文章目录
- 前言
- 一、比较
- 1.比较运算符
- 2.compare函数
- 二、复制
- 1.copy函数
- 总结
前言
本系列STL使用VS2022+C++20版本
在C++标准库中,string类是一个功能强大的字符串处理类,提供了丰富的操作函数。本文将详细介绍string类的比较、复制、查找字串、返回字串、交换等常用操作。通过深入浅出的解析,让读者对这些操作有更清晰的理解和掌握。
一、比较
1.比较运算符
1、重载比较运算符, 结果是真和假。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "Hello";
std::string str2 = "World";
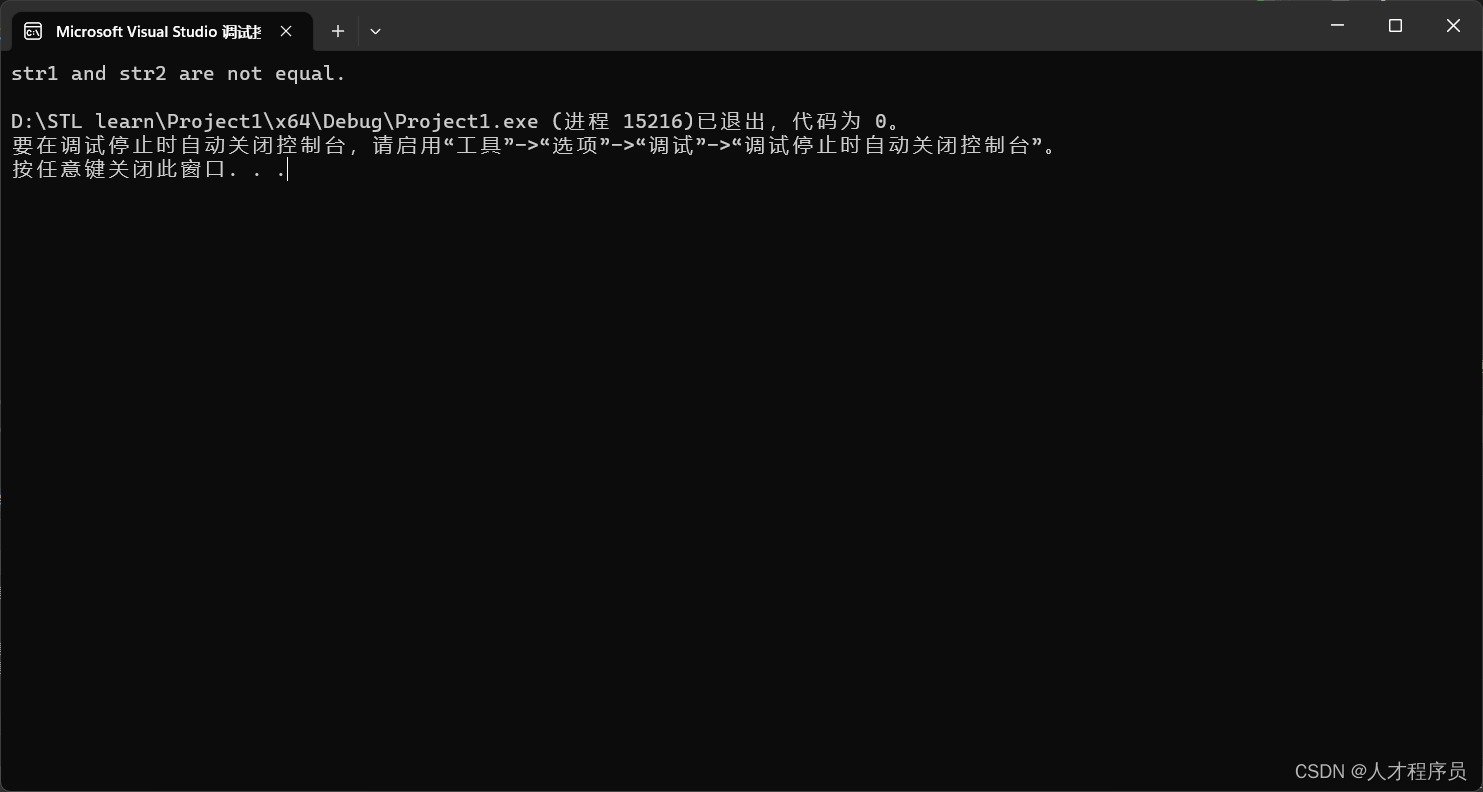
if (str1 == str2) {
std::cout << "str1 and str2 are equal." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "str1 and str2 are not equal." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
2.compare函数
1、int compare( const basic_string &str );
作用:用于比较当前字符串对象与给定的 basic_string 对象 str 是否相等。
参数:str 是要进行比较的目标字符串对象。
返回值:返回一个整数,表示比较结果。如果当前字符串小于 str,则返回一个负数;如果当前字符串等于 str,则返回 0;如果当前字符串大于 str,则返回一个正数。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "apple";
std::string str2 = "banana";
int result = str1.compare(str2);
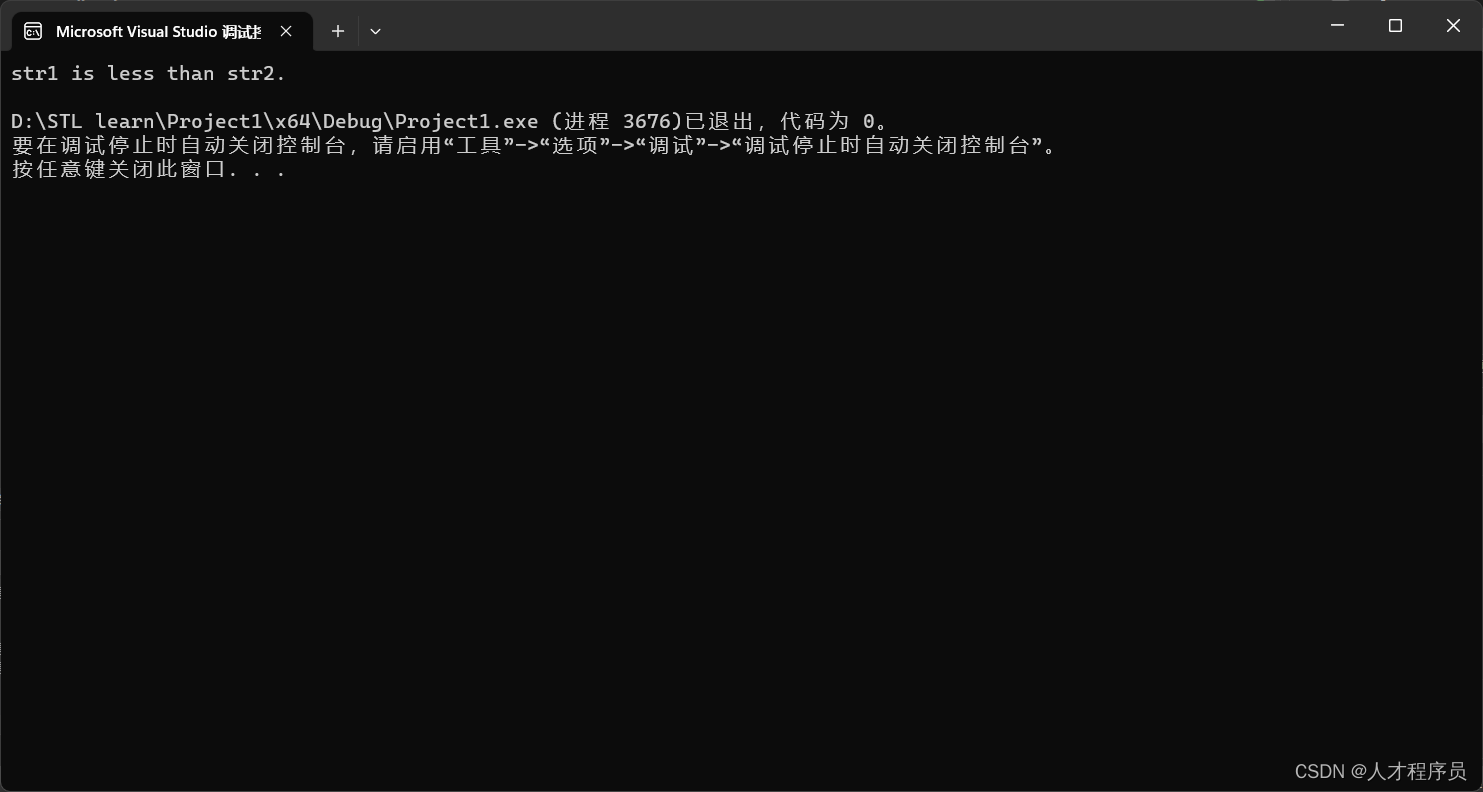
if (result < 0) {
std::cout << "str1 is less than str2." << std::endl;
} else if (result > 0) {
std::cout << "str1 is greater than str2." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "str1 is equal to str2." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、int compare( const char *str );
作用:用于比较当前字符串对象与以 null 结尾的 C-Style 字符串 str 是否相等。
参数:str 是要进行比较的 C-Style 字符串。
返回值:返回一个整数,表示比较结果。如果当前字符串小于 str,则返回一个负数;如果当前字符串等于 str,则返回 0;如果当前字符串大于 str,则返回一个正数。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "hello";
int result = str.compare("world");
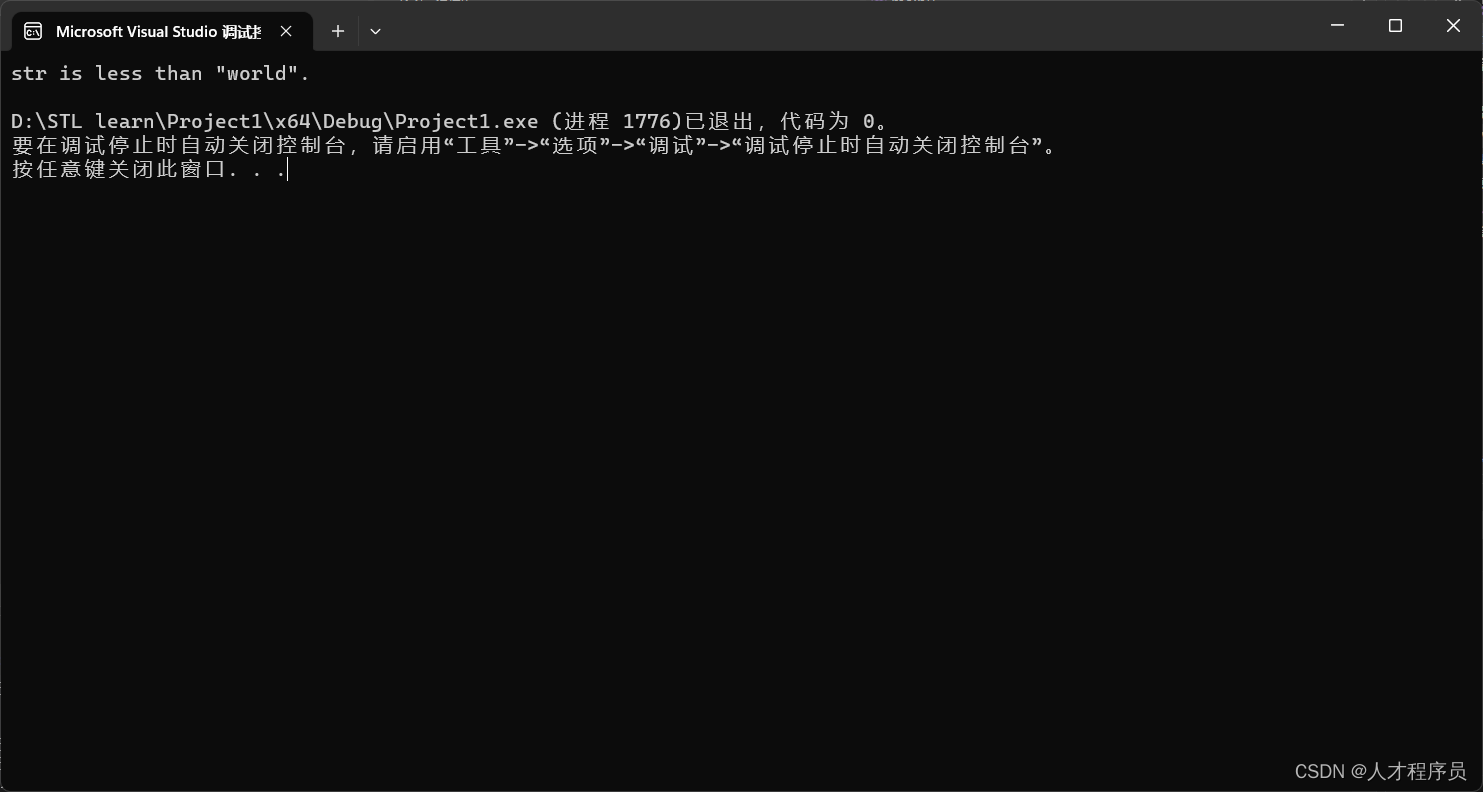
if (result < 0) {
std::cout << "str is less than \"world\"." << std::endl;
} else if (result > 0) {
std::cout << "str is greater than \"world\"." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "str is equal to \"world\"." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、int compare( size_type index, size_type length, const basic_string &str );
作用:用于从当前字符串的指定位置开始,比较 length 个字符与给定的 basic_string 对象 str 是否相等。
参数:index 是当前字符串的起始位置,length 是要比较的字符数,str 是要进行比较的目标字符串对象。
返回值:返回一个整数,表示比较结果。如果子字符串小于 str,则返回一个负数;如果子字符串等于 str,则返回 0;如果子字符串大于 str,则返回一个正数。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str = "helloworld";
int result = str.compare(0, 5, "hello");
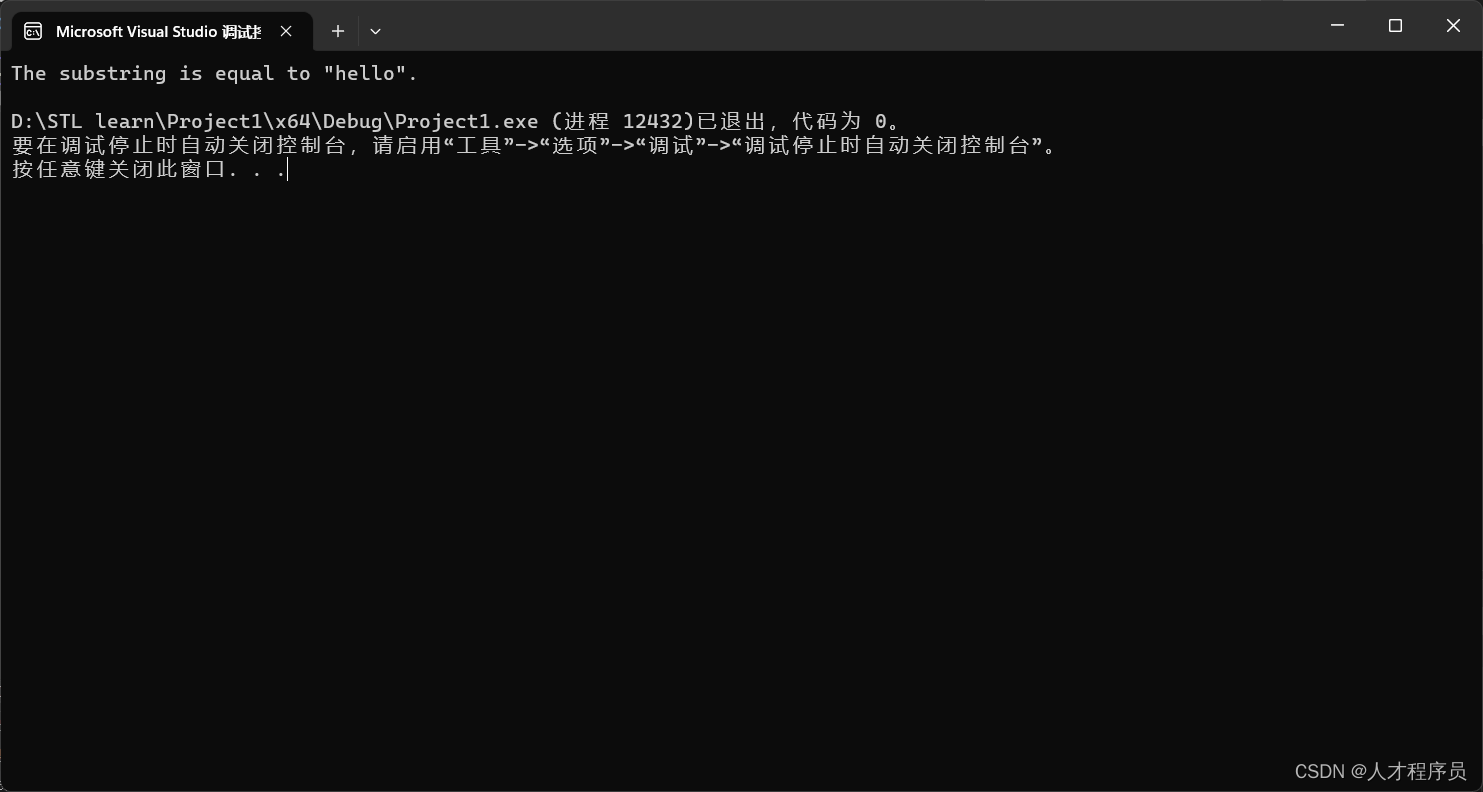
if (result < 0) {
std::cout << "The substring is less than \"hello\"." << std::endl;
} else if (result > 0) {
std::cout << "The substring is greater than \"hello\"." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "The substring is equal to \"hello\"." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
4、int compare( size_type index, size_type length, const basic_string &str, size_type index2,size_type length2 );
作用:用于从当前字符串的指定位置开始,比较 length 个字符与给定的 basic_string 对象 str 的子字符串是否相等。
参数:index 是当前字符串的起始位置,length 是要比较的字符数,str 是要进行比较的目标字符串对象,index2 是目标字符串的起始位置,length2 是要比较的目标字符串的字符数。
返回值:返回一个整数,表示比较结果。如果子字符串小于目标字符串的子字符串,则返回一个负数;如果子字符串等于目标字符串的子字符串,则返回 0;如果子字符串大于目标字符串的子字符串,则返回一个正数。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str1 = "helloworld";
std::string str2 = "ello";
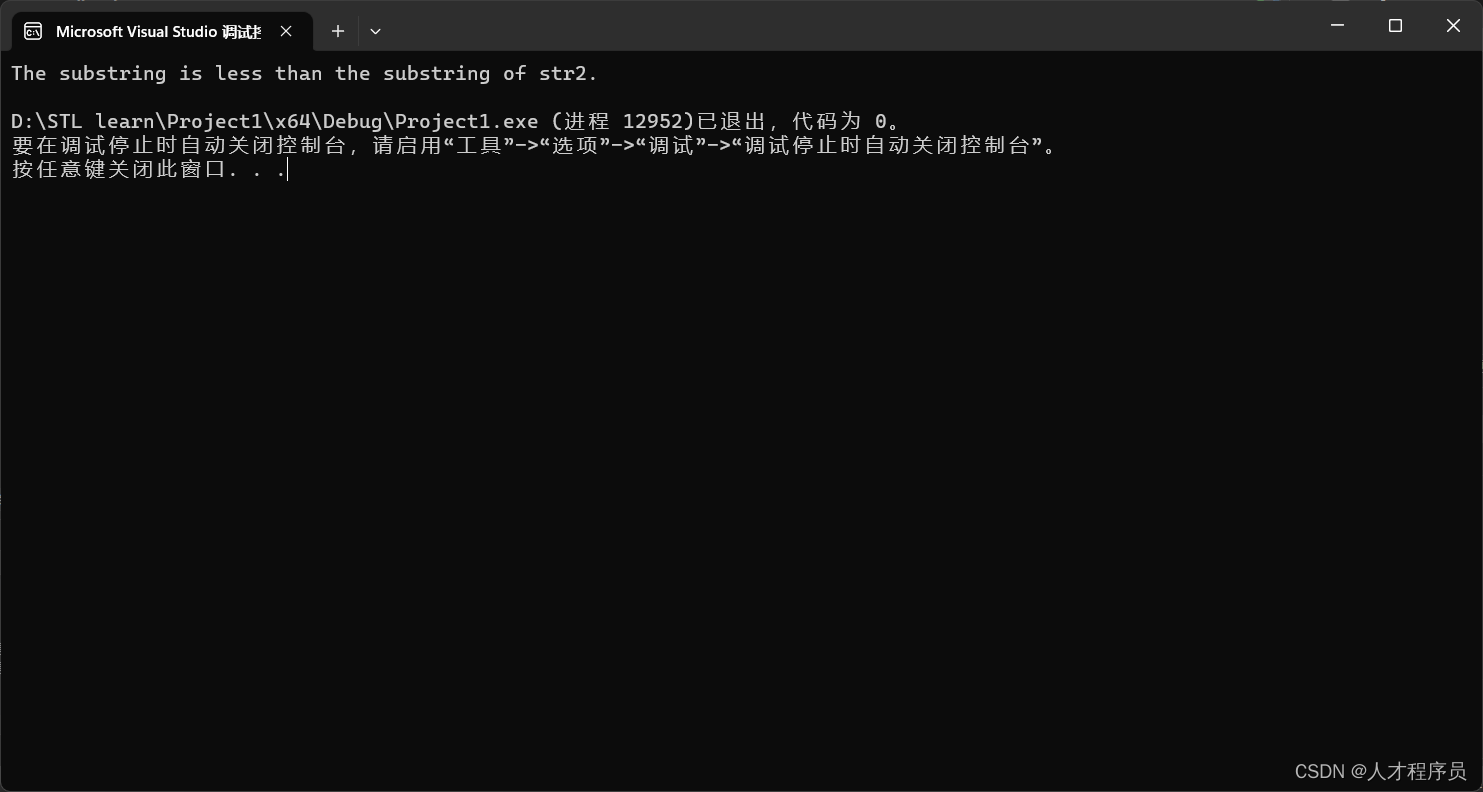
int result = str1.compare(1, 5, str2, 1, 3);
if (result < 0) {
std::cout << "The substring is less than the substring of str2." << std::endl;
} else if (result > 0) {
std::cout << "The substring is greater than the substring of str2." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "The substring is equal to the substring of str2." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
二、复制
1.copy函数
1、size_type copy( char *str, size_type num, size_type index );
作用是从调用函数的字符串中复制指定数量的字符到目标字符数组中。
参数的作用如下:
str:指向目标字符数组的指针,用于存储复制的字符。
num:要复制的最大字符数。
index:开始复制的位置索引。
返回值的作用:
size_type:实际复制的字符数。如果这个值小于 num,表示被复制字符串的长度不足以满足要求。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string source = "hello world";
char destination[10];
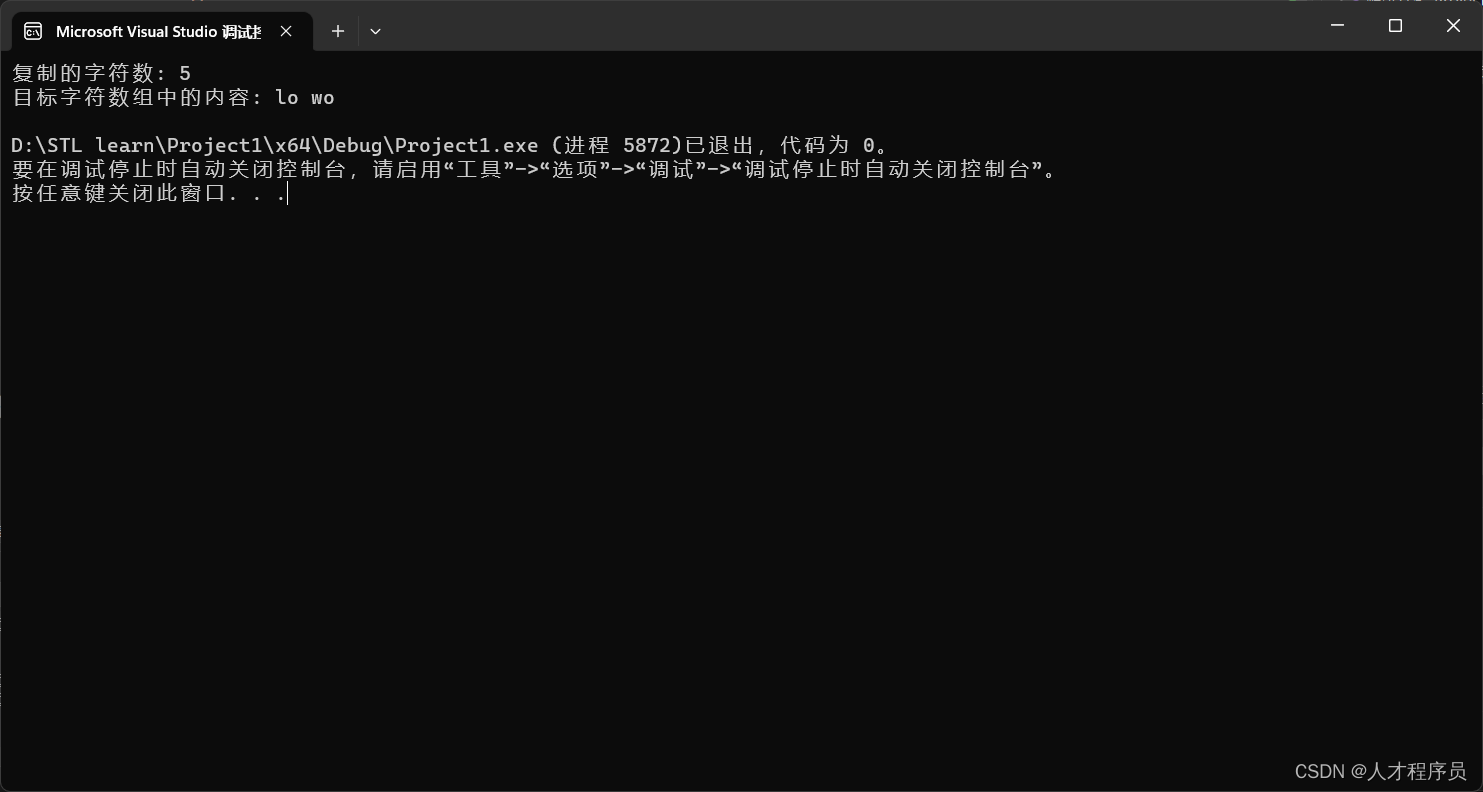
size_t copiedChars = source.copy(destination, 5, 3);
destination[copiedChars] = '\0'; // 添加字符串结束符
std::cout << "复制的字符数: " << copiedChars << std::endl;
std::cout << "目标字符数组中的内容: " << destination << std::endl;
return 0;
}
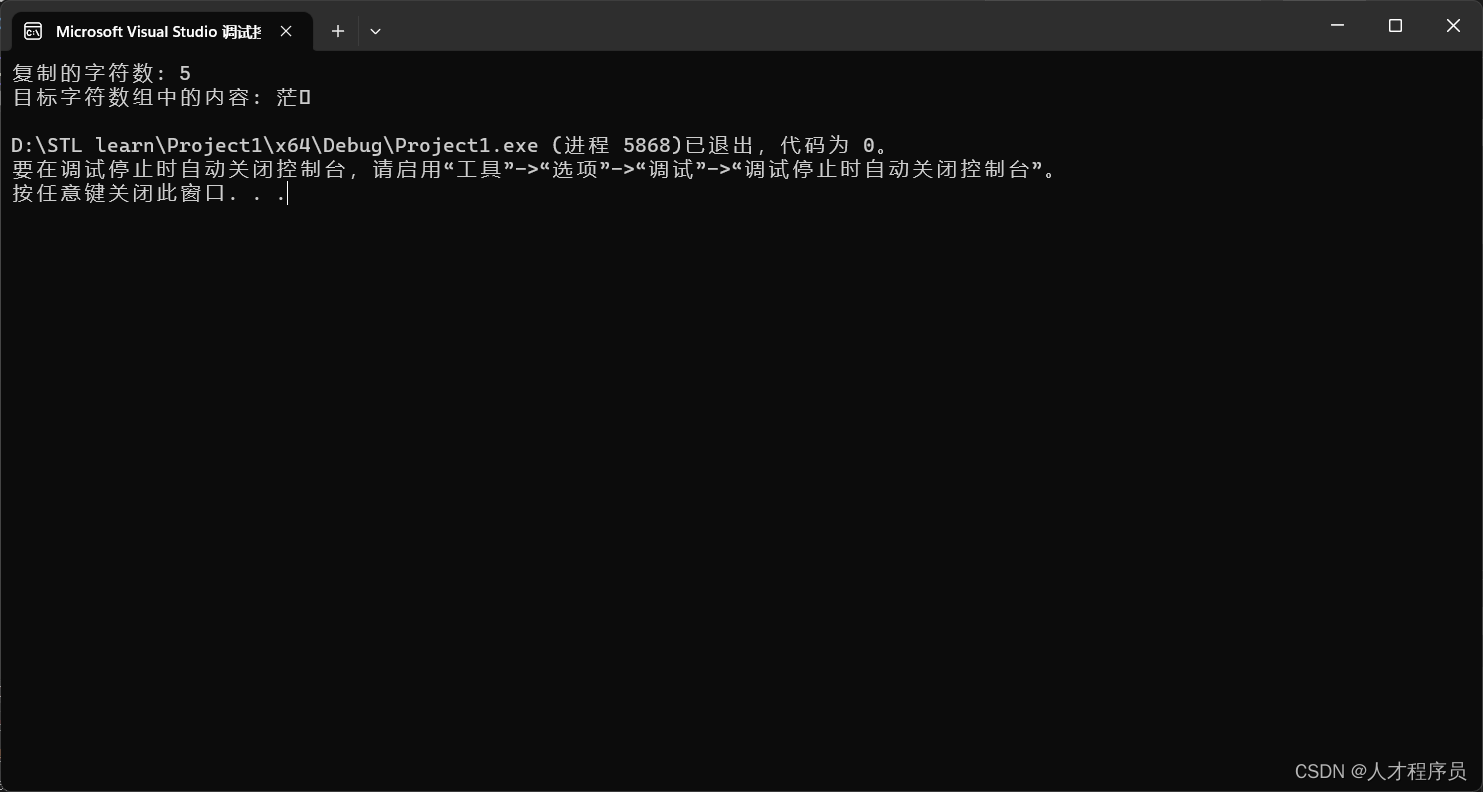
虽然有乱码但是不影响,我们可以通过断点来查看.
总结
本文深入浅出地介绍了string类的比较、复制常用操作。通过对这些操作的解析和示例,读者可以更加清晰地理解和掌握这些功能。熟练使用string类的操作函数,将有助于提高字符串处理的效率和代码质量,更好地应对实际开发需求。