1.notify和wait方法的使用
1.1快递到站通知
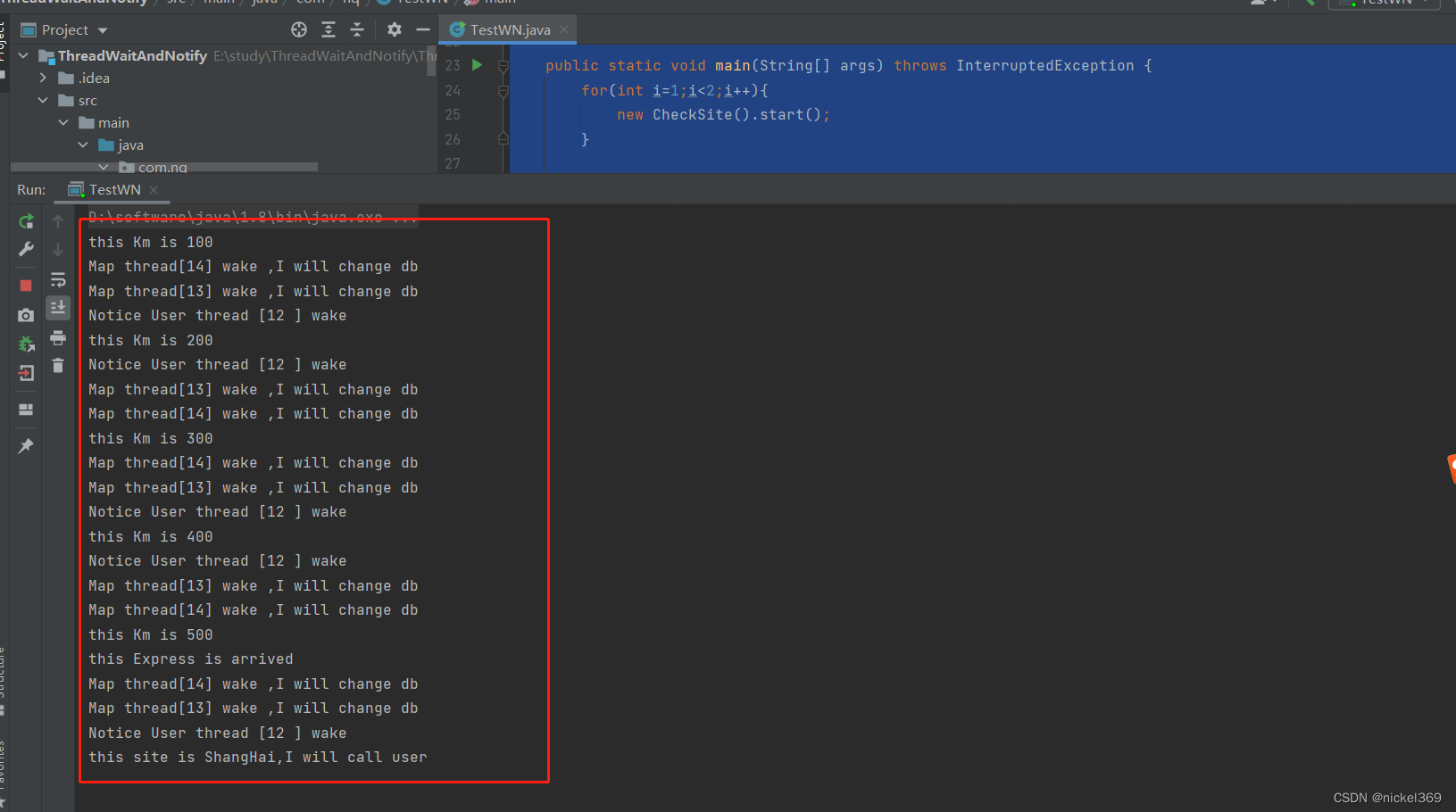
说明:快递的地点在上海,离快递发货地相聚500km,每次进行改变,快递将会前进100km,当快递前进100km时,需要通知快递当前的位置,当快递到达目的地时,需要通知用户取快递。
1.Express快递初始化方法
package com.nq;
public class Express {
public final static String DIST_CITY="ShangHai";
public final static int TOTAIL=500;
private int km;
private String site;
public Express(){
}
public Express(int km, String site) {
this.km = km;
this.site = site;
}
public void change(){
if(km<TOTAIL){
km=km+100;
System.out.println("this Km is "+this.km);
}
if(km>=TOTAIL){
site=DIST_CITY;
System.out.println("this Express is arrived");
}
}
/**
* 线程等待公里的变化
*/
public synchronized void waiKm(){
while (this.km<=TOTAIL){
try{
wait();
System.out.println("Map thread["+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"] wake ,I will change db");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*线程等待目的地变换*/
public synchronized void waiSite(){
while (!this.site.equals(DIST_CITY)){
try {
wait();
System.out.println("Notice User thread ["+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" ] wake");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("this site is "+this.site+",I will call user");
}
}
2.TestWN测试方法
package com.nq;
public class TestWN {
private static Express express=new Express(0,"WUHAN");
private static class CheckKm extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
express.waiKm();
}
}
private static class CheckSite extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
express.waiSite();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=1;i<2;i++){
new CheckSite().start();
}
for (int i=0;i<2;i++){
new CheckKm().start();
}
Thread.sleep(500);
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
synchronized (express){
express.change();
express.notifyAll();
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
1.2数据库连接池方法
1.SqlConnectImpl获取连接池
package com.nq.pool;
import com.nq.tool.SleepTools;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
/**
*@Author: Nickel
*@DATE: 2023/8/19 0:19
*@Description:
*/
public class SqlConnectImpl implements Connection {
/**
*@Author: Nickel
*@DATE: 2023/8/19 0:18
*@Description:拿一个数据库链接
*/
public static final Connection fetchConnection(){
return new SqlConnectImpl();
}
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
}
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
SleepTools.ms(70);
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
}
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
}
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
}
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
}
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
}
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
}
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
}
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
}
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
}
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
}
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
}
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
}
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
2.DBPool初始化连接池
package com.nq.pool;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DBPool {
/**
* 容器,存放链接
*/
private static LinkedList<Connection> pool=new LinkedList<Connection>();
/**
* 限制连接池大小为=20
*/
public DBPool(int initialSize){
if(initialSize>0){
for(int i=0;i<initialSize;i++){
pool.addLast(SqlConnectImpl.fetchConnection());
}
}
}
/**
*@Author: Nickel
*@DATE: 2023/8/19 0:21
*@Description: 释放链接,通知其他的等待连接的线程
*/
public void releaseConnection(Connection connection){
if(connection!=null){
synchronized (pool){
pool.addLast(connection);
//通知其他等待连接的线程
pool.notifyAll();
}
}
}
/**
*@Author: Nickel
*@DATE: 2023/8/19 0:26
*@Description: 获取mills内无法获取,将会返回null 1s
*/
public Connection fetchConnect(long mills) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (pool){
//永不超时
if(mills<=0){
while (pool.isEmpty()){
pool.wait();
}
return pool.removeFirst();
}else{
//超时时刻
long future=System.currentTimeMillis()+mills;
//等待时长
long remaining=mills;
while (pool.isEmpty()&&remaining>0){
pool.wait(remaining);
/*唤醒一次,重新计算等待时常*/
remaining=future-System.currentTimeMillis();
}
Connection connection=null;
if(!pool.isEmpty()){
connection=pool.removeFirst();
}
return connection;
}
}
}
}
3.测试连接池
package com.nq.pool;
import com.nq.tool.SleepTools;
import javafx.concurrent.Worker;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/19 0:45
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class DBPoolTest {
static DBPool pool=new DBPool(10);
//控制器:控制main线程将会等待所有Worker结束才能继续执行
static CountDownLatch end;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//线程数量
int threadCount=50;
end=new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
int count=20;//每个线程的操作次数
AtomicInteger got=new AtomicInteger();//计数器:统计可以拿到连接的线程
AtomicInteger notGot=new AtomicInteger();//计数器:统计没有拿到连接的线程
for(int i=0;i<threadCount;i++){
Thread thread=new Thread(new Worker(count,got,notGot),"worker"+i);
thread.start();
}
}
static class Worker implements Runnable{
int count;
AtomicInteger got;
AtomicInteger notGot;
public Worker(int count, AtomicInteger got, AtomicInteger notGot) {
this.count = count;
this.got = got;
this.notGot = notGot;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (count>0){
try {
//从线程池中获取连接,如果1000ms内无法获取到,将会返回null
//分别统计连接获取的数量got和未获取的数量notGot
Connection connection = pool.fetchConnect(1000);
if(connection!=null){
SleepTools.ms(2);
pool.releaseConnection(connection);
got.incrementAndGet();
}else{
notGot.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待超时!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
count--;
}
}
}
}
}
2. CompletableFuture方法的使用
2.1 SupplyAsync和RunAsync的使用
1.SupplyAsync方法使用
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/19 23:44
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*
* supplyAsync方法的使用
*/
public class SupplyAsync {
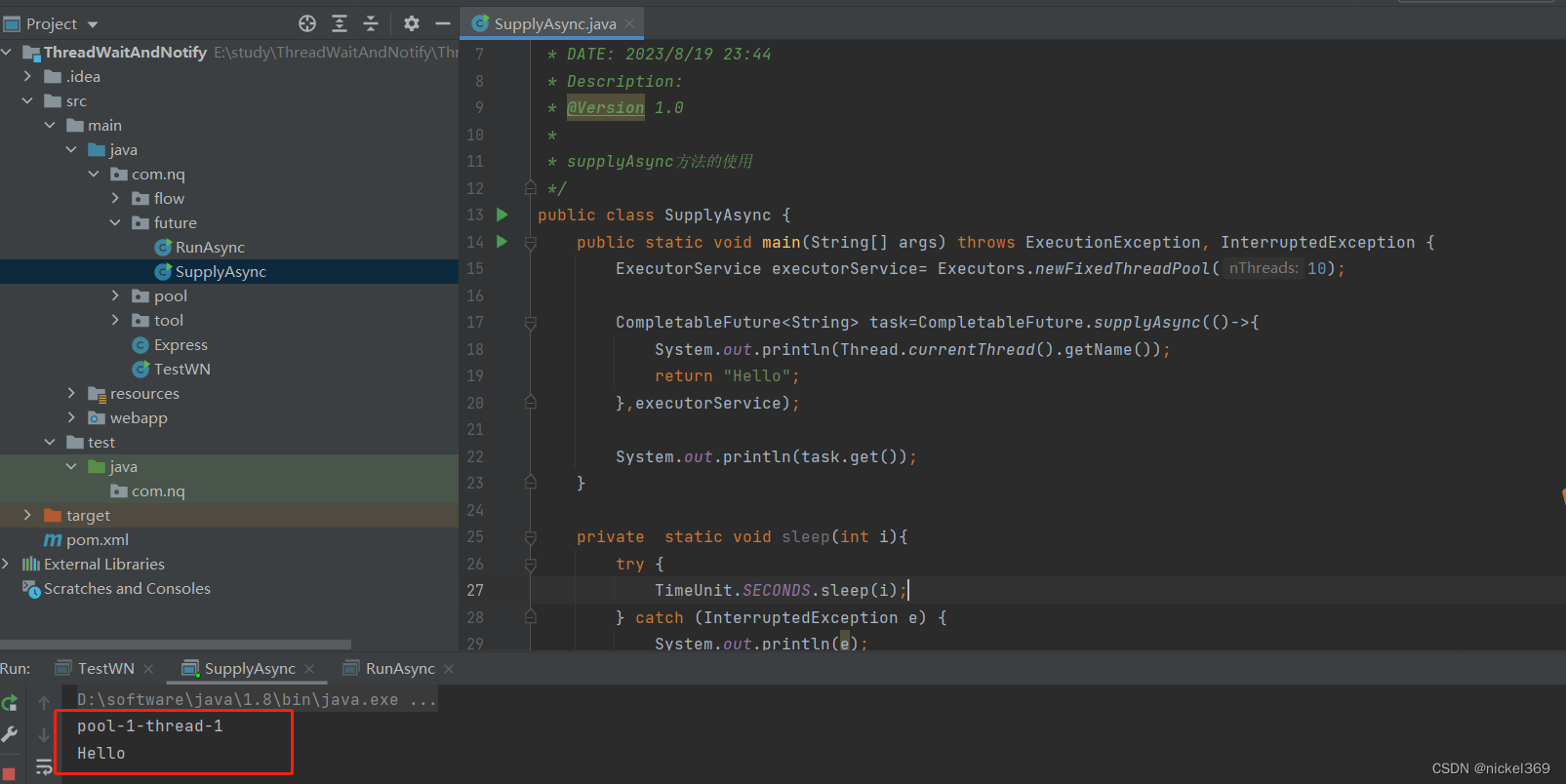
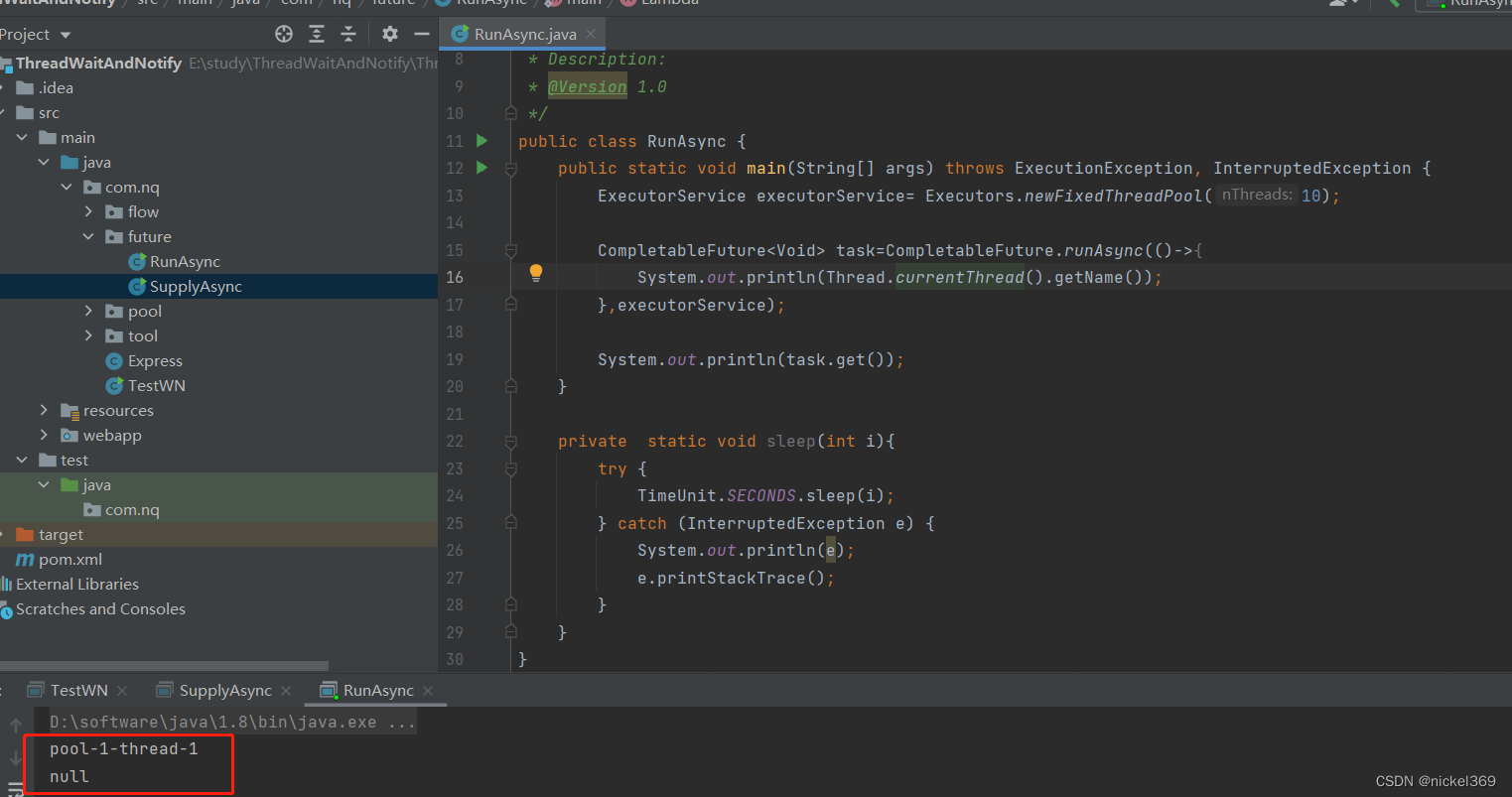
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> task=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
},executorService);
System.out.println(task.get());
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.RunAsync方法使用
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/19 23:53
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class RunAsync {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<Void> task=CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
},executorService);
System.out.println(task.get());
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.2 CompletableFuture中的then*API的使用
1.thenApply、thenApplyAsync、thenAccept
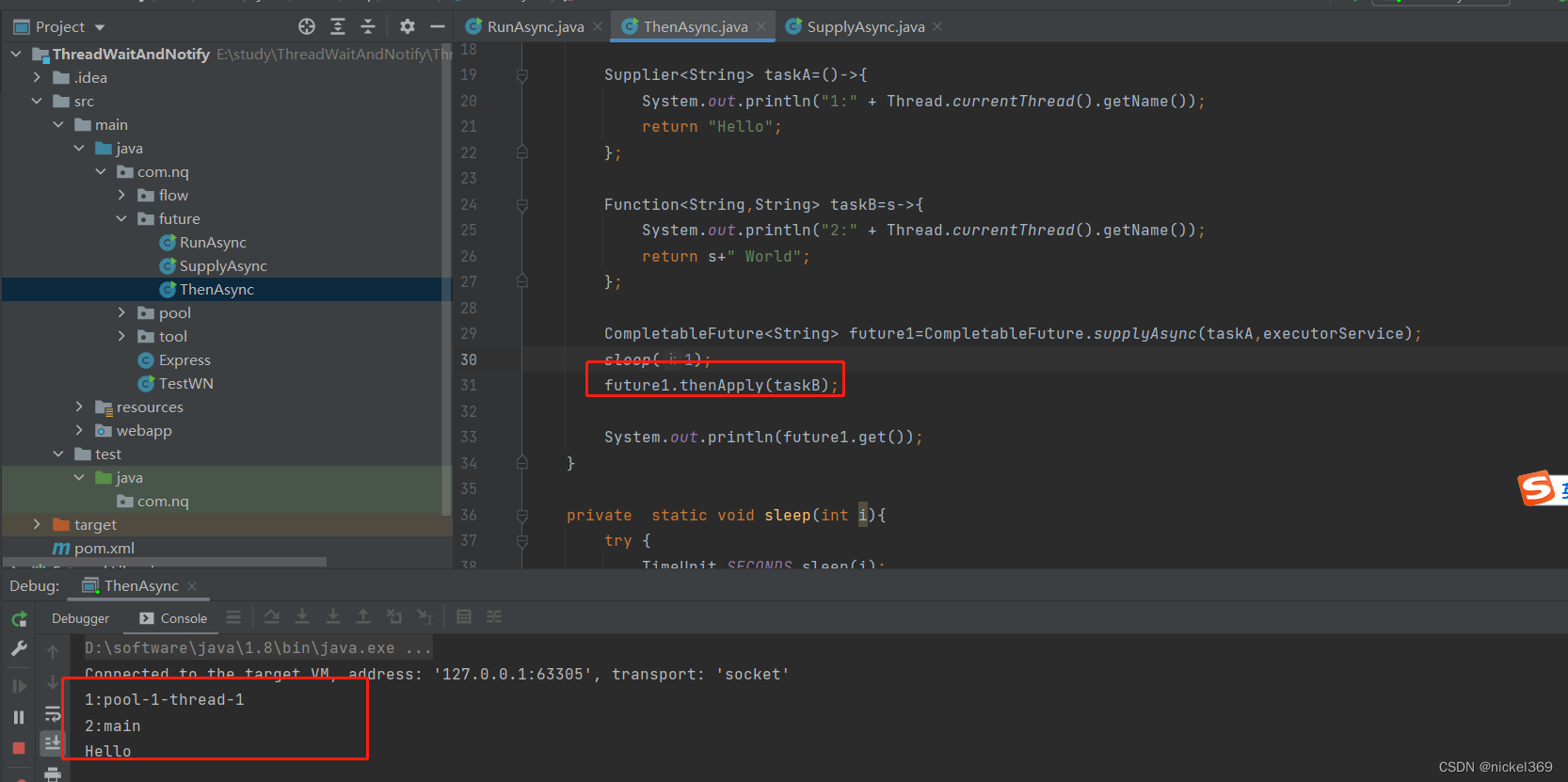
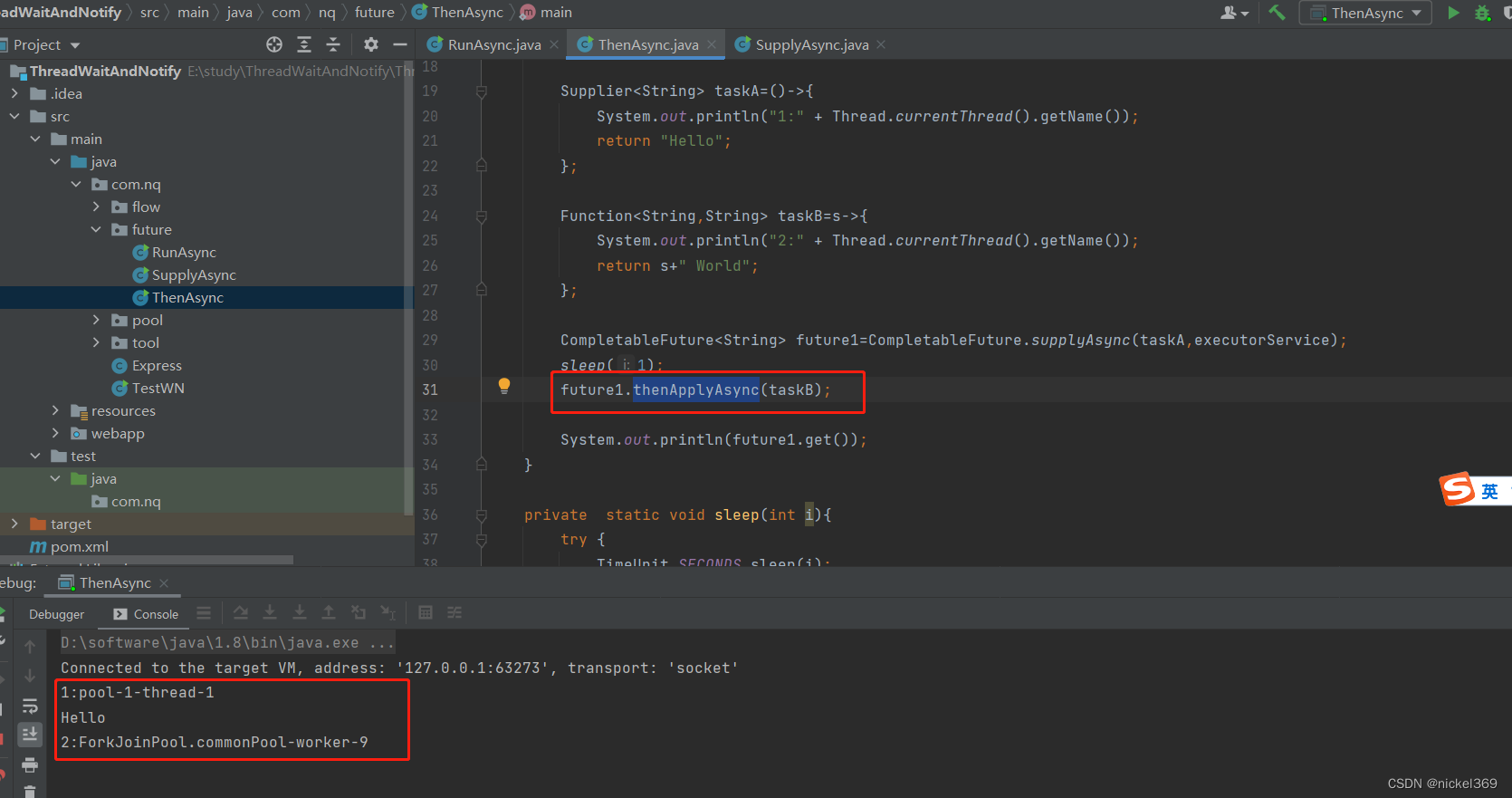
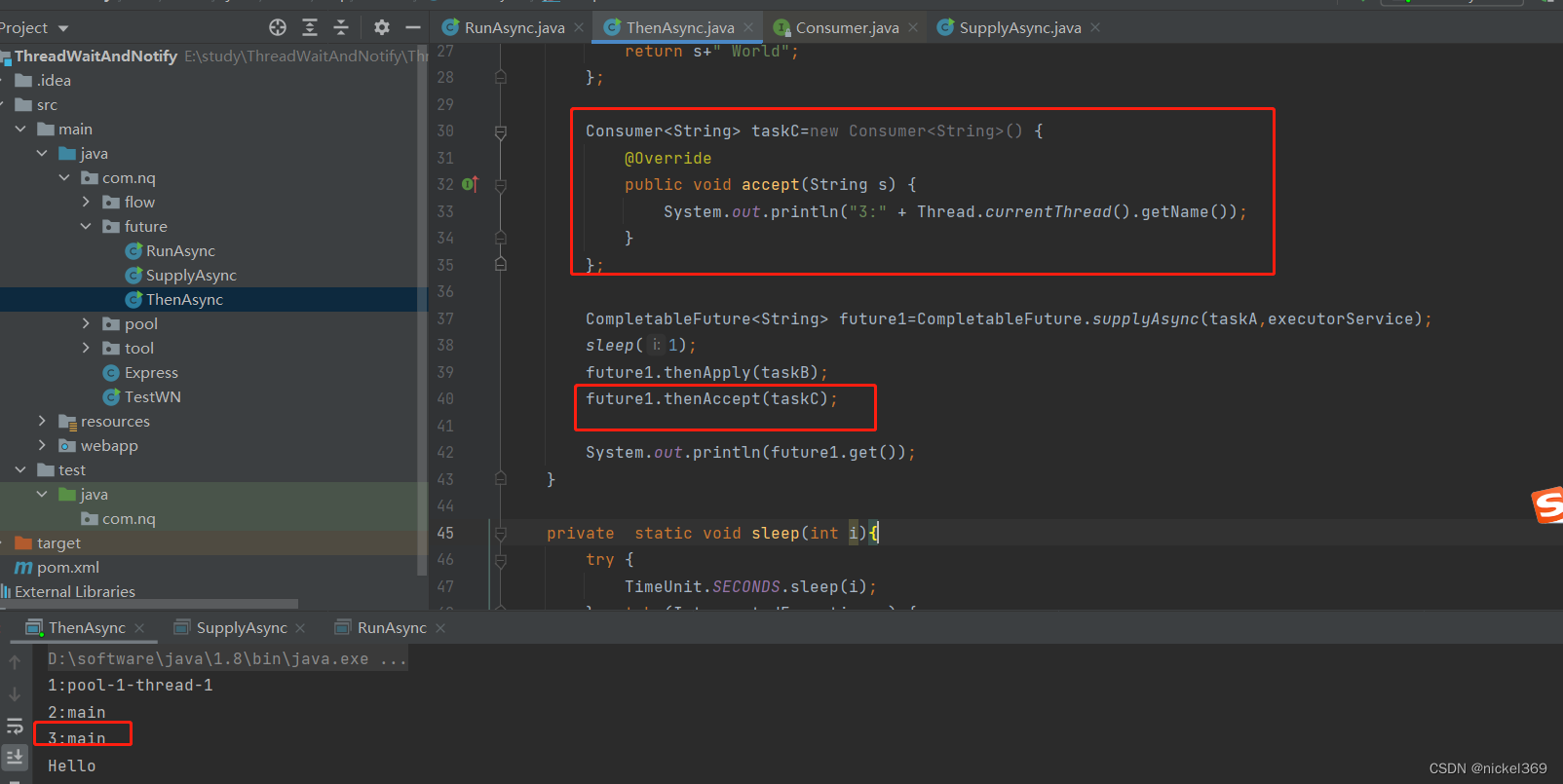
说明:在多线程执行中,任务A执行完成后才能执行任务B
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 0:03
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*
* 任务A执行完成后执行任务B
*/
public class ThenAsync {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Supplier<String> taskA=()->{
System.out.println("1:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
};
Function<String,String> taskB=s->{
System.out.println("2:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return s+" World";
};
CompletableFuture<String> future1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(taskA,executorService);
sleep(1);
future1.thenApply(taskB);
System.out.println(future1.get());
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.ThenCombine
说明:表示futureA执行完成再执行futureB得到合并的结果
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 0:32
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ThenCombine {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> futureA=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sleep(3);
return "Hello";
},executorService);
CompletableFuture<String> futureB=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sleep(3);
return " World!";
});
CompletableFuture<String> result=futureA.thenCombine(futureB,(resultA,resultB)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return resultA+resultB;
});
System.out.println(result.get());
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
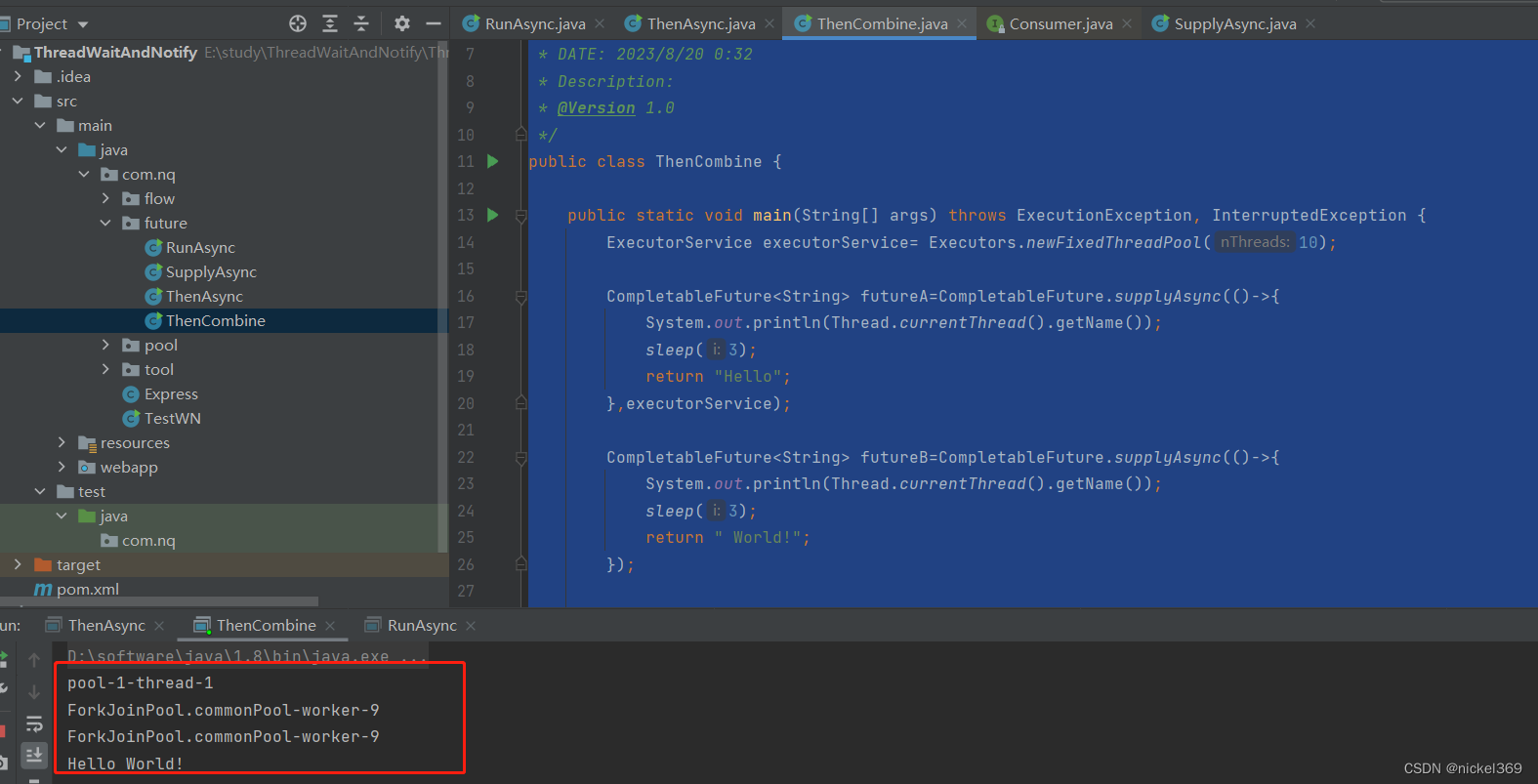
3.runAfterEither、runAfterBoth
说明:runAfterEither表示其中之一执行完成,返回结果,runAfterBoth表示两者都执行完成后,返回结果,而在方法futureB抛出异常,所以无法执行完成,所以runAfterBoth无法执行。
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 0:49
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class RunAfter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> futureA=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sleep(3);
return "Hello";
},executorService);
CompletableFuture<String> futureB=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sleep(3);
throw new NullPointerException();
// return " World!";
},executorService);
System.out.println("-------------");
futureB.runAfterEither(futureA,()->{
System.out.println("!!");
});
System.out.println("-------------");
futureB.runAfterBoth(futureA,()->{
System.out.println("11111");
});
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
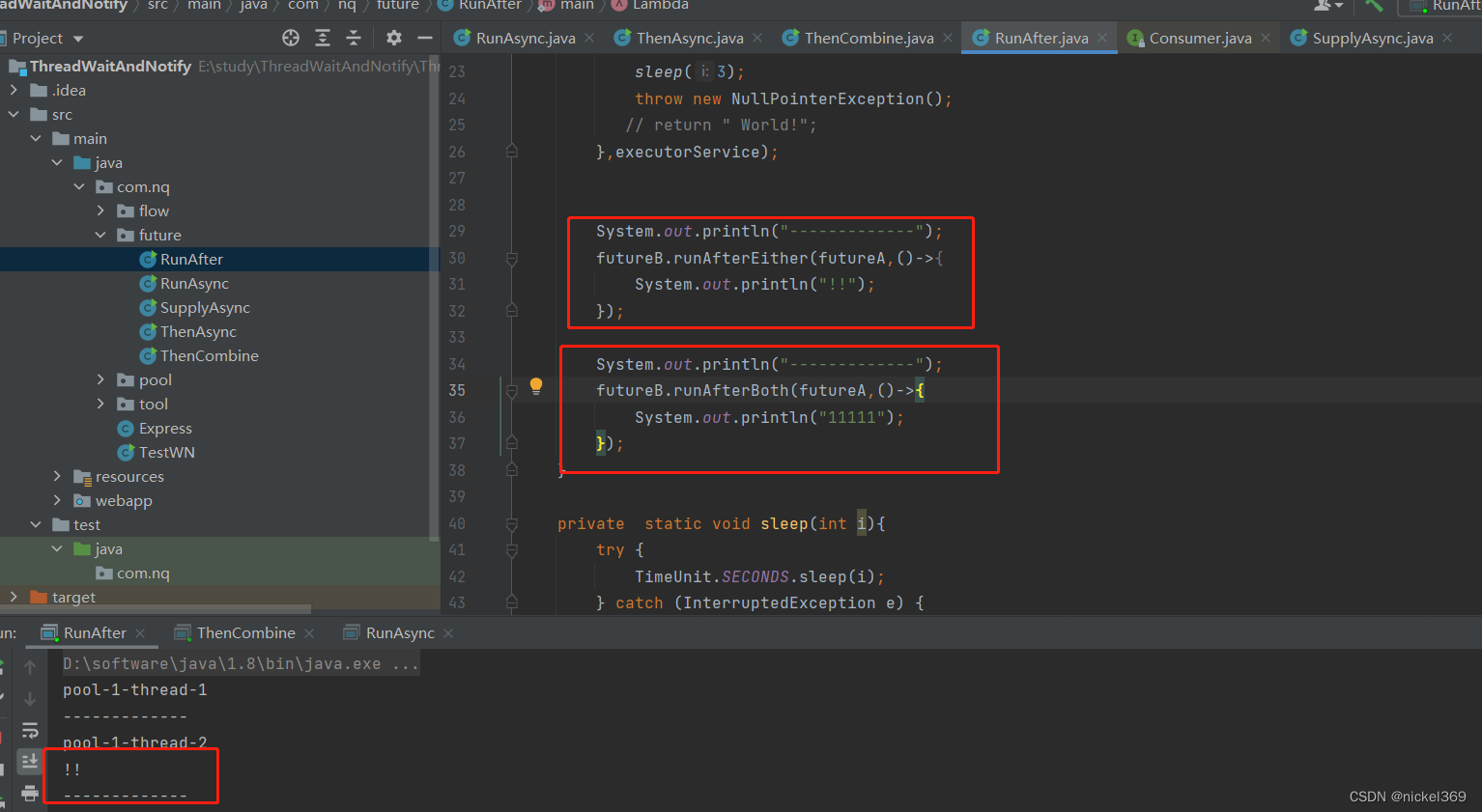
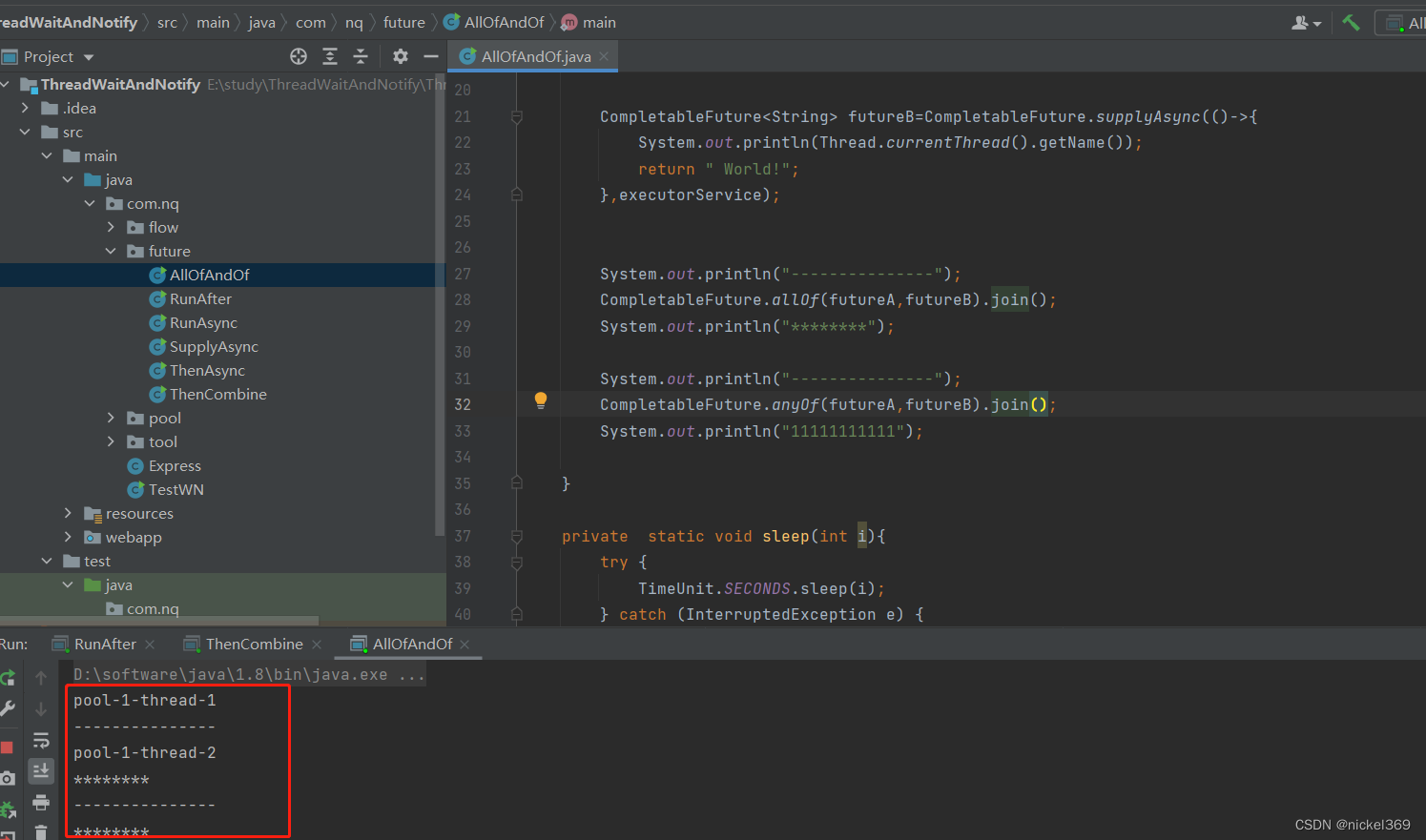
4.allOf、anyOf
说明:allOf表示futureA和futureB都执行完成才会输出,anyOf表示两者只要其中之一执行完成就会输出
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 0:49
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class AllOfAndOf {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> futureA=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sleep(5);
return "Hello";
},executorService);
CompletableFuture<String> futureB=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return " World!";
},executorService);
System.out.println("---------------");
CompletableFuture.allOf(futureA,futureB).join();
System.out.println("********");
System.out.println("---------------");
CompletableFuture.anyOf(futureA,futureB).join();
System.out.println("11111111111");
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
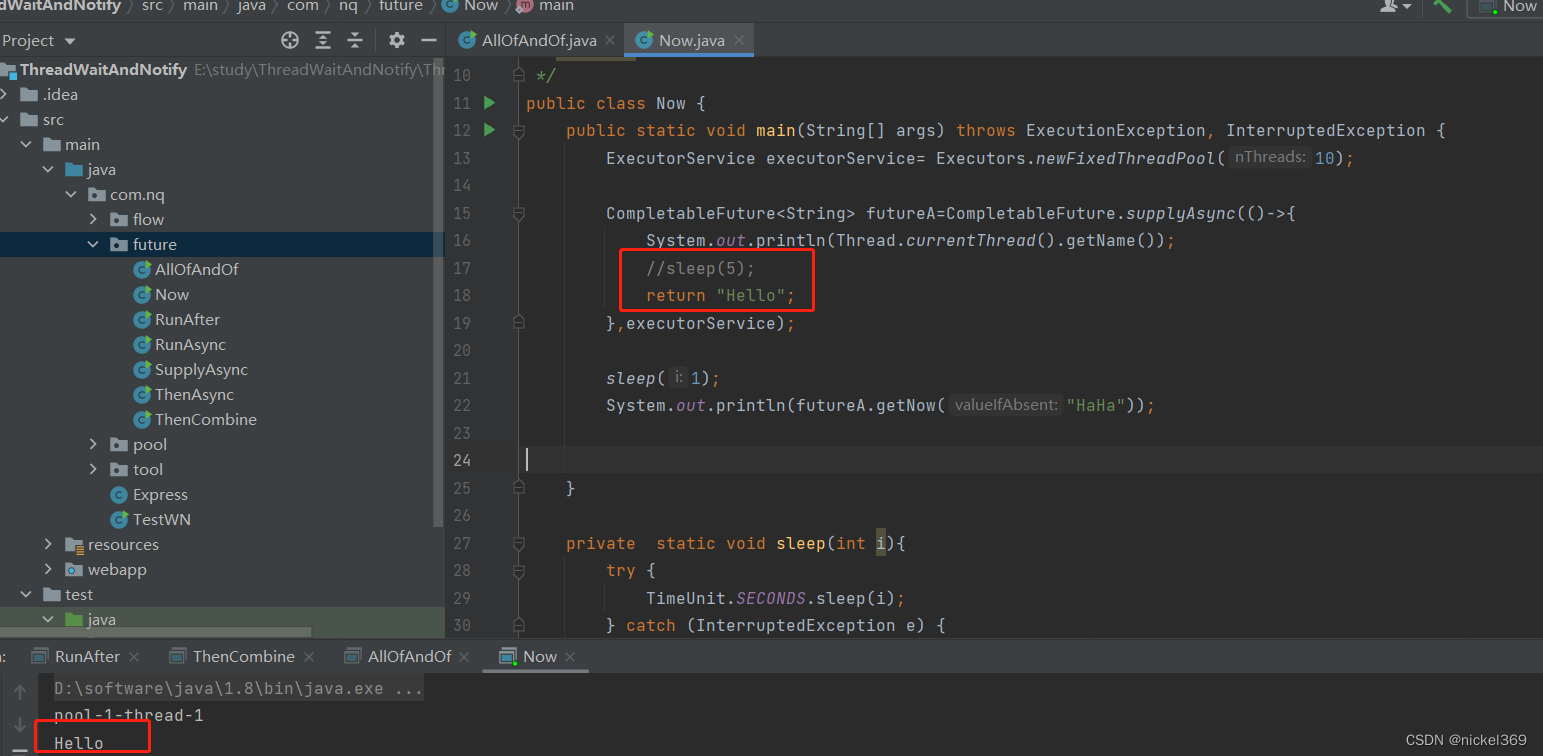
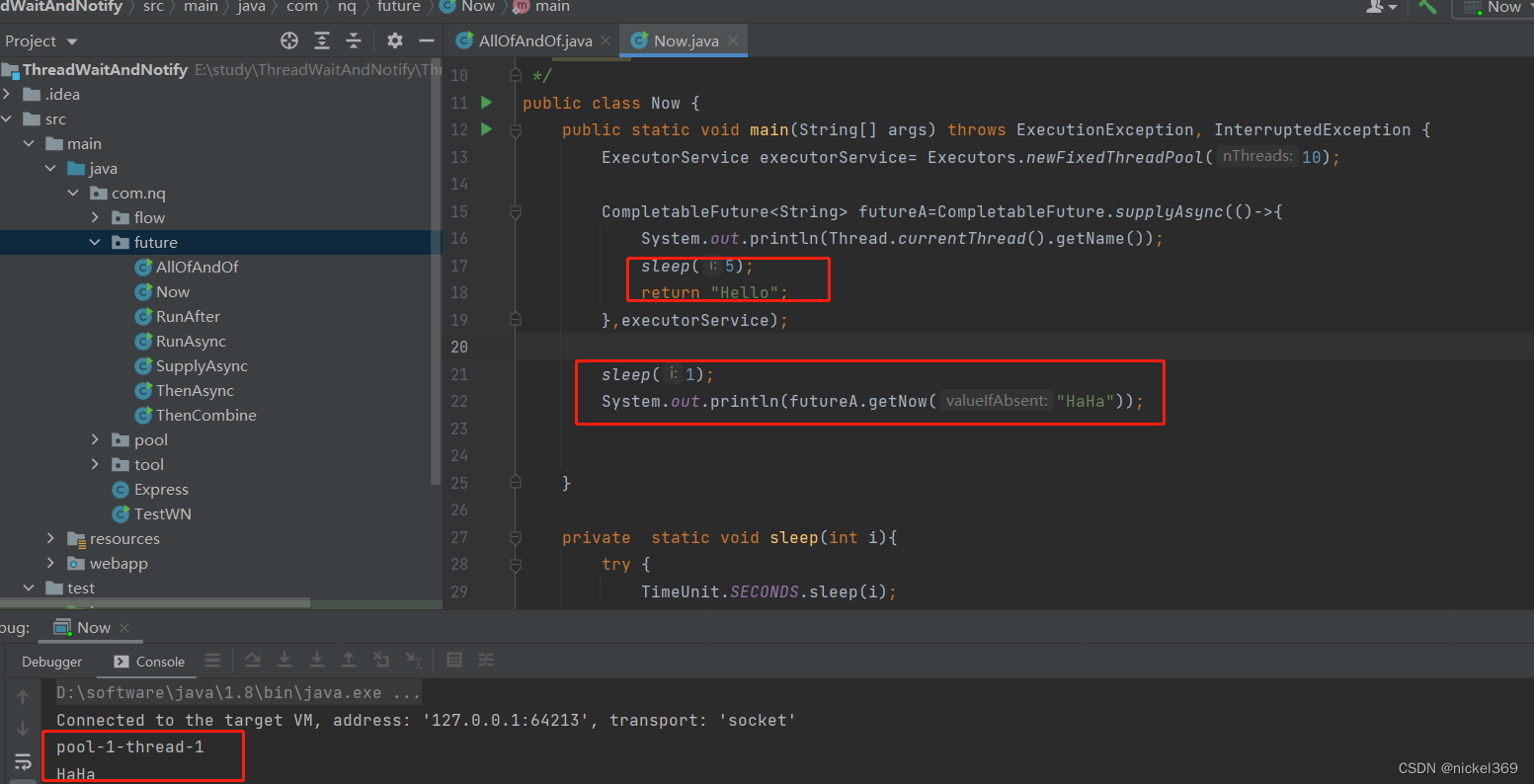
5.getNow
说明:当任务futureA休眠时,拿到的结果是getNow里面的值,当futureA不休眠时,拿到的结果是futureA的值
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 1:09
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Now {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> futureA=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//sleep(5);
return "Hello";
},executorService);
sleep(1);
System.out.println(futureA.getNow("HaHa"));
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
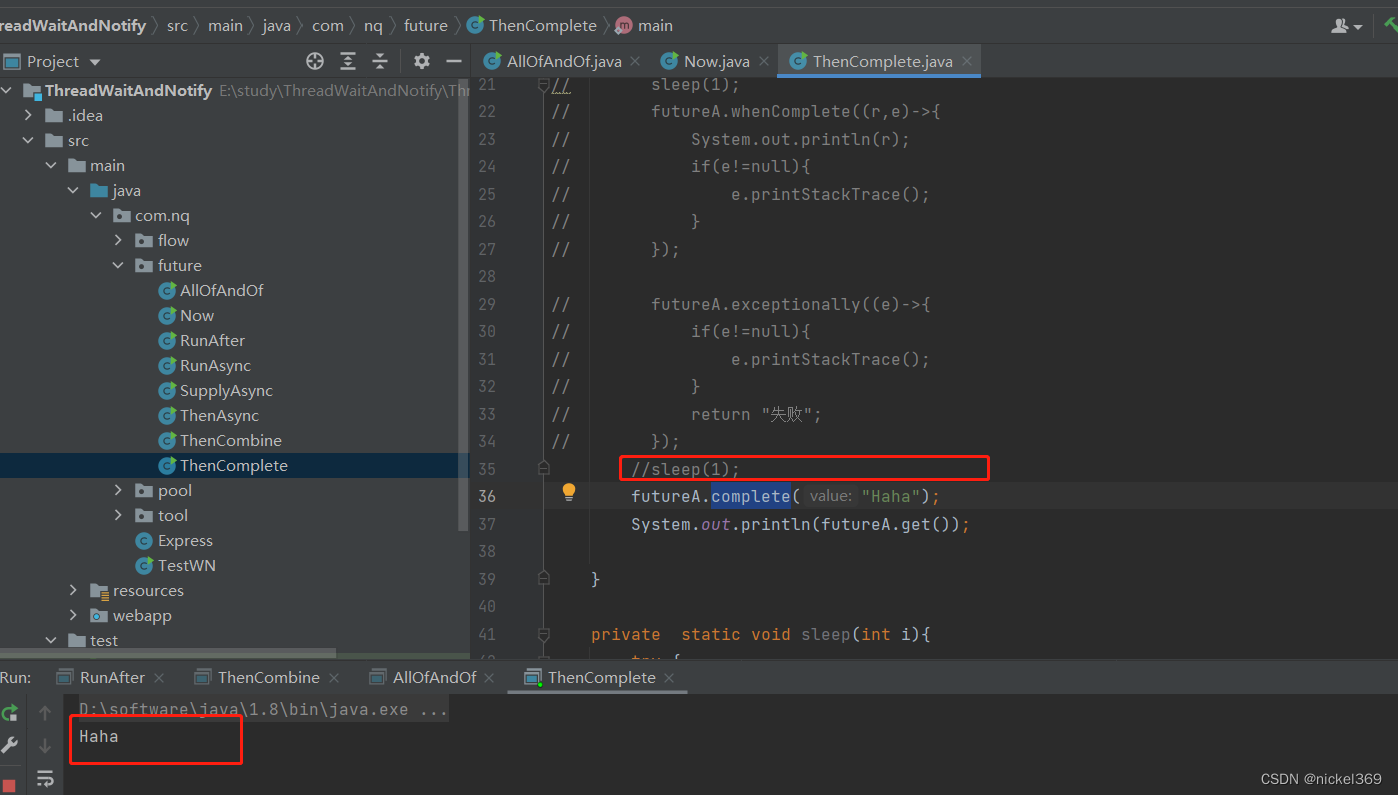
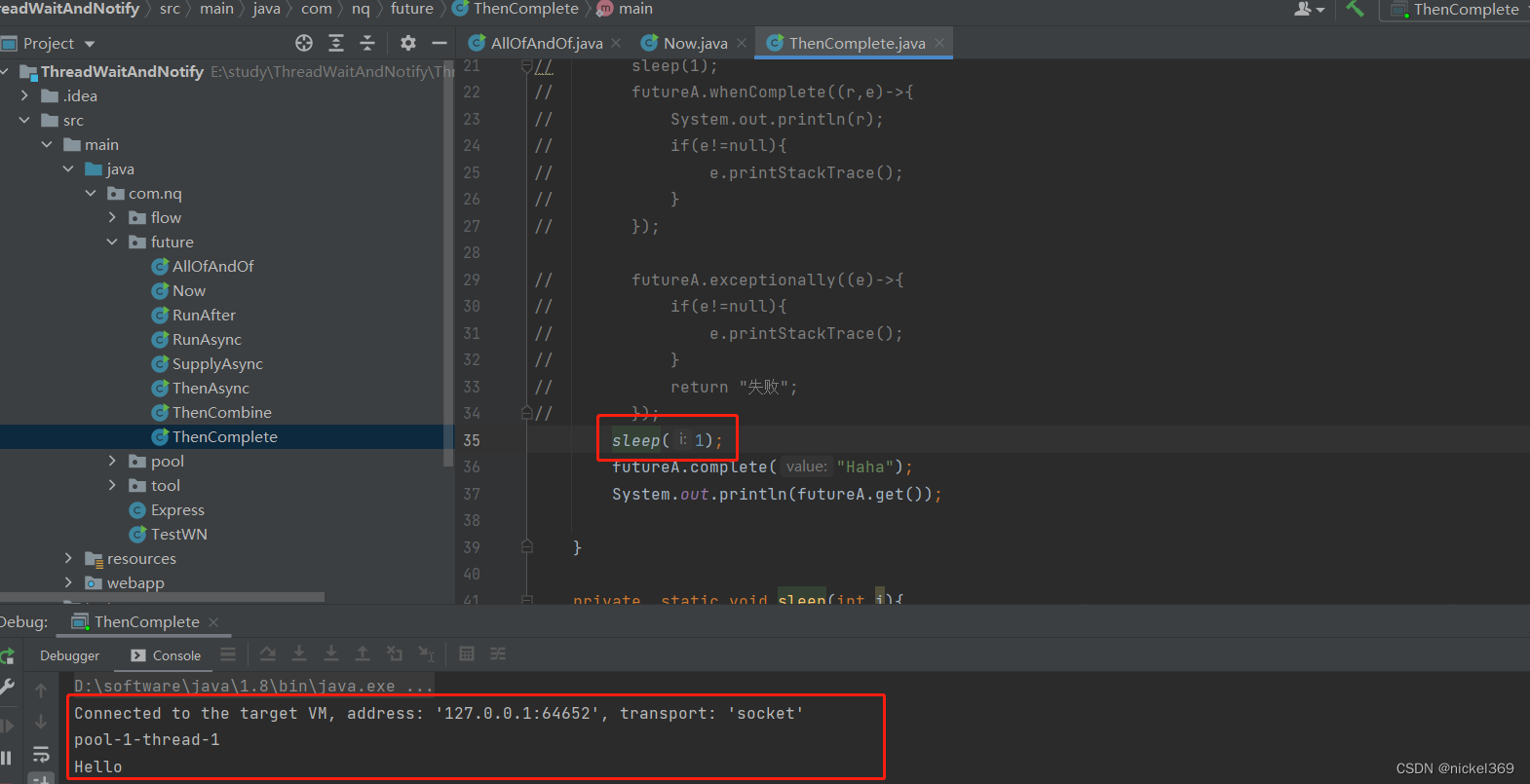
6.whenComplete、exceptionally、complete
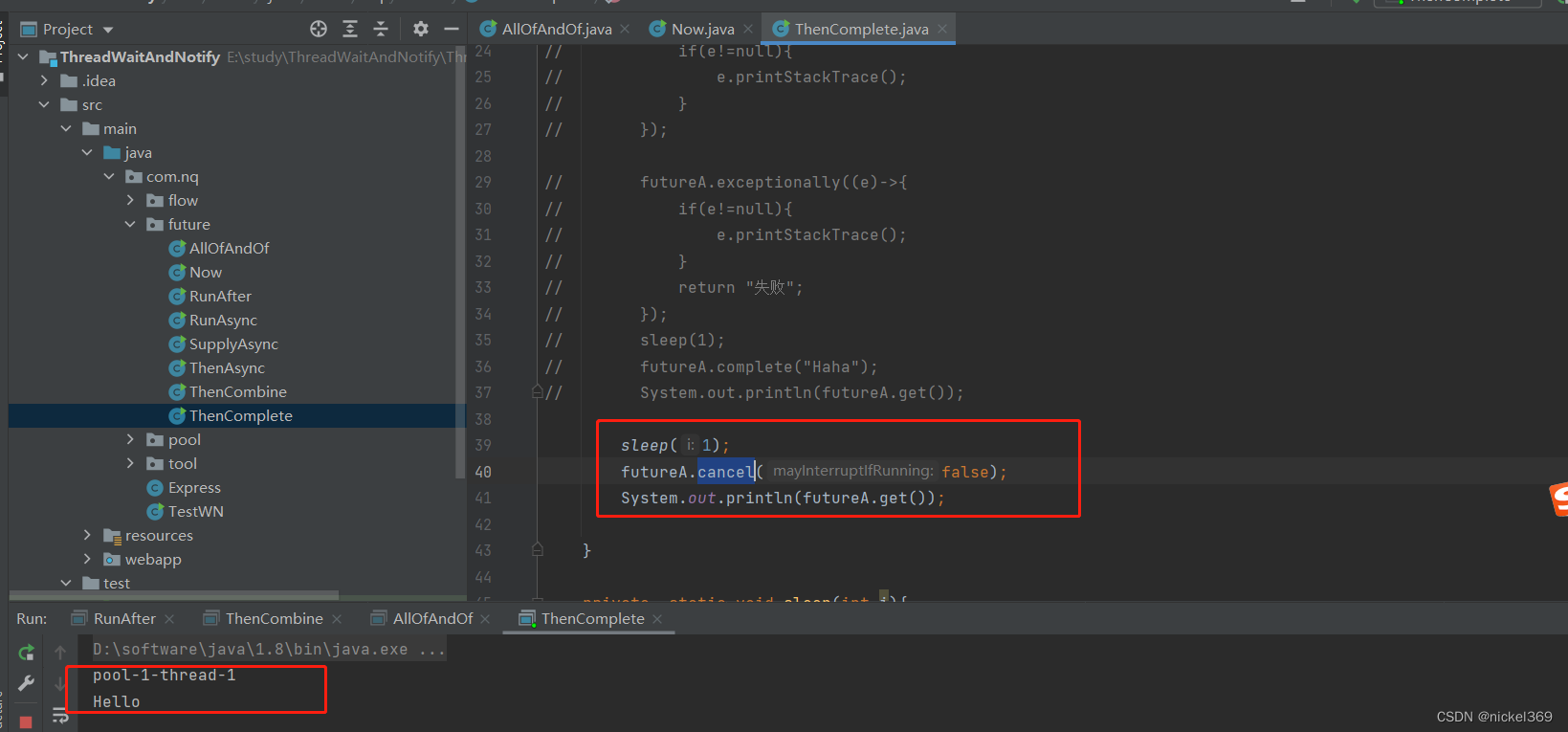
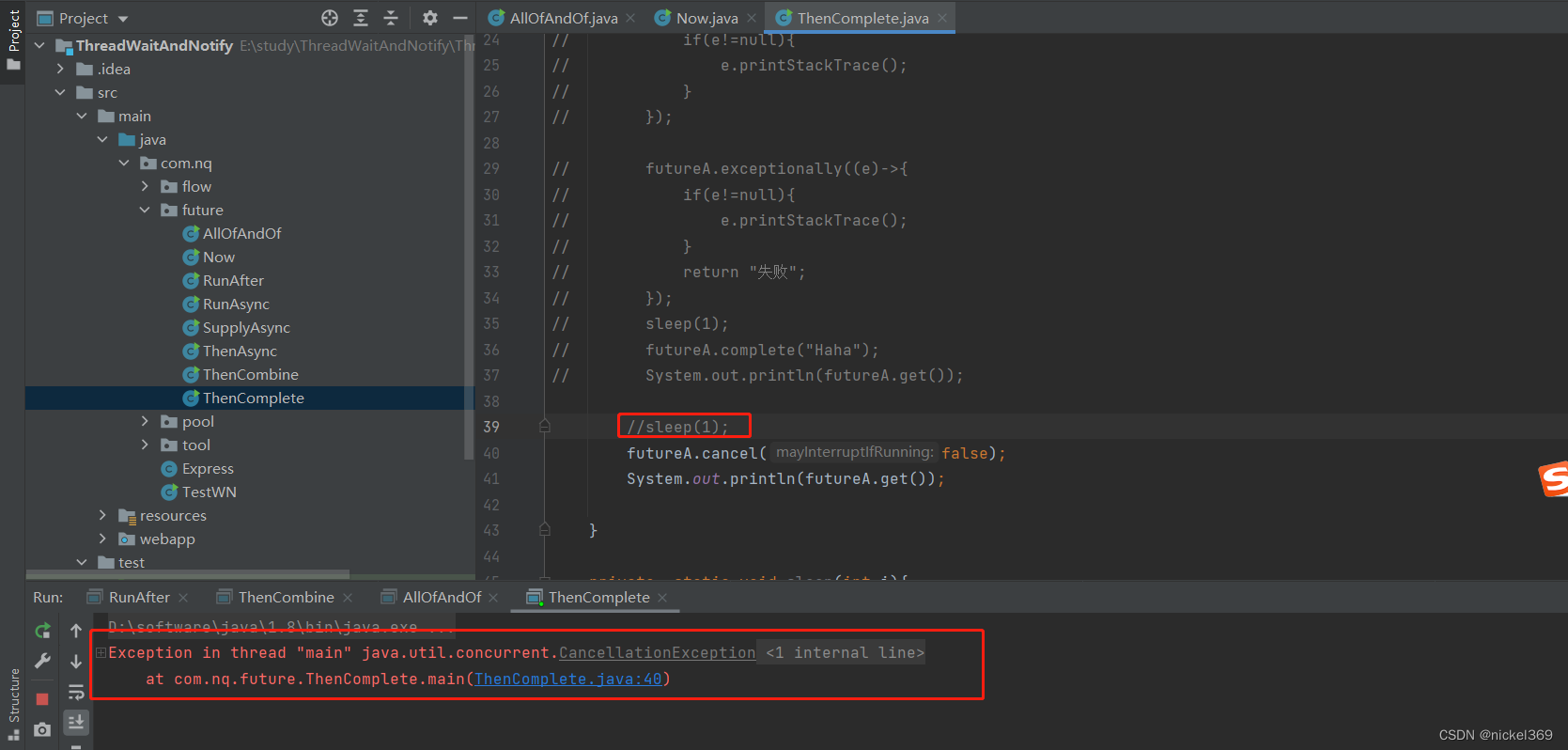
说明:whenComplete表示有异常执行异常,没有异常,执行正常的逻辑;exceptionally只能执行异常的逻辑;complete表示休眠执行complete中的返回值,不休眠执行complete中的返回值;cancel标记执行线程,不一定真的取消
package com.nq.future;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Auther: Nickel
* DATE: 2023/8/20 1:15
* Description:
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ThenComplete {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> futureA=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
//throw new NullPointerException();
},executorService);
sleep(1);
futureA.whenComplete((r,e)->{
System.out.println(r);
if(e!=null){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
futureA.exceptionally((e)->{
if(e!=null){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "失败";
});
}
private static void sleep(int i){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
whenComplete
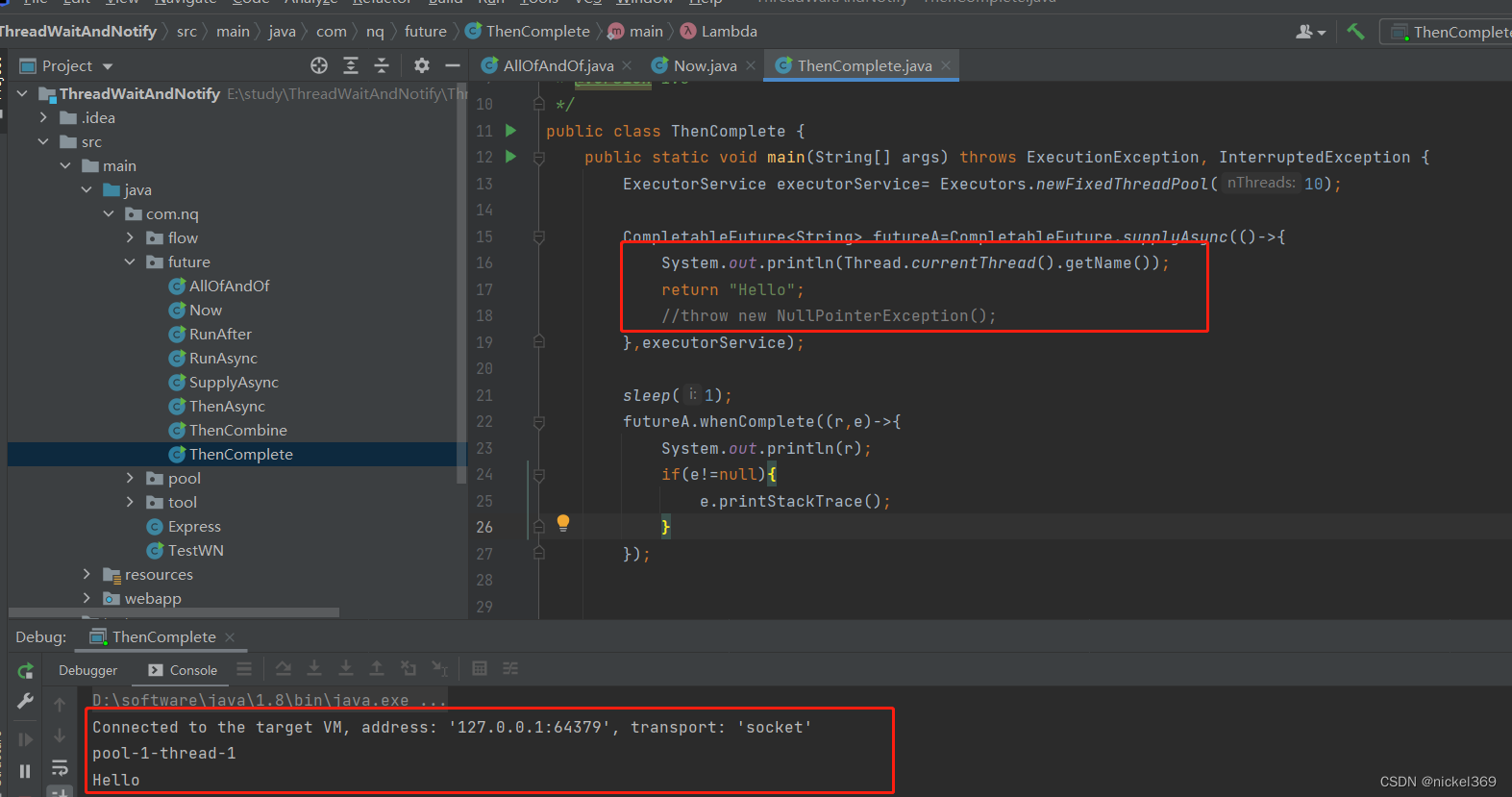
whenComplete
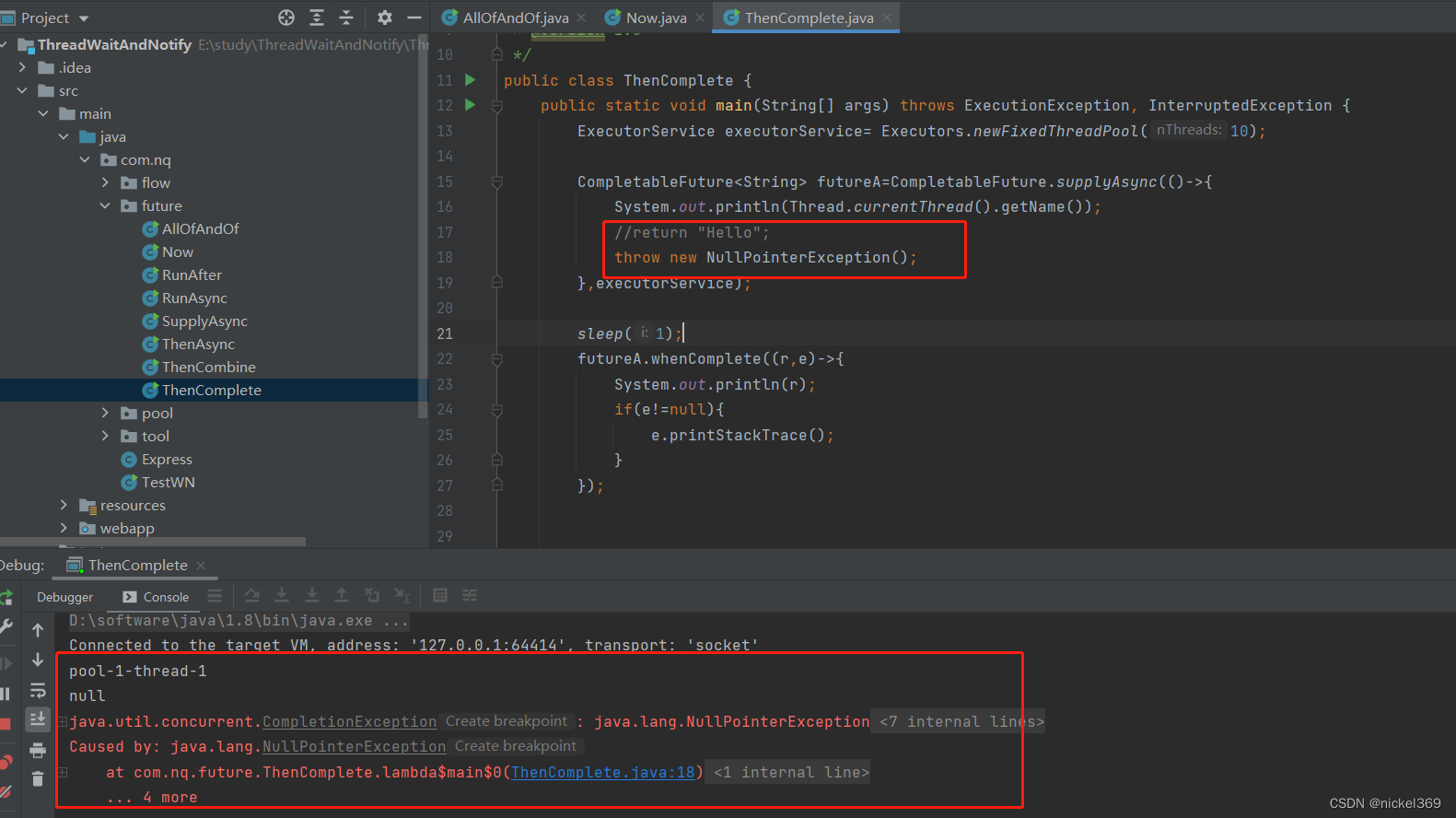
exceptionally
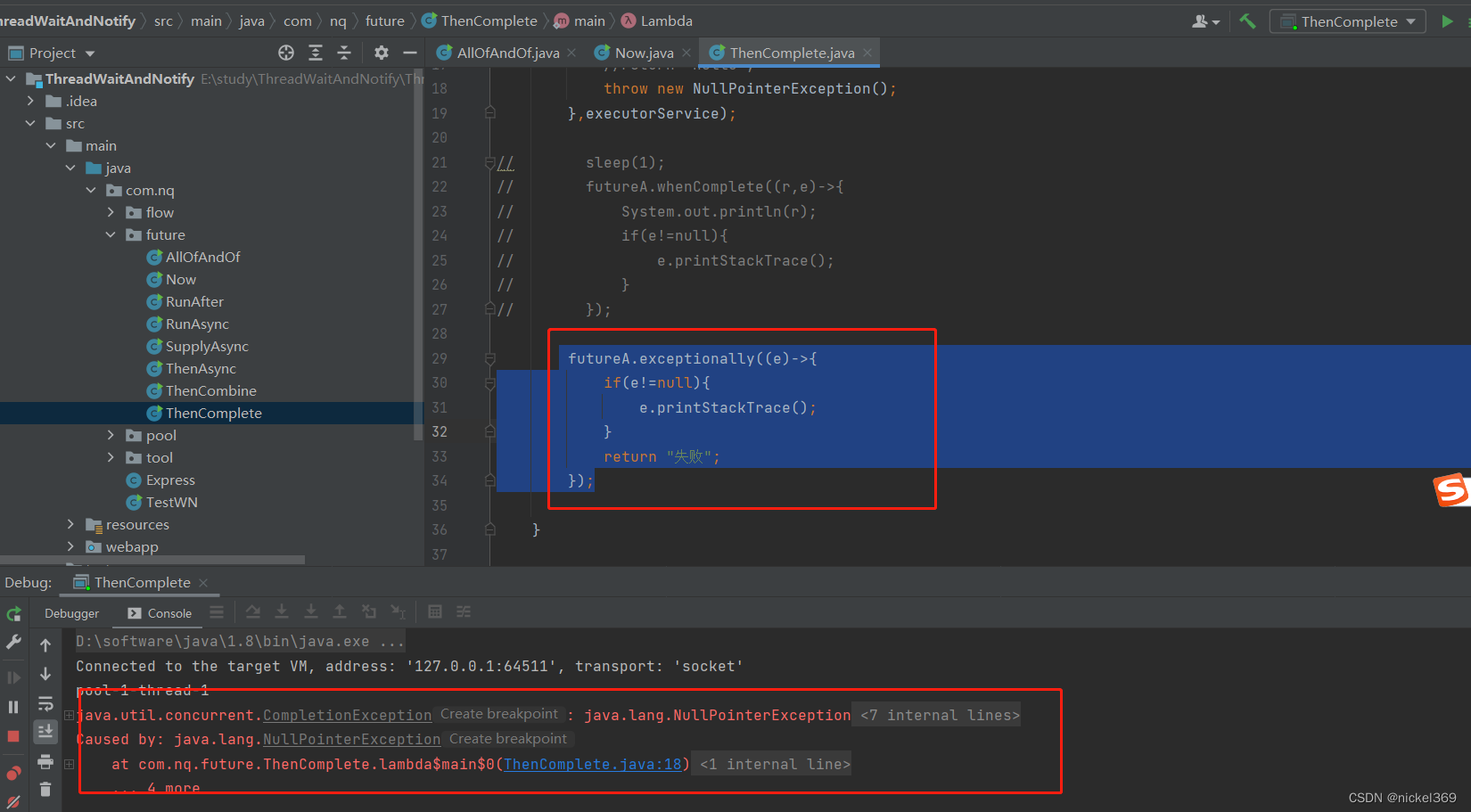
complete
cancel