[oneAPI] 使用序列到序列网络和注意力进行翻译
- oneAPI特殊写法
- 使用序列到序列网络和注意力进行翻译
- Intel® Optimization for PyTorch
- 导入包
- 加载数据并对数据进行处理
- 序列到序列网络和注意力模型与介绍
- 编码器
- 解码器
- 简单解码器
- 注意力解码器
- 训练过程
- 准备训练数据
- 训练模型
- 可视化注意力代码
- 结果
- 参考资料
比赛:https://marketing.csdn.net/p/f3e44fbfe46c465f4d9d6c23e38e0517
Intel® DevCloud for oneAPI:https://devcloud.intel.com/oneapi/get_started/aiAnalyticsToolkitSamples/
oneAPI特殊写法
import intel_extension_for_pytorch as ipex
# Device configuration
device = torch.device('xpu' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
encoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
'''
Apply Intel Extension for PyTorch optimization against the model object and optimizer object.
'''
encoder, encoder_optimizer = ipex.optimize(encoder, optimizer=encoder_optimizer)
decoder, decoder_optimizer = ipex.optimize(decoder, optimizer=decoder_optimizer)
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
使用序列到序列网络和注意力进行翻译
让神经网络将法语翻译成英语
[KEY: > input, = target, < output]
> il est en train de peindre un tableau .
= he is painting a picture .
< he is painting a picture .
> pourquoi ne pas essayer ce vin delicieux ?
= why not try that delicious wine ?
< why not try that delicious wine ?
> elle n est pas poete mais romanciere .
= she is not a poet but a novelist .
< she not not a poet but a novelist .
> vous etes trop maigre .
= you re too skinny .
< you re all alone .
我们的模型通过序列到序列网络的简单但强大的思想实现的,其中两个循环神经网络一起工作将一个序列转换为另一个序列。编码器网络将输入序列压缩为向量,解码器网络将该向量展开为新序列
Intel® Optimization for PyTorch
在本次实验中,我们利用PyTorch和Intel® Optimization for PyTorch的强大功能,对PyTorch进行了精心的优化和扩展。这些优化举措极大地增强了PyTorch在各种任务中的性能,尤其是在英特尔硬件上的表现更加突出。通过这些优化策略,我们的模型在训练和推断过程中变得更加敏捷和高效,显著地减少了计算时间,提高了整体效能。我们通过深度融合硬件和软件的精巧设计,成功地释放了硬件潜力,使得模型的训练和应用变得更加快速和高效。这一系列优化举措为人工智能应用开辟了新的前景,带来了全新的可能性。
导入包
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division
from io import open
import unicodedata
import re
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader, RandomSampler
import intel_extension_for_pytorch as ipex
device = torch.device("xpu" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
加载数据并对数据进行处理
该项目的数据是一组数千个英语到法语的翻译对。
数据地址 https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/data.zip
data/eng-fra.txt 请先下载,该文件是制表符分隔的翻译对列表:I am cold. J'ai froid.
与字符级 RNN 教程中使用的字符编码类似,我们将语言中的每个单词表示为一个单热向量,或除单个 1(在单词索引处)之外的由 0 组成的巨大向量。与语言中可能存在的几十个字符相比,单词的数量要多得多,因此编码向量要大得多。然而,我们将数据修剪为每种语言仅使用几千个单词。
准备数据的完整流程是:
- 读取文本文件并分成行,将行分成对
- 标准化文本,按长度和内容过滤
- 从成对的句子中制作单词列表
我们需要每个单词有一个唯一的索引,以便稍后用作网络的输入和目标。为了跟踪所有这些,我们将使用一个名为的==帮助器类Lang==,它具有 word → index ( word2index) 和 index → word ( index2word) 字典,以及每个单词的计数 word2count,稍后将用于替换稀有单词。
######################################################################
# Loading data files
# ==================
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.word2index = {}
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
self.addWord(word)
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
将 Unicode 字符转换为 ASCII,将所有内容变为小写,并修剪大部分标点符号
######################################################################
# The files are all in Unicode, to simplify we will turn Unicode
# characters to ASCII, make everything lowercase, and trim most
# punctuation.
#
# Turn a Unicode string to plain ASCII, thanks to
# https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# Lowercase, trim, and remove non-letter characters
def normalizeString(s):
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z!?]+", r" ", s)
return s.strip()
为了读取数据文件,我们将文件分成行,然后将行分成对。这些文件都是英语→其他语言,所以如果我们想从其他语言→英语翻译,我添加了标志reverse 来反转对。
######################################################################
# To read the data file we will split the file into lines, and then split
# lines into pairs. The files are all English → Other Language, so if we
# want to translate from Other Language → English I added the ``reverse``
# flag to reverse the pairs.
#
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# Read the file and split into lines
lines = open('data/%s-%s.txt' % (lang1, lang2), encoding='utf-8').\
read().strip().split('\n')
# Split every line into pairs and normalize
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines]
# Reverse pairs, make Lang instances
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
序列到序列网络和注意力模型与介绍
序列到序列网络,或 seq2seq 网络,或编码器解码器网络,是由两个称为编码器和解码器的 RNN 组成的模型。编码器读取输入序列并输出单个向量,解码器读取该向量以产生输出序列。
编码器
seq2seq 网络的编码器是一个 RNN,它为输入句子中的每个单词输出一些值。对于每个输入单词,编码器输出一个向量和一个隐藏状态,并将隐藏状态用于下一个输入单词。
######################################################################
# The Seq2Seq Model
# =================
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, dropout_p=0.1):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_p)
def forward(self, input):
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input))
output, hidden = self.gru(embedded)
return output, hidden
解码器
简单解码器
在最简单的 seq2seq 解码器中,我们仅使用编码器的最后一个输出。最后一个输出有时称为上下文向量,因为它对整个序列的上下文进行编码。该上下文向量用作解码器的初始隐藏状态。
在解码的每一步,解码器都会获得一个输入令牌和隐藏状态。初始输入标记是字符串开始 标记,第一个隐藏状态是上下文向量(编码器的最后一个隐藏状态)。
######################################################################
# Simple Decoder
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size):
super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden, target_tensor=None):
batch_size = encoder_outputs.size(0)
decoder_input = torch.empty(batch_size, 1, dtype=torch.long, device=device).fill_(SOS_token)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoder_outputs = []
for i in range(MAX_LENGTH):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = self.forward_step(decoder_input, decoder_hidden)
decoder_outputs.append(decoder_output)
if target_tensor is not None:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the target as the next input
decoder_input = target_tensor[:, i].unsqueeze(1) # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teacher forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
_, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze(-1).detach() # detach from history as input
decoder_outputs = torch.cat(decoder_outputs, dim=1)
decoder_outputs = F.log_softmax(decoder_outputs, dim=-1)
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden, None # We return `None` for consistency in the training loop
def forward_step(self, input, hidden):
output = self.embedding(input)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = self.out(output)
return output, hidden
注意力解码器
如果仅在编码器和解码器之间传递上下文向量,则该单个向量承担对整个句子进行编码的负担。
注意力机制允许解码器网络针对解码器自身输出的每一步“关注”编码器输出的不同部分。首先我们计算一组注意力权重。这些将乘以编码器输出向量以创建加权组合。结果(attn_applied在代码中调用)应包含有关输入序列特定部分的信息,从而帮助解码器选择正确的输出单词。
######################################################################
# Attention Decoder
class BahdanauAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size):
super(BahdanauAttention, self).__init__()
self.Wa = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.Ua = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.Va = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
def forward(self, query, keys):
scores = self.Va(torch.tanh(self.Wa(query) + self.Ua(keys)))
scores = scores.squeeze(2).unsqueeze(1)
weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
context = torch.bmm(weights, keys)
return context, weights
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size)
self.attention = BahdanauAttention(hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(2 * hidden_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_p)
def forward(self, encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden, target_tensor=None):
batch_size = encoder_outputs.size(0)
decoder_input = torch.empty(batch_size, 1, dtype=torch.long, device=device).fill_(SOS_token)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoder_outputs = []
attentions = []
for i in range(MAX_LENGTH):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, attn_weights = self.forward_step(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs
)
decoder_outputs.append(decoder_output)
attentions.append(attn_weights)
if target_tensor is not None:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the target as the next input
decoder_input = target_tensor[:, i].unsqueeze(1) # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teacher forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
_, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze(-1).detach() # detach from history as input
decoder_outputs = torch.cat(decoder_outputs, dim=1)
decoder_outputs = F.log_softmax(decoder_outputs, dim=-1)
attentions = torch.cat(attentions, dim=1)
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden, attentions
def forward_step(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs):
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input))
query = hidden.permute(1, 0, 2)
context, attn_weights = self.attention(query, encoder_outputs)
input_gru = torch.cat((embedded, context), dim=2)
output, hidden = self.gru(input_gru, hidden)
output = self.out(output)
return output, hidden, attn_weights
训练过程
准备训练数据
为了训练,对于每一对,我们需要一个输入张量(输入句子中单词的索引)和目标张量(目标句子中单词的索引)。在创建这些向量时,我们会将 EOS 附加到两个序列中。
######################################################################
# Training
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(1, -1)
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
def get_dataloader(batch_size):
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'fra', True)
n = len(pairs)
input_ids = np.zeros((n, MAX_LENGTH), dtype=np.int32)
target_ids = np.zeros((n, MAX_LENGTH), dtype=np.int32)
for idx, (inp, tgt) in enumerate(pairs):
inp_ids = indexesFromSentence(input_lang, inp)
tgt_ids = indexesFromSentence(output_lang, tgt)
inp_ids.append(EOS_token)
tgt_ids.append(EOS_token)
input_ids[idx, :len(inp_ids)] = inp_ids
target_ids[idx, :len(tgt_ids)] = tgt_ids
train_data = TensorDataset(torch.LongTensor(input_ids).to(device),
torch.LongTensor(target_ids).to(device))
train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_data)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=batch_size)
return input_lang, output_lang, train_dataloader
训练模型
通过编码器运行输入句子,并跟踪每个输出和最新的隐藏状态。然后,解码器将令牌作为其第一个输入,并将编码器的最后一个隐藏状态作为其第一个隐藏状态。
######################################################################
# Training the Model
def train_epoch(dataloader, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer,
decoder_optimizer, criterion):
total_loss = 0
for data in dataloader:
input_tensor, target_tensor = data
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor)
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder(encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden, target_tensor)
loss = criterion(
decoder_outputs.view(-1, decoder_outputs.size(-1)),
target_tensor.view(-1)
)
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
return total_loss / len(dataloader)
打印已用时间和估计剩余时间
######################################################################
# This is a helper function to print time elapsed and estimated time
# remaining given the current time and progress %.
import time
import math
def asMinutes(s):
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def timeSince(since, percent):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
es = s / (percent)
rs = es - s
return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs))
train多次调用并偶尔打印进度(示例的百分比、到目前为止的时间、估计时间)和平均损失
######################################################################
# The whole training process looks like this:
#
# - Start a timer
# - Initialize optimizers and criterion
# - Create set of training pairs
# - Start empty losses array for plotting
def train(train_dataloader, encoder, decoder, n_epochs, learning_rate=0.001,
print_every=100, plot_every=100):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = []
print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every
plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every
encoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.Adam(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
'''
Apply Intel Extension for PyTorch optimization against the model object and optimizer object.
'''
encoder, encoder_optimizer = ipex.optimize(encoder, optimizer=encoder_optimizer)
decoder, decoder_optimizer = ipex.optimize(decoder, optimizer=decoder_optimizer)
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
for epoch in range(1, n_epochs + 1):
loss = train_epoch(train_dataloader, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
if epoch % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, epoch / n_epochs),
epoch, epoch / n_epochs * 100, print_loss_avg))
if epoch % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
showPlot(plot_losses)
绘图
######################################################################
# Plotting results
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.switch_backend('agg')
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
import numpy as np
def showPlot(points):
plt.figure()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# this locator puts ticks at regular intervals
loc = ticker.MultipleLocator(base=0.2)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(loc)
plt.plot(points)
评估
######################################################################
# Evaluation
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, input_lang, output_lang):
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor)
decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden, decoder_attn = decoder(encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden)
_, topi = decoder_outputs.topk(1)
decoded_ids = topi.squeeze()
decoded_words = []
for idx in decoded_ids:
if idx.item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('<EOS>')
break
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[idx.item()])
return decoded_words, decoder_attn
######################################################################
# We can evaluate random sentences from the training set and print out the
# input, target, and output to make some subjective quality judgements:
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=10):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('>', pair[0])
print('=', pair[1])
output_words, _ = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0], input_lang, output_lang)
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('<', output_sentence)
print('')
训练和评估
hidden_size = 128
batch_size = 32
input_lang, output_lang, train_dataloader = get_dataloader(batch_size)
encoder = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
decoder = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words).to(device)
train(train_dataloader, encoder, decoder, 80, print_every=5, plot_every=5)
######################################################################
# Set dropout layers to ``eval`` mode
encoder.eval()
decoder.eval()
evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder)
可视化注意力代码
def showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(attentions.cpu().numpy(), cmap='bone')
fig.colorbar(cax)
# Set up axes
ax.set_xticklabels([''] + input_sentence.split(' ') +
['<EOS>'], rotation=90)
ax.set_yticklabels([''] + output_words)
# Show label at every tick
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
plt.show()
def evaluateAndShowAttention(input_sentence):
output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, input_sentence, input_lang, output_lang)
print('input =', input_sentence)
print('output =', ' '.join(output_words))
showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions[0, :len(output_words), :])
evaluateAndShowAttention('il n est pas aussi grand que son pere')
evaluateAndShowAttention('je suis trop fatigue pour conduire')
evaluateAndShowAttention('je suis desole si c est une question idiote')
evaluateAndShowAttention('je suis reellement fiere de vous')
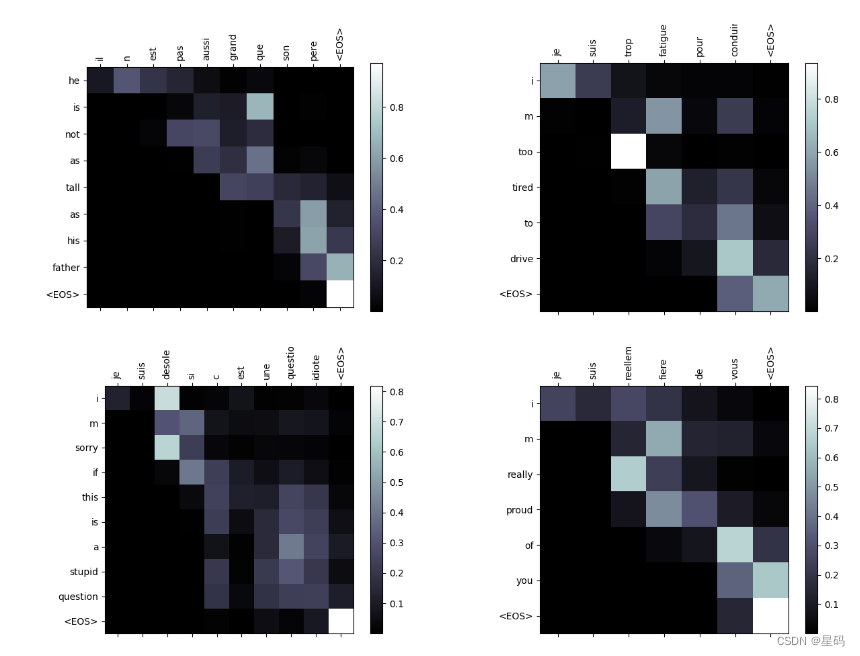
结果

可以发现得到的翻译结果比较好
参考资料
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/seq2seq_translation_tutorial.html#







![[ MySQL ] — 基础增删查改的使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f584cd2d7e1e47c8a95db4f8c26b2dbc.png)