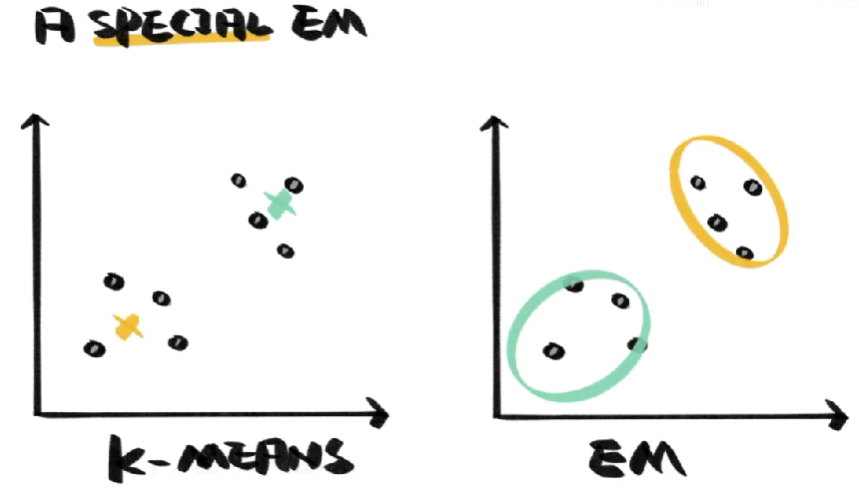
目录
Linux Shell
数据类型
变量类型
运算符
算术运算符
赋值运算符
拼接运算符
比较运算符
关系运算符
控制结构
顺序结构
条件分支结构
if 条件语句
case 分支语句
循环结构
for 循环
while 循环
until 循环
break 语句
continue语句
函数
函数定义
函数名
函数体
返回值
参数
函数的局部性
简单函数示例
函数的递归
实例操作
数组遍历操作
九九乘法表
基本上,每一门编程语言,都能从数据类型、变量、运算符、控制结构、函数五个方面着手,初步掌握这些内容就可以快速入门为一名初级程序员。
Linux Shell
Shell是Linux命令行解释器,主要用于执行操作系统命令和脚本。Linux Shell编程语言是一种用于与操作系统内核进行交互的命令行脚本语言,属于解释型、弱类型的动态语言。
数据类型
bool、数字、字符串、数组
变量类型
环境变量、用户变量、全局变量、只读变量
set let export readonly env
运算符
算术运算符
+ - * / %
赋值运算符
=,没有+=、-=、*=、/=这类复合赋值
拼接运算符
+= ,只能用于字符串的拼接
比较运算符
==、!=
关系运算符
-eq 检测两个数是否相等,相等返回 true。
-ne 检测两个数是否不相等,不相等返回 true。
-gt 检测左边的数是否大于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。
-lt 检测左边的数是否小于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。
-ge 检测左边的数是否大于等于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。
-le 检测左边的数是否小于等于右边的,如果是,则返回 true。
控制结构
顺序结构
顺序结构是最简单的算法结构,语句与语句之间是按从上到下的顺序进行的,它是由若干个依次执行的处理步骤组成的。
注:同一行可以有多个语句,只要用分号“;”来分隔即可。
条件分支结构
if 条件语句
可以细分为 if , if-else , if-elif-else 多种形式
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m if
NAME
if - Execute commands based on conditional.
SYNOPSIS
if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; ]... [ else COMMANDS; ] fi
DESCRIPTION
Execute commands based on conditional.
The `if COMMANDS' list is executed. If its exit status is zero, then the
`then COMMANDS' list is executed. Otherwise, each `elif COMMANDS' list is
executed in turn, and if its exit status is zero, the corresponding
`then COMMANDS' list is executed and the if command completes. Otherwise,
the `else COMMANDS' list is executed, if present. The exit status of the
entire construct is the exit status of the last command executed, or zero
if no condition tested true.
Exit Status:
Returns the status of the last command executed.
......case 分支语句
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m case
NAME
case - Execute commands based on pattern matching.
SYNOPSIS
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...) COMMANDS ;;]... esac
DESCRIPTION
Execute commands based on pattern matching.
Selectively execute COMMANDS based upon WORD matching PATTERN. The
`|' is used to separate multiple patterns.
Exit Status:
Returns the status of the last command executed.
......
循环结构
for 循环
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m for
NAME
for - Execute commands for each member in a list.
SYNOPSIS
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMANDS; done
DESCRIPTION
Execute commands for each member in a list.
The `for' loop executes a sequence of commands for each member in a
list of items. If `in WORDS ...;' is not present, then `in "$@"' is
assumed. For each element in WORDS, NAME is set to that element, and
the COMMANDS are executed.
Exit Status:
Returns the status of the last command executed.
......
while 循环
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m while
NAME
while - Execute commands as long as a test succeeds.
SYNOPSIS
while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
DESCRIPTION
Execute commands as long as a test succeeds.
Expand and execute COMMANDS as long as the final command in the
`while' COMMANDS has an exit status of zero.
Exit Status:
Returns the status of the last command executed.
......until 循环
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m until
NAME
until - Execute commands as long as a test does not succeed.
SYNOPSIS
until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
DESCRIPTION
Execute commands as long as a test does not succeed.
Expand and execute COMMANDS as long as the final command in the
`until' COMMANDS has an exit status which is not zero.
Exit Status:
Returns the status of the last command executed.
......
break 语句
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m break
NAME
break - Exit for, while, or until loops.
SYNOPSIS
break [n]
DESCRIPTION
Exit for, while, or until loops.
Exit a FOR, WHILE or UNTIL loop. If N is specified, break N enclosing
loops.
Exit Status:
The exit status is 0 unless N is not greater than or equal to 1.
......
continue语句
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m continue
NAME
continue - Resume for, while, or until loops.
SYNOPSIS
continue [n]
DESCRIPTION
Resume for, while, or until loops.
Resumes the next iteration of the enclosing FOR, WHILE or UNTIL loop.
If N is specified, resumes the Nth enclosing loop.
Exit Status:
The exit status is 0 unless N is not greater than or equal to 1.
......两者的区别
break语句:
break语句用于退出本层循环,当执行到break会立即跳出当前循环,执行后续代码。
在多层嵌套循环中,break只会跳出最近的一层循环。
continue语句:
continue语句用于结束本次循环,跳过本次循环中剩余的代码,直接进入下一次循环。
在多层嵌套循环中,continue只会跳过最近的一层循环。
函数
hann@HannYang:~$ help -m function
NAME
function - Define shell function.
SYNOPSIS
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name () { COMMANDS ; }
DESCRIPTION
Define shell function.
Create a shell function named NAME. When invoked as a simple command,
NAME runs COMMANDs in the calling shell's context. When NAME is invoked,
the arguments are passed to the function as $1...$n, and the function's
name is in $FUNCNAME.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless NAME is readonly.函数定义
函数名
Shell函数用关键字 function 声明,跟在后面的 name 即函数名。声明后就用"函数名 [参数]"来调用函数。function 非必须,也能用函数名加一对括号 name() { ... } 来声明定义函数。
函数体
函数名后的 { Commands; } 即函数体,是实现函数功能的主体。
返回值
Shell函数可以有一个返回值,可以使用return语句返回一个值。返回值的范围是0到255之间,0表示成功,非零值表示错误。如果函数中没有return语句,或者使用exit命令退出函数,则函数的返回值为退出命令的返回值。
参数
Shell函数可以通过参数接收输入的值。在函数定义时,可以在括号中指定参数列表。参数可以在函数体中使用,也可以通过特殊变量$#获取函数的参数个数,通过特殊变量$@获取所有的参数。
函数的局部性
Shell函数的变量是局部的,即在函数内部定义的变量只在该函数内部可见,不会影响到函数外部的变量。如果要使用全局变量,需要在函数外部定义。
简单函数示例
hann@HannYang:~$ function add {
> num1=$1
> num2=$2
> sum=$((num1 + num2))
> echo "The sum of $num1 and $num2 is $sum."
> }
hann@HannYang:~$ add 10 20
The sum of 10 and 20 is 30.语句比较少的函数可以在一行内完成,函数体中的语句间用分号“;”来分隔即可。
hann@HannYang:~$ function sub { num1=$1; num2=$2; sum=$((num1 - num2)); echo "The difference between $num1 and $num2 is $sum."; }
hann@HannYang:~$ sub 30 20
The difference between 30 and 20 is 10.函数的递归
Shell函数可以递归调用自身,这在处理嵌套数据结构或递归算法时非常有用。需要注意的是,递归调用可能会导致栈溢出或效率低下的问题,因此在使用时需要谨慎。
示例:阶乘函数
hann@HannYang:~$ factorial() {
> if [ $1 -le 1 ]
> then
> echo 1
> else
> echo $(( $1 * $(factorial $(( $1 - 1 ))) ))
i
}> fi
> }
hann@HannYang:~$ read -p "请输入一个整数:" num
请输入一个整数:6
hann@HannYang:~$ result=$(factorial $num)
hann@HannYang:~$ echo "$num 的阶乘为 $result"
6 的阶乘为 720实例操作
数组遍历操作
hann@HannYang:~$ for i in 1 2 3 4 5; do echo -n $i; done; echo
12345
hann@HannYang:~$ for i in {1..5}; do echo -n $i; done; echo
12345
hann@HannYang:~$ sum=0;for i in {1..100};do let sum+=i;done;echo $sum
5050
hann@HannYang:~$ for i in {1..5}{8..10}; do echo -n $i; done; echo
18191102829210383931048494105859510
hann@HannYang:~$ for i in {1..5}{8..10}; do echo -n $i" "; done; echo
18 19 110 28 29 210 38 39 310 48 49 410 58 59 510
hann@HannYang:~$ for i in {A..C}{a..d}; do echo -n $i" "; done; echo
Aa Ab Ac Ad Ba Bb Bc Bd Ca Cb Cc Cd九九乘法表
hann@HannYang:~$ cat 99mul.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..9}
do
for j in {1..9}
do
if [ $j -le $i ]
then
echo -n "$j*$i=$(($i*$j)) "
fi
done
echo ""
donehann@HannYang:~$ bash 99mul.sh
1*1=1
1*2=2 2*2=4
1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9
1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16
1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
hann@HannYang:~$ cat 99mul.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..9}
do
for j in {1..9}
do
if [ $j -le $i ]
then
printf "%d*%d=%2d " $j $i $(($i*$j))
fi
done
echo ""
donehann@HannYang:~$ bash 99mul.sh
1*1= 1
1*2= 2 2*2= 4
1*3= 3 2*3= 6 3*3= 9
1*4= 4 2*4= 8 3*4=12 4*4=16
1*5= 5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
1*6= 6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
1*7= 7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
1*8= 8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
1*9= 9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
hann@HannYang:~$ cat 99mul.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..9}
do
for j in {1..9}
do
if [ $j -le $i ]
then
if [ $j -eq 1 ]
then
printf "%d*%d=%d " $j $i $(($i*$j))
else
printf "%d*%d=%2d " $j $i $(($i*$j))
fi
fi
done
echo ""
donehann@HannYang:~$ bash 99mul.sh
1*1=1
1*2=2 2*2= 4
1*3=3 2*3= 6 3*3= 9
1*4=4 2*4= 8 3*4=12 4*4=16
1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
本文简单提一下Linux Shell编程语言的入门要点,之后再对各个环节进行分类详细举例说明。




![[机器学习]特征工程:特征降维](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/2a8b90e49d26044b819bcabd2ce63cd7.png)