Java里面单向链表实现
- 说明
- 代码
说明
这里记录下单向链表实现。并在类里面写了一些新增和删除方法。
代码
package com.example.test;
//单向链表类
public class Node {
//结点的值
public int val;
//当前结点的后继结点,当 next == null 时,代表这个结点是所在链表的最后一个结点
public Node next;
//构造方法
public Node(int val){
this.val=val;
this.next=null;//初始化时,默认首结点为null
}
//依次遍历链表里面的数据,从头结点开始遍历
public static void printAllElements(Node head){
Node current=head;
while(current!=null){
int value=current.val;
System.out.print(value+" ");
current=current.next;//指向下一个结点
}
System.out.println();
}
//统计链表里面的元素数量
public static int sizeOf(Node head){
int count=0;
for(Node cur=head;cur!=null;cur=cur.next){
count++;
}
return count;
}
//在链表中的头部插入元素
public static Node headInsertNode(Node head,int value){
Node node=new Node(value);
//当前结点的下一个结点为以前的头结点
node.next=head;
return node;
}
//在链表中的尾部插入元素
public static Node tailInsertNode(Node head ,int value){
Node node=new Node(value);
//一是链表是一个空的链表,没有头结点或者只有头结点,那么就是头结点和尾结点的值都为null
if(head==null){
node.next=null;
return node;
}
//声明一个最后结点
Node last=head;
//从头结点开始遍历,如果头结点下一个结点不为null,将下一个结点给last,直到last为最后一个结点
while(last.next!=null){
last=last.next;//找最后一个结点
}
//在最后一个节点的尾部插入当前需要插入的结点
last.next=node;
return head;
}
//在链表的任意位置插入新结点,如A->B->C,在B后面加入一个新节点,指针指向B->newNode->C
public static void insertNode(Node node,int value){
Node newNode = new Node(value);
//插入新结点为你当前传的原来node结点下一个结点
newNode.next=node.next;
//当前传的node结点下一个结点就是新结点
node.next=newNode;
}
//删除头结点
public static Node headDeleteNode(Node head){
if(head==null){
throw new RuntimeException("链表是空的,无法进行头删操作");
}
return head.next;
}
//删除尾结点
public static Node tailDeleteNode(Node head){
//第一种情况判断是否是空链表
if(head==null){
throw new RuntimeException("空链表,不能进行删除");
}
//第二种情况判断是否只有一个结点,从头结点开始遍历,如果下一个结点为空就是只有头结点
if(head.next==null){
return null;
}
Node lastOfLast=head;
//如果结点数量大于等于3,从第三个结点判断是否为null
while(lastOfLast.next.next!=null){//找到倒数第二个结点
//将后面的结点向前移动一位
lastOfLast=lastOfLast.next;
}
lastOfLast.next=null;//删除最后一个结点
//返回头结点供printAllElements方法从头遍历元素
return head;
}
//删除结点指定值,只删除一次
public static void deleteNode(Node head,int value) {
//第一种情况判断是否是空链表
if (head == null) {
return;
}
//第二种情况判断是否当前头结点满足条件
if (head.val == value) {
head = head.next;
printAllElements(head);
return;
}
Node current = head;
//判断当前结点下一个结点是否为null
while ( current.next != null) {
//如果当前结点下一个结点值为删除的值
if (current.next.val == value) {
//那么就把当前结点的下一个结点指向下下个结点
current.next = current.next.next;
printAllElements(head);
return;
}
//将结点往后移一位给while做判断
current = current.next;
}
}
}
测试类代码:
package com.example.deesign_patterns.test;
public class Test2Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个链表并赋值,首结点
Node head=new Node(1);
//第二个结点
Node node2=new Node(2);
//第三个结点
Node node3=new Node(3);
//第四个结点
Node node4=new Node(4);
//将结点链接起来
//head头结点的下一个结点为node2
head.next=node2;
//node2下一个结点为node3
node2.next=node3;
//node3下一个结点为node4
node3.next=node4;
node4因为是尾结点,所以下一个结点为null
node4.next=null;
//遍历结点数据,从头结点开始遍历
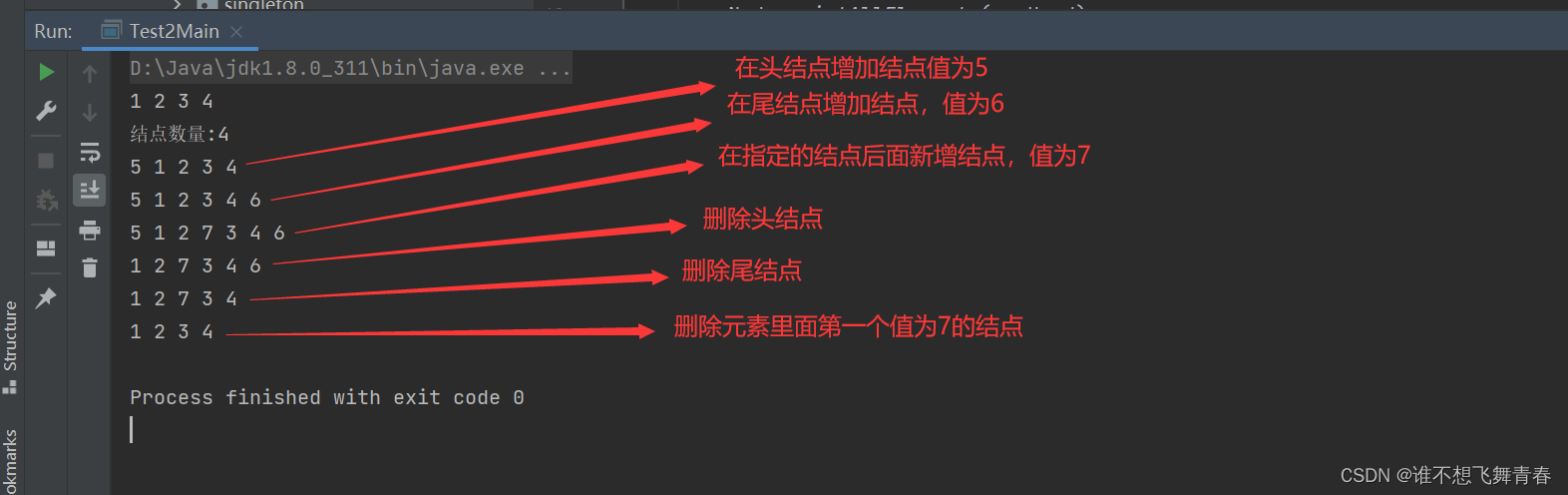
Node.printAllElements(head);
//统计结点数量
System.out.println("结点数量:"+Node.sizeOf(head));
//在链表中的头部插入一个值为5的结点
Node newHead=Node.headInsertNode(head,5);
Node.printAllElements(newHead);
//在链表中的尾部插入一个值为6的结点
Node.tailInsertNode(head,6);
Node.printAllElements(newHead);
//在链表的任意位置插入新结点,在node2结点后面新加一个结点,值为7
Node.insertNode(node2,7);
Node.printAllElements(newHead);
//删除头结点
Node newNode=Node.headDeleteNode(newHead);
Node.printAllElements(newNode);
//删除尾结点
Node.printAllElements(Node.tailDeleteNode(newNode));
//删除任意值,只删除一次
Node.deleteNode(newNode,7);
}
}
执行结果如下: