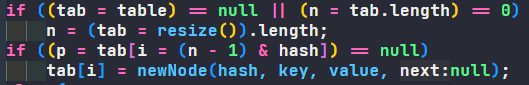
FlowDroid 一、处理流程学习
- 下载配置
- 源码概况
- 代码逻辑分析
- analyzeAPKFile
- runInfoflow
- processEntryPoint
- calculateCallbacks(sourcesAndSinks)
- 再次回到processEntryPoint
自己做一些笔记
下载配置
参照我前面的文章可以使用FlowDroid安装初体验
为了看代码了解FlowDroid如何处理,clone其官方仓库FlowDroid GitHub
源码概况
下载下来的内容还是挺多的,主要分了以下几个文件夹
- soot-infoflow: 核心功能代码
- soot-infoflowandroid: 安卓数据流分析代码
- soot-infoflow-summaries:字面意思函数摘要
- soot-infoflow-cmd:使用cmd的解释运行流程
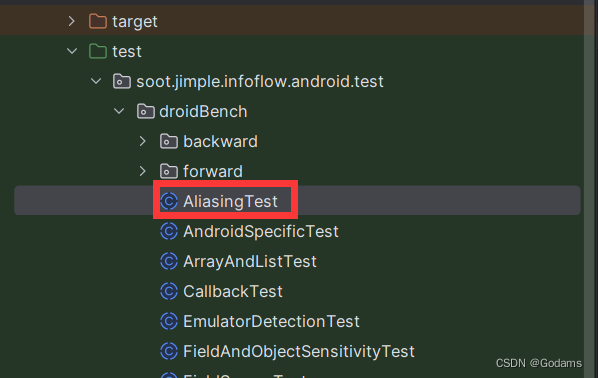
下面对AliasingTest进行案例分析
代码逻辑分析
analyzeAPKFile
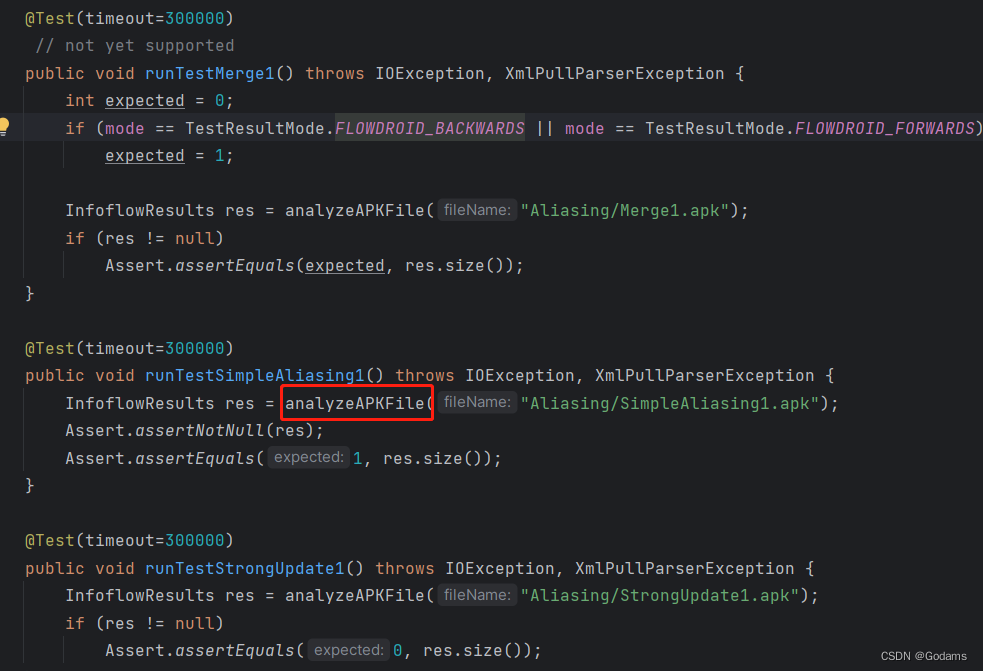
这部分跟进去是一个自定义的测试代码片段,跟进去看具体实现,可以看到不同的接口
ICC model(GPT4的回答):
在FlowDroid中,ICC(Inter-Component Communication,组件间通信)模型用于表示和处理安卓应用中各个组件(例如活动、服务、广播接收器等)之间如何相互通信。在Android中,组件通常通过Intent机制来相互通信。ICC模型旨在建模这种Intent传递机制,以更准确地进行数据流分析。
具体来说,FlowDroid的ICC模型可能包括以下几方面的信息:
- 哪个组件发送了Intent。
- Intent中包含哪些数据。
- Intent被发送到哪个组件。
- 如何处理接收到的Intent。
通过精确地建模这些交互,FlowDroid可以更准确地追踪可能的数据流路径,从而更有效地检测潜在的安全问题。该模型对于理解应用如何处理敏感数据,以及这些数据可能如何泄露(通过组件间的不安全通信)等问题非常有用。
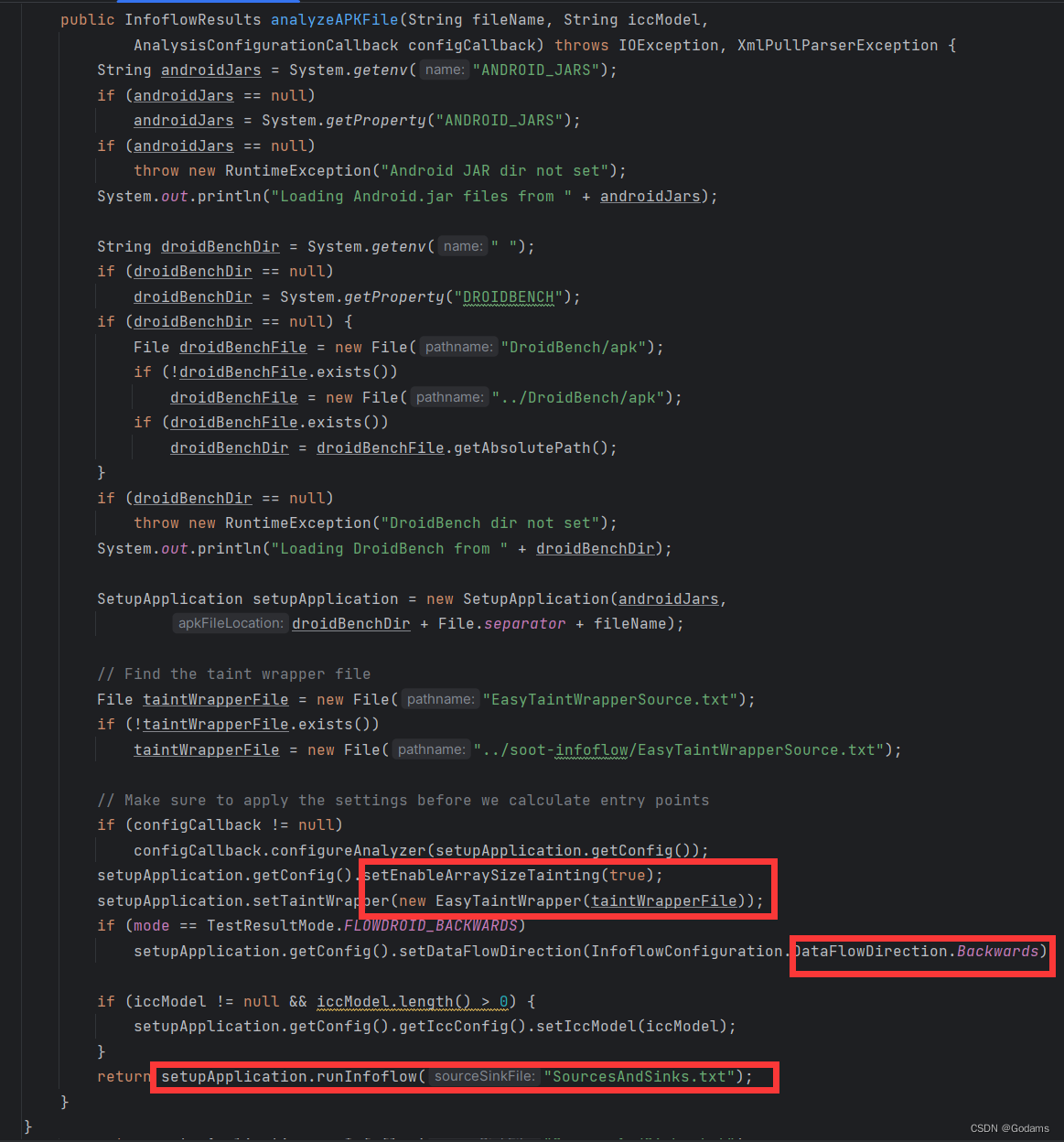
再往下跟就是一些配置信息,读取环境变量等,跟进runInfoflow函数,是比较关键的
runInfoflow
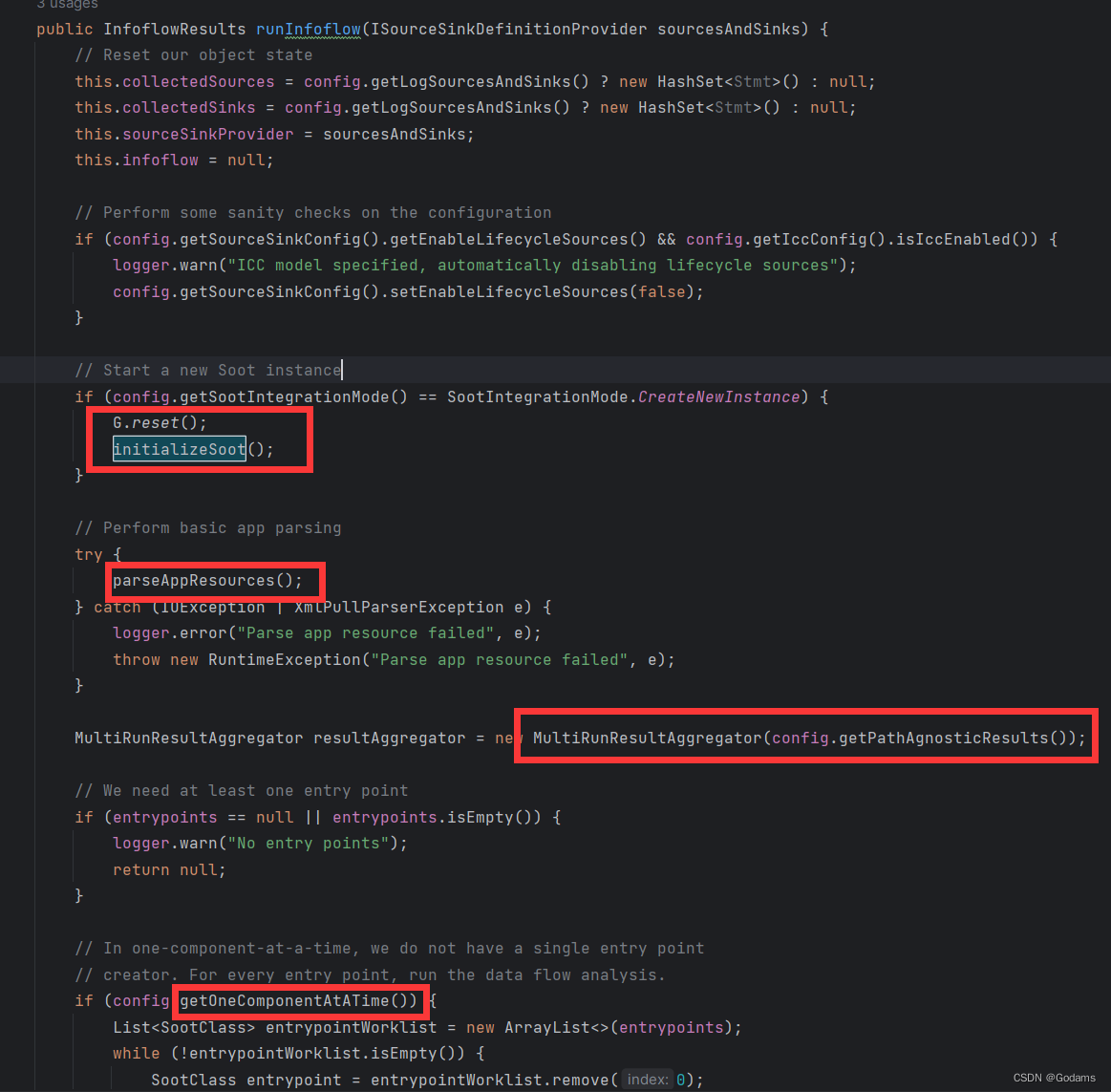
//这两行代码做了soot的初始化
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode() == SootIntegrationMode.CreateNewInstance) {
G.reset();
initializeSoot();
}
//soot初始化关键函数,比较常规
private void initializeSoot() {
logger.info("Initializing Soot...");
final String androidJar = config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getAndroidPlatformDir();
final String apkFileLocation = config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getTargetAPKFile();
// Clean up any old Soot instance we may have
G.reset();
Options.v().set_no_bodies_for_excluded(true);
Options.v().set_allow_phantom_refs(true);
if (config.getWriteOutputFiles())
Options.v().set_output_format(Options.output_format_jimple);
else
Options.v().set_output_format(Options.output_format_none);
Options.v().set_whole_program(true);
Options.v().set_process_dir(Collections.singletonList(apkFileLocation));
if (forceAndroidJar)
Options.v().set_force_android_jar(androidJar);
else
Options.v().set_android_jars(androidJar);
Options.v().set_src_prec(Options.src_prec_apk_class_jimple);
Options.v().set_keep_offset(false);
Options.v().set_keep_line_number(config.getEnableLineNumbers());
Options.v().set_throw_analysis(Options.throw_analysis_dalvik);
Options.v().set_process_multiple_dex(config.getMergeDexFiles());
Options.v().set_ignore_resolution_errors(true);
// Set soot phase option if original names should be used
if (config.getEnableOriginalNames())
Options.v().setPhaseOption("jb", "use-original-names:true");
// Set the Soot configuration options. Note that this will needs to be
// done before we compute the classpath.
if (sootConfig != null)
sootConfig.setSootOptions(Options.v(), config);
Options.v().set_soot_classpath(getClasspath());
Main.v().autoSetOptions();
configureCallgraph();
// Load whatever we need
logger.info("Loading dex files...");
Scene.v().loadNecessaryClasses();
// Make sure that we have valid Jimple bodies
PackManager.v().getPack("wjpp").apply();
// Patch the callgraph to support additional edges. We do this now,
// because during callback discovery, the context-insensitive callgraph
// algorithm would flood us with invalid edges.
LibraryClassPatcher patcher = getLibraryClassPatcher();
patcher.patchLibraries();
}
接下来对apk资源文件进行解析,分析入口点
try {
parseAppResources();
} catch (IOException | XmlPullParserException e) {
logger.error("Parse app resource failed", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Parse app resource failed", e);
}
protected void parseAppResources() throws IOException, XmlPullParserException {
final File targetAPK = new File(config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getTargetAPKFile());
if (!targetAPK.exists())
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format("Target APK file %s does not exist", targetAPK.getCanonicalPath()));
// Parse the resource file
long beforeARSC = System.nanoTime();
this.resources = new ARSCFileParser();
this.resources.parse(targetAPK.getAbsolutePath());
logger.info("ARSC file parsing took " + (System.nanoTime() - beforeARSC) / 1E9 + " seconds");
// To look for callbacks, we need to start somewhere. We use the Android
// lifecycle methods for this purpose.
this.manifest = createManifestParser(targetAPK);
SystemClassHandler.v().setExcludeSystemComponents(config.getIgnoreFlowsInSystemPackages());
Set<String> entryPoints = manifest.getEntryPointClasses();
this.entrypoints = new HashSet<>(entryPoints.size());
for (String className : entryPoints) {
SootClass sc = Scene.v().getSootClassUnsafe(className);
if (sc != null)
this.entrypoints.add(sc);
}
}
processEntryPoint
Runs the data flow analysis on the given entry point class
if (config.getOneComponentAtATime()) {
List<SootClass> entrypointWorklist = new ArrayList<>(entrypoints);
while (!entrypointWorklist.isEmpty()) {
SootClass entrypoint = entrypointWorklist.remove(0);
processEntryPoint(sourcesAndSinks, resultAggregator, entrypointWorklist.size(), entrypoint);
}
} else
processEntryPoint(sourcesAndSinks, resultAggregator, -1, null);
resultAggregator 记录结果的地方
protected void processEntryPoint(ISourceSinkDefinitionProvider sourcesAndSinks,
MultiRunResultAggregator resultAggregator, int numEntryPoints, SootClass entrypoint) {
long beforeEntryPoint = System.nanoTime();
// Get rid of leftovers from the last entry point
resultAggregator.clearLastResults();
// Perform basic app parsing
long callbackDuration = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (config.getOneComponentAtATime())
calculateCallbacks(sourcesAndSinks, entrypoint);
else
calculateCallbacks(sourcesAndSinks);
} catch (IOException | XmlPullParserException e) {
logger.error("Callgraph construction failed: " + e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RuntimeException("Callgraph construction failed", e);
}
callbackDuration = Math.round((System.nanoTime() - callbackDuration) / 1E9);
logger.info(
String.format("Collecting callbacks and building a callgraph took %d seconds", (int) callbackDuration));
final Collection<? extends ISourceSinkDefinition> sources = getSources();
final Collection<? extends ISourceSinkDefinition> sinks = getSinks();
final String apkFileLocation = config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getTargetAPKFile();
if (config.getOneComponentAtATime())
logger.info("Running data flow analysis on {} (component {}/{}: {}) with {} sources and {} sinks...",
apkFileLocation, (entrypoints.size() - numEntryPoints), entrypoints.size(), entrypoint,
sources == null ? 0 : sources.size(), sinks == null ? 0 : sinks.size());
else
logger.info("Running data flow analysis on {} with {} sources and {} sinks...", apkFileLocation,
sources == null ? 0 : sources.size(), sinks == null ? 0 : sinks.size());
// Create a new entry point and compute the flows in it. If we
// analyze all components together, we do not need a new callgraph,
// but can reuse the one from the callback collection phase.
if (config.getOneComponentAtATime() && config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph()) {
createMainMethod(entrypoint);
constructCallgraphInternal();
}
// Create and run the data flow tracker
infoflow = createInfoflow();
infoflow.addResultsAvailableHandler(resultAggregator);
infoflow.runAnalysis(sourceSinkManager, entryPointCreator.getGeneratedMainMethod());
// Update the statistics
if (config.getLogSourcesAndSinks() && infoflow.getCollectedSources() != null)
this.collectedSources.addAll(infoflow.getCollectedSources());
if (config.getLogSourcesAndSinks() && infoflow.getCollectedSinks() != null)
this.collectedSinks.addAll(infoflow.getCollectedSinks());
// Print out the found results
{
int resCount = resultAggregator.getLastResults() == null ? 0 : resultAggregator.getLastResults().size();
if (config.getOneComponentAtATime())
logger.info("Found {} leaks for component {}", resCount, entrypoint);
else
logger.info("Found {} leaks", resCount);
}
// Update the performance object with the real data
{
InfoflowResults lastResults = resultAggregator.getLastResults();
if (lastResults != null) {
InfoflowPerformanceData perfData = lastResults.getPerformanceData();
if (perfData == null)
lastResults.setPerformanceData(perfData = new InfoflowPerformanceData());
perfData.setCallgraphConstructionSeconds((int) callbackDuration);
perfData.setTotalRuntimeSeconds((int) Math.round((System.nanoTime() - beforeEntryPoint) / 1E9));
}
}
// We don't need the computed callbacks anymore
this.callbackMethods.clear();
this.fragmentClasses.clear();
// Notify our result handlers
for (ResultsAvailableHandler handler : resultsAvailableHandlers)
handler.onResultsAvailable(resultAggregator.getLastICFG(), resultAggregator.getLastResults());
}
calculateCallbacks(sourcesAndSinks)
传进来的参数即为读取的sources和sinks
Calculates the sets of sources, sinks, entry points, and callbacks methods
for the entry point in the given APK file.
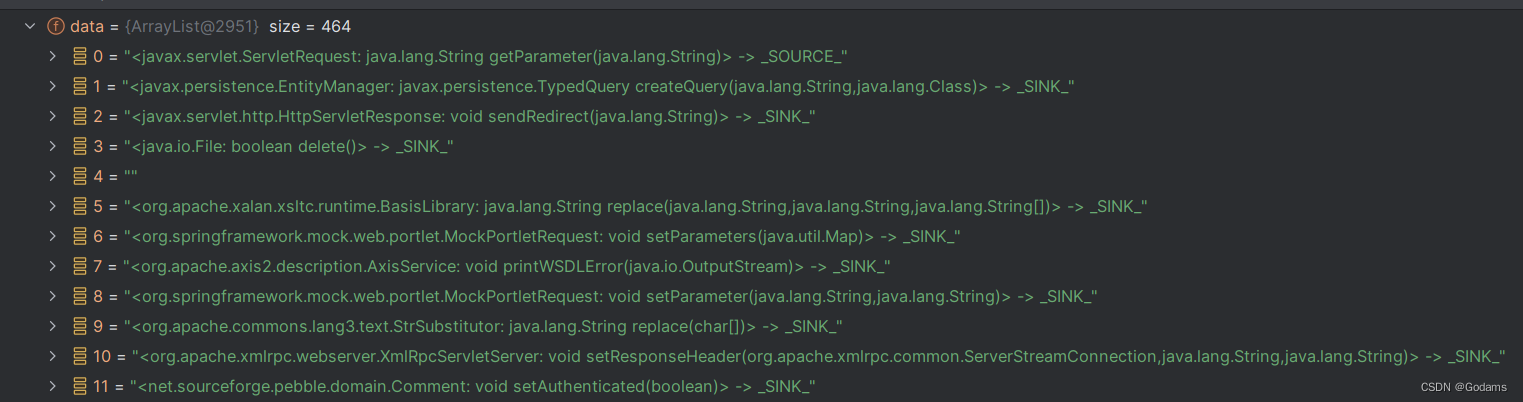
private void calculateCallbacks(ISourceSinkDefinitionProvider sourcesAndSinks, SootClass entryPoint)
throws IOException, XmlPullParserException {
// Add the callback methods
LayoutFileParser lfp = null;
final CallbackConfiguration callbackConfig = config.getCallbackConfig();
if (callbackConfig.getEnableCallbacks()) {
// If we have a callback file, we use it
String callbackFile = callbackConfig.getCallbacksFile();
if (callbackFile != null && !callbackFile.isEmpty()) {
File cbFile = new File(callbackFile);
if (cbFile.exists()) {
CollectedCallbacks callbacks = CollectedCallbacksSerializer.deserialize(callbackConfig);
if (callbacks != null) {
// Get our callback data from the file
entrypoints = callbacks.getEntryPoints();
fragmentClasses = callbacks.getFragmentClasses();
callbackMethods = callbacks.getCallbackMethods();
// Create the callgraph
createMainMethod(entryPoint);
constructCallgraphInternal();
createSourceSinkProvider(entryPoint, lfp);
return;
}
}
}
if (callbackClasses != null && callbackClasses.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("Callback definition file is empty, disabling callbacks");
} else {
lfp = createLayoutFileParser();
switch (callbackConfig.getCallbackAnalyzer()) {
case Fast:
calculateCallbackMethodsFast(lfp, entryPoint);
break;
case Default:
calculateCallbackMethods(lfp, entryPoint);
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown callback analyzer");
}
}
} else if (config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph()) {
// Create the new iteration of the main method
createMainMethod(entryPoint);
constructCallgraphInternal();
}
logger.info("Entry point calculation done.");
createSourceSinkProvider(entryPoint, lfp);
}
在此过程中给对Layout进行了解析LayoutFileParser(this.manifest.getPackageName(), this.resources);
lfp = createLayoutFileParser();
calculateCallbackMethods(lfp, entryPoint);
下面这是真正的计算了
private void calculateCallbackMethods(LayoutFileParser lfp, SootClass component) throws IOException {
final CallbackConfiguration callbackConfig = config.getCallbackConfig();
// Load the APK file
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph())
releaseCallgraph();
// Make sure that we don't have any leftovers from previous runs
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.lfp");
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.ajc");
// Get the classes for which to find callbacks
Set<SootClass> entryPointClasses = getComponentsToAnalyze(component);
// Collect the callback interfaces implemented in the app's
// source code. Note that the filters should know all components to
// filter out callbacks even if the respective component is only
// analyzed later.
AbstractCallbackAnalyzer jimpleClass = callbackClasses == null
? new DefaultCallbackAnalyzer(config, entryPointClasses, callbackMethods, callbackFile)
: new DefaultCallbackAnalyzer(config, entryPointClasses, callbackMethods, callbackClasses);
if (valueProvider != null)
jimpleClass.setValueProvider(valueProvider);
jimpleClass.addCallbackFilter(new AlienHostComponentFilter(entrypoints));
jimpleClass.addCallbackFilter(new ApplicationCallbackFilter(entrypoints));
jimpleClass.addCallbackFilter(new UnreachableConstructorFilter());
jimpleClass.collectCallbackMethods();
// Find the user-defined sources in the layout XML files. This
// only needs to be done once, but is a Soot phase.
lfp.parseLayoutFile(config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getTargetAPKFile());
// Watch the callback collection algorithm's memory consumption
FlowDroidMemoryWatcher memoryWatcher = null;
FlowDroidTimeoutWatcher timeoutWatcher = null;
if (jimpleClass instanceof IMemoryBoundedSolver) {
// Make sure that we don't spend too much time and memory in the callback
// analysis
memoryWatcher = createCallbackMemoryWatcher(jimpleClass);
timeoutWatcher = createCallbackTimeoutWatcher(callbackConfig, jimpleClass);
}
try {
int depthIdx = 0;
boolean hasChanged = true;
boolean isInitial = true;
while (hasChanged) {
hasChanged = false;
// Check whether the solver has been aborted in the meantime
if (jimpleClass instanceof IMemoryBoundedSolver) {
if (((IMemoryBoundedSolver) jimpleClass).isKilled())
break;
}
// Create the new iteration of the main method
createMainMethod(component);
int numPrevEdges = 0;
if (Scene.v().hasCallGraph()) {
numPrevEdges = Scene.v().getCallGraph().size();
}
// Since the generation of the main method can take some time,
// we check again whether we need to stop.
if (jimpleClass instanceof IMemoryBoundedSolver) {
if (((IMemoryBoundedSolver) jimpleClass).isKilled()) {
logger.warn("Callback calculation aborted due to timeout");
break;
}
}
if (!isInitial) {
// Reset the callgraph
releaseCallgraph();
// We only want to parse the layout files once
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.lfp");
}
isInitial = false;
// Run the soot-based operations
constructCallgraphInternal();
if (!Scene.v().hasCallGraph())
throw new RuntimeException("No callgraph in Scene even after creating one. That's very sad "
+ "and should never happen.");
lfp.parseLayoutFileDirect(config.getAnalysisFileConfig().getTargetAPKFile());
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").apply();
// Creating all callgraph takes time and memory. Check whether
// the solver has been aborted in the meantime
if (jimpleClass instanceof IMemoryBoundedSolver) {
if (((IMemoryBoundedSolver) jimpleClass).isKilled()) {
logger.warn("Aborted callback collection because of low memory");
break;
}
}
if (numPrevEdges < Scene.v().getCallGraph().size())
hasChanged = true;
// Collect the results of the soot-based phases
if (this.callbackMethods.putAll(jimpleClass.getCallbackMethods()))
hasChanged = true;
if (entrypoints.addAll(jimpleClass.getDynamicManifestComponents()))
hasChanged = true;
// Collect the XML-based callback methods
if (collectXmlBasedCallbackMethods(lfp, jimpleClass))
hasChanged = true;
// Avoid callback overruns. If we are beyond the callback limit
// for one entry point, we may not collect any further callbacks
// for that entry point.
if (callbackConfig.getMaxCallbacksPerComponent() > 0) {
for (Iterator<SootClass> componentIt = this.callbackMethods.keySet().iterator(); componentIt
.hasNext();) {
SootClass callbackComponent = componentIt.next();
if (this.callbackMethods.get(callbackComponent).size() > callbackConfig
.getMaxCallbacksPerComponent()) {
componentIt.remove();
jimpleClass.excludeEntryPoint(callbackComponent);
}
}
}
// Check depth limiting
depthIdx++;
if (callbackConfig.getMaxAnalysisCallbackDepth() > 0
&& depthIdx >= callbackConfig.getMaxAnalysisCallbackDepth())
break;
// If we work with an existing callgraph, the callgraph never
// changes and thus it doesn't make any sense to go multiple
// rounds
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode() == SootIntegrationMode.UseExistingCallgraph)
break;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error("Could not calculate callback methods", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
// Shut down the watchers
if (timeoutWatcher != null)
timeoutWatcher.stop();
if (memoryWatcher != null)
memoryWatcher.close();
}
// Filter out callbacks that belong to fragments that are not used by
// the host activity
AlienFragmentFilter fragmentFilter = new AlienFragmentFilter(invertMap(fragmentClasses));
fragmentFilter.reset();
for (Iterator<Pair<SootClass, AndroidCallbackDefinition>> cbIt = this.callbackMethods.iterator(); cbIt
.hasNext();) {
Pair<SootClass, AndroidCallbackDefinition> pair = cbIt.next();
// Check whether the filter accepts the given mapping
if (!fragmentFilter.accepts(pair.getO1(), pair.getO2().getTargetMethod()))
cbIt.remove();
else if (!fragmentFilter.accepts(pair.getO1(), pair.getO2().getTargetMethod().getDeclaringClass())) {
cbIt.remove();
}
}
// Avoid callback overruns
if (callbackConfig.getMaxCallbacksPerComponent() > 0) {
for (Iterator<SootClass> componentIt = this.callbackMethods.keySet().iterator(); componentIt.hasNext();) {
SootClass callbackComponent = componentIt.next();
if (this.callbackMethods.get(callbackComponent).size() > callbackConfig.getMaxCallbacksPerComponent())
componentIt.remove();
}
}
// Make sure that we don't retain any weird Soot phases
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.lfp");
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.ajc");
// Warn the user if we had to abort the callback analysis early
boolean abortedEarly = false;
if (jimpleClass instanceof IMemoryBoundedSolver) {
if (((IMemoryBoundedSolver) jimpleClass).isKilled()) {
logger.warn("Callback analysis aborted early due to time or memory exhaustion");
abortedEarly = true;
}
}
if (!abortedEarly)
logger.info("Callback analysis terminated normally");
// Serialize the callbacks
if (callbackConfig.isSerializeCallbacks()) {
CollectedCallbacks callbacks = new CollectedCallbacks(entryPointClasses, callbackMethods, fragmentClasses);
CollectedCallbacksSerializer.serialize(callbacks, callbackConfig);
}
}
这段代码首先对调用图进行重置
protected void releaseCallgraph() {
// If we are configured to use an existing callgraph, we may not release
// it
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode() == SootIntegrationMode.UseExistingCallgraph)
return;
Scene.v().releaseCallGraph();
Scene.v().releasePointsToAnalysis();
Scene.v().releaseReachableMethods();
G.v().resetSpark();
}
接下来两行代码不懂问了GPT
// Make sure that we don't have any leftovers from previous runs
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.lfp");
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp").remove("wjtp.ajc");
PackManager.v().getPack("wjtp"):
这部分获取名为 “wjtp” 的分析阶段组(pack)。Soot框架将各种分析和转换任务组织在不同的阶段组(如 “wjtp”, “jtp”, “cg” 等)中。
remove(“wjtp.lfp”) 和 remove(“wjtp.ajc”):这两行代码从 “wjtp” 阶段组中移除特定的分析或转换阶段。具体来说,它们移除名为 “wjtp.lfp” 和 “wjtp.ajc” 的阶段。
这两行代码确保在新一轮的Soot分析或转换开始之前,清除先前可能添加到 “wjtp” 阶段组的 “wjtp.lfp” 和 “wjtp.ajc” 分析阶段。这样做主要是为了避免先前运行的残留影响到当前的运行。这是一种清理机制,确保每次运行都是在干净、一致的环境中进行。
再次回到processEntryPoint
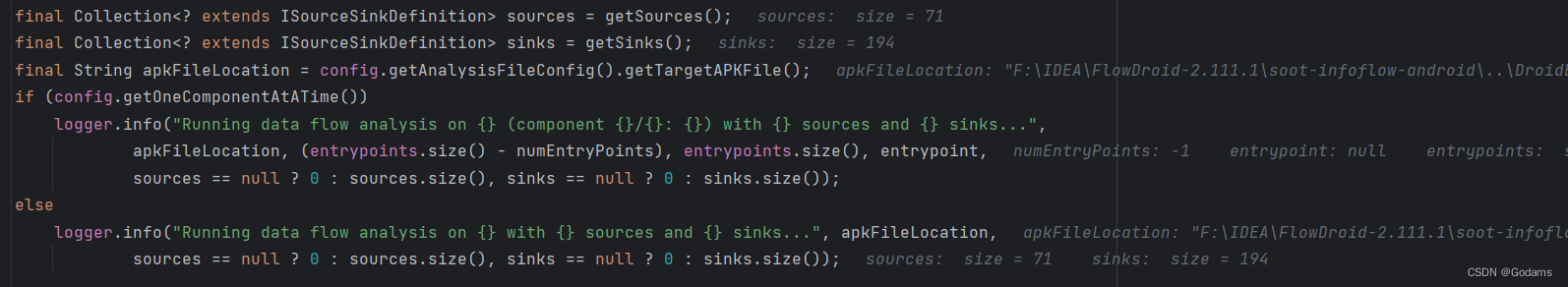
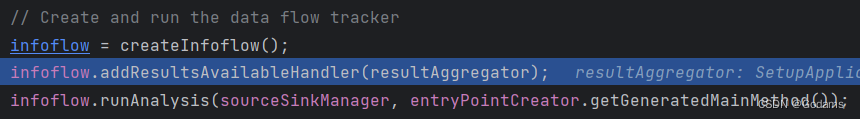
Instantiates and configures the data flow engine
private IInPlaceInfoflow createInfoflow() {
// Some sanity checks
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph()) {
if (entryPointCreator == null)
throw new RuntimeException("No entry point available");
if (entryPointCreator.getComponentToEntryPointInfo() == null)
throw new RuntimeException("No information about component entry points available");
}
// Get the component lifecycle methods
Collection<SootMethod> lifecycleMethods = Collections.emptySet();
if (entryPointCreator != null) {
ComponentEntryPointCollection entryPoints = entryPointCreator.getComponentToEntryPointInfo();
if (entryPoints != null)
lifecycleMethods = entryPoints.getLifecycleMethods();
}
// Initialize and configure the data flow tracker
IInPlaceInfoflow info = createInfoflowInternal(lifecycleMethods);
if (ipcManager != null)
info.setIPCManager(ipcManager);
info.setConfig(config);
info.setSootConfig(sootConfig);
info.setTaintWrapper(taintWrapper);
info.setTaintPropagationHandler(taintPropagationHandler);
info.setAliasPropagationHandler(aliasPropagationHandler);
// We use a specialized memory manager that knows about Android
info.setMemoryManagerFactory(new IMemoryManagerFactory() {
@Override
public IMemoryManager<Abstraction, Unit> getMemoryManager(boolean tracingEnabled,
PathDataErasureMode erasePathData) {
return new AndroidMemoryManager(tracingEnabled, erasePathData, entrypoints);
}
});
info.setMemoryManagerFactory(null);
// Inject additional post-processors
info.setPostProcessors(Collections.singleton(new PostAnalysisHandler() {
@Override
public InfoflowResults onResultsAvailable(InfoflowResults results, IInfoflowCFG cfg) {
// Purify the ICC results if requested
final IccConfiguration iccConfig = config.getIccConfig();
if (iccConfig.isIccResultsPurifyEnabled()) {
// no-op at the moment. We used to have a purifier here, but it didn't make
// any sense. Removed it for the better.
}
return results;
}
}));
return info;
}
接下来进入到runAnalysis函数内部,这个函数似乎比较关键
Conducts a taint analysis on an already initialized callgraph
protected void runAnalysis(final ISourceSinkManager sourcesSinks, final Set<String> additionalSeeds) {
final InfoflowPerformanceData performanceData = createPerformanceDataClass();
try {
// Clear the data from previous runs
results = createResultsObject();
results.setPerformanceData(performanceData);
// Print and check our configuration
checkAndFixConfiguration();
config.printSummary();
// Register a memory watcher
if (memoryWatcher != null) {
memoryWatcher.clearSolvers();
memoryWatcher = null;
}
memoryWatcher = new FlowDroidMemoryWatcher(results, config.getMemoryThreshold());
// Initialize the abstraction configuration
Abstraction.initialize(config);
// Build the callgraph
long beforeCallgraph = System.nanoTime();
constructCallgraph();
performanceData
.setCallgraphConstructionSeconds((int) Math.round((System.nanoTime() - beforeCallgraph) / 1E9));
logger.info(String.format(Locale.getDefault(), "Callgraph construction took %d seconds",
performanceData.getCallgraphConstructionSeconds()));
// Initialize the source sink manager
if (sourcesSinks != null)
sourcesSinks.initialize();
// Perform constant propagation and remove dead code
if (config.getCodeEliminationMode() != CodeEliminationMode.NoCodeElimination) {
long currentMillis = System.nanoTime();
eliminateDeadCode(sourcesSinks);
logger.info("Dead code elimination took " + (System.nanoTime() - currentMillis) / 1E9 + " seconds");
}
// After constant value propagation, we might find more call edges
// for reflective method calls
if (config.getEnableReflection()) {
releaseCallgraph();
constructCallgraph();
}
if (config.getCallgraphAlgorithm() != CallgraphAlgorithm.OnDemand)
logger.info("Callgraph has {} edges", Scene.v().getCallGraph().size());
IInfoflowCFG iCfg = icfgFactory.buildBiDirICFG(config.getCallgraphAlgorithm(),
config.getEnableExceptionTracking());
if (config.isTaintAnalysisEnabled())
runTaintAnalysis(sourcesSinks, additionalSeeds, iCfg, performanceData);
// Gather performance data
performanceData.setTotalRuntimeSeconds((int) Math.round((System.nanoTime() - beforeCallgraph) / 1E9));
performanceData.updateMaxMemoryConsumption(getUsedMemory());
logger.info(String.format("Data flow solver took %d seconds. Maximum memory consumption: %d MB",
performanceData.getTotalRuntimeSeconds(), performanceData.getMaxMemoryConsumption()));
// Provide the handler with the final results
for (ResultsAvailableHandler handler : onResultsAvailable)
handler.onResultsAvailable(iCfg, results);
// Write the Jimple files to disk if requested
if (config.getWriteOutputFiles())
PackManager.v().writeOutput();
} catch (Exception ex) {
StringWriter stacktrace = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(stacktrace);
ex.printStackTrace(pw);
if (results != null)
results.addException(ex.getClass().getName() + ": " + ex.getMessage() + "\n" + stacktrace.toString());
logger.error("Exception during data flow analysis", ex);
if (throwExceptions)
throw ex;
}
}
constructCallgraph();
构造调用图
protected void constructCallgraph() {
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph()) {
// Allow the ICC manager to change the Soot Scene before we continue
if (ipcManager != null)
ipcManager.updateJimpleForICC();
// Run the preprocessors
for (PreAnalysisHandler tr : preProcessors)
tr.onBeforeCallgraphConstruction();
// Patch the system libraries we need for callgraph construction
LibraryClassPatcher patcher = getLibraryClassPatcher();
patcher.patchLibraries();
// To cope with broken APK files, we convert all classes that are still
// dangling after resolution into phantoms
for (SootClass sc : Scene.v().getClasses())
if (sc.resolvingLevel() == SootClass.DANGLING) {
sc.setResolvingLevel(SootClass.BODIES);
sc.setPhantomClass();
}
// We explicitly select the packs we want to run for performance
// reasons. Do not re-run the callgraph algorithm if the host
// application already provides us with a CG.
if (config.getCallgraphAlgorithm() != CallgraphAlgorithm.OnDemand && !Scene.v().hasCallGraph()) {
PackManager.v().getPack("wjpp").apply();
PackManager.v().getPack("cg").apply();
}
}
// If we don't have a FastHierarchy, we need to create it - even if we use an
// existing callgraph
hierarchy = Scene.v().getOrMakeFastHierarchy();
if (config.getSootIntegrationMode().needsToBuildCallgraph()) {
// Run the preprocessors
for (PreAnalysisHandler tr : preProcessors)
tr.onAfterCallgraphConstruction();
}
}
runAnalysis分析结束后回到了processEntryPoint