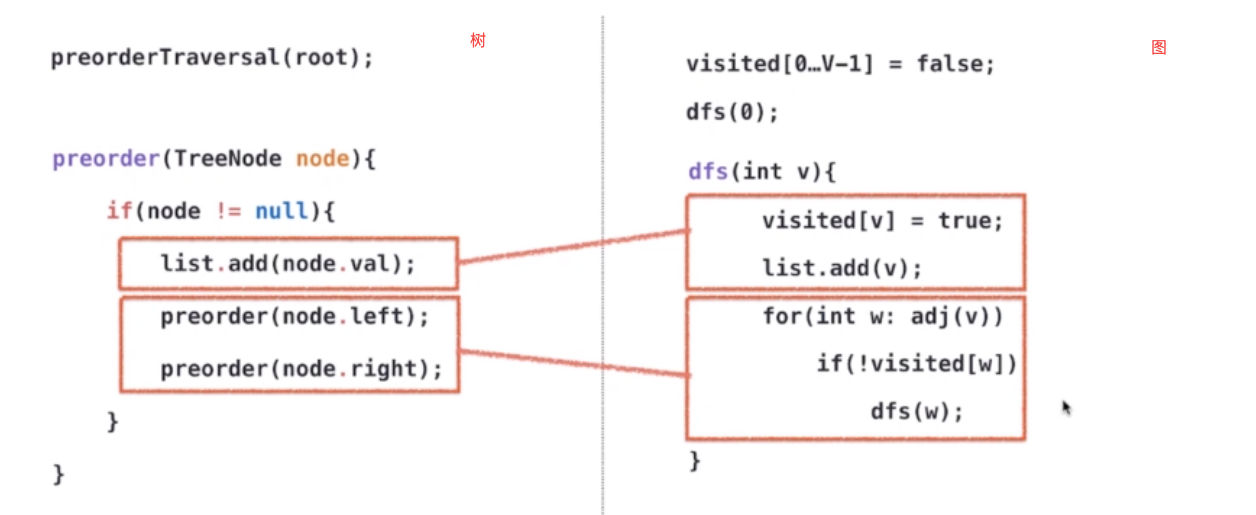



public GraphDFS(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
dfs(0);
}
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
order.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
}
3.2 图遍历改进

不和0 相连 的顶点,就不会遍历
原因是只针对0 调用
改进:对每一个节点进行调用

public GraphDFS(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v])
dfs(v);
}
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
pre.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
post.add(v);
}
public Iterable<Integer> pre(){
return pre;
}
public Iterable<Integer> post(){
return post;
}
3.3 先中后
在树中有先中后遍历

图也可以分为 先 后序遍历

3.4 复杂度
遍历的复杂度:O(V+E)
四、深度遍历的应用
4.1 求联通分量

4.2 单源路径问题
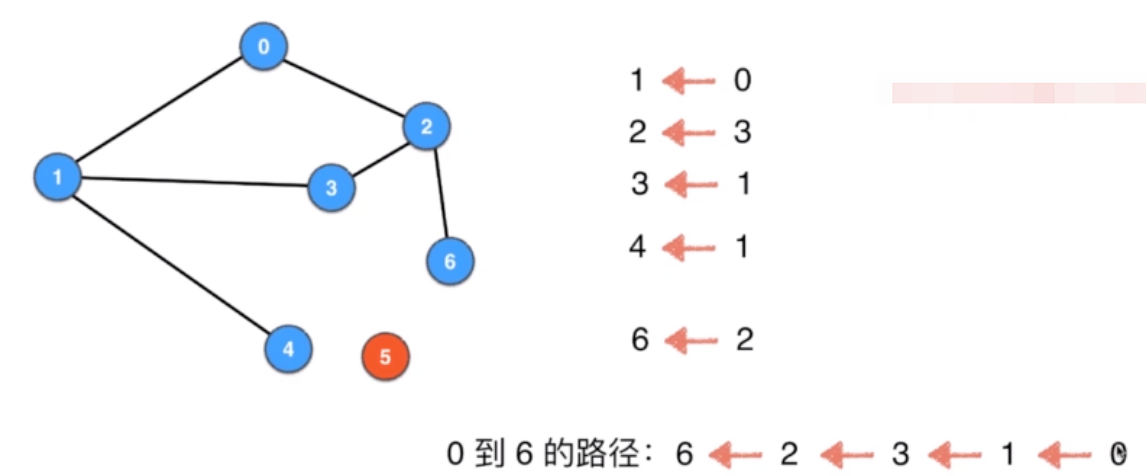
依然做了深度优先遍历,记录这个顶点的pre:从哪里来的
单源路径:从一个顶点出发的路径,不能反向查找
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SingleSourcePath {
private Graph G;
private int s;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){
G.validateVertex(s);
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];
dfs(s, s);
}
private void dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true;
pre[v] = parent;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w, v);
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);
return visited[t];
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6));
System.out.println("0 -> 5 : " + sspath.path(5));
}
}

4.3 检测无向图中的环

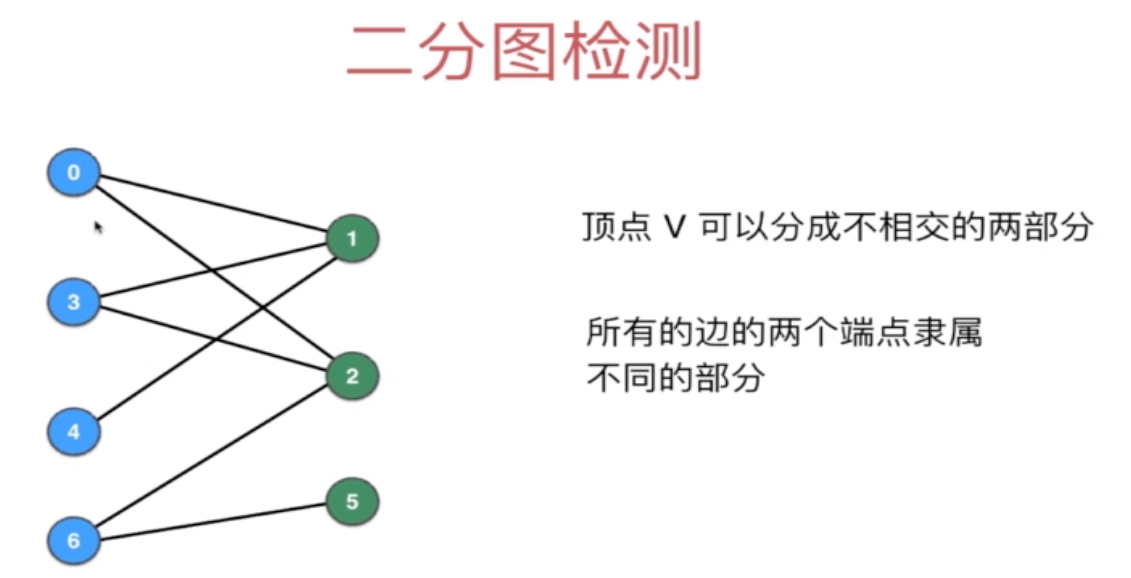
4.4 二分图检测
二分图:
五、图的广度优先遍历

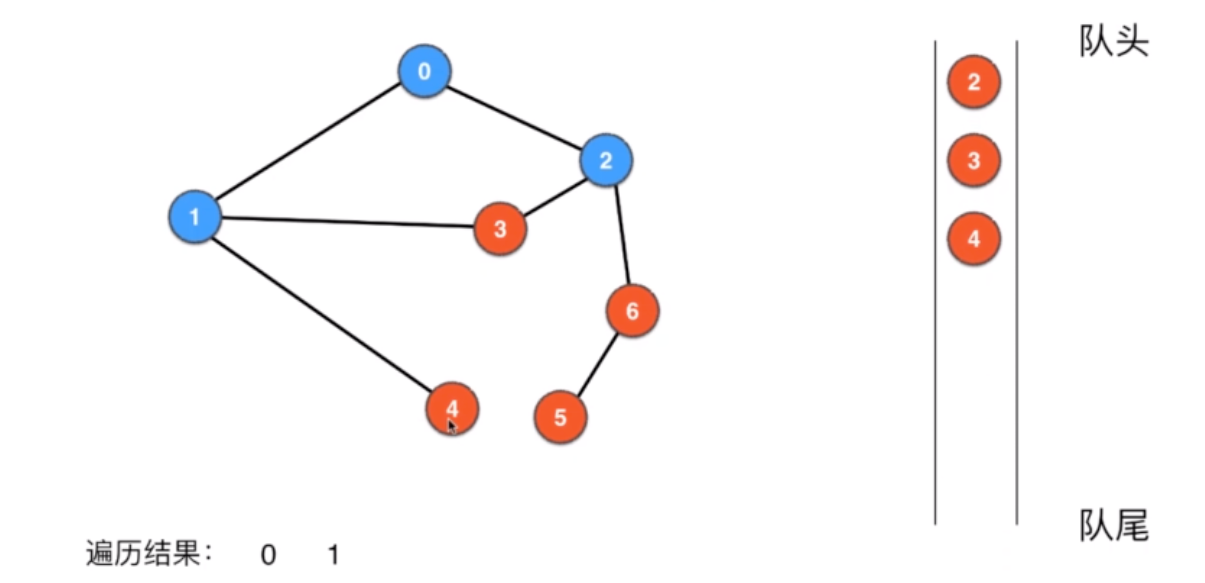

public GraphBFS(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v])
bfs(v);
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
order.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);
visited[w] = true;
}
}
}
public Iterable<Integer> order(){
return order;
}
复杂度:O(V+E)
六、图论问题的建模
七、图论和AI
十一、最小生成树
11.1 带权图
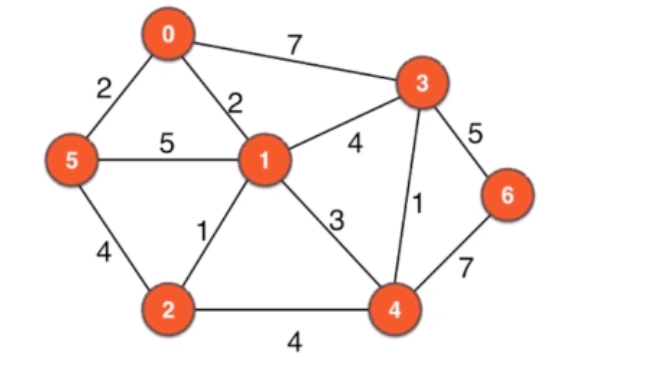
/// 暂时只支持无向带权图
public class WeightedGraph implements Cloneable{
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeMap<Integer, Integer>[] adj;
public WeightedGraph(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeMap[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)
adj[i] = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
int weight = scanner.nextInt();
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
if(adj[a].containsKey(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
adj[a].put(b, weight);
adj[b].put(a, weight);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
十二、最短路径
带权图的最短路径不一定 走的边最少

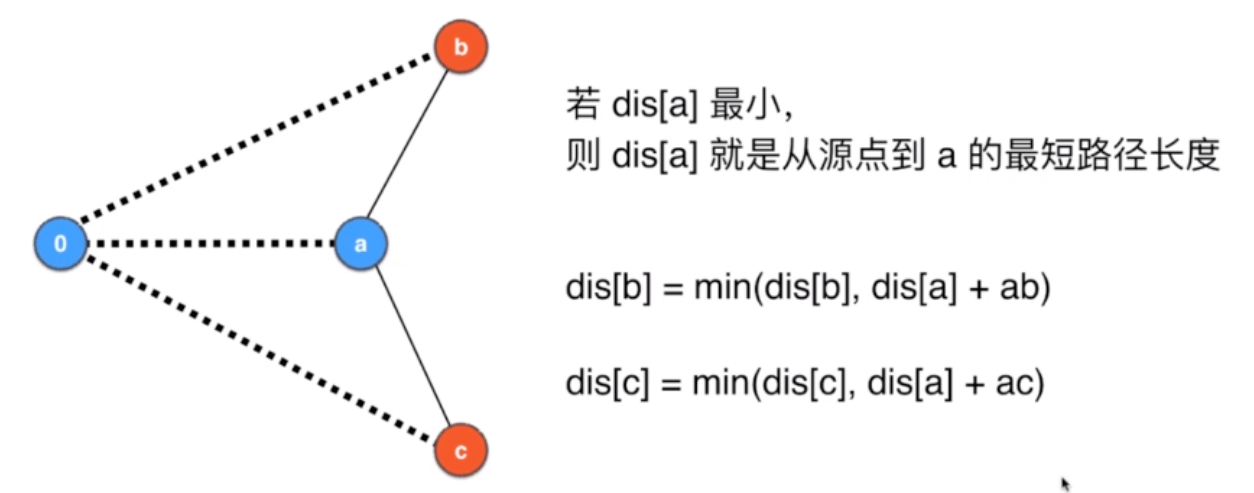
12.1 迪杰斯特拉算法
12.1.1 Dijkstra原理
-
指定dis:源到各个顶点的路径,先初始为MAX
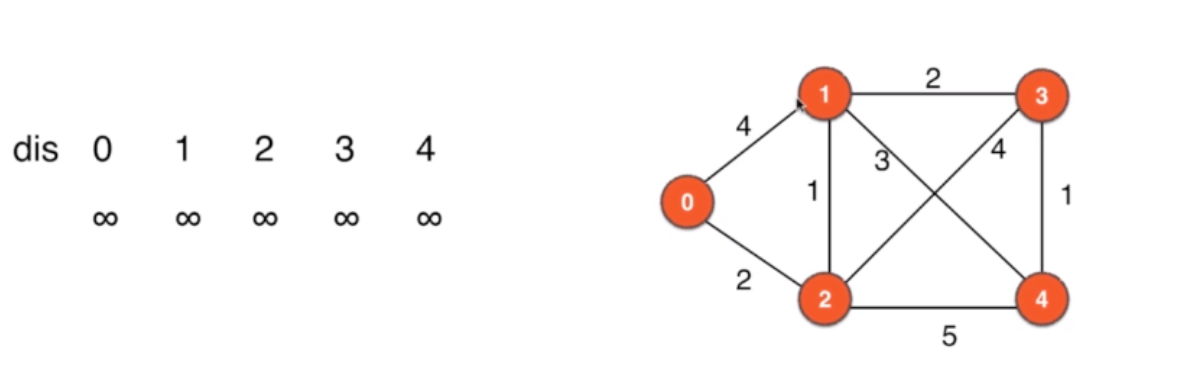
-
找顶点,更新dis

-
找当前最短的路径,确定这个就是到顶点的最短路径:确定2位0到2的最短路径
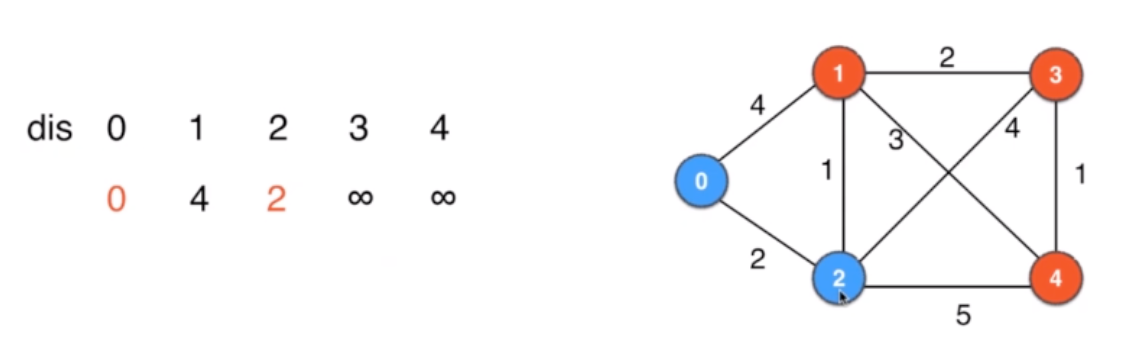
-
根据2顶点,来做更新
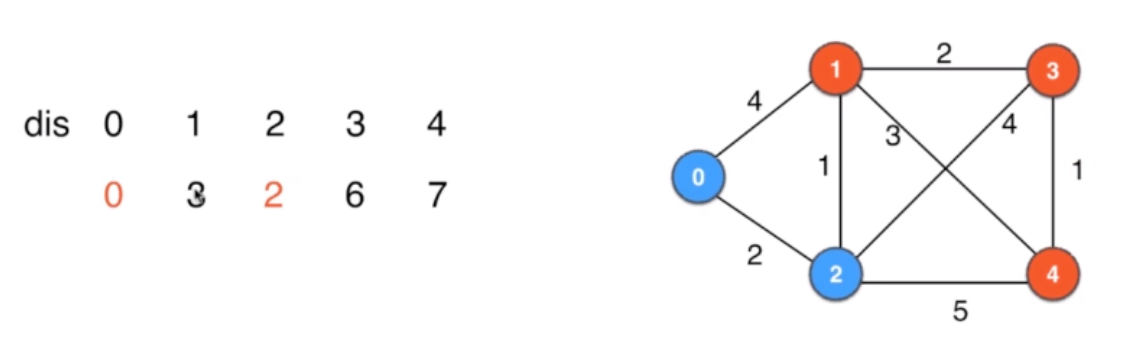
这里更新了2 到各个顶点的路径,1 从 4 更新到了3 -
再从当前的路径中找最小的,为3 顶点1,
所以确定顶点1 的最短路径为3

- 再根据顶点1 ,更新dis

- 确定当前最短的距离为5 ,顶点3

- 更新dis,到顶点4都为6

每轮循环:
- 初始化源到其他顶点的dis,默认都为MAX
- 找到当前没有访问的最短路节点
- 确定这个节点的最短路径就是当前大小
- 根据这个节点的最短路径大小,更新到其他节点的路径长度,如果比dis中的要小,那么就更新dis
#from ChatGPT
1.初始化距离数组dist和标记数组visited。将起始地点设置为起点,其他地点的距离初始化为无穷大,visited数组初始化为false。
2.从起点开始遍历所有地点,选择当前距离最小且未被访问过的地点u。
3.对于地点u,更新与其相邻的地点v的距离,如果新的距离小于原来的距离,则更新距离数组dist和路径数组path。
4.标记地点u为已访问,重复上述过程,直到所有地点都被访问。
5.最终得到起点到每个地点的最短距离和路径。